资助项目:国家重点研发计划课题(2017YFC0404701); 国家自然科学基金(51779271)
第一作者:崔豪(1992—),男,河南新乡人,硕士,研究方向为气候变化对水资源的影响及其响应。E-mail:chiwhr@163.com 通信作者:王贺佳(1990—),男,山西晋城人,工程师,博士后,主要从事陆面水文模拟研究。E-mail:hjwang@iwhr.com
(1.中国水利水电科学研究院 流域水循环模拟与调控国家重点实验室, 北京 100038; 2.广西大学 土木建筑工程学院, 南宁 530004)
(1.State Key Laboratory of Simulation and Regulation of Water Cycle in River Basin, China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research, Beijing 100038, China; 2.College of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Guangxi University, Nanning 530004, China)
Three Gorges Reservoir area; actual evapotranspiration; spatiotemporal variation characteristics; meteorological factors
蒸散发(Evapotranspiration)是联系陆—气间水循环过程的关键因子,是陆地水循环过程中的重要环节之一[1]。实际蒸散发由地面蒸发、植被冠层截留蒸发(以下简称植被蒸发)及植被蒸腾量组成,其中地面蒸发包括水面及裸地的蒸发量。在区域陆地水循环过程中,大气中的水分通过降雨、降雪等方式迁移到地表,而陆地的水分则主要通过蒸散发这一水循环过程迁移回大气中[2]。研究表明,约有70%的降水通过蒸散发这一水循环过程返回到大气[3]。准确计算实际蒸散发量,分析其时空分布特征及气候因子与蒸散发量的相互关系,对变化环境下的水资源管理与生态环境保护战略具有重要实践指导意义。
目前对于蒸散发量的计算方法主要有空气动力学方法[4]、能量平衡法[5]和经验公式法[6]、蒸散发互补相关模型[7]、遥感反演法等[8]。吴家兵等[9]通过涡动相关法与波文比—能量平衡法测算森林蒸散发量,得出两种方法具有较好的相关性,阔叶红松林的主要热量消耗为蒸散发。其中,实际蒸散发可通过蒸渗仪法[10],涡动相关法等方法进行观测获得,但蒸渗仪、涡动相关等方法价格昂贵,只能针对点尺度进行观测,无法适应区域甚至流域等大尺度地区,普及成本较高; 刘曼晴等[11]选用8期Landsat遥感数据,利用SEBAL模型估算辽河三角洲湿地植被生长季的蒸散量,反演相对误差为9%左右,蒸散量在研究区内具有显著空间分异特征。但遥感反演法受到卫星发射时间、观测的连续性影响及观测图像质量影响,解析校正可能存在误差,无法获得长序列高时间精度资料; 对潜在蒸发量的分析大多采用了气象站点蒸发皿监测的蒸发量数据或者是由经验公式计算的潜在蒸发量,蒸发皿是一种常见的观测数据测量方法,成本相对较低,但是蒸发皿测得的潜在蒸散发只能代表蒸散发的趋势过程,无法准确刻画区域实际蒸散发的情况。孙从建等[6]通过Penman-Monteith公式分析了黄土塬面保护区1960—2017年潜在蒸发量变化特征,得出研究区ET0总体呈增长状态且存在10,30,50 a的周期变化; 地球物理模式可以通过已有的观测资料利用空气动力学方法计算实际蒸散发,可以模拟长时间序列高时间精度以及空间精度的蒸散发分布特征。Wang等[12]通过陆面模式模拟与遥感相互验证,定量分析了1993—2013年气候变化与土地利用变化对三峡库区蒸散发的影响,得出气候变暖和土地利用的变化使得蓄水后平均ET0增加13.76 mm。
