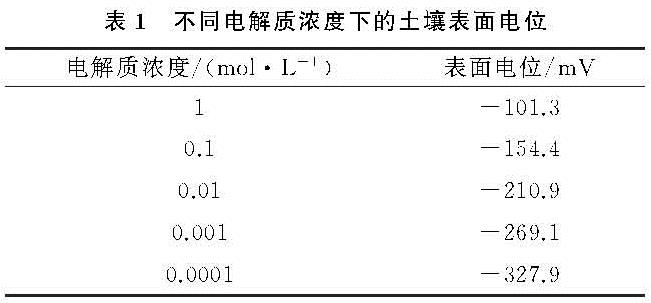
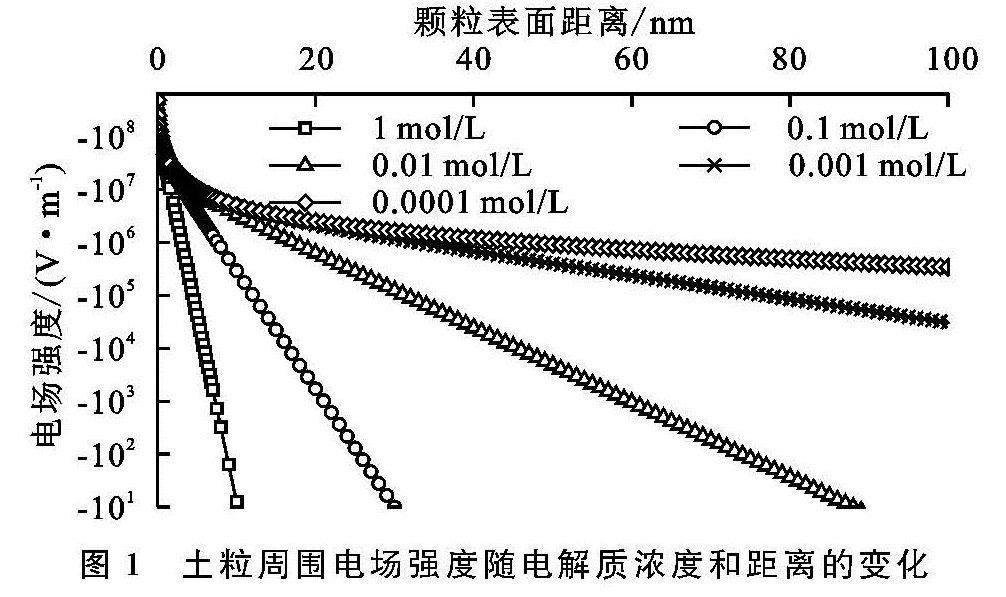
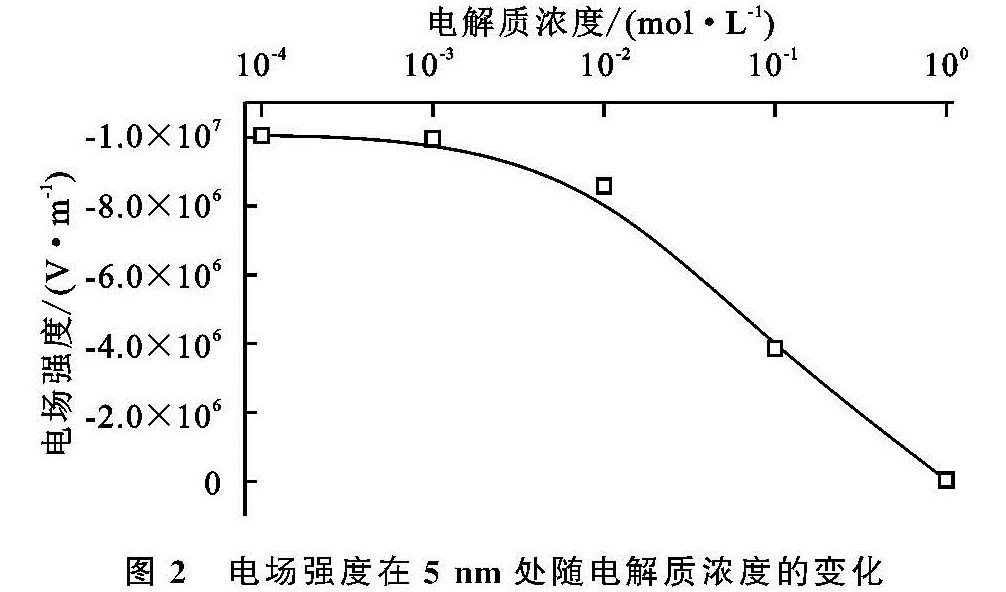
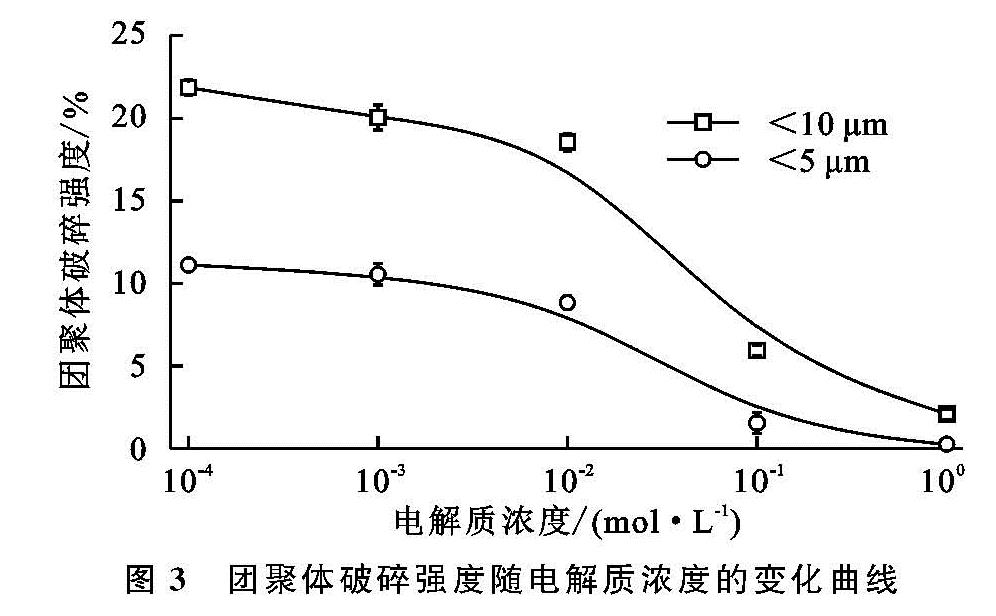
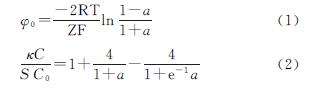当水分进入土壤后,土壤团聚体遭到破坏,其稳定性下降,进而会改变土壤孔隙状况,影响水分入渗特性。本研究发现,随着溶液电解质浓度的降低,土壤团聚体破碎强度表现为先急剧增大而后保持稳定的趋势,即团聚体稳定性总体表现为降低的趋势,0.01 mol/L是团聚体破碎强度发生改变的电解质浓度,该结果与其他土壤(紫色土和典型黄土)的研究结果一致[11-12,14],说明对于不同的土壤类型,电场对团聚体稳定性皆有一定的影响,但是由于颗粒组成、有机质含量、离子特异性等因素的差异,其影响程度不同。