资助项目:国家重点研发计划政府间/港澳台重点专项项目(2018YFE0184300); 云南基础研究重点项目(2019FA017); 国家自然科学基金(41561048); 云南省高校科技创新团队
第一作者:祁兰兰(1992—),女,江苏盐城人,硕士生,主要从事资源与环境遥感技术应用研究。E-mail:1691439830@qq.com 通信作者:王金亮(1963—),男,云南昆明人,教授,主要从事资源与环境遥感技术应用研究。E-mail:jlwang@ynnu.edu.cn
(1.云南师范大学 地理学部, 昆明 650500; 2.云南省高校资源与环境遥感重点实验室, 昆明 650500; 3.云南省地理空间信息工程技术研究中心, 昆明 650500)
(1.Faculty of Tourism and Geographic Sciences, Yunnan Normal University, Kunming 650500, China; 2.Key Laboratory of Resources and Environmental Remote Sensing for Universities in Yunnan, Kunming 650500, China; 3.Center for Geospatial Information Engineering and Technology of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650500, China)
land use; landscape pattern; lake basin; water quality; correlation analysis
水资源是支撑社会经济发展的战略性资源,对于维持生态社会经济系统的可持续发展至关重要[1-2]。近几十年,随着人类活动的扩大,城镇化进程的加快,河流湖泊的水质恶化成为影响生态文明建设的主要制约因素[3]。人为活动改变了土地利用方式和自然景观格局,土地利用在污染物产生,迁移和转化过程中起着重要作用[4],而景观格局控制着一个流域的各种生物地球化学和物理过程,景观格局的变化会引起许多水文过程,如地表径流、地球化学循环等,会导致大量污染物进入水体,因此,土地利用和景观格局的变化是影响水质的重要驱动因素[5-6]。探讨土地利用和景观格局与湖泊水质之间的关系,不仅可以为流域的景观格局规划提供参考,也对流域水资源可持续利用及识别水质的主要威胁具有重要意义。
针对土地利用景观格局与水环境质量的关系,相关学者进行了很多研究。自20世纪70年代以来,土地利用/覆被与水质的空间耦合关系就是早期研究的重点[7]。不合理的人类活动通常会改变地表特征,产生污染,增加污染物负荷[8]。强烈的农业活动与快速的城市化进程增加了污染物入湖、入河的数量,进一步恶化了水质。农业生产过程中,化肥农药的使用引起的非点源污染是水环境污染的重要来源[9],农业用地面积占比与水质呈显著正相关[10]。城市化进程中过多的人造地表改变了径流方式,导致污染物无法被截留、吸收,直接进入水体,进而对水质产生负面影响[11]。林草地对污染物的截留起到了积极作用[12]。2000年以后,从景观生态学角度探索土地利用景观格局与水质的关系成为许多学者重点关注问题[13-14]。主要集中分析了景观构成属性[15]、景观格局空间属性[16]、不同景观类型的空间尺度下对水质的影响[17-18]。目前研究景观格局与水质的关系多采用模型与数理统计方法[10]。但是由于研究区的地域差异性、选取的景观指标及水质参数不同,使得土地利用/景观格局对水质的影响关系这一论题的结论不一致,甚至在同一区域内,若区域内自然特征、土地利用结构及景观格局特征有差异,也会导致研究结论产生不确定性。因此,有必要针对存在的问题开展进一步地研究,剖析二者之间的关系。
