2.1 数据来源与预处理
遥感数据采用美国航空航天局(NASA)全球监测与模型研究组(global inventory modeling and mapping studies,GIMMS)发布的15 d最大值合成的NOAA/AVHRR NDVI全球数据集,空间分辨率为 8 km×8 km。该数据集已经过几何校正,辐射校正和大气校正等处理,并在全球及区域植被变化的大尺度动态研究中广泛使用[20]。本研究采用最大值合成法MVC(Maximum Value Composites)获取每月NDVI最大值,代表当月植被生长的最佳状况及其动态变化,同时也可以有效减少大气、视角以及太阳高度角的影响[21]。利用ENVI和ArcGIS软件对数据进行分析,包括格式和投影转换、图像拼接、图像裁剪以及重采样等,最后得到本研究所需要的空间分辨率为1 km的NDVI数据。在此基础上,对月最大NDVI求取平均值得到长江经济带年NDVI值。
气象数据、土地利用数据、DEM数据均来源于中国科学院资源环境科学数据中心(http://www.resdc.cn)。本研究采用的是中国1980年以来逐年年平均气温、年降水量空间插值数据集,空间分辨率重采样为1 km; 以及选取了2000年和2015年两期1 km的土地利用数据。土地利用类型包括6个一级类型(耕地、林地、草地、水域、居民地和未利用土地),25个二级类型。
2.2 研究方法
2.2.1 空间变化趋势分析
趋势分析法主要是采用最小二乘法来逐像元拟合,通过分析单个像元上的变化特征来反映整个空间上的变化规律[22]。本研究通过该方法分析2000—2015年研究区内每个像元NDVI的年际变化趋势。计算公式为:
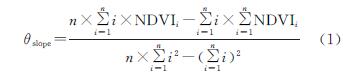
式中:θslope为NDVI变化趋势的斜率; n为研究总年数; NDVIi为第i年的NDVI。当θslope>0或<0时,表明NDVI呈增加或下降趋势,θslope的绝对值越大,表示植被变化越大。变化趋势显著性检验采用F检验[7],显著性仅代表趋势性变化可置信程度的高低,与变化快慢无关。计算公式为:
F=U×(n-2)/Q (2)
式中:U=∑ni=1((^overy))2为误差平方和; Q=∑ni=1(yi-(^overy)i)2为回归平方和; yi为第i年的NDVI; (^overy)i为其回归值; y^-为多年平均NDVI; n为16。
综合θslope和F检验结果,将研究区NDVI变化趋势划分为5个等级:显著减少(-0.055<θslope<-0.009,p<0.01)、轻度减少(-0.009<θslope<0.002,0.01<p<0.05)、无明显变化(0.002<θslope<0.006,p>0.05)、轻度增加(0.006<θslope<0.012,0.01<p<0.05)、显著增加(0.012<θslope<0.078,p<0.01)。
2.2.2 波动性分析
变异系数是一个统计量,可监测一组观测数中各观测量的变异程度[15],本文运用该统计量基于像元尺度对NDVI在时间序列上的变异程度进行分析,以此来评估NDVI随时间变化的波动性。计算公式为:
CV=σ/μ (3)
式中:CV为变异系数; σ为16 a的NDVI标准差; μ为均值。值越大,表明数据变化越剧烈,即波动性越大; 反之则表明数据变化趋于稳定即波动性小。
2.2.3 偏相关性分析
偏相关系数可用来表示多个因素间变化的相关程度。偏相关性分析的过程主要是:当3个变量中有两个同时与另一个变量都相关时,先排除另一个变量的影响,分析两个变量间的相关程度[6]。本研究基于年尺度分别计算各像元2000—2015年NDVI与年降水量、年均气温的偏相关系数,显著性检验用T检验。
先计算NDVI与气候因子间的相关系数r,公式[23]如下:
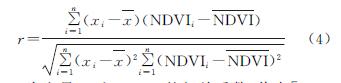
式中:r为变量X和NDVI的相关系数,值在[-1,1],r>(<)0,表示呈正(负)相关; i为年序号; n=16; NDVIi为第i年的NDVI; NDVI^-为对应16 a的年平均NDVI; x为气候因子即年平均气温或年降水; x^-为对应气候因子16 a的平均值。
再计算偏相关系数:

式中:Rabc为保持变量c不变,变量a和b之间的偏相关系数; rab,rac,rbc分别为变量a,b,c两两之间的相关系数。Rabc为正(负),表示两个变量之间呈正(负)偏相关且绝对值越大,两者偏相关性就越大。本研究中变量a,b,c分别为NDVI、气温和降水。
T检验[24]计算公式:

式中:r为相关系数; f为自由度。根据求得的R结果与T检验结果分别将气温和降水两个因子的偏相关性分为5个等级:显著正偏相关、弱显著正偏相关、无显著偏相关、弱显著负偏相关和显著负偏相关。
2.2.4 地形因子提取
为进一步分析研究区NDVI变化对地形因子的响应,本研究选取海拔、坡度、坡向3个地形因子并进行等级划分。其中,研究区高程范围为-181~6 511 m,在李炳元等[25]提出的分级指标基础上,结合研究区实际情况及相关研究[12,14],将高程划分为10个等级; 研究区坡度范围为0°~81°,根据实际情况及相关研究[12,26],坡度在35°以下的以5°为间隔划分,大于35°的分为两级,共分为9个等级; 坡向上,依据相关研究[26-27]分为9个坡向带:平地(-1)、正北(337.5°~360°和0°~22.5°)、东北(22.5°~67.5°)、正东(67.5°~112.5°)、东南(112.5°~157.5°)、正南(157.5°~202.5°)、西南(202.5°~247.5°)、正西(247.5°~292.5°)和西北(292.5°~337.5°)。分级及面积占比见表1。
2.2.5 土地利用变化
本研究在ArcGIS平台支持下,对2000年和2015年两期土地利用数据进行叠加,分析其空间分布特征,并计算面积转移矩阵分析土地利用类型转变情况。另外将NDVI变化趋势重分类为3类:减少、稳定和增加,利用空间叠置分析功能,将其与两期土地利用类型图进行叠加,分析土地利用类型变化与NDVI变化间的空间动态分布特征。另外将土地利用转化面积在500 km2以上的变化类型作为主要类型提取出来,统计不同NDVI变化趋势范围内主要土地利用变化类型的面积,了解主要土地利用变化对植被的动态影响,进一步分析土地利用变化与植被动态变化间的响应关系。