举世瞩目的三峡大坝作为世界迄今为止最大水利枢纽工程,作为与干旱、洪涝抗争的重要大型水利工程,其可能的区域环境效应已引起了国家政府以及众多学者的广泛关注。科学解析大型库坝对区域水循环的变化,定量分析区域水循环关键过程之一的蒸散发,对分析三峡库区水资源和气候变化的关系具有重要的意义。
本文选取以三峡大坝建成后所形成的库区为研究区。三峡库区位于长江上游尾段,地处长江中下游和四川盆地之间,处于东经105°25'49″—111°7'39″,北纬28°15'43″—31°43'41″,东起湖北省宜昌市三峡大坝处,西至重庆市朱沱水文站,因三峡大坝的修建蓄水形成的区域(图1)。
研究区气象数据来源于Chen等[13]开发的中国区域高时空分辨率地面气象要素驱动数据集(CMFD),该数据集是以Princeton再分析资料、GLDAS资料、GEWEX-SRB辐射资料,以及TRMM降水资料为背景场,融合了中国气象局站点观测数据制作而成。其时间分辨率为3 h,水平空间分辨率0.1°,包含近地面气温、近地面气压、近地面空气比湿、近地面全风速、地面向下短波辐射、地面向下长波辐射、地面降水率,共7个要素(变量)。本研究提取了库区内1990—2015年的驱动数据进行模拟分析,并通过库区范围内12个气象站点的降水、气温、风速和相对湿度月尺度数据进行验证,其中降水、气温和相对湿度相关系数均在0.9以上、风速相关系数中位数为0.8左右,但波动较大。本文构建库区范围的陆面模型分辨率为0.1°,CMFD数据精度满足模拟需求,故无需对CMFD数据进行降尺度处理。
通用陆面模式(Community Land Model,简称CLM)4.5是由美国国家大气研究中心[14]开发的,它是通用地球系统模型(Community Earth System Model简称CESM)1.2.0的陆面分量模型[15]。CLM4.5是基于过程的模型,可模拟生物地球物理过程和生物地球化学过程。生物地球物理过程包括在地表和大气层间交换的辐射、显热和潜热通量,土壤和雪中的热传递以及水循环过程环节中包括降水、截留、渗透、蒸散和径流[16]。生物地球化学过程包括植被光合作用、植被物候学以及碳氮循环[17]。
CLM4.5模型以网格为基本计算单元进行模拟计算,为体现网格单元的空间异质性,模型以一个3层嵌套的次网格层次结构来表达。每个网格由多个陆地单元,土柱和植被功能类型组成。陆地单元主要是捕捉第一层次网格最广泛的空间异质性。第二层次网格是土柱,它是用于表征一个陆地单元内土壤和积雪状态变量的潜在变异性。第三层次网格涉及植被功能类型,它主要表示生物物理和化学上的差异。该模型在每个次网格进行独立模拟,且每个次网格都有其诊断变量。对于ET的过程,模型中分为由气孔生理和光合作用控制的蒸腾以及蒸发,蒸发根据植被功能类型又可分为地面蒸发和冠层蒸发。基于CLM4.5模拟的实际蒸散发量由地面蒸发量、植被蒸发量及植被蒸腾量构成,故本文对实际蒸发量及其各分量进行时空演变规律分析。
在模型中,将陆—气间的水汽通量分为裸土、雪盖、水面表面与大气边界层之间的水汽通量以及植被冠层与大气边界层之间的水汽通量,总水汽通量可表示如下
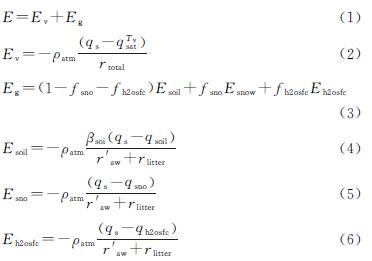
式中:E为水汽通量[kg/(m·s)]; Ev为植被产生的水汽通量[kg/(m·s)]; Eg为地面产生的水汽通量[kg/(m·s)]; Esoil,Esnow,Eh2osfc分别为土壤、雪和地表水产生的水汽通量[kg/(m·s)]; ρatm为大气密度(kg/m3); qs为饱和水汽的湿度(kg/kg); qTvsat为饱和水汽在植被温度下的比湿度(kg/kg); fsno,fh2osfc分别为网格单元表面被雪、被水覆盖的部分; qsoil,qsno和qh2osfc分别为土壤、雪和地表水的特定湿度(%); r'aw为地面高度与冠层高度中空气对水汽传递的气动阻力(s/m); βsoi为土壤水分的经验函数; rlitter为植物凋落物层的阻力(s/m)。rtotal为冠层对水汽从冠层向冠层空气传递的总阻力,包括叶片边界层的贡献以及光照和阴影气孔阻力。