本文选取的研究对象(三湖流域)呈现出了地域差异性这一特点,三湖流域均分布于云贵高原区,海拔较高,生态系统较为脆弱。三湖同属断层陷落淡水湖,湖泊换水周期长,自净能力不足,湖泊生态平衡状态极易被打破。三湖虽然自然条件类似、地理位置相近,但是由于各个湖泊流域内人为土地开发强度、经济发展模式及湖泊内部特征不同,使得3个湖泊水质差异明显,不同程度地制约了三湖流域的生态环境建设和社会经济可持续发展。其中,抚仙湖是深水贫营养湖泊,水质较好; 星云湖是典型地高原浅水湖泊,由中营养过渡为富营养; 杞麓湖与抚仙湖、星云湖距离较近,而水污染较为严重,呈中度至重度富营养状态。基于此,本研究采用Pearson相关分析及冗余分析法分析抚仙湖流域、星云湖流域、杞麓湖流域这3个高原湖滨区不同土地利用变化对水质的影响,探讨景观指数与水质之间是否具有相关性,综合分析土地利用/景观格局对水质的影响,为高原湖泊生态系统保护和水环境保护措施的制定提供理论依据。
抚仙湖(24°21'—24°38'N,102°49'—102°57'E)、星云湖(24°17'—24°23'N,102°45'—102°48'E)、杞麓湖(24°4'—24°14'N,102°33'—102°52'E)均位于滇中腹地(云南省玉溪市境内),同属珠江流域南盘江水系,为滇中经济区的社会发展、生态环境等方面提供重要的水资源基础。三湖流域地处亚热带季风气候区,属于中亚热带湿润高原季风气候,具有四季温和,干湿季明显等特征,5—10月为雨季,且流域内地形错综复杂,以山区和坝区为主,呈西北高、东南低地势。
抚仙湖为珠江源头湖泊,平均水深95.3 m,流域面积675.48 km2。自1990年至今,玉溪市政府进行抚仙湖流域水污染综合防治“十五”“十一五”“十二五”规划,使其水质整体保持在Ⅰ类,但是湖滨区及流域北岸受到工农业及旅游业发展的影响,局部水质为Ⅱ类,由于湖泊换水周期长达167 a,生态系统极易受到破坏。
星云湖是抚仙湖的上游湖泊,通过隔河与抚仙湖相连,其流域面积409.36 km2。星云湖平均水深仅4.73 m,蓄水量2.3亿 m3,流域内磷矿资源丰富,磷矿产业较为聚集,是星云湖总磷含量居高不下的主要原因。1994年以前,星云湖整体水质为Ⅲ类,2002—2018年,水质始终处于Ⅴ类甚至劣Ⅴ类的位置,由中营养向富营养状态转变。
杞麓湖距离抚仙湖不到100 km,有4条主要入湖河流,无明出流口,为典型的封闭性高原陷落性湖泊。根据文献[19],杞麓湖流域是云南省九大高原湖泊人口高度密集,城市化率较高,受环境资源约束较大的地区,流域内以农业面源污染及工业污染为主,导致湖体水质整体污染严重,1990—2018年水质呈Ⅳ类—劣Ⅴ类—Ⅴ类的趋势。
综上所述,抚仙湖属于深水贫营养湖泊,湖泊容量大,但是受到流域周边人类活动的影响,水质较易受污染; 星云湖属于典型的浅水性富营养湖泊,生态系统较为脆弱,当前水质污染严重; 杞麓湖流域周边土地开发程度高,加重水质受污染风险。
三湖流域土地利用数据来源于中国科学院资源环境科学数据中心(http://www.resdu.cn/lds.aspx)1990年、1995年、2000年、2005年、2010年、2015年、2018年的30 m×30 m精度的全国土地利用遥感监测数据。参照中科院一、二级分类体系,结合研究区实际情况,将研究区分为耕地、林地、草地、湖泊、水库坑塘、建设用地6种土地利用类型。评价水环境污染程度时,选用多种环境质量参数。本研究结合研究区的实际污染状况,选取与土地利用数据对应的7个年份的高锰酸盐、生化需氧量、总磷、总氮4个水质指标的年均值作为水质数据。水质数据主要来源于相关的文献资料[20-22]、《云南省环境状况公报》、星云湖“十一五”规划、杞麓湖流域水污染综合防治“十一五”规划。
基于7期土地利用数据,利用ArcGIS 10.6软件分析1990—2018年的三湖流域土地利用面积变化及转移情况,阐明土地利用类型空间变化特征。景观指数是反映景观格局的定量指标,可从斑块、类型、景观3个类别上反映土地利用空间格局信息[23]。为了分析整体景观结构,研究从表征景观破碎度、聚集度、连通性指数、多样性指数中选取了5个景观指数反映景观格局特征(表1)。采用Fragstata 4.2景观指数分析软件计算7期土地利用数据的PD,LSI,CONTAG,COHESION,SHDI。
