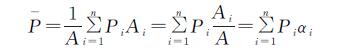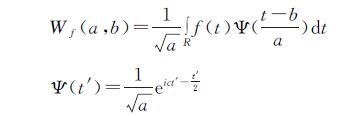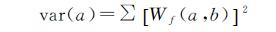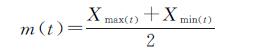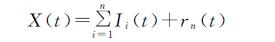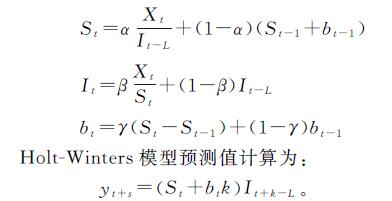2.1 降水量年内特征分析
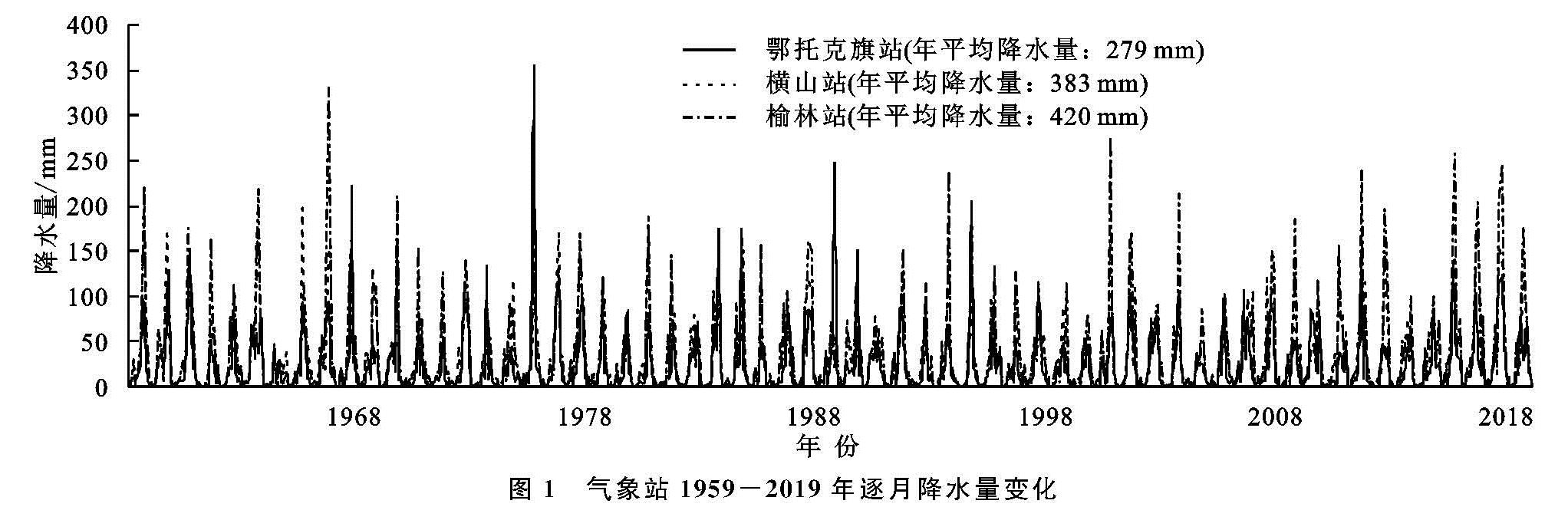
海流兔河流域北侧的鄂托克旗站距流域约65 km,1959—2019年平均降水量为274 mm; 流域南侧的横山站距流域约12 km,1959—2019年平均降水量为383 mm; 流域东侧的榆林站距流域约38 km,1959—2019年平均降水量为420 mm,流域从北向南,从西向东降水量逐渐增大。三站61 a线性降水量趋势均呈上升状态,气象站记录的降水量越大,则线性上升趋势越明显(图1)。
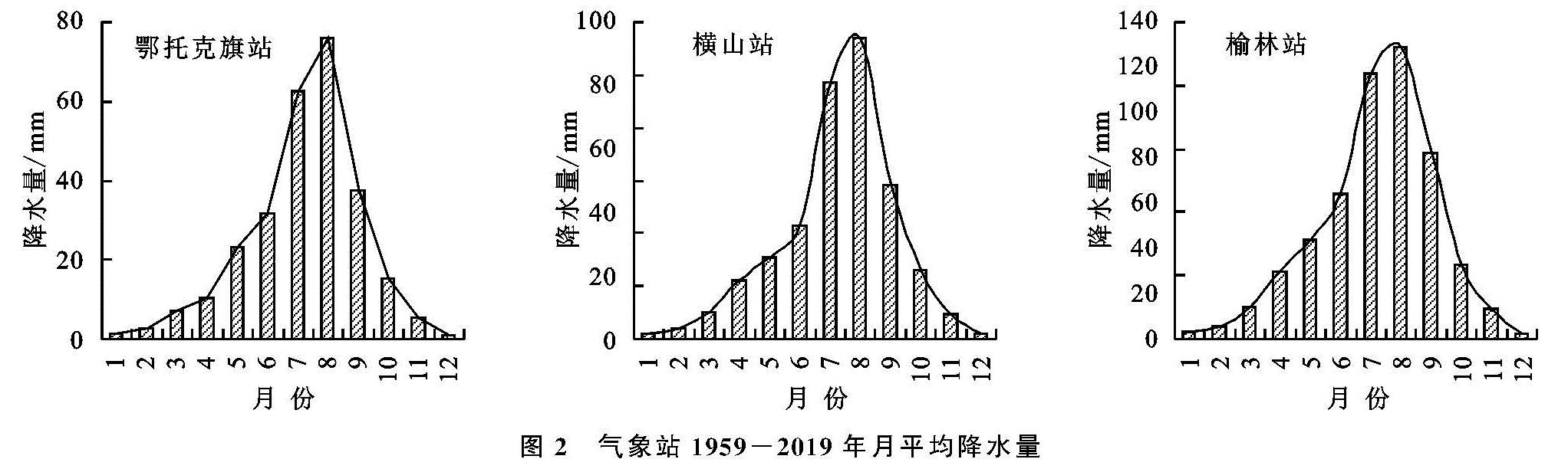
通过分析三站61 a的月平均降水量可以发现(图2),海流兔河流域多年平均月降水量呈明显的单峰型,年内降水主要集中在7—9月份,分别占年均降水量的64.16%(鄂托克旗站),61.19%(横山站)和64.21%(榆林站),基本占全年一半以上,具体表现为春冬枯,夏秋丰的降水时间分布格局。三站年内降水分布基本类似,降水峰值都集中在8月份,其中鄂托克旗站5月份降水趋势明显增大,其他站点5月降水趋势相对稳定,直到进入7月份,三站降水趋势显著增大,流域进入汛期。海流兔河流域降水在年内分布集中,使年际间降水特征区分明显,将有助于年际降水规律的分析。
