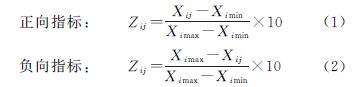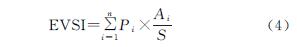3.2.1 生态脆弱性时空分布特征
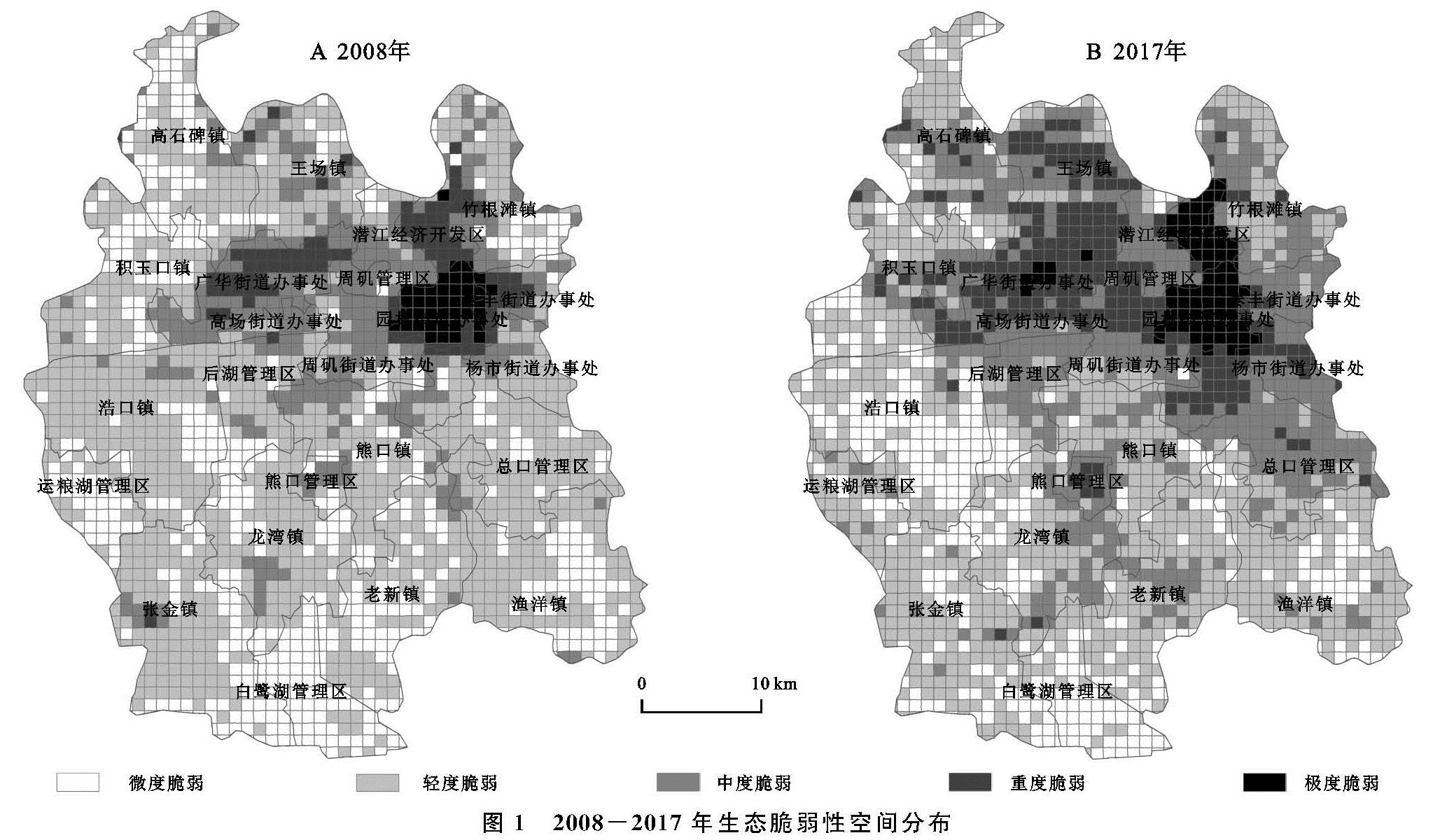
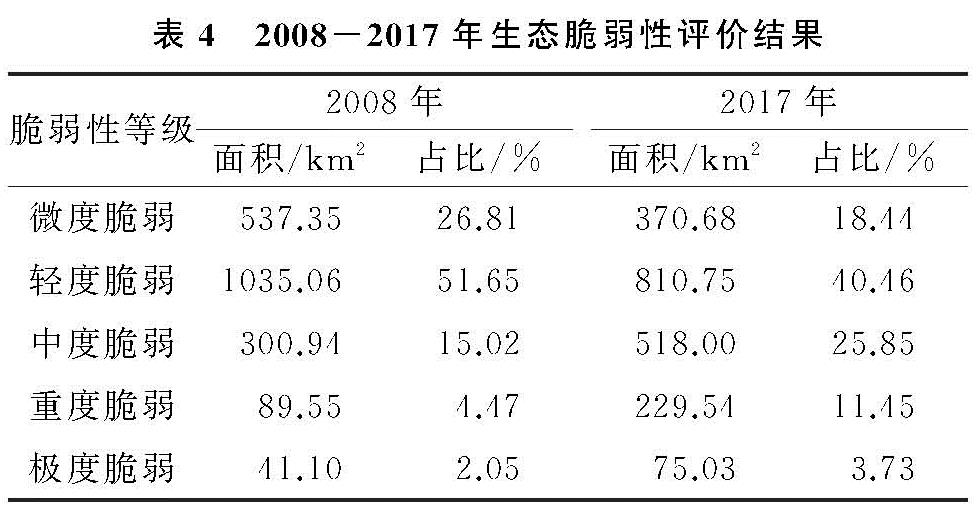
基于SPCA计算结果,借助ArcGIS 10.2软件得到潜江市2008—2017年空间分布图(图1)及生态脆弱性评价结果(表4)。可以发现,2008—2017年潜江市生态脆弱性主要分布在微度脆弱、轻度脆弱和中度脆弱3个等级。其中,微度与轻度脆弱面积总占比均在70%左右,说明潜江市的生态脆弱性整体处于良好水平,且潜江市生态脆弱性主要表现为微度和轻度脆弱面积减少、中度和重度脆弱面积增加的趋势; 此外,潜江市生态脆弱性在空间分布上表现出一定的规律性,即由建成区向外,极度、重度、中度、轻度和微度脆弱依次呈圈层结构发散分布。
2008年,轻度脆弱面积占比居首位,所占比例达51.65%,主要集中分布在城市建成区以南的熊口镇、龙湾镇、张金镇等农业生产区; 其次为微度脆弱,面积占比为26.81%,主要分布在高石碑镇、渔洋镇、白鹭湖管理区; 中度脆弱面积占比15.02%,集中分布于周矶管理区、周矶街道、高场街道; 重度和极度脆弱面积占比较小,分别为4.47%,2.05%,重度脆弱主要分布在广华街道和潜江经开区,而极度脆弱集中于园林街道这一城市核心区。