基于SPSS软件,采用Pearson相关系数分析土地利用/景观指数与湖泊水质之间相关性,Pearson相关性分析实质上是研究两组变量之间的线性相关程度,公式如下:
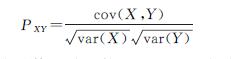
式中:PXY为总体相关系数; cov(X,Y)为随机变量X/Y的协方差; var(X)/var(Y)分别代表X和Y的方差。样本相关系数的计算公式为:
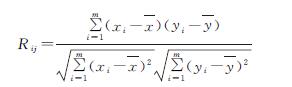
式中:xi,yi为变量,i=1,2,…,m; x^-,y^-为xi,yi的均值; Rij为样本相关系数,采用T检验对样本显著性差异进行计算。最终相关系数为正时,表明该因素对湖泊水体污染物起到了正向作用,加重污染; 系数为负时,表明影响因素对污染物产生了负效应,减轻污染。
借助Canoco 5软件进行土地利用/景观指数与湖泊水质的冗余分析(Redundancy Analysis,RDA)。RDA是一种从统计学角度阐释一组变量与另一组多变量之间的排序分析方法,该方法起源于生态学,用来揭示物种与环境变量之间的关系,后来被应用于地理学中土地利用覆被与水质等方面。该方法既能揭示各个环境变量(土地利用/景观指数)对湖泊水质变化的贡献率,又能以二维排序图直观地呈现出环境变量与水质间的关系[24]。因此,以RDA方法分析土地利用/景观指数与水质间的关系,首先对水质参数进行降趋式对应分析(Detrended Correspondence Analysis,DCA),若Lengths of gradient第一轴大于4,则选择CCA分析,介于3~4,则两种模型均可,若小于3,RDA的效果更佳。结果显示Lengths of gradient第一轴的结果为0.3,所以选择冗余分析(RDA)。排序图中一种箭头表示水质数据,另一种箭头表示土地利用/景观指数,箭头夹角之间的余弦值代表了二者的相关性,两者之间夹角的余弦值小于0时,两者呈正相关,夹角越小,相关性越高; 两者之间夹角余弦值为0时,两者无相关性; 二者之间夹角余弦值大于0时为负相关,夹角越大,相关程度越高。箭头长度代表了该影响因子所占比重,箭头越长影响程度越高。
由图1可知,抚仙湖流域以林地和湖泊为主要土地利用类型,面积占比分别平均达到25.75%,32.53%,变化幅度微弱。建设用地面积持续增加,但占比较小(2.07%~2.78%),增加了34.81%。星云湖流域耕地、林地面积占比较大,分别为(32.16%~36.25%,30.15%~32.11%),并且波动式下降,其余土地利用类型占比较小,其中建设用地呈波动式上升趋势,面积占比增加了1.01%。杞麓湖流域耕地、林地为优势景观类型,面积占比最显著,分别平均达到44.63%,26.52%,而湖泊水面在2000—2018年面积占比变化幅度大,主要由于2010—2015年,受围湖修坝影响,湖泊水面缩小,湖滨带出现大面积滩地,2015—2018年为维护水环境,滩地又转为湖泊水面。总之,1990—2018年,三湖流域的耕地面积波动式减少,建筑用地逐年递增,剩余土地利用类型变化趋势幅度小(图1)。不同土地利用类型由于受人类活动的干扰,相互之间会发生转移。1990—2018年,三湖流域的土地利用类型转移以耕地、林地、草地、建设用地为主,根据转出面积的大小排序依次为耕地>林地>草地>建设用地,其余土地利用类型的转移幅度较小。三湖流域内耕地基本上转为林地、草地,这与三湖流域土地利用规划中退耕还林、还草政策相关; 林地大部分转为耕地、草地; 草地多数转为林地。建设用地的增加量主要来源于耕地的转入,抚仙湖、星云湖、杞麓湖流域耕地分别向建设用地转入了5.56,5.39,8.51 km2,表明三湖流域内人类活动增强,城镇化发展占据了大量的耕地,同时利用林地、草地填补耕地,保护区域生态环境。
