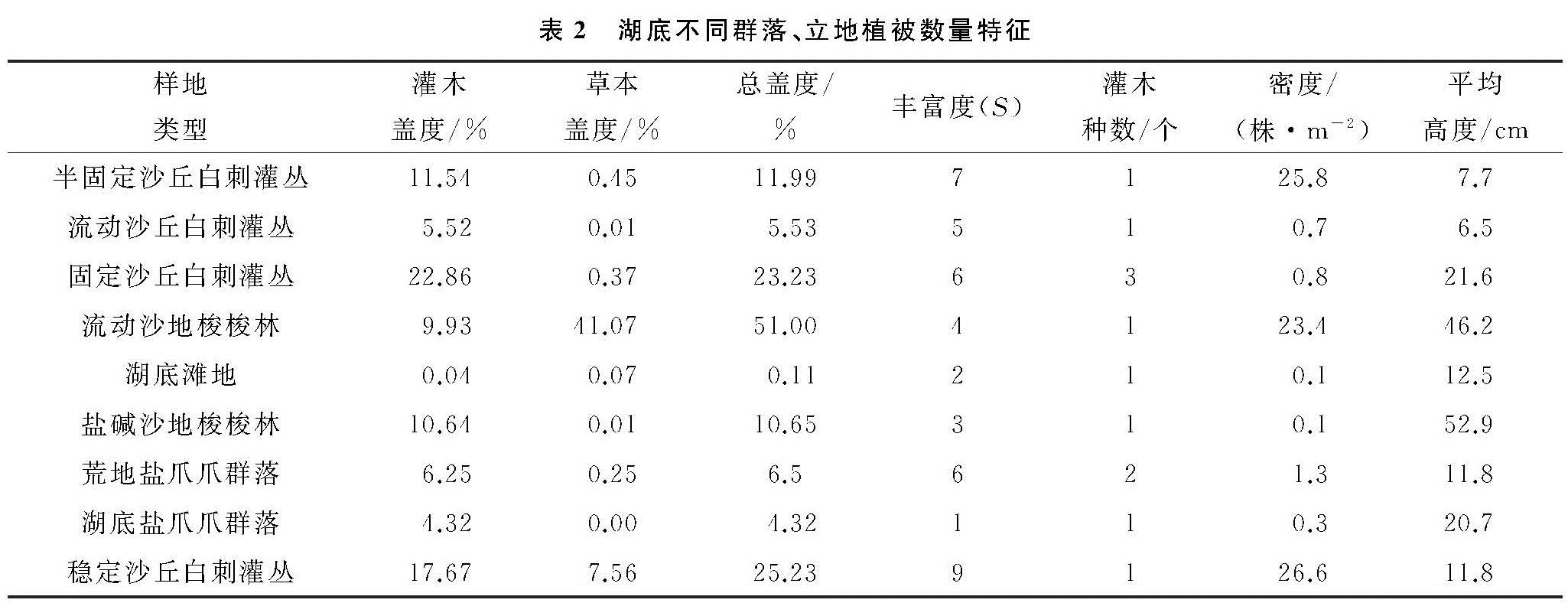
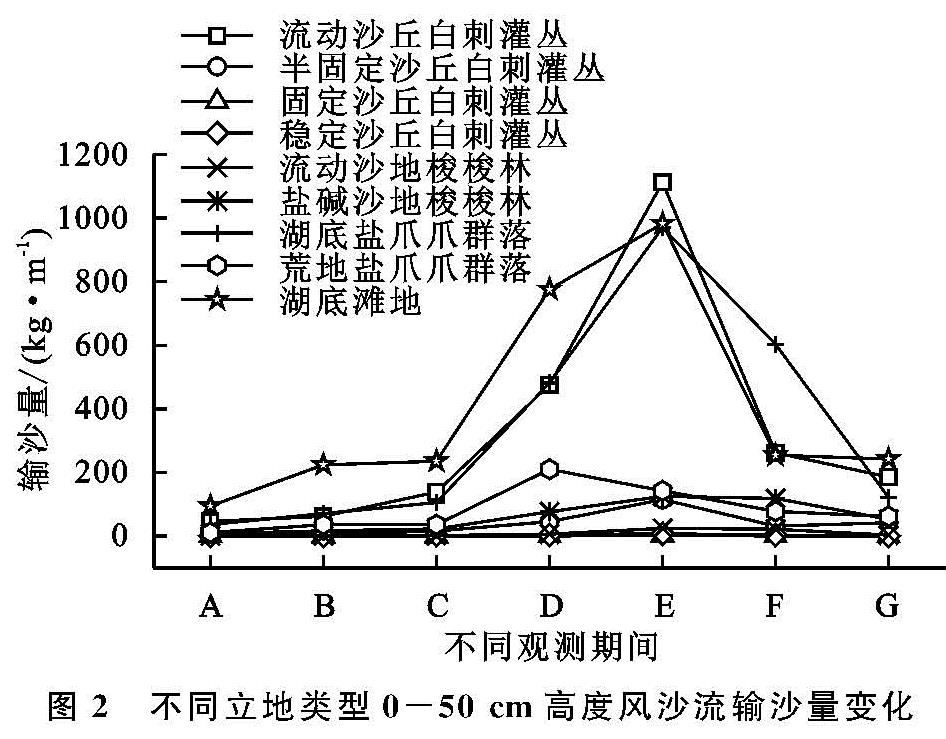
在干旱区干涸湖底影响植被群落的诸多因素中,土壤盐分是影响物种多样性的决定性因素之一[21],青土湖属于干涸盐湖,多为耐盐植物构成的单优势种群落,通过测定流动沙丘白刺灌丛含盐量达到9.0 g/kg,湖底土壤含盐量高是湖底植被稀疏、植物群落结构简单、物种多样性低的重要影响因素。通过对青土湖湖底2018年12月至2019年7月风沙流输沙量数据的分析,湖底4月、5月、6月地表0—50 cm高度风沙流输沙量较高,说明研究区风沙运动活跃期存在季节性分布,主要发生在春末夏初时间段,这与青土湖湖底风速呈现明显季节性变化特征且年内较大风速分布在4—6月[19]有密切关系。其次,研究区降水甚少,植被稀疏,春季地表异常干燥松散,抗风蚀能力很弱,在较在风力条件下地表更容易形成风沙流。
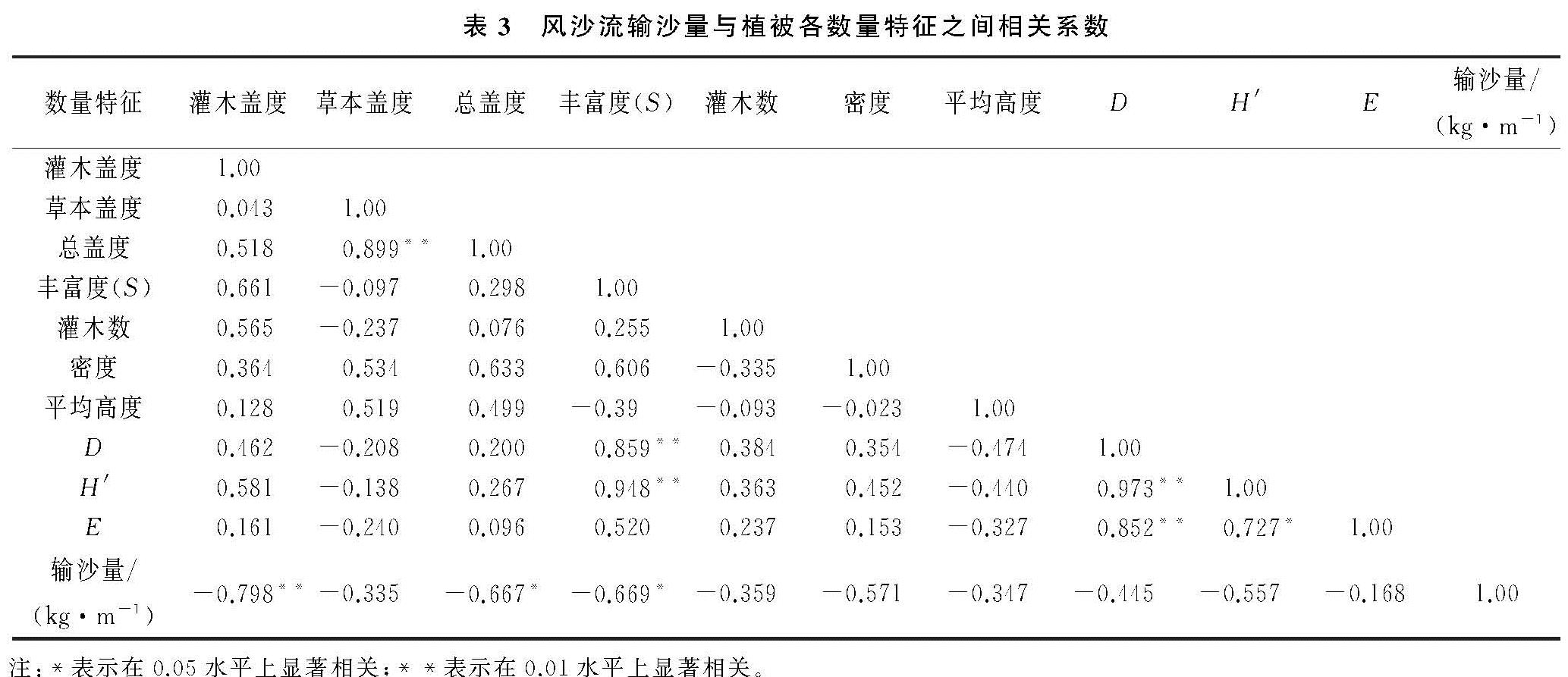