采用线性回归方程来评估三峡地区1990—2015年期间的实际蒸散发的趋势。公式如下:
y=ax+b (7)
式中:x为年; y为实际蒸散发; a,b分别为斜率和截距。a的正值表示上升趋势; a的负值表示下降趋势。
对于时间序列X={x1,x2,x3,…,xn},其中n(n>10)为时间序列的长度,统计量Z可由下式计算:
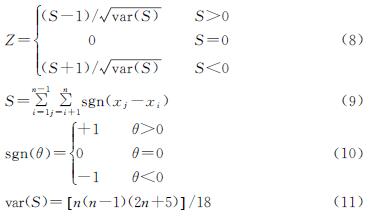
式中:t为数据点时长。
统计量Z符合标准正态分布。Z>0则表示检测的时间序列呈上升趋势,而Z<0时,检测的时间序列呈下降趋势,Z=0认为检测时间序列未有趋势变化。当Z<-1.96或Z>1.96时,则通过95%的显著性检验。
传统运用气象站点实测值对于大尺度的蒸散发精度研究,往往由于站点分布不均,空间实测数据很难获取,无法得到较好的空间精度验证,并且需要站点数据质量较好[18],故本文采用遥感数据来验证模型模拟精度。ET-MOD16产品是基于Penman-Monteith方程改进的,将地表分为裸地和冠层两种类别,分别根据不同下垫面物理过程计算各自表面阻抗,估算陆地表面蒸发和植物冠层蒸腾量[19]。MOD16数据因其时空分辨率较高,且数据容易获取,在全球陆面过程模型、水文模型以及站点数据的验证中展现出较好的应用效果[20-21]。
本文选用2000—2013年的MOD16月度ET产品(ET-MOD16)的数据用于验证ET-CLM的模拟结果。ET-MOD16的散点图和由CLM4.5(ET-CLM)模拟的相应月度值见图2,验证结果R2为0.91,RMSE为14.16 mm/月、BIAS为-9.92 mm/月,模型模拟结果较好。此外,发现散点的分布相对均匀,这表明CLM4.5模型可以更好地反映三峡库区ET的季节变化特征。但是,在低值(<40 mm/月)中,低估更为明显,这表明夏季的模拟效果要好于冬季。
变化环境下三峡库区蒸散发时空变化的模拟存在一定的不确定性,本文构建的CLM4.5模型在研究区具有良好的适用性,但仍然存在模拟误差。由于陆面模型计算的尺度较大,可能会降低用水文模拟的实际蒸发量、土壤湿度等水文气候变量的可靠性和准确性。此外,模型构建没有考虑土地利用年际动态的变化,而实际库区范围内土地利用变化是随着三峡水利枢纽的调度而动态变化的,从而可能影响蒸散发的模拟效果。气候和土地利用变化对蒸散发过程的影响是复杂的,各因素间相互影响及反馈,将其与水文循环间的互馈影响耦合在一起。不同类型的人类活动对水循环可能有积极或消极的影响,气候和人类活动变化使得土地利用发生变化,反之亦然。虽然CLM模拟方法存在一些不确定性和局限性,但本研究通过ET-MOD16产品与模拟数据相互验证,定量分析了三峡库区实际蒸散发及其各分项的时空变化规律,探讨了其与气象因子的关系。在未来的研究将侧重于这些不确定性,以提高量化的结果,通过进一步的研究以充分了解三峡库区蒸散发对气候变化和人类活动的响应。
分析研究区1990—2015年的实际蒸散发量(图3),实际蒸发量最大值出现在2007年,最小值出现在1993年。蓄水前平均实际蒸发量值为579.5 mm,其实际蒸散发范围在532.3~622.6 mm,变化率为0.077 mm/10 a,呈波动上升趋势,变化趋势不显著; 蓄水后平均实际蒸发量值为602.0 mm,其实际蒸散发范围在534~698.6 mm,呈微弱下降趋势,变化率为-0.022 mm/10 a,变化趋势不显著。
分项来看,对实际蒸散发3个部分进行变化特征的分析,蓄水前从变化趋势来(图3),1990—2002年三峡库区的年均植被冠层蒸发量呈波动下降趋势,变化率为-0.035 mm/10 a,年均地面蒸发量呈上升趋势,变幅不大,变化率为0.028 mm/10 a,植被冠层蒸腾量呈显著上升趋势(表1),变化率为0.084 mm/10 a; 蓄水后,2003—2015年三峡库区的年均地面蒸发量呈下降趋势,变化率为-0.019 mm/10 a,年均植被冠层蒸发量呈上升趋势,变化率为0.024 mm/10 a,植被冠层蒸腾量呈下降趋势,变化率为-0.027 mm/10 a。
