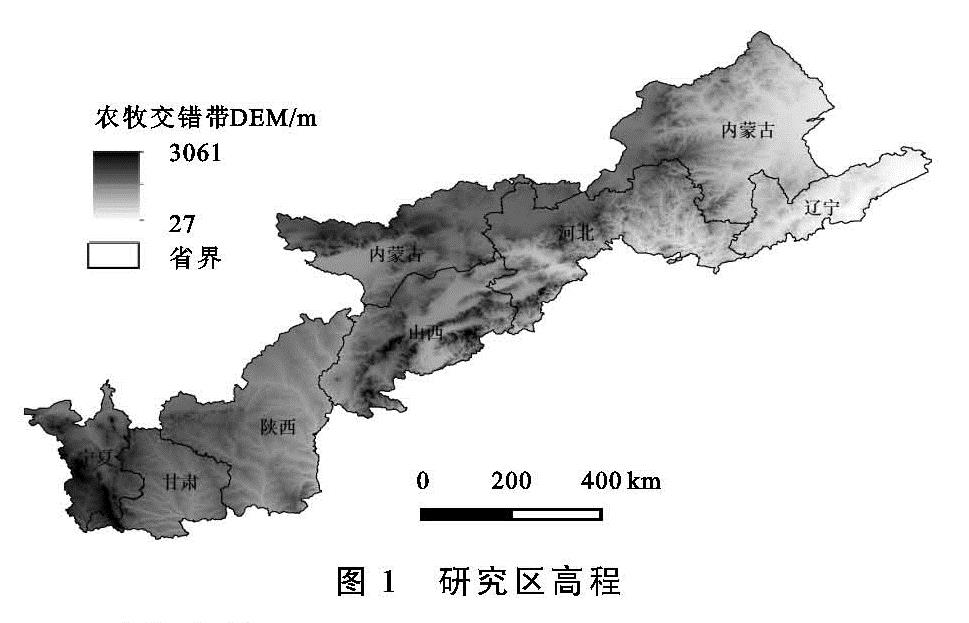
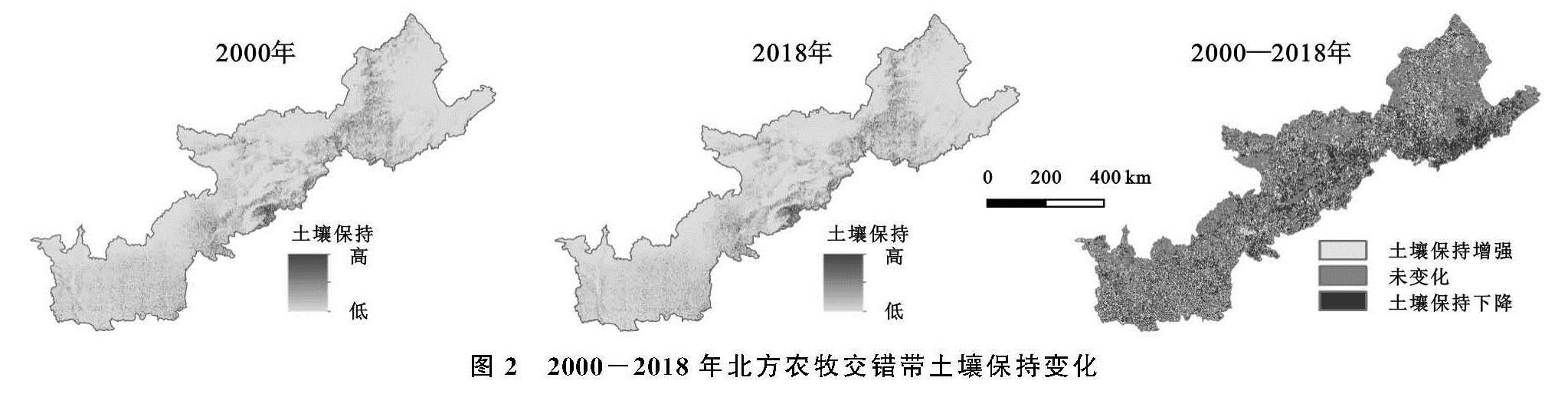
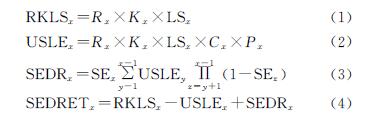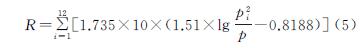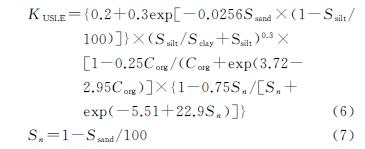2.1 各省土壤保持量变化分析
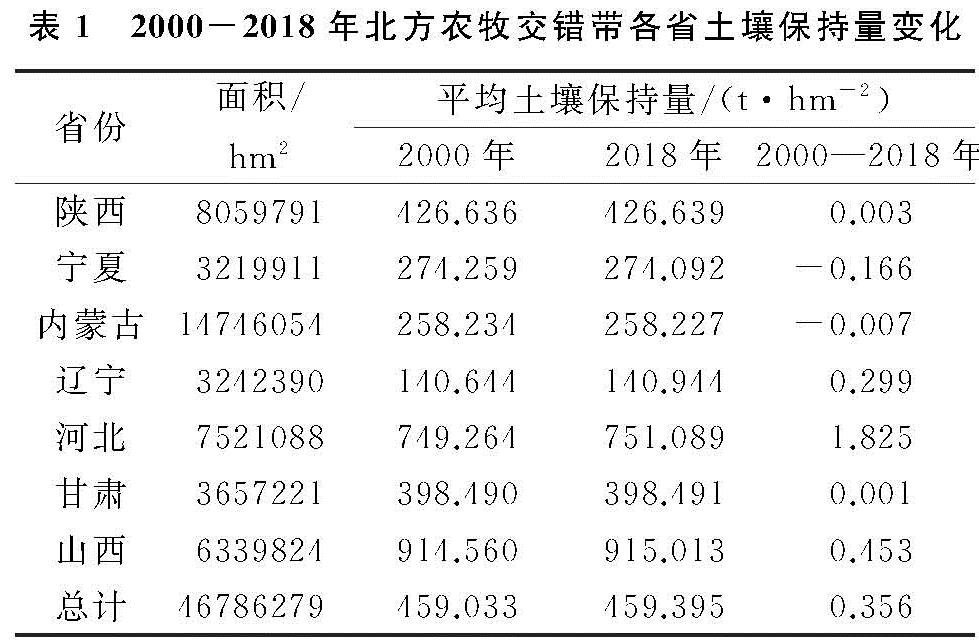
2000年、2018年北方农牧交错带土壤保持及其变化由InVEST模型和ArcMap软件量化与绘制(图2)。根据统计,2000年、2018年研究区土壤保持总量分别为214.76亿t,214.93亿t,研究期间共计增长0.17亿t。结合表1分析,土壤保持量增长区域主要分布在河北、辽宁和山西,因为在研究期间上述3省的平均土壤保持量呈增长趋势,近20 a来分别增加了1.825,0.299,0.453 t/hm2; 相反地,宁夏和内蒙古土壤保持量呈减少趋势,2000—2018年分别由274.259,258.234 t/hm2减少到274.092,258.227 t/hm2; 陕西和甘肃在2000年、2018年土壤保持量相差不大。