2.2 降水量年际特征分析
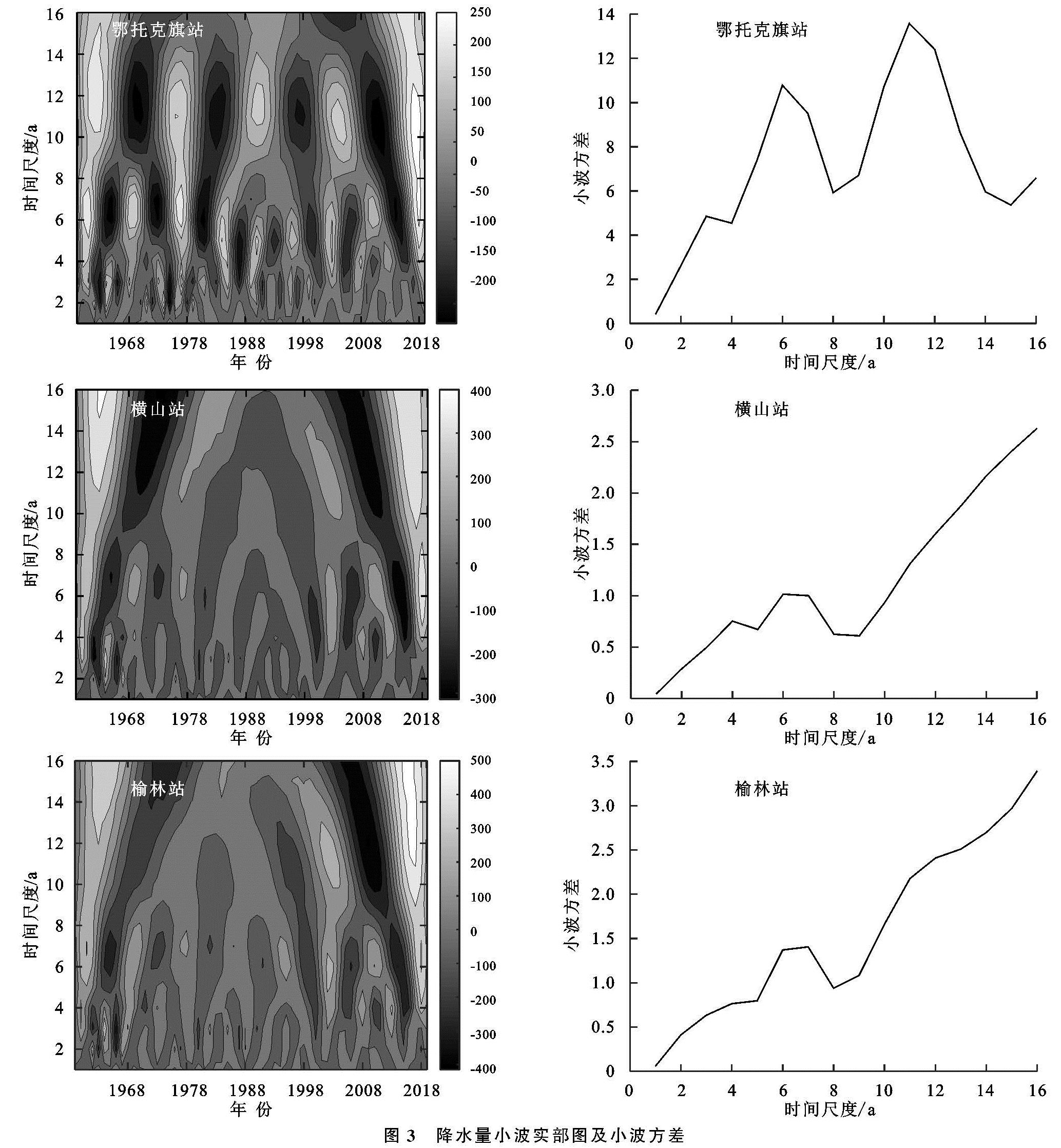
本文利用Morlet小波分析以16 a为时间尺度对3个气象站1959—2019年的年降水量进行了周期分析(图3)。鄂托克旗站的显著性周期比横山站和榆林站明显,而横山站与榆林站的差异性比较一致。鄂托克旗站在5~6 a的时间尺度和11~12 a的时间尺度信号能量变化较为强烈,干湿变化明显; 在5~6 a的尺度下共有8次干湿交替,2019年后的交替循环还未结束,表明该站未来的降水量是呈增加状态的; 在11~12 a的尺度下共有4次干湿交替,2019年后的交替循环还未闭合,大时间尺度上显示该站还处于降水量少的区间内。榆林站和横山站的小波实部和小波方差图基本类似,干湿尺度在16 a以下的时间尺度上不甚明显,在6~7 a的尺度下,主要发生在1959—1983年和1998—2019年度,其余信号能量变化较弱; 在16 a以上的尺度下,横山站和榆林站的干湿交替循环还未闭合,大时间尺度下这两站未来还处在降水量少的时期内。
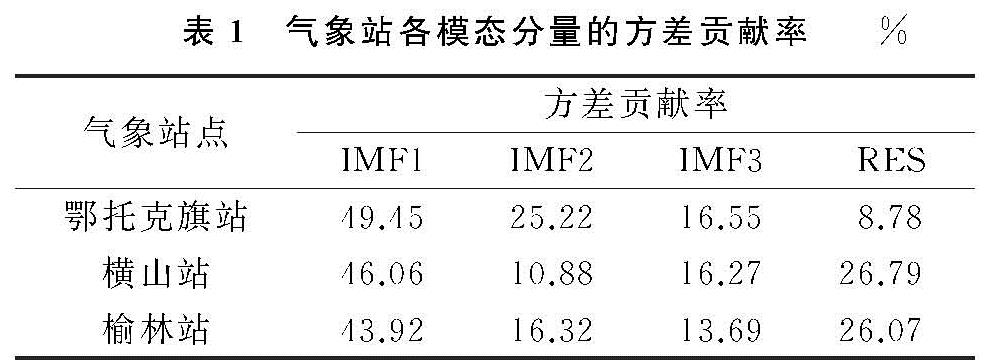
通过经验模态分解法(EMD),对3个气象站61 a的年降水量序列进行了分解,为了保证降水量信息的信号强度,均得到了方差贡献率最大的3个IMF分量和1个趋势分量(RES),各分量表示的是不同时间尺度下的震荡周期(表1)。