对蓄水前实际蒸散发各分项进行季节变化趋势特征的分析,从地面蒸散发变化趋势可以看出(图4),1990—2002年三峡库区的春季、秋季和冬季地面蒸发量呈上升趋势,上升趋势为0.024,0.01,0.002 mm/10 a,夏季地面蒸发量呈下降趋势,下降趋势为-0.008 mm/10 a; 春季、夏季、秋季、冬季四季的植被冠层蒸发量均呈略微下降趋势,分别为-0.011,-0.014,-0.008,-0.002 mm/10 a; 而植被冠层蒸发量各季植被冠层蒸腾量均呈上升趋势,变化率为0.029,0.016,0.033,0.006 mm/10 a。
蓄水后,从地面蒸发变化趋势可以看出,2003—2015年三峡库区的春季、秋季、冬季地面蒸发量呈略微下降趋势,下降趋势分别为-0.012,-0.008,-0.004 mm/10 a,夏季地面蒸发量呈上升趋势,上升趋势为0.005 mm/10 a; 植被冠层蒸发量春季、夏季、秋季三季的植被蒸发量均呈略微上升趋势,上升趋势分别为0.004,0.011,0.01 mm/10 a,冬季呈下降趋势,下降趋势为-0.001 mm/10 a; 植被冠层蒸腾量夏季、冬季呈略微上升趋势,变化率为0.007,0.000 6 mm/10 a,春季和秋季植被冠层蒸腾量呈下降趋势,变化率均为-0.011,-0.022 mm/10 a。
分析库区内实际蒸发量及其分项在基准期和变化期的变化情况(图5),对于实际蒸发量,全年各月基本蓄水后较蓄水前有一定的增加,其中,3月、4月、7月的实际蒸发量呈上升且变化量较大,其余月的实际蒸散量有所增加,变化量较小,仅9月、11月两月有较小下降变化; 对于地面蒸发量,全年各月基本蓄水后较蓄水前有一定的增加,其中,趋势上升且变化量较大的月份与实际蒸发量较大月份相一致,其余月的地面蒸散量有所增加,变化量较小,9月、11月、12月地面蒸发量有较小下降变化; 对于植被蒸发量,蓄水后较蓄水前各月份整体均有所减少,其中,7月的植被蒸发量呈下降变化量较大,其余月的植被蒸发量有所下降,变化量较小,仅9月、11月两月有较小上升变化; 对于植被蒸腾量,全年各月基本蓄水后较蓄水前有一定的增加,其中,7月的植被蒸腾量呈上升且变化量较大,其余月的植被蒸腾量有所增加,变化量较小,仅9月有较小下降变化。
三峡库区蓄水前后年平均蒸散发量的空间变化见图6,流域内平均实际蒸散发量的范围在400~720 mm,具有明显空间差异性。可以看出,在库区接近库首东北地区实际蒸散发量较高,而在接近库区边缘的南部及库首北部实际蒸散发量则较小。整体而言,实际蒸散发量在长江及其支流范围内蒸发量较高,在库区边缘地区实际蒸发量较小。蓄水后实际蒸发量较蓄水前均有不同程度增加(图7),在流域库中东北部及库尾东部,实际蒸发增长趋势变幅达8%~12%; 仅在库首东部地区实际蒸发量呈变少趋势,减少变幅达-1%~-8%; 其他区域都有小幅增幅。
库区内平均地面蒸发量的范围在100~300 mm,差异显著。空间上来看,在库区西北地区和东北地区地面蒸发量较高。地面蒸发量180~280 mm集中在长江干流沿线区域,地面蒸发值小于140 mm分布在三峡库区的库首、库中南部地区。整体而言,地面蒸发量在长江及其支流范围内较其他区域有显著区别,这是由于库区内河流的大水面条件下,水分充足而造成的地面蒸发量相对较高。分析蓄水前后空间差异性,在库中,地面蒸发呈增长趋势,变幅达12%~20%; 而在库首地面蒸发量整体蓄水后呈变少趋势,减少变幅达-8%~-1%; 库尾地面蒸发量蓄水后呈小幅增加。