2009年潜江市被确定为资源枯竭型城市以后,与石油相关的产业持续萎缩,潜江市走上转型发展道路,不断布局新产业、新业态,城镇化水平在近十年间不断提高,经济增长与环境保护的矛盾日益突出。2017年,中度、重度和极度脆弱面积均有所增加,其中,中度脆弱面积增幅最大,新增比例为10.83%,重度和极度脆弱面积分别增加为6.98%,1.68%,极度脆弱主要分布在园林街道和潜江经开区,重度脆弱主要分布在极度脆弱区周边的广华街道、高场街道和周矶街道,而中度脆弱主要集中在熊口管理区及重度脆弱区周围的杨市街道、泰丰街道和后湖管理区; 轻度和微度脆弱面积分别下降8.37%,11.19%,二者交替分布在建成区以南的白鹭湖管理区、浩口镇、龙湾镇、渔洋镇等区域。
3.2.2 生态脆弱性综合分布特征
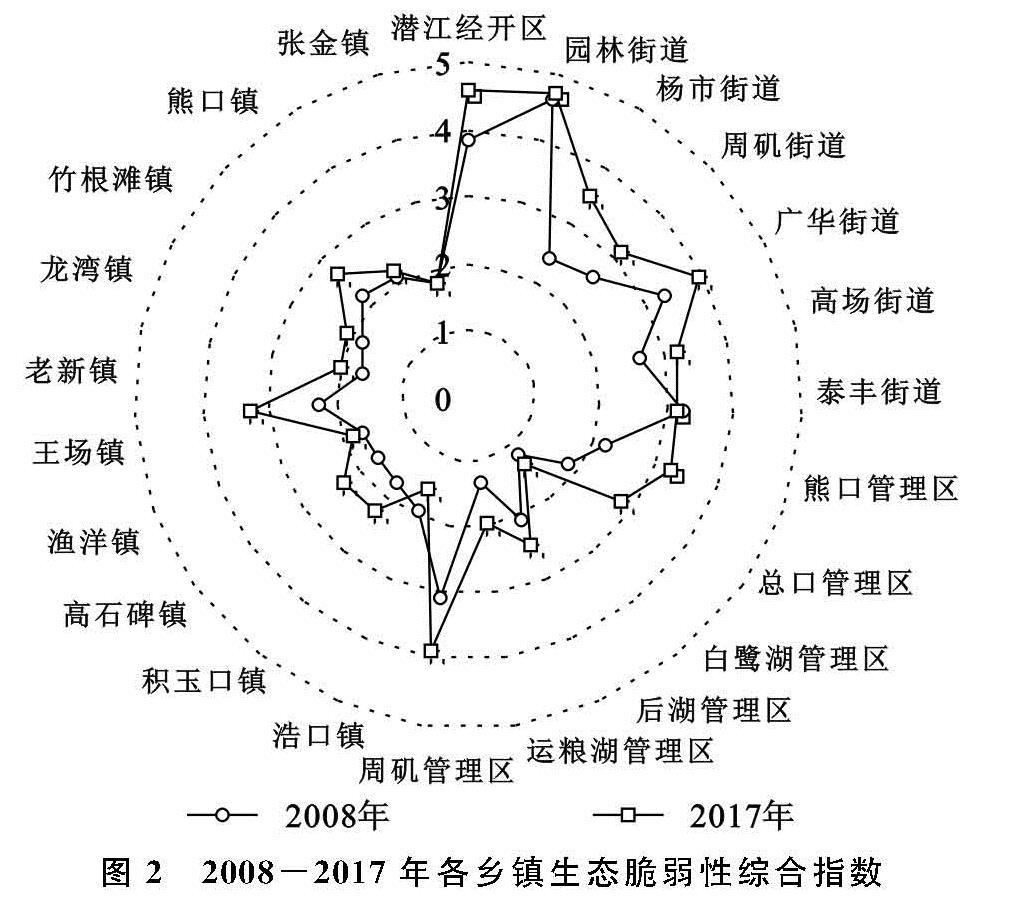
根据公式(4)计算得到潜江市2008年和2017年的生态脆弱性综合指数(EVSI)分别为2.034,2.413,EVSI有所增加,但仍处于相对较低水平,这主要是由于重度脆弱和中度脆弱面积增加、轻度脆弱和微度脆弱面积基数较大导致。