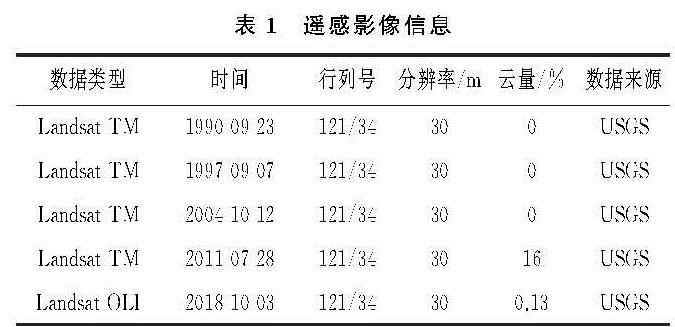
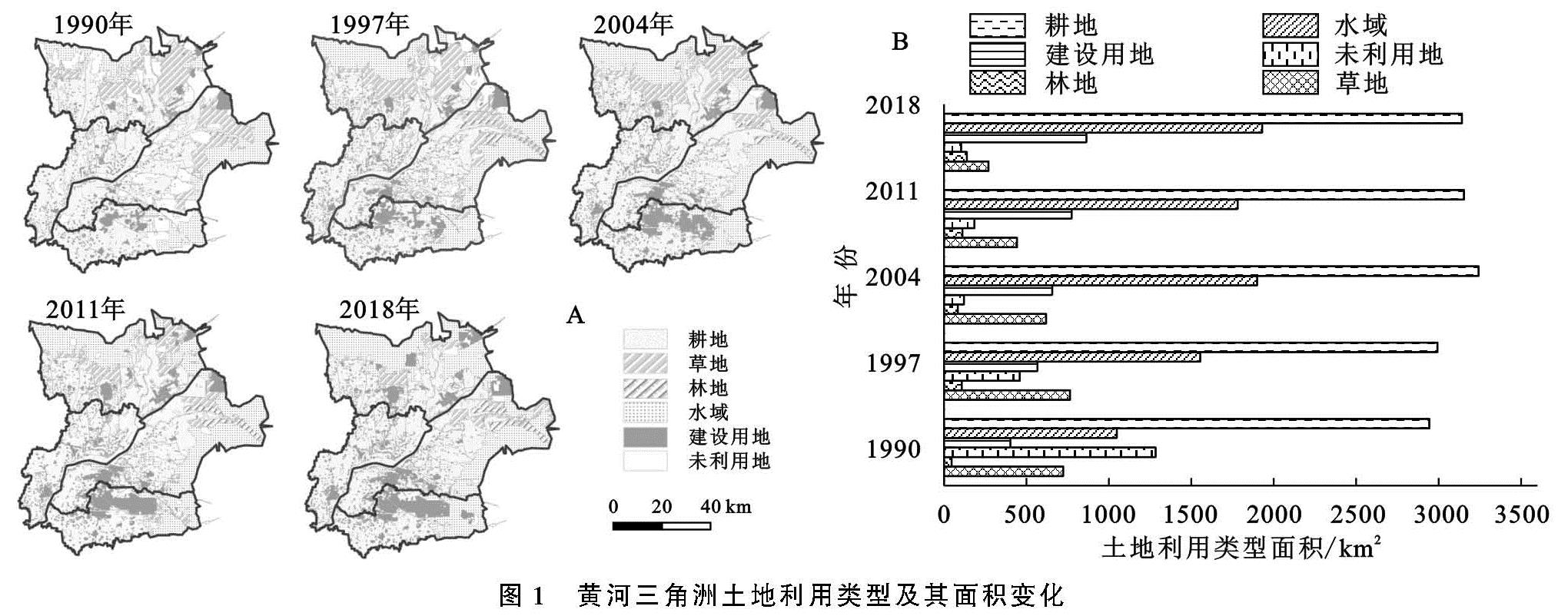
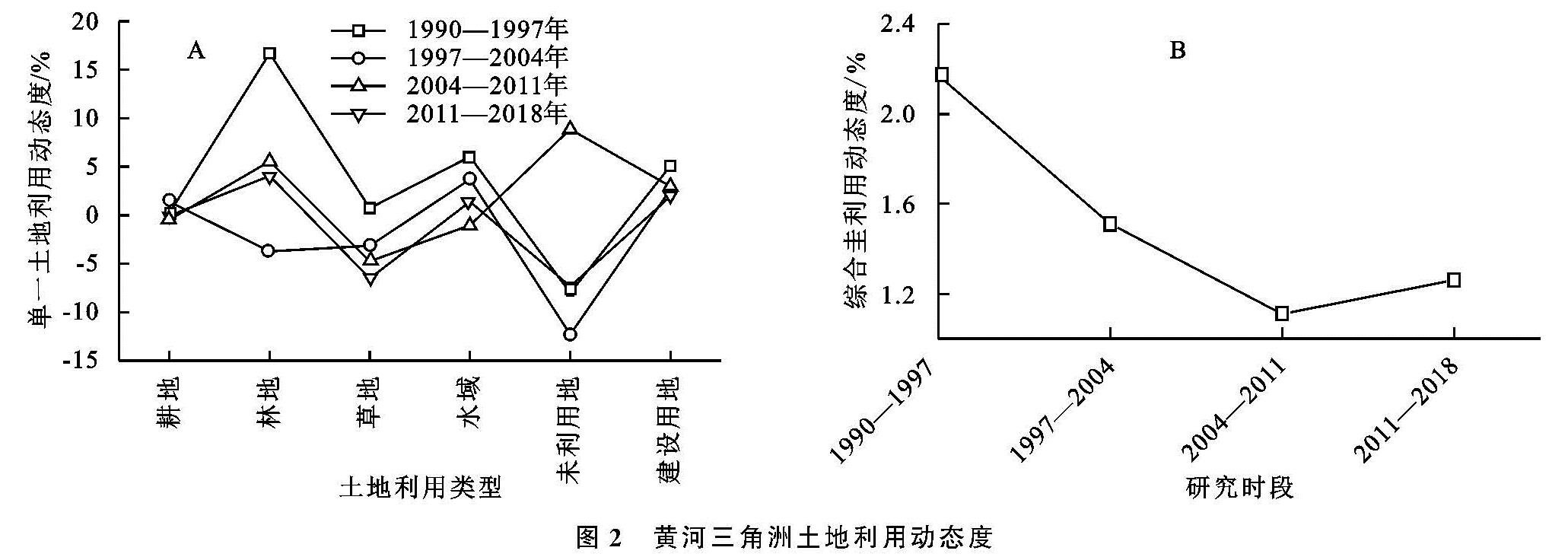
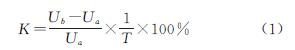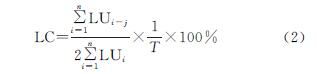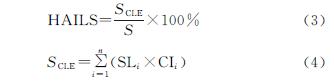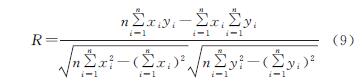(1)近30 a间黄河三角洲土地利用格局演变剧烈,其中,水域面积增加幅度最大,共增加了881.69 km2; 