鄂托克旗站IMF1分量的波动周期为3~6 a,1977年前的波动幅度较大,1978—1982年波动幅度较小,1983—2019年波动幅度总体稳定,2019年之后未来2 a的降水趋势是短幅下降后上升; IMF2分量的波动周期为7~12 a,1988年前的波动幅度较为明显,1989—2015年波动幅度衰弱,2016—2019年波动幅度略有增大,2019年之后几年的降水趋势呈明显下降状态; IMF3分量的波动周期为30 a左右,2019年后的波动幅度大于前期水平,未来多年的降水量值将维持在2019年水平左右; RSE趋势分量从20世纪60年代,降水量幅度处于历史高位,未来该站降水整体仍将处于同位水平。横山站IMF1分量的波动周期为3~7 a,1968年前的波动幅度较大,1969—2000年波动幅度逐渐衰弱,波动周期较短,2010—2019年振幅增大,波动周期较长,2019年之后的2~3 a的降水趋势将会是短幅下降后上升; IMF2分量的波动周期为4~15 a,1988年前波动幅度明显,1989—2000年波动幅度衰弱,2001年后波动周期增大,2019年之后的几年将在高降水量持续一段时间后开始下降; IMF3分量的波动周期为35 a左右,1978—1988年处于波峰,1998—2008年处于波谷,2018年后期开始进入波峰时期,预计未来多年的降水量呈增长状态; RSE趋势分量在1988年处于波谷最低点,预计2019年之后该站的降水整体将处于高位。榆林站IMF1分量的波动周期为3~6 a,1968年前的波动幅度较大,1969—2001年波动幅度减弱,波动周期较短,2002年后波动幅度平稳,波动周期增加2 a左右,2019年后的2~3 a的降水趋势也将是在短幅度下降后上升; IMF2分量的波动周期为5~10 a,1975年前的波动幅度具有一致性,1978—1988年波动幅度明显,1989—1998年和2006—2014年期间波动幅度衰弱,2015年后的波动幅度明显增强,2019年之后几年间的降水趋势将在短幅下降后上升; IMF3分量的波动周期为15~20 