进一步计算各乡镇(街道、管理区、开发区)的EVSI发现(图2),2008年除潜江经开区、园林街道、泰丰街道、广华街道以外,其余各乡镇的EVSI均在3以下; 2017年EVSI大于3的新增乡镇有杨市街道、周矶街道、高场街道、周矶管理区和王场镇,其余乡镇EVSI变化的幅度大小不一。
具体来看,2008—2017年绝大多数乡镇EVSI有所增加,浩口镇和泰丰街道EVSI分别下降0.32,0.10。研究期内,潜江经开区、园林街道和广华街道EVSI始终保持在较高水平; 此外,潜江经开区、杨市街道、王场镇、熊口管理区、总口管理区增加幅度最大,周矶管理区、后湖管理区、运粮湖管理区、高场街道、周矶街道、高石碑镇增幅次之。究其原因,近十年间潜江市政府大力推动产业集中布局,潜江经开区现已成为潜江市产业高度集中区,产业快速发展加速了建设用地的扩张; 快速城镇化使得以园林街道为核心的5个街道近年来吸引了不少周边乡镇的人口,推动了建设用地对生态型用地的大面积占用; 周矶管理区、熊口管理区、总口管理区、后湖管理区、运粮湖管理区、王场镇和高石碑镇人类活动相对剧烈,高强度农业生产活动、自然水面减少及建设用地无序扩张对生态环境造成了严重破坏。此外,泰丰街道通过植树造林、增加绿化使区域生态环境质量得到有效恢复,浩口镇有序推动虾稻共作替代传统水面渔业,这既保护了湖泊资源,也减少了化肥、农药的使用,加上较好的自然本底条件,区域生态环境水平不断提升。