从分布来看,北方农牧交错带东南部(河北和山西)土壤保持量较高,并且呈增长状态; 相反地,西北部(陕西、宁夏、甘肃、内蒙古)以及辽宁在土壤保持量能力上表现不突出。综上来看,北方农牧交错带7省土壤保持量变化的特点是“三增两减两不变”,分布上呈现“东南强,西北弱”的趋势。
图2 2000-2018年北方农牧交错带土壤保持变化
表1 2000-2018年北方农牧交错带各省土壤保持量变化
2.2 不同坡度等级土壤保持量分析
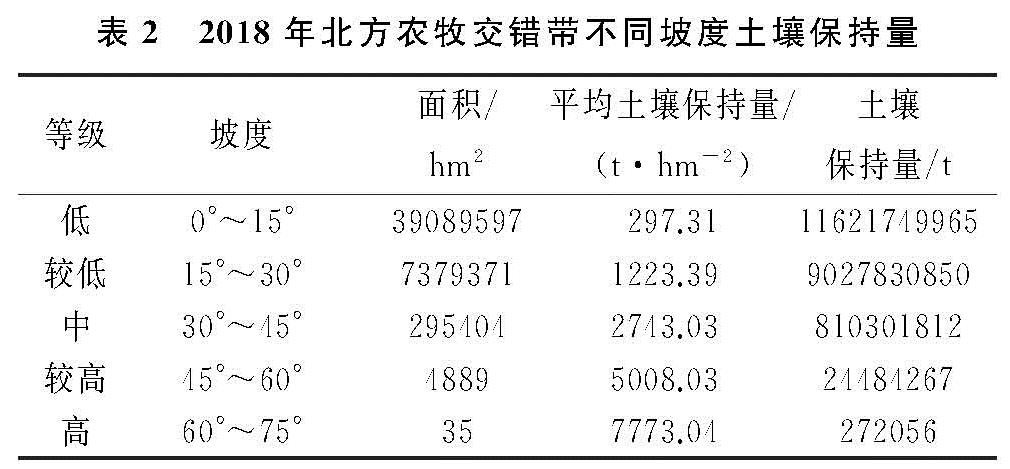
北方农牧交错带范围较广,但为了更好区分不同坡度区域的土壤保持水平,本文采用了坡度每隔15°一段的等距划分法,并赋予等级(表2)。实际上,表2中数据与2000年数据并无差异,本文选择了邻近年份2018年的统计数据进行分析。北方农牧交错带低坡度(0°~15°)土地面积居多,总面积3 908.96万hm2,占比约83.58%; 其次是较低坡度(15°~30°),737.94万hm2,占比15.78%。中等及中等以上坡度面积占比不到1%。尽管低坡度(0°~15°)区域土壤保持总量最多,约116.22亿t(54.09%),但其平均土壤保持量最低,仅297.31 t/hm2。