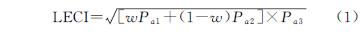近年来,随着人类活动和全球环境的加速变化,人类对环境资源高强度的开发和利用,对生态环境以及经济社会可持续发展构成了极大威胁[1]。因此,如何全面准确评价生态环境状况的研究,成为国内外学者关注的研究方向[2-3]。景观格局作为多种景观镶嵌体在空间上的排列组合,与生态过程的变迁有着密切关联,对于保护自然资源和维持物种多样性等生态功能具有深刻影响,不同的景观组成和配置又将影响生态作用各异的景观功能[4-6]。从景观生态学角度出发,基于景观格局和景观功能来构建涵盖多尺度、多指标影响因素的景观生态状况评价体系,全面准确反映区域敏感性变化趋势和吸收外界干扰能力,同时在一定程度上可以掌握景观生态环境状况优劣和相应的区域特征,为恢复区域生态环境提供科学指导。
景观生态敏感性是指在各种自然和人为干扰下,通过特定的阈值测定景观生态环境状况的变化特征。当前国内外学者关于生态环境脆弱性和生态环境敏感性研究较多[7-10],基于景观角度研究区域景观生态环境状况及景观生态敏感性相对较少。在自然状态下,受外来干扰和自身调节的双重作用下的景观生态系统演变发展具有特定结构、功能和特征,其变化受干扰程度和系统稳定的影响,而景观格局能够反映景观生态系统中不同景观单元之间的空间格局及关系[6],景观功能可体现着各类景观单元所拥有的生态服务功能,景观功能的消退或丧失将直接导致区域间生态敏感性的加剧[11-12]。