图2 2008-2017年各乡镇生态脆弱性综合指数
3.3 生态脆弱性图谱特征分析
3.3.1 生态脆弱性变化图谱分析
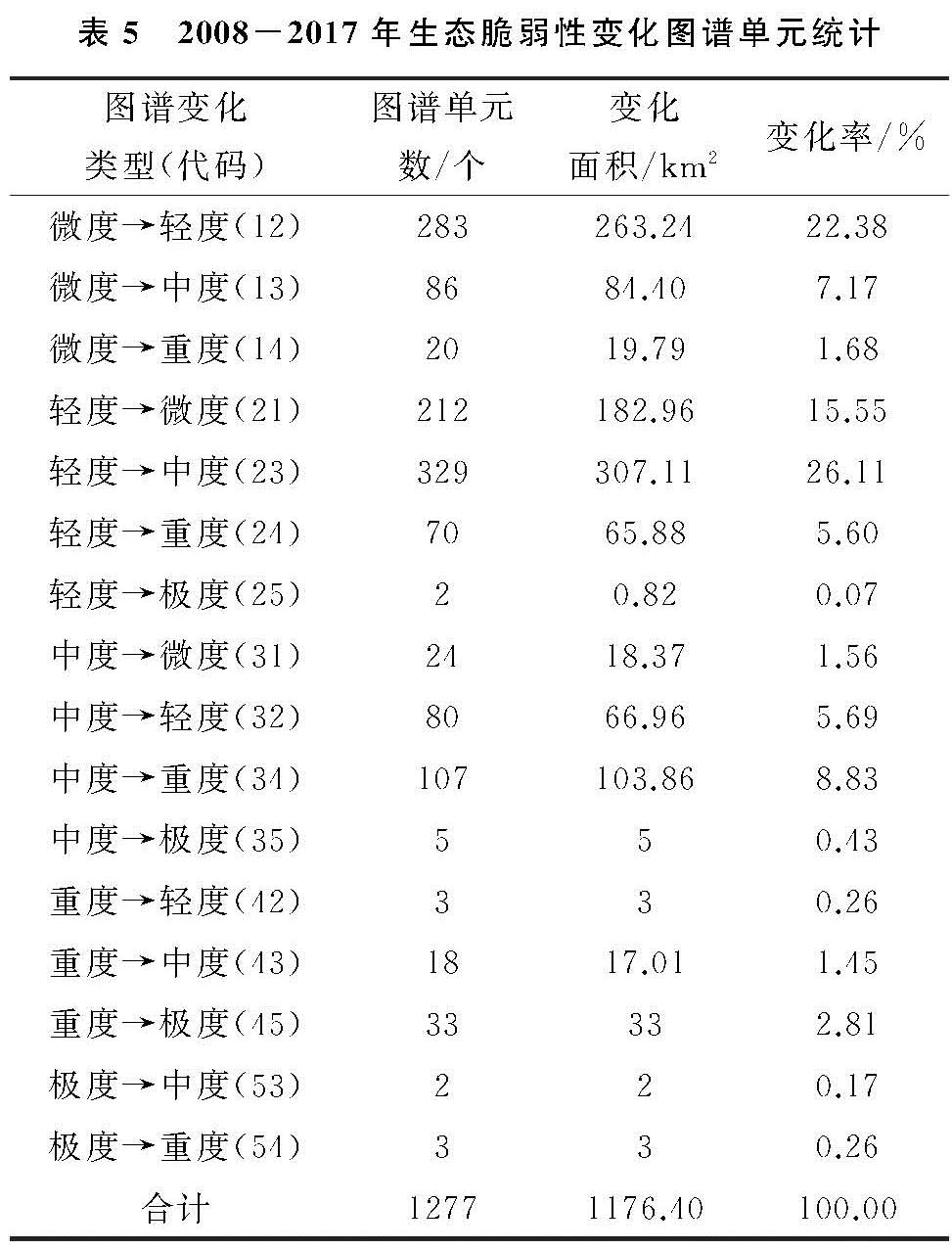
2008—2017年潜江市生态脆弱性变化图谱共生成21类图谱单元,其中16类图谱单元生态脆弱性等级发生变化,变化单元的总面积为1 176.40 km2,占潜江市总面积的58.70%。生态脆弱性等级上升和下降的图谱单元面积分别为883.09 km2,293.31 km2,分别占变化单元面积的75.07%,24.93%(表5)。
在所有变化图谱单元中,前4类图谱单元占变化单元面积的72.87%。其中,“轻度→中度”(代码23)图谱类型最为显著,主要分布在总口管理区和后湖管理区。究其原因,总口管理区和后湖管理区是潜江市最主要的国营农场区,现代农业机械的快速发展促使人们加强了对土地的垦殖力度,直接导致化肥、农药施用量的大幅上升。其次为“微度→轻度”(代码12),主要分布在高石碑镇和运粮湖管理区。第三是“轻度→微度”(代码21),主要集中在浩口镇。