景观指数可反映景观格局的空间结构,研究区内,1990—2018年总体景观指数变化如下(图2)。三湖流域的PD,LSI,SHDI指数均增加,表明研究区受人为干扰影响强烈,景观破碎化程度加深,异质性增强,不同景观类型的斑块朝着不规则多边形方向发展。抚仙湖与杞麓湖流域CONTAG减小,星云湖流域CONTAG增大; 同时3个湖泊流域的COHESION值介于98.8~99.1,表明3个湖泊流域相邻斑块间的空间连接性增强,空间连通性好,抚仙湖与杞麓湖流域内不同斑块类型团聚程度下降,星云湖流域内不同斑块类型聚集度提升。
抚仙湖、星云湖、杞麓湖水质变化见图3。根据中华人民共和国《地表水环境质量标准》(GB3838—2002)将地表水域环境功能分为Ⅰ类、Ⅱ类、Ⅲ类、Ⅳ类、Ⅴ类。当CODMn≤2,4,6,10,15; BOD5≤3,3,4,6,10; TP≤0.01,0.025,0.05,0.1,0.2; TN≤0.2,0.5,1.0,1.5,2.0时,分别对应Ⅰ类、Ⅱ类、Ⅲ类、Ⅳ类、Ⅴ类。1990—2018年,抚仙湖CODMn,BOD5有显著增长趋势,TP与TN的变化不明显,且4个水质指标均处于Ⅰ类水标准,水质始终保持在Ⅰ类。星云湖CODMn,BOD5,TP,TN总体呈上升趋势,其中在1990—2010年,浓度持续上升,2015—2018年浓度指数下降,且TP,TN是星云湖的主要污染物,TP在2010—2018年一直稳定在Ⅴ类,水质污染严重。杞麓湖BOD5,TP,TN增长趋势明显,CODMn波动较大趋势不明显。BOD5,TP在2010—2015年分别处于Ⅴ类,Ⅳ类水标准,TN一直处在Ⅴ类水标准。可见,2015年之前三湖水质受污染程度较高,2018年水质均有所改善。
(1)土地利用变化与水质相关性。由表2可知,抚仙湖流域耕地面积比与水质指标呈负相关,且与CODMn呈极显著负相关; 林地面积比与CODMn,BOD5呈负相关,草地及水库坑塘与水质呈正相关,林地、草地、水库坑塘与水质的相关性均不显著; 建设用地面积比与CODMn的相关系数为0.875,显著性概率p小于0.01,呈极显著正相关状态。星云湖流域耕地面积比、水库坑塘面积比、建设用地面积比与水质均呈正相关; 林地、草地面积比均与水质呈负相关,但是相关性均不显著,只有林地面积比与水质的相关系数较高,相关系数介于-0.684~-0.504。杞麓湖流域耕地面积比与BOD5呈极显著负相关状态; 林地与草地面积比与水质无显著相关性; 水库坑塘面积比与建设用地面积比与水体污染物均呈正相关,其中水库坑塘与CODMn,建设用地与BOD5之间相关性显著,相关系数分别达到0.820,0.882,显著性概率分别小于0.01,0.05。
综上,抚仙湖流域内耕地对CODMn表现出显著的正效应,建设用地对CODMn具有较明显的负效应,耕地与建设用地是预测抚仙湖水质变化的重要因子。星云湖流域内林地对净化水质有重要作用。杞麓湖流域耕地、建设用地分别对BOD5有相当明显的正效应和负效应,水库坑塘对CODMn具有相对明显的负效应,对于CODMn浓度的增长,贡献较大,耕地、水库坑塘、建设用地可作为杞麓湖水质变化的重要预测因子。
(2)景观格局与水质相关性。抚仙湖流域仅有PD,LSI,SHDI与表征湖泊水质下降指标CODMn呈显著正相关,相关系数分别为0.791,0.773,0.820,其显著性概率p小于0.05。星云湖流域CONTAG分别与CODMn,TP,TN呈显著正相关性,相关性系数分别达到0.807,0.788,0.833,而PD,LSI,COHESION,SHDI与水质指标均无显著相关性。杞麓湖流域PD,LSI与CODMn具有极显著正相关性,相关性系数分别为0.886,0.890,其与BOD5呈显著正相关关系,相关性系数分别为0.848,0.797,COHESION与BOD5的相关系数为-0.944,显示明显的负相关关系,其显著性概率小于0.01,CONTAG与SHDI分别与BOD5的相关性系数为-0.808,0.843,两者间的相关关系均较显著。综上,选取的景观格局指数可有效地预测研究区内水质变化。