现目前,学者们大多采用景观格局指数或生态要素等方法对区域展开景观生态状况评价或景观敏感性研究[13-14],而基于景观功能以及景观格局相结合的研究较为薄弱[15-16]。同时,当前关于生态环境状况的敏感性影响因素多为定性考量,定量考量较为缺乏[17]。因此,从景观格局和景观功能整体出发,研究区域的景观生态环境状况及其敏感性显得尤为重要,不仅能够充分体现研究区的景观生态敏感性综合特征,其评价结果还能直观且全面反映区域景观生态环境状况[18],也能为区域生态保护和修复策略提出一定的研究基础。
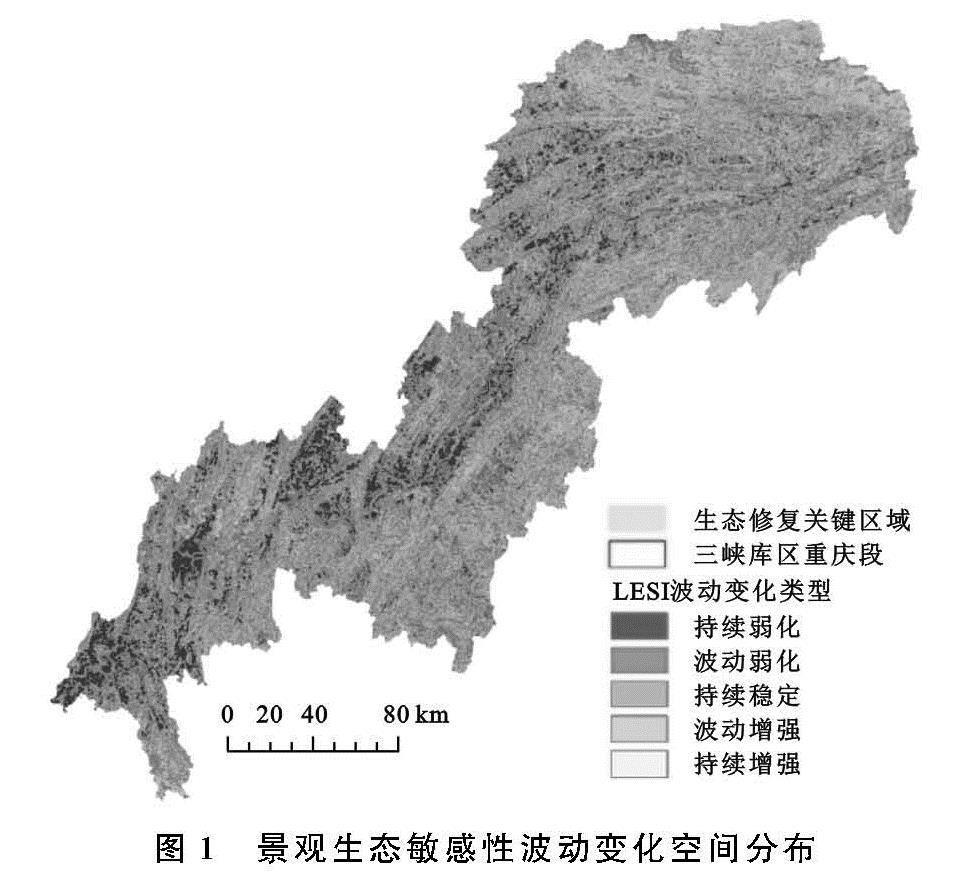
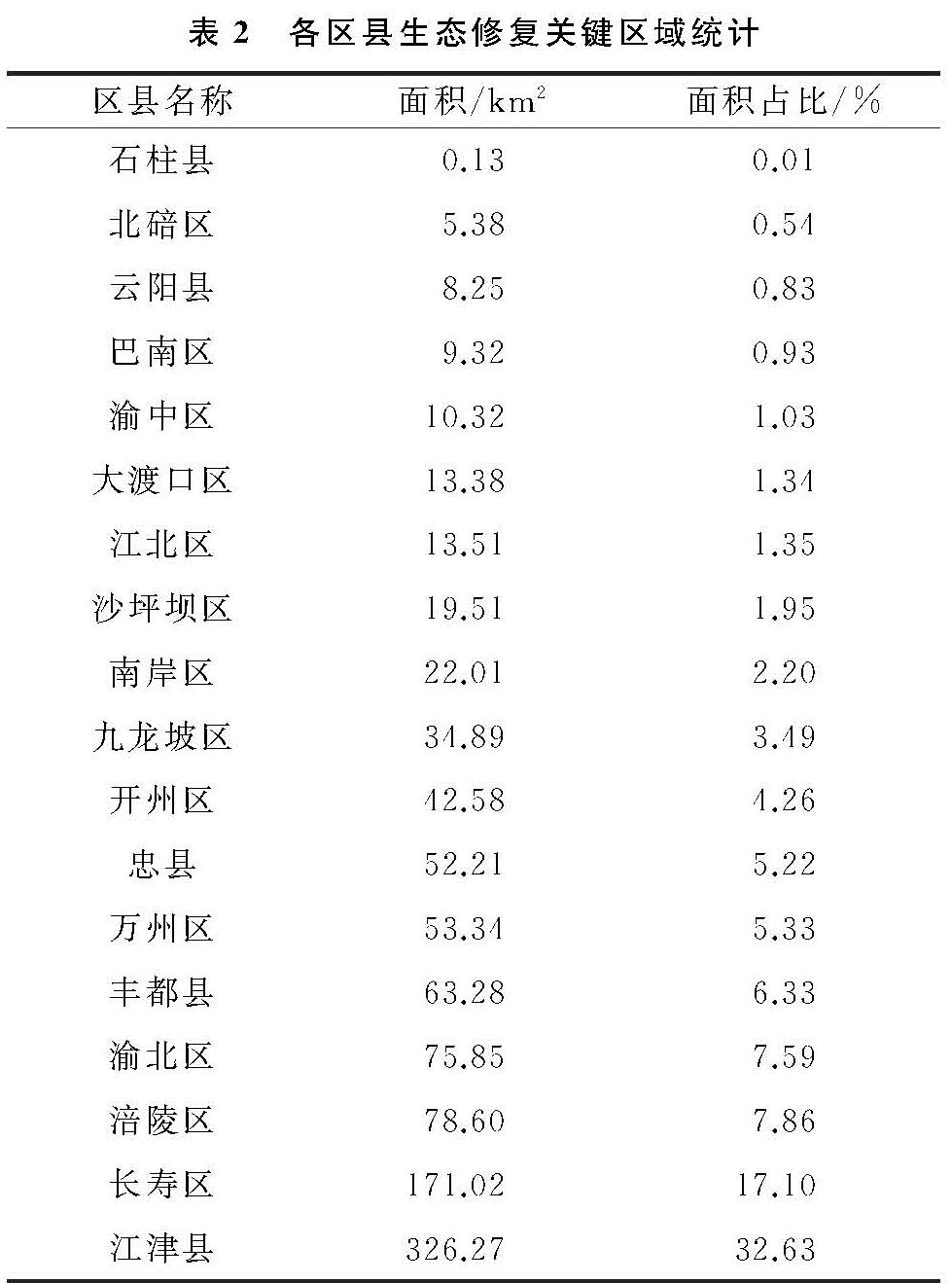
三峡库区土地结构复杂,生态环境脆弱敏感,资源不合理的开发利用引发的植被破坏、水土流失、物种多样性丧失等突出问题严重威胁着库区的生态安全[19]。本研究从景观功能和景观格局整体出发,选取多影响因子指标构建景观生态状况评价模型,基于景观格局的组成和配置要素,并结合景观功能构建新的LECI(景观生态状况指数)和LESI(景观生态敏感性指数)评价体系来研究三峡库区重庆段景观生态状况及敏感性时空变化。该评价方法同时选取多期三峡库区遥感数据,通过静态与动态结合分析方式,对库区景观生态敏感性进行时空变化特征的研究与评估,识别区域景观生态敏感区,为研究区域的关键生态修复区提供一定的参考依据。