微度和轻度的相互转换可归因于农业生产方式的发展变化,高石碑镇和运粮湖管理区为水源的相对集中区,传统的水面养殖渔业面积较大,很多坑塘水面在粗放的利用方式下被破坏,养殖用建设用地在这个过程中也有所扩张; 相反,浩口镇的自然水面相对较少,稻虾、稻鱼等一些生态综合种养农业有效替代了部分传统水面渔业和耕种农业。“中度→重度”(代码34)图谱类型的面积也超过100 km2,主要集中在周矶管理区、周矶街道和广华街道。这主要是因为周矶街道和广华街道在近年来吸引了大量周边乡镇的人口并承接了园林街道一些转移的企业,区内人类经济活动加剧对自然景观的完整性造成了破坏,同时使得建设用地面积急剧增加、绿地和湿地面积逐渐萎缩; 此外,周矶管理区受周边街道影响农业生产强度不断加大,原来的湿地和林地被大面积开垦用来补充耕地。
表5 2008-2017年生态脆弱性变化图谱单元统计
3.3.2 生态脆弱性涨势、落势图谱分析
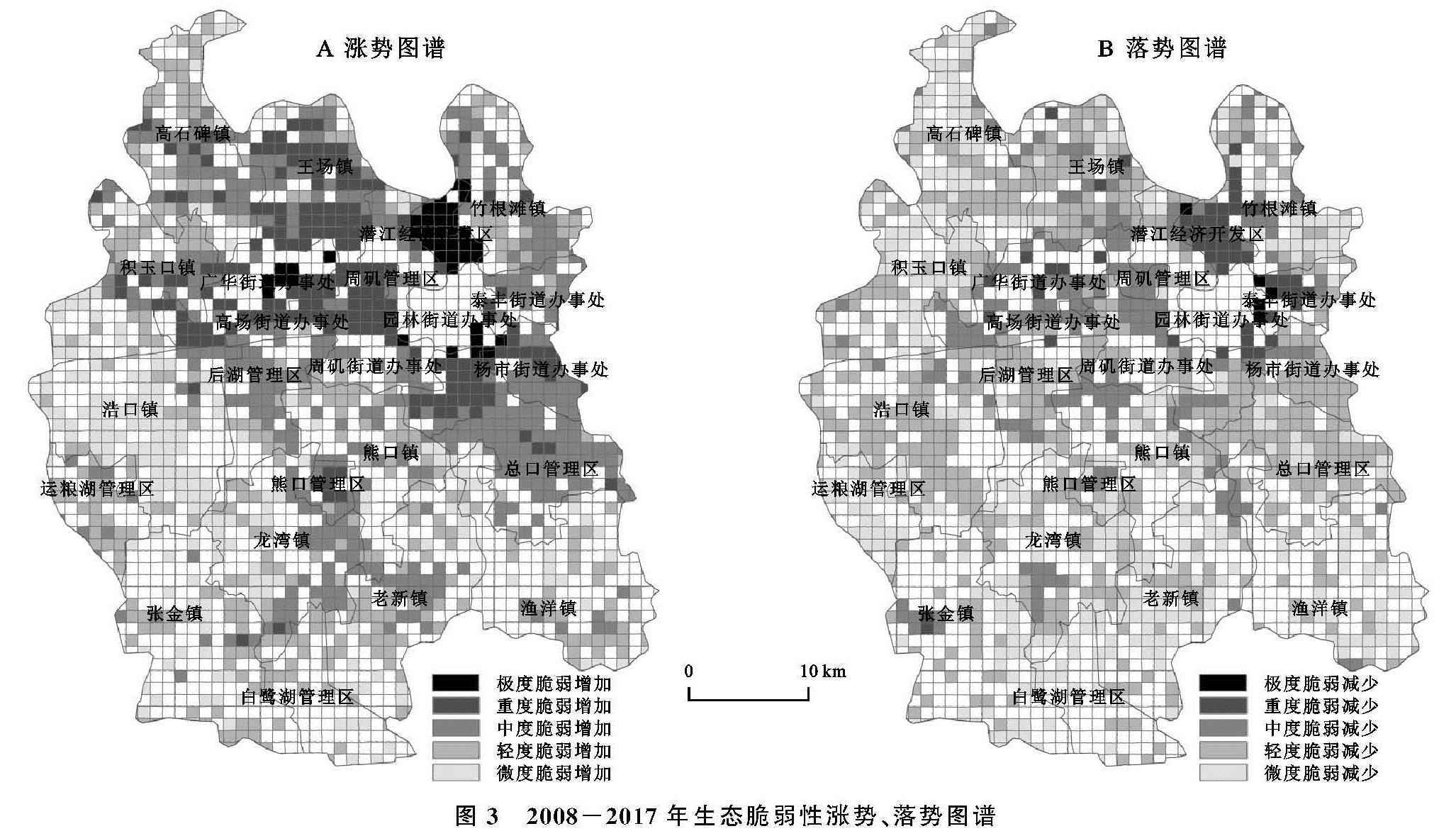
根据图3的结果,2008—2017年潜江市生态脆弱性中度脆弱涨势最强,转入面积高达410.52 km2,占变化图谱单元面积的34.90%,主要分布在总口管理区和后湖管理区。其次为轻度脆弱、微度脆弱、重度脆弱,转入面积分别为333.20 km2,201.32 km2,192.53 km2,新增轻度脆弱单元主要分布在老新镇、高石碑镇和运粮湖管理区,新增微度脆弱单元主要集中在浩口镇,新增重度脆弱单元主要集中在周矶管理区、周矶街道和王场镇。极度脆弱转入面积最小。