未利用地缩减最显著,至2018年面积缩减至103.27 km2,共减少了1 179.71 km2,其余土地利用类型变化幅度不大。研究时段内,综合土地利用动态度呈先下降后上升的趋势,不同时段人类活动对土地利用干扰程度不同。其中,1990—1997年人类活动对土地利用的影响最强烈,综合土地利用动态度为2.17%。根据单一土地利用动态度结果,该时段人类活动主要表现形式为建造林地、修建水域和扩张建设用地,其单一土地利用动态度分别为16.70%,6.03%和5.10%。
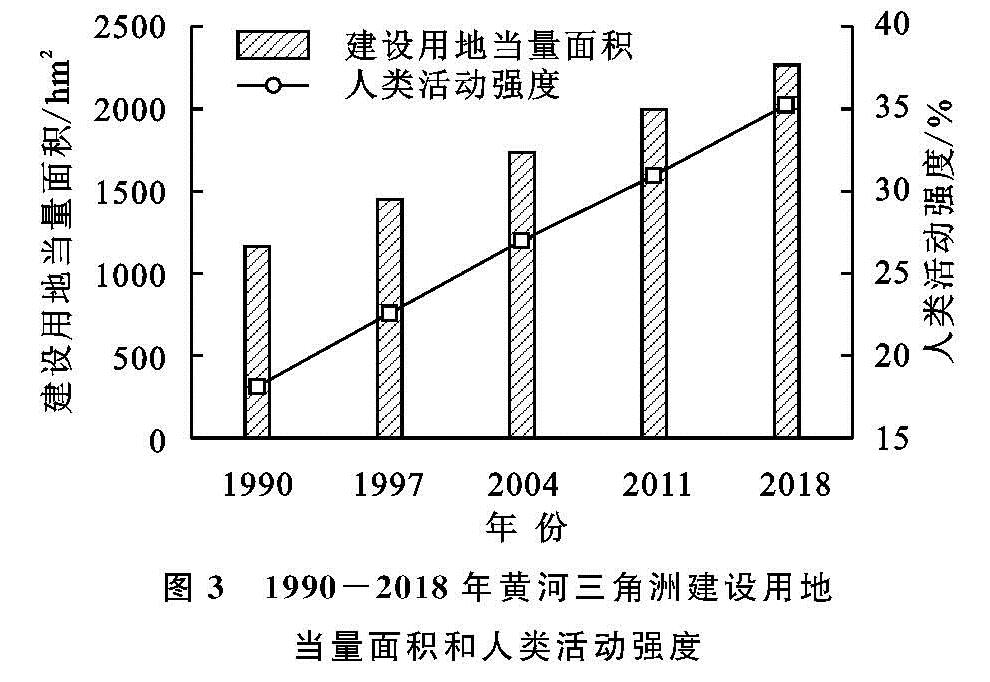
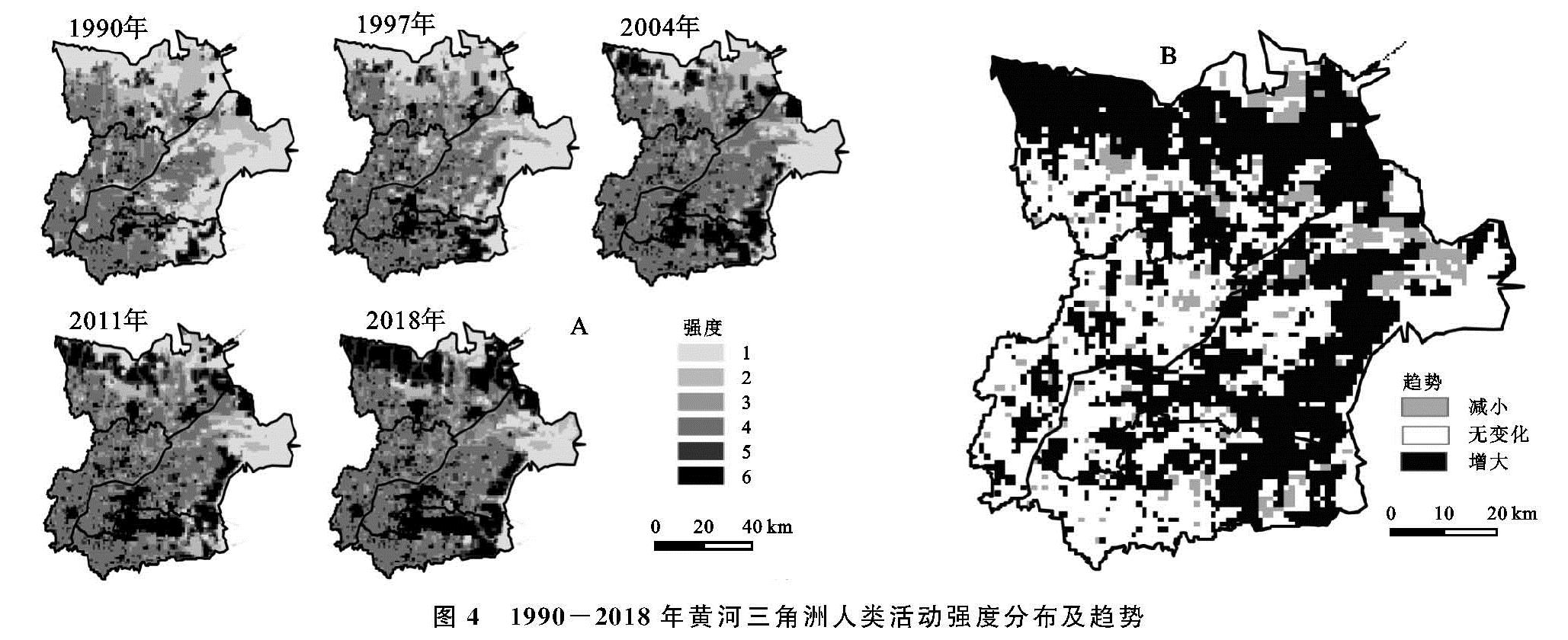