较低坡度(15°~30°)区域面积约为研究区总面积的15.78%,但占据了研究区42.02%的土壤保持总量,约92.28亿t。中等及中等坡度以上区域面积占比0.64%,土壤保持总量比重达到3.89%。综上,随着坡度的上升,土壤保持总量减少,但单位面积的土壤保持量增多,即坡度越陡,土壤保持能力越强。多数研究表明,大于15°以上的土地更易发生土壤侵蚀,随着坡度越陡且越发严重[26],但地表植被会对土壤潜在侵蚀产生一定的阻控,土壤保持能力随之增强[27]。总的来看,北方农牧交错带整个区域处于低坡度区,坡度在0°~15°的土地面积占比83.58%,同时该区土壤保持量在坡度分布上呈现梯级上升式的“总量减、均值增”的趋势。
2.3 不同土地利用类型土壤保持量分析
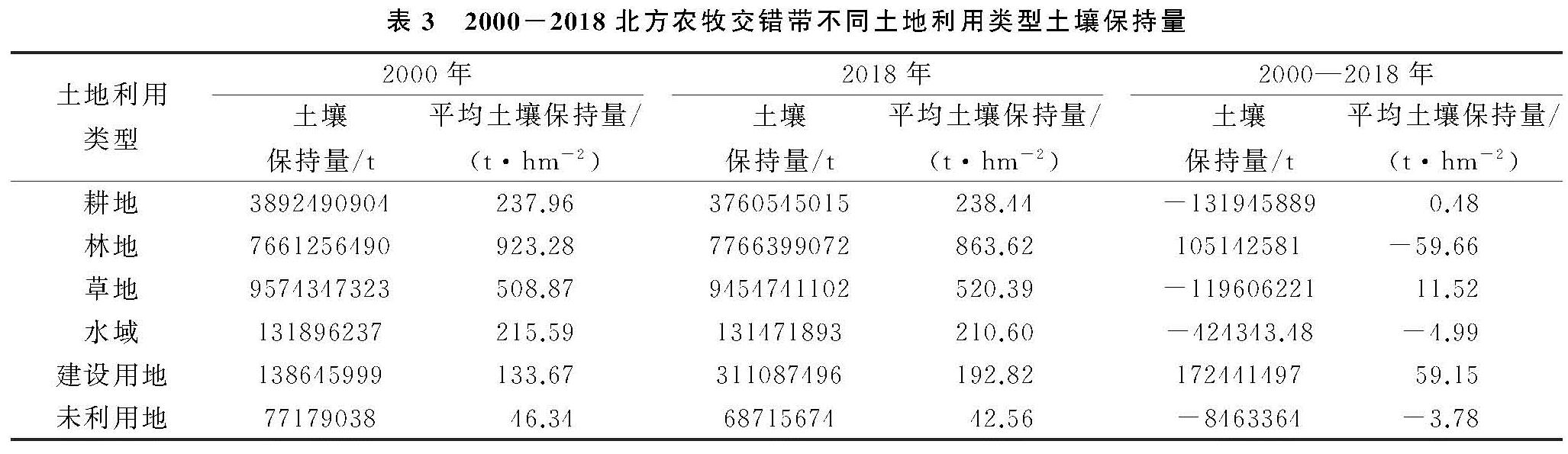
北方农牧交错带不同土地利用类型的单位面积土壤保持量在2000年、2018年及其期间的变化统计见表3。2018年研究区林、草、耕地土壤保持总量分别为76.61,95.74,38.92亿t,分别占据土壤保持总量的36.14%,43.99%,17.50%。研究期间,林地相较于其他土地利用类型,平均土壤保持量在整个研究时期均保持最高,在2000年、2018年分别为923.28,863.62 t/hm2,下降了59.66 t/hm2; 其次是草地,由2000年的208.87 t/hm2上升到2018年的520.39 t/hm2,近11.52 t/hm2的增长。