根据经典胶体化学理论,土壤表面电位(绝对值)和电场强度会随着土壤溶液电解质浓度的增大而减小[11-14],电场强度的减小意味着颗粒间的静电排斥力会急剧减小,这与本研究定量计算的结果一致。已有研究表明,土粒间的静电排斥力可高达上千个大气压,远大于通常人们所认为的消散作用和雨滴打击等作用力,它是团聚体遇水破碎的主要内在动因[11-13]。因此,当溶液电解质浓度降低后,土粒间的电场作用会急剧增强进而导致团聚体发生破碎,这必然会引起土壤孔隙状况发生改变。
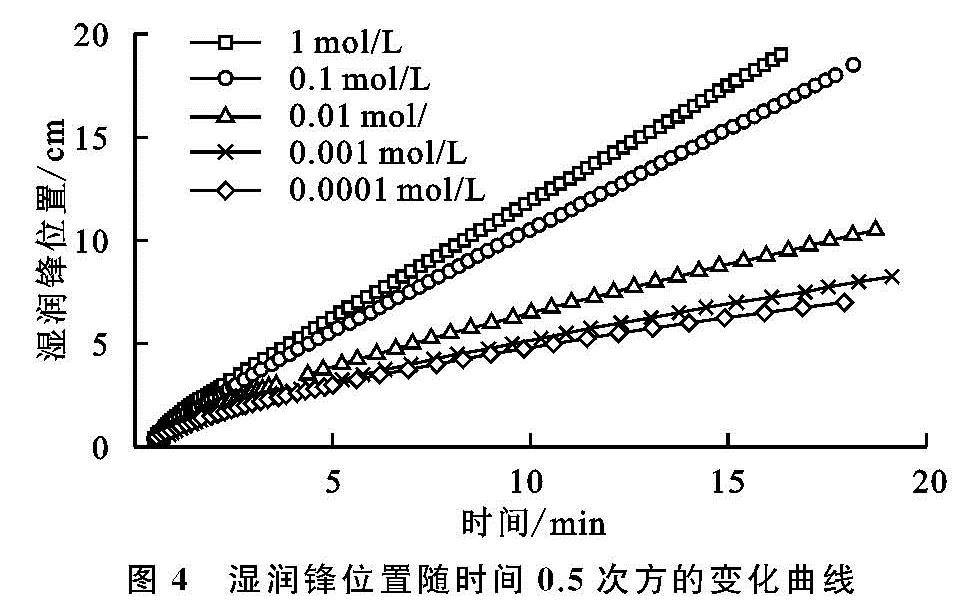
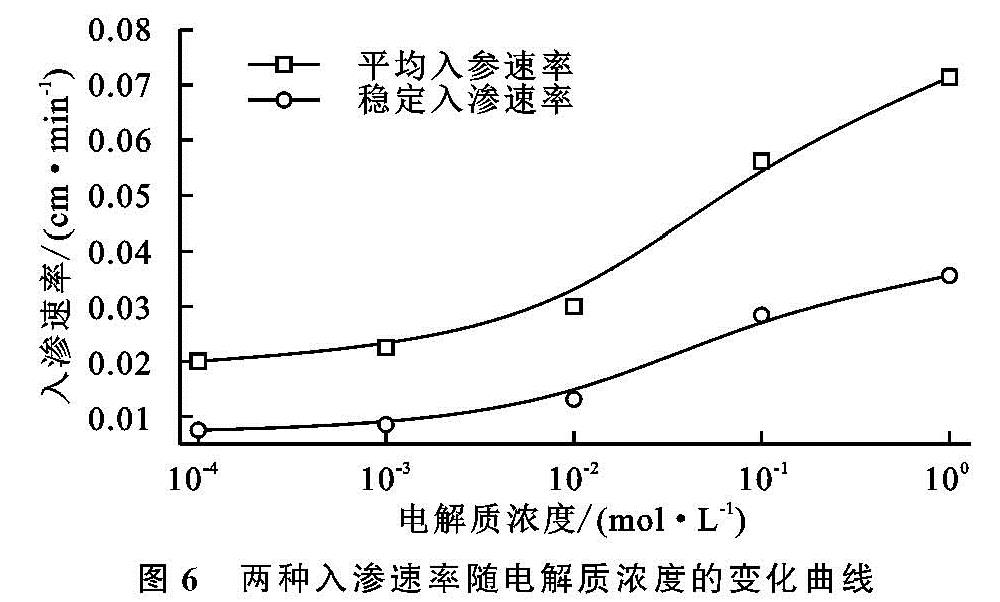
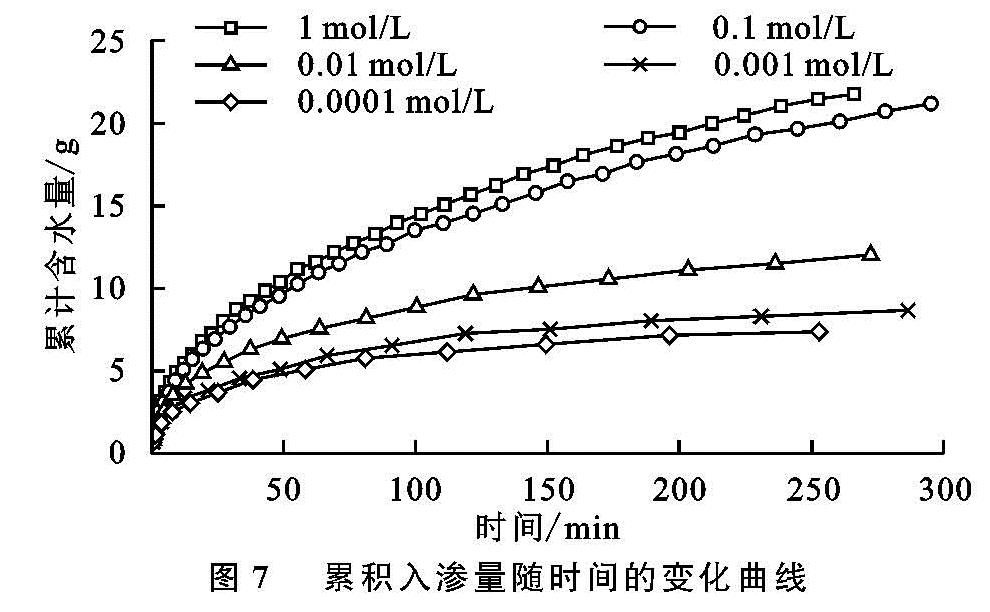