(2)1990—2018年黄河三角洲人类活动强度总体呈上升趋势,1990年黄河三角洲人类活动强度为18.14%,2018年达到35.24%,增长了16.90%。增长幅度大致以2011年为界,前期不断下降,后期增长幅度上升,其中1990—1997年增长幅度最大,年均增长0.64%。从总体上看,研究年限内黄河三角洲人类活动强度分布格局大致呈5,6级强度带向北部及东部边缘地区推进且范围不断扩大、低强度带自内陆向沿海方向消退的特征。其中东营区城镇建设用地和胜利油田地区人类活动较集中,人类活动强度一直较高; 河口区盐田随着时间的变化逐渐从低强度带转变为高强度带。
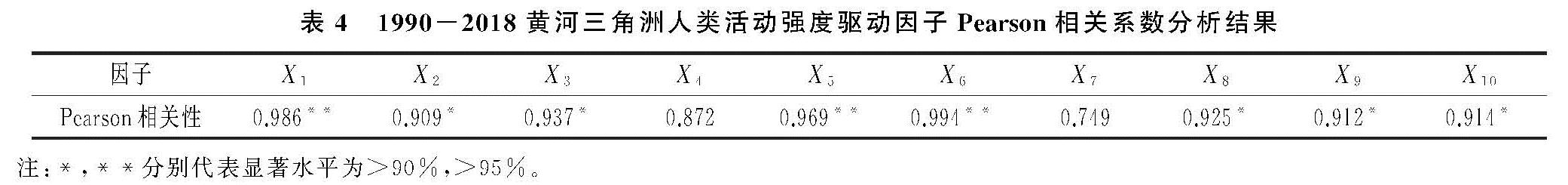
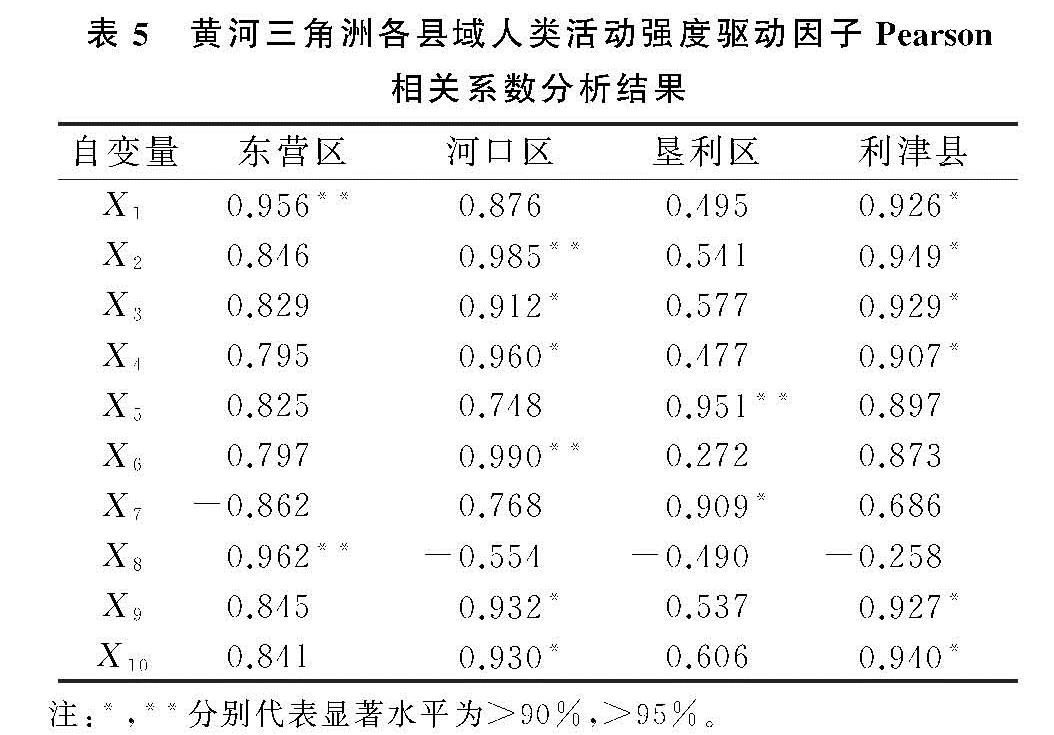
(3)黄河三角洲人类活动强度演变的主要驱动因子是人口密度、原油开采量和盐田开采量。各驱动因素区域差异性显著,东营区主要驱动因子为城镇化率,盐田开采量是河口区主要驱动因子,原油开采量与GDP变化率分别是垦利区和利津县的主要驱动因子。由于本文根据研究区独特的生态要素[15]选取相关指标进行驱动分析,因此主要驱动因子除人口密度外还有盐田开采量和油田开采量,虽与相关研究[28]略有不同,但符合黄河三角洲的特性。
人类活动强度影响因素多样,由于数据获取的限制,本文指标体系有待进一步完善。在复杂的人类活动体系中,量化重要影响因素如土地利用政策、经济发展政策等对人类活动强度的影响很难实现。因此,寻找合适的量化方法分析人类活动强度演变的驱动机制,是未来值得考虑的问题。