耕地的平均土壤保持量变化不显著,在研究初、末期分别为237.96,238.44 t/hm2,未利用地的平均土壤保持量最低,2018年仅42.56 t/hm2,不足林地的1/20。综上来看,对研究区土壤保持功能提高贡献最大的是林地和草地
表3 2000-2018北方农牧交错带不同土地利用类型土壤保持量
2.4 “退耕还林”区域对土壤保持的影响
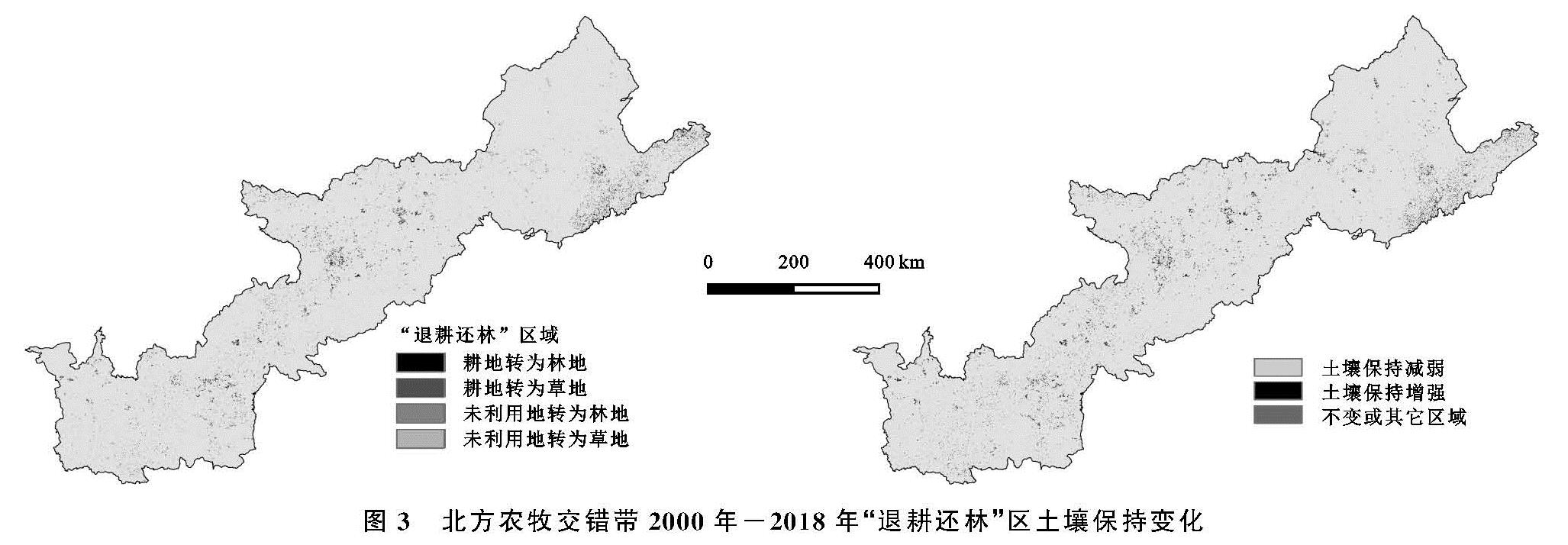
为定量评估退耕还林(草)工程对北方农牧交错带地区的2000—2018年的土壤保持功能影响,在InVEST模型中,分别以该区2000年、2018年的土地利用数据作为变量,其余参数均以2000年数据为基准代入到模型中分别进行了2组试验。同时,提取了研究区2000—2018年期间耕地转林地、耕地转草地、未利用地转林地、未利用转草地的的4个图层。通过ArcMap软件将2000—2018年土壤保持变化栅格图与耕地转林、草地图层叠加分析,得到结果为研究区退耕还林(草)区域土壤保持量变化栅格图(图3)。
图3 北方农牧交错带2000年-2018年“退耕还林”区土壤保持变化