库区内平均植被蒸腾量的范围在260~440 mm,整体蒸腾量较高。植被蒸腾量380 mm以上集中在库中北部,植被蒸腾量小于300 mm分布在三峡库区流域的库首北部、库尾东南部地区。库区内整体植被蒸腾量差异较大,库中及河流干支流地区明显高于其他区域,由于三峡库区河流周边区域内水热条件良好,植被覆盖度高,从而使得库中及河流干支流地区明显高于其他区域。从三峡库区蓄水前后植被蒸腾量变幅来看。在库尾东南部,植被蒸腾量呈增长趋势最为显著,变幅达12%~20%,在库中东南部和库首西部植被蒸腾量呈增加趋势,增加变幅达8%~12%; 而仅在库首东部,蒸腾量有减少的趋势,变幅为-8%~-1%。
库区内平均植被蒸发量的范围在30~120 mm,整体差异并不太大。植被蒸发量在90~120 mm,集中在库首、库中南部及库尾西南部,植被蒸发量小于70 mm,分布在三峡库区的库首西部及库尾西北部地区。空间上来看,在库区中部、西南部植被蒸发量较高。从蓄水前后植被蒸发变幅来看,整体蓄水后较蓄水前为较少趋势。可以看出,在库中西部和库尾南部和库首南部局部地区植被蒸发呈明显的减少趋势,变幅达-20%~-12%; 库中和库首北部局部地区植被蒸发量呈增加趋势,增加幅度为4%~16%; 其余区域蓄水前后为小幅减少降幅。
气候变化是影响区域水热分布的重要因素[22],实际蒸散发不仅与温度有着密切联系,降水量同样影响着区域内水分条件[8,23],故本文以表示气温表征热力条件,降水量表征水分条件分析气象因子与实际蒸散发的关系。通过分析年内蒸散发变化特征与气候因子的相关性分析,可以探究该区域水热变化规律与其的相互联系。本文选用水分条件(降水量)和热力条件(气温)作为影响三峡库区的主要气候因子进行相关分析,进而分析讨论研究区内蒸散发的驱动类型。由图8—9可以看出,年内三峡库区蓄水前蒸散发与降水相关性整体一般,其中植被蒸发量与温度的相关性较高,R2达到0.82-0.89; 实际蒸散发量、地面蒸发量和植被蒸腾量与温度相关性较低,R2达到0.50,0.32,0.45。而三峡库区流域蓄水后蒸散发与降水相关性来看,植被蒸发量与降水的相关性较高,R2达到0.89; 实际蒸发量、地面蒸发量和植被蒸腾量与降水相关性稍低,R2达到0.55,0.35,0.49。对比蓄水前后蒸散发量,实际蒸散发量及各分量蓄水后与降水的相关性均有所增加。由于植被冠层截留的影响,蓄水前后植被蒸发量与降水有着较高的相关性。
由图 10可以看出,年内三峡库区蓄水前蒸散发与温度相关性整体均较高,其中实际蒸散发量和植被蒸腾量与温度的相关性较高,R2达到0.95,0.95; 地面蒸发量和植被蒸发量与温度相关性稍低,R2达到0.76,0.76。而从三峡库区蓄水后蒸发与温度相关性来看(图 11),实际蒸发量和植被蒸腾量与温度的相关性较高,R2达到0.94,0.94; 地面蒸发量和植被蒸发量与温度相关性稍低,R2达到0.71,0.84。对比蓄水前后蒸散发量,实际蒸散发量、地面蒸发量及植被蒸腾量蓄水后相关性均有所降低,植被蒸发量相关性有所增加。分析其原因,可能是由于蓄水后水系调度及人类活动影响下蒸发量的影响因子受到更多复杂的影响而使得相关性有所降低。
(1)时间趋势上,年均实际蒸散发以及其分项植被蒸发量和植被蒸腾量年内分配不均,具有明显的季节变化特征,四季多年均实际蒸发量和植被蒸腾量由大到小分别为:夏季>春季>秋季>冬季,具有典型的季节差异性; 地面蒸发量没有明显的季节性差异,各季节差异较小。蓄水后年平均实际蒸散发量及植被蒸腾量、植被蒸发量较蓄水前有所增加; 地面蒸发量蓄水后较蓄水前有所减少。
(2)空间趋势上,年均实际蒸散发以及其分项地面蒸发量和植被蒸腾量蓄水前后变化趋势较为一致,在库中及库尾东南部均呈增加趋势; 而植被蒸发量在蓄水后库中较蓄水前呈现减少趋势。变动幅度上,实际蒸散发量在库中东北部及库尾东部范围内增加幅度较大,植被蒸发量在库中范围内减少幅度较大,地面蒸发量在库中增幅最大,植被蒸腾量在库尾东南范围内增幅较大。
(3)气温是影响研究区蒸散发变化的主导因素。蓄水前后实际蒸散发及各分项与温度的相关性在0.71~0.95,其中实际蒸发量、植被蒸腾量与温度相关性最高,蓄水后相关性除植被蒸发量外整体低于蓄水前; 蓄水前后实际蒸散发及各分项与降水的相关性在0.32~0.89,其中植被蒸发量与降水相关性最高,蓄水后相关性整体高于蓄水前。