a,1988年之前的波动幅度具有一致性,1989年之后波动衰弱,一直下降至2008年、2009年后振幅明显增大,2016年达到波峰后开始下降,预计未来多年的降水量将处于下降状态; RSE趋势分量同横山站类似,预计2019年之后该站的降水整体也是处于高位。
以上3个气象站的降水序列震荡周期表明,各站方差贡献率最高的IMF1分量波动周期类似,短期预测其降水趋势均为短幅下降后上升,中长周期下IMF2和IMF3的波动周期和未来趋势性具有差异性,三站趋势分量RES对未来的降水展望均呈增加态势。
2.3 降水量预测
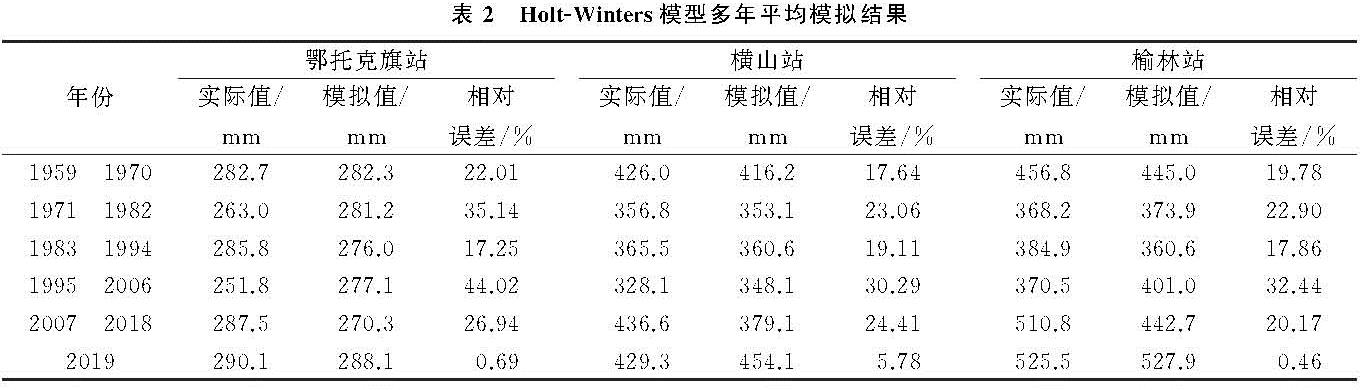
根据以上3个气象站降水量数据的周期性分析可以看到,鄂托克旗站的小波分析显著性周期分别为12 a和6 a,横山站和榆林站的小波分析显著性周期为6 a; EMD分析表明在中长周期下,三站的波动周期均为12 a左右,基于此本文利用乘性Holt-Winters模型以12 a为周期对历史降水量数据提取信息模拟后,进行了未来12 a的降水量预测分析(表2)。在预测之前本文将61 a历史数据划分为49 a的识别期和12 a的验证期,对该模型进行了适用性评估,结果表明鄂托克旗站12 a的验证模拟值相对误差为4.2%,横山站为16.45%,榆林站为8.73%,震荡周期类似,模拟效果较为理想。最终对61 a的数据进行模拟后得到鄂托克旗站Holt-Winters模型历史降水数据估计下的参数α,γ,β分别为0,0.52,0.22,模拟值的平均相对误差为28.61%,模拟值比实际值的震荡强度较为剧烈,表明基于现有的人类活动及全球气候变化下,未来几年的预测趋势为轻微下降后上升。