(1)土地利用变化与水质冗余分析。由图4可知,三湖流域土地利用面积比与水质变化分析的结果与表2中Pearson相关性分析结果一致。抚仙湖、星云湖、杞麓湖流域土地利用面积比第一轴和第二轴分别累积解释了89.15%,96.37%,88.06%的水质变化。抚仙湖流域耕地、林地均与CODMn,BOD5呈负相关,其中耕地对CODMn的影响程度较大; 草地、水库坑塘与所有水质指标呈正相关; 建设用地与CODMn,BOD5呈正相关,且与CODMn相关性程度较高。星云湖流域耕地、水库坑塘、建设用地面积比与水化学指标呈正相关,其中耕地的箭头最长,对水质影响较大; 林地、草地面积比与湖泊水质指标均呈负相关,林地强烈影响着水质变化。杞麓湖流域耕地与所有水质参数呈负相关关系; 水库坑塘、建设用地与所有水质指标呈正相关,耕地对水质的影响程度较其他土地利用类型高。
(2)景观格局与水质冗余分析。三湖流域景观指数1轴和2轴分别累积解释了89.72%,97.05%,88.23%的水质变化。抚仙湖流域PD,LSI,SHDI与CODMn呈极显著正相关,SHDI对水质影响最大。星云湖流域PD,LSI,CONTAG,SHDI与所有水质指标呈正相关,COHESION与湖泊水质指标均呈负相关,CONTAG对水质影响较大。杞麓湖流域COHESION,CONTAG与所有水质参数呈负相关关系,PD,LSI,SHDI与所有水质指标呈正相关,COHESION对水质的影响程度较其他指数高。
根据表3,得出土地利用类型面积占比与景观指数对水质的解释程度。抚仙湖流域建设用地、SHDI对水质有较高的解释量,分别为61.9%,58.7%。星云湖流域土地利用类型对水质的解释量较低,CONTAG对水质变化具有最高51.5%的解释量。杞麓湖流域耕地、建设用地、PD、COHESION的解释量最高,依次为69.9%,52.3%,59.9%,64%。
同一地域条件下,不同土地利用类型由于自身空间布局及不同强度的人类活动干扰也会使得土地利用类型对水质影响效果产生差异。相关研究表明[25-26],耕地和建设用地对污染物的输出贡献较大,两者作为水体潜在污染物的“源”景观,对水质具有正效应,由于农业用地施肥等原因,土壤中的污染物随着地表径流进入水体,而生活污染物导致建设用地本来就是污染源,加上地表不透水面的增加,为污染物向水体的输出提供了新的途径。而林草地是水体污染物的“汇”景观,能够较好地截留和消减污染物,净化水质。
根据本研究结果,抚仙湖、杞麓湖流域耕地与所有水化学指标呈负相关,且与耗氧污染物(CODMn,BOD5)显著负相关,这与其他研究结果不一致[10]。究其原因,抚仙湖流域内耕地是次要土地用地,且面积在1990—2018年不断减少,而CODMn,BOD5的变化趋势与其相反,表明流域内耕地对CODMn,BOD5具有一定的削弱作用。杞麓湖流域内耕地为首要土地利用类型,其中农业旱地经济作物(烤烟、玉米等)根系部分对氨氮类等化学物质具有吸收作用,使得耕地与所有水质指标负相关。另外,抚仙湖、杞麓湖两个湖泊流域的林地均与CODMn,BOD5负相关,且与TN中度正相关,主要因为两湖流域内林地与其他地类相间分布,发挥了污染源“汇”的作用,减少了CODMn,BOD5两类污染物的入湖量; 同时两湖流域内均呈四周高、中间低的地势,而落地的枯枝,腐叶含有丰富的有机质,通过地表径流的方式将营养物带入湖泊。抚仙湖流域内建设用地主要分布于湖滨区,集中在北部澄江县,同时澄江县内磷矿企业较多,造成了流域内建设用地与CODMn显著正相关。杞麓湖流域内建设用地主要分布于坝区水田周边,二者共同带来的面源及生活污染,对湖泊水质造成威胁。杞麓湖流域内水库坑塘与CODMn显著正相关,这一结果源于杞麓湖是一浅水性湖泊,水库坑塘与湖泊水体相连,通过径流方式携带营养盐入湖,导致湖泊底泥营养物质越积越多,成为湖泊水质潜在的污染源。星云湖流域耕地、水库坑塘、建设用地与所有水污染指数正相关、林地、草地与所有水质指标负相关,但均无显著性,只有林地与水质之间的相关系数稍高,其结论与已有研究成果类似[27]。其次星云湖流域内耕地与林地为主要景观类型,且面积占比相差不大,二者对水质的影响作用互相减弱,其次建设用地扩张缓慢是导致不同土地利用类型与水质指标相关性不显著的主要原因。
三湖流域在各个湖泊流域内自然环境特征、土地利用类型变化及分布影响下,结合表3土地利用/景观格局对水质的解释量,耕地、建设用地是影响抚仙湖、杞麓湖水质的主要土地利用类型。星云湖流域林地对其解释量稍高。