本研究发现,随本体溶液电解质浓度的增加,水分入渗过程中累积入渗量、湿润锋前行位置和水分入渗速率和均增大。张俐等研究表明,在一定范围内,随着入渗水分矿化度的增大,在相同入渗时间内的湿润锋运移速率呈增加的趋势[29],此结果与本研究结果相一致。当水分进入土壤后,土壤结构体并不是始终保持不变的刚性颗粒[14-15,23]。其中,团聚体的稳定与分散被认为是影响土壤孔隙状况和水分迁移的重要因素[14-15]。结合本研究中团聚体稳定性试验结果可以发现,随本体溶液电解质浓度的变化,各水分入渗特参数和团聚体稳定性参数的变化趋势一致。即随溶液电解质浓度的降低,团聚体稳定性降低,水分入渗过程中累积入渗量、湿润锋的迁移距离和水分入渗速率均降低。电解质浓度为0.01 mol/L是相同作用距离下电场强度的转折点,也是团聚体稳定性的转折点,这与水分入渗过程的转折点相同。理论计算与宏观试验结果相对应,这说明土壤电场可通过影响团聚体稳定性而最终影响水分入渗过程[14-15,21]。
尽管本研究是采用不同浓度电解质溶液来模拟研究水分入渗特性,并指出了土壤电场作用对水分入渗过程的重要影响,但是该结果具有一定的普适性。例如:在自然条件下,当雨水或灌溉水进入土壤后,土壤溶液浓度将会迅速被稀释,根据本研究结果可知,此时的土壤带电颗粒周围电场会急速增强,颗粒间的静电斥力增大,导致团聚体结构发生破碎,改变土壤孔隙状况,最终影响水分入渗过程,加速地表径流的形成,导致土壤侵蚀加重。我们的研究结果也定量地解释了,在一定范围内,随灌溉水质矿化度的增加,土壤水分入渗性能增强的原因[10]。这是因为入渗液浓度增大后,土粒表面电位绝对值和电场强度将会降低,土粒间排斥力作用下降,团聚体稳定性增强,水分入渗性能将会增大,这一试验结果为东北地区土壤水分和水土流失调控提供了一定的理论依据,对于我国淡水资源的保护具有重要意义。