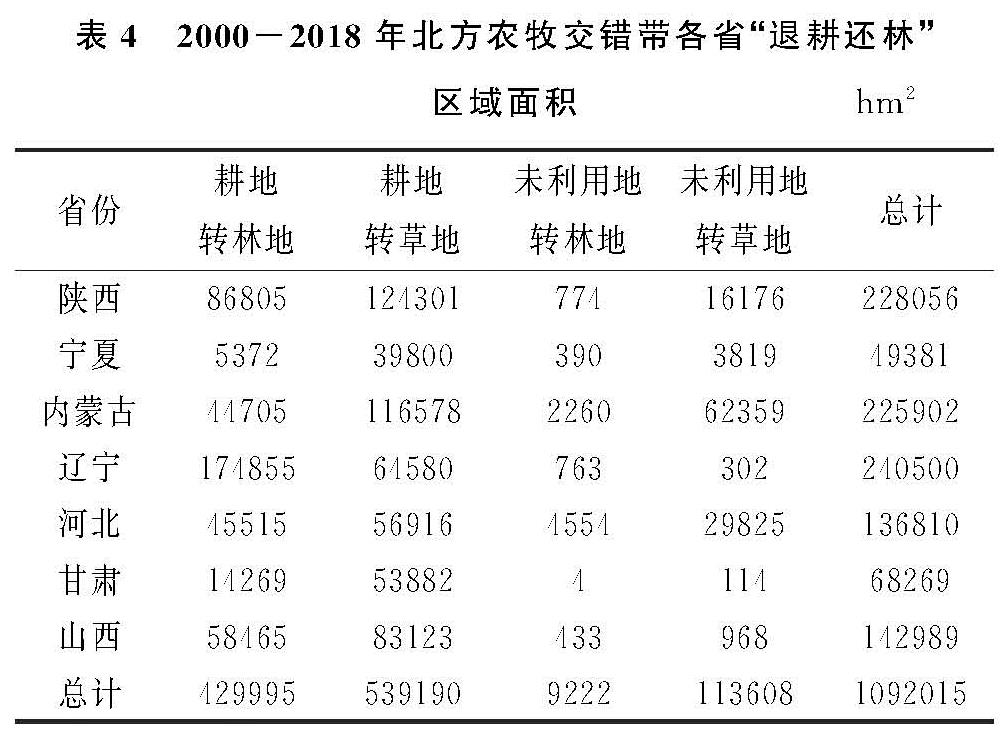
北方农牧交错带2000—2018年各个省“退耕还林”区统计见表4。整个研究区由耕地、未利用地转变为林地和草地的总面积约为109.20万hm2,其中耕地转林地、耕地转草地、未利用地转林地、未利用地转为草地的面积分别为43.00(39.38%),53.92(49.38%),0.92(0.84%),11.36(10.40%)万hm2。“退耕还林”实施的主体仍然是耕地,未利用地植被重建只占到11%。在各个省中,辽宁、陕西、内蒙古“退耕还林”面积最多,分别为24.05(22.02%),22.81(20.88%),22.59(20.69%)万hm2; 河北和山西次之,分别为13.68(12.53%),14.30(13.09%)万hm2; 宁夏和甘肃最少,分别为4.94万(4.50%)hm2,6.83(6.25%)万hm2。陕西省和甘肃省是最早的第一批退耕还林试点区,而研究区内陕西省的林、草地恢复显然是显著于甘肃省的; 内蒙古相较于其余省虽然在“退耕还林”面积中处于前列,但其区域面积最大,“退耕还林”面积相对并不显著。
表4 2000-2018年北方农牧交错带各省“退耕还林”区域面积 hm2