横山站的α,γ,β分别为0.12,0.08,0.2,平均相对误差为22.62%,预测值在1985—1998年的震荡强度普遍较大,未来几年的趋势预测为上升。榆林站的α,γ,β分别为0.05,0.38,0.24,平均相对误差为22.27%,预测值的极端低值明显,未来降水量的预测趋势为显著上升。整体上3个气象站的模拟值多集中在平均值附近,极值明显程度高于实际值,模拟情况系统性偏低,预测精度还有很大的提升空间。
表2 Holt-Winters模型多年平均模拟结果
2.4 流域降水特征分析
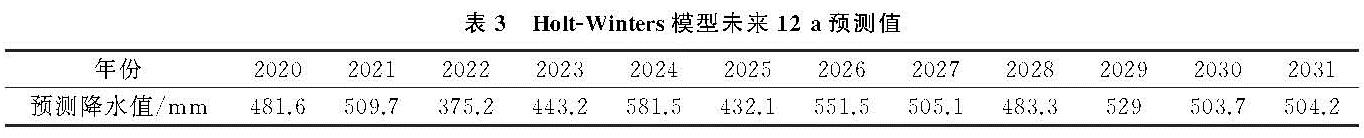
海流兔河流域是鄂尔多斯剥蚀高原向陕北黄土高原过渡的洼地小流域,整个流域处在毛乌素沙地之上,为蒙陕煤炭开采区水土流失严重的典型小流域,为更好地描述及预测该流域的降水量情况,本文利用泰森多边形法对气象站点数据进行加权分配,分割得到鄂托克旗站对该流域的控制面积为10.41%,横山站为89.58%,榆林站为0.01%,其中横山站的降水数据为主要流域控制项。通过数据加权后的小波及EMD分析得到海流兔河流域的基础干湿交替周期尺度为6 a,震荡以1988—1998年最为不明显,16 a以上的尺度均显示流域处在降水量上升期,未来流域整体降水趋势预测呈显著上升状态。乘性Holt-Winters模型模拟预侧值与横山站类似,α,γ,β分别为0.12,0.09,0.21,平均相对误差为22.28%,模拟精度不太理想,但结合小波及DEM可预测基于现有人类活动及全球气候变化的影响下未来12 a流域降水量整体趋势呈增加态势(表3)。
表3 Holt-Winters模型未来12 a预测值