通过对青土湖干涸湖底9种不同立地类型植被特征和地表风沙流平均输沙量的监测,并进行相关性分析,结果表明平均输沙量与灌木盖度呈显著负相关,而与总盖度呈负相关关系,而与草本层盖度相关性不显著,这主要是由于草本层植被在干旱区4—6月才开始萌发、生长,或在降雨少的年份,未能萌发,而在风季4—6月草本层植被未能发挥较大的防风固沙效能。而物种丰富度与输沙量的关系不显著,主要原因是湖底植物种类少,物种丰富度低,特别是每个植物群落中灌木植物数量少,且优势种明显,因此丰富度对输沙量影响较小。在试验区9种类型中虽然不同立地条件植物种平均高度差异性较大,但是人工梭梭林、白刺灌丛、盐爪爪植物群落物种高度与地表输沙量相关关系不显著,是由于湖底大面积人工梭梭林造林后地表还处于流动状态,风蚀较为严重。
研究结果表明青土湖干涸湖底灌木层植被发挥着重要的防风固沙效能,灌木层盖度的增加显著影响了风沙流输沙量变化。这一研究结果与韩旭娇[22]、汪季[11] 、余沛东[23]、董治宝[24]、邢恩德[25]、刘芳[26]等研究的在相同风速条件下,植被盖度是影响风沙流输沙量的重要影响因素的结论是一致的,但是本研究分析结果表明灌木层盖度大小是影响湖底地表风沙流输沙量的主要因素之一,比上述研究结果更进了一步。