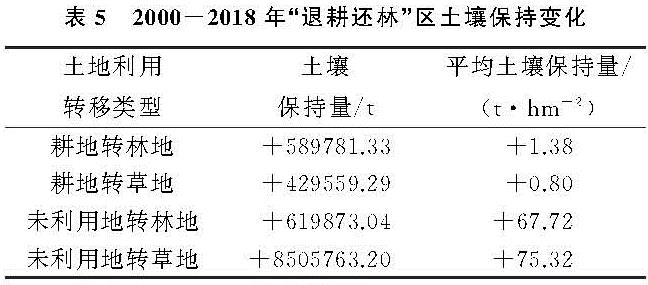
“退耕还林”区域的土壤保持量变化见表5。整个研究区耕地、未利用地转化成林、草地带来的土壤保持增量为1 014.50万t,占研究区土壤保持量总增量(约1 700万t)的59.68%。每1 hm2的耕地转为林、草地增长的土壤保持增量分别为1.38,0.80 t,但每1 hm2的未利用地转变为林、草地后土壤保持量分别增加67.72,75.32 t。这是因为耕地中的植被年内季节变化性较大,植被覆盖水平相对林、草地植被较低,当耕地的植被覆盖较高时,土壤中植被根系具有一定的固定土壤的能力; 而未利用地以盐碱地、裸地为主,植被覆盖度极低,因此其土壤保持功能不如耕地,这导致了耕地和未利用地转成林、草地时的平均土壤保持量上存在较大差距(表5)。综上可以认为,北方农牧交错带近20 a来的土壤保持能力提升的主要原因是由于“退耕还林”的实施。其中,未利用地到林、草地的土地转入对土壤保持功能的提升贡献最大,转变区域内土壤保持量增加了近912.56万t,占研究区土壤保持总增量的89.95%; 耕地转成林、草地的总面积占“退耕还林”区域面积的88.76%,转变区域内土壤保持增量仅占总增量的10.05%,约101.93万t。
表5 2000-2018年“退耕还林”区土壤保持变化