不同湖泊流域内,水质不仅受到土地利用类型的影响,更受到不同流域内景观类型的空间配置及格局的制约。通过建立景观指数与湖泊水体污染物浓度之间的关系,能够更好地预测湖泊水质的变化[27]。
本研究显示,抚仙湖流域中,PD,LSI与CODMn显著正相关。PD,LSI反映景观的破碎度和景观形状复杂度,斑块边界越不规则、景观破碎化程度越严重,湖泊水质越容易被污染,SHDI反映斑块类型的异质性与多样性,其与水质的相关关系受到流域内景观类型的影响。抚仙湖流域内“汇”景观林地受到人为干扰,斑块结构整体性下降,使得吸收“源”景观污染物的能力减弱,随着SHDI指数的增大,促进了污染物的扩散,导致SHDI与CODMn显著正相关,且相关系数较高。结合RDA分析,SHDI,LSI对抚仙湖水体的解释程度较高,因此,SHDI,LSI可作为预测抚仙湖水质变化的关键因子。
本文结果表明,星云湖流域CONTAG与CODMn,TP,TN显著正相关,其余景观指数与剩余水质参数间的相关性不显著。这可能与流域内的景观类型有关系,CONTAG代表不同斑块类型间的团聚蔓延程度,反映景观的分离和散布程度。值越大,斑块间的聚集程度越高。流域内以耕地为主要景观类型,且多分布于湖泊近岸相对集中,斑块间连通性好,造成农业污染物通过地表径流的方式直接入湖,水体污染物浓度增加,湖泊水质下降,与浑太河流域研究相似[17],但也有研究结果与其相反[28],若研究区内以林草地等为优势景观,则在一定程度上有助于减少湖泊污染。此外结合表3中的不同环境因子对星云湖水体的解释程度,CONTAG可有效预测星云湖水质的变化。
在本研究中,通过杞麓湖流域景观—水质相关性分析、RDA分析可知,对杞麓湖水质影响较大的景观指标为PD,LSI,COHESION。PD,LSI均与CODMn极显著正相关的同时,仍与BOD5显著正相关。杞麓湖流域内湖盆坝区是耕地与建设用地的集中区域,耕地面积的减少,建设用地的增长造成斑块类型重复出现的频率上升,景观类型被分割成小的斑块,意味着流域内破碎度的加大会导致斑块间物质流动强度大,有利于污染物的迁移输出。COHESION是衡量斑块连接度的重要指标,杞麓湖流域COHESION与BOD5呈极显著负相关,与徐启渝等[29]在鄱阳湖流域研究的结论相同。表明杞麓湖流域内随着COHESION值的增大,景观趋于高联通方向发展,流域内耕地为优势斑块类型,而旱地小麦等作物的根系部分对水质的净化作用已被其他土地利用类型的零散不规则的斑块分布引起的污染物的聚集所掩盖,导致无法有效净化水质。结合表3中COHESION,LSI,PD对整个湖泊水质具有较高的解释率可推断COHESION,LSI,PD可作为杞麓湖流域湖泊水质的有效预测因子[29]。
(1)1990—2018年,三湖流域的土地利用景观格局变化明显,耕地减少、建设用地占比上升,是主要变化土地类型; PD,LSI,SHDI均增加,流域景观格局异质性增强,破碎化程度加深。
(2)三湖流域土地利用类型对水质影响显著,但不同流域内影响结果存在差异。抚仙湖流域耕地与建设用地是影响水质变化的重要因子,耕地与水质指标负相关,建设用地面积比与CODMn和BOD5呈正相关,表明耕地面积的减少有助于水环境质量提升,而建设用地扩张对于水体污染物浓度的减小起到阻碍作用。星云湖流域内林草地对水质呈现出正面效应,可相对减弱水质受污染风险。杞麓湖流域仅耕地、建设用地与BOD5的相关性极显著,对水质影响较大。
(3)三湖流域景观格局变化对各个湖泊水质的影响效果也存在差异。抚仙湖流域中SHDI,LSI与CODMn表现出显著正相关,且对湖泊水体的解释量较高,可有效预测湖泊水质的变化。星云湖流域仅CONTAG与水质呈现较好的相关性,是引起湖泊水质变化的重要因素。杞麓湖流域景观破碎度越高,斑块间连通性较好,湖泊水质受污染程度越高; PD和LSI与CODMn极显著正相关,对水质污染物浓度的减小起到负效应; 另COHESION,PD,LSI这3个因子均对湖泊水质具有较高的解释量,可以在景观尺度上预测杞麓湖未来水质的变化。