2008—2017年潜江市生态脆弱性轻度脆弱落势最强,转出面积为556.77 km2,占变化图谱单元面积的比例高达47.33%,主要集中分布在王场镇、浩口镇、总口管理区、后湖管理区和杨市街道。其次为微度脆弱,转出面积为367.44 km2,主要集中在老新镇和运粮湖管理区。第三为中度脆弱,转出面积为194.18 km2,要集中分布在周矶管理区和广华街道。重度脆弱和极度脆弱转出面积较小。
图3 2008-2017年生态脆弱性涨势、落势图谱
对比生态脆弱性变化图谱和涨落势图谱可以发现:2008—2017年潜江市生态脆弱性涨势图谱中新增中度脆弱面积410.52 km2,落势图谱中轻度脆弱减少面积556.77 km2,同时,生态脆弱性变化图谱中轻度脆弱转变为中度脆弱(代码23)面积为307.11 km2,3个数据间的数量关系说明研究期间新增中度脆弱主要来源于轻度脆弱的减少; 此外,三者的空间分布都主要集中在总口管理区和后湖管理区等地,进一步说明高强度的垦殖活动加深了生态脆弱性水平。对轻度和微度脆弱进行分析发现上述规律同样存在,这说明研究期内潜江市生态脆弱性涨落势图谱和生态脆弱性变化优势图谱的空间分布基本对应。