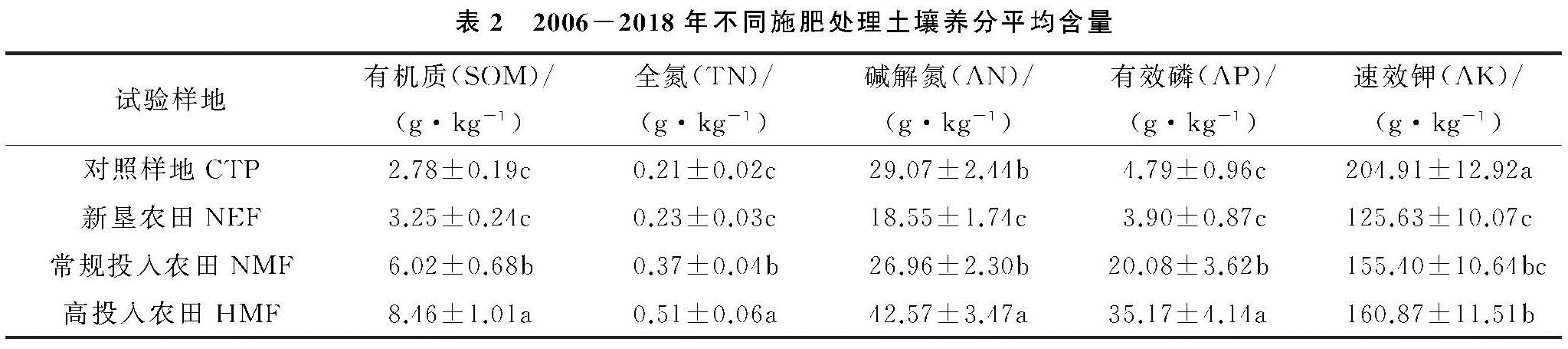
研究不同施肥对土壤养分的影响,有利于土壤养分的可持续利用管理[18]。在2006—2018年,通过对研究区4块不同施肥处理样地土壤表层养分进行数据分析,结果表明 HMF样地各养分指标值显著高于其他3块样地(p<0.05),NMF样地各养分指标值显著高于NEF样地和CTP样地(p<0.05),NEF样和CTP样地各养分指标值处于最低水平,但CTP样地土壤速效钾含量显著高于其他3块样地(p<0.05)。不同施肥处理对干旱区绿洲农田土壤养分指标产生显著影响,这和桂东伟[19]和周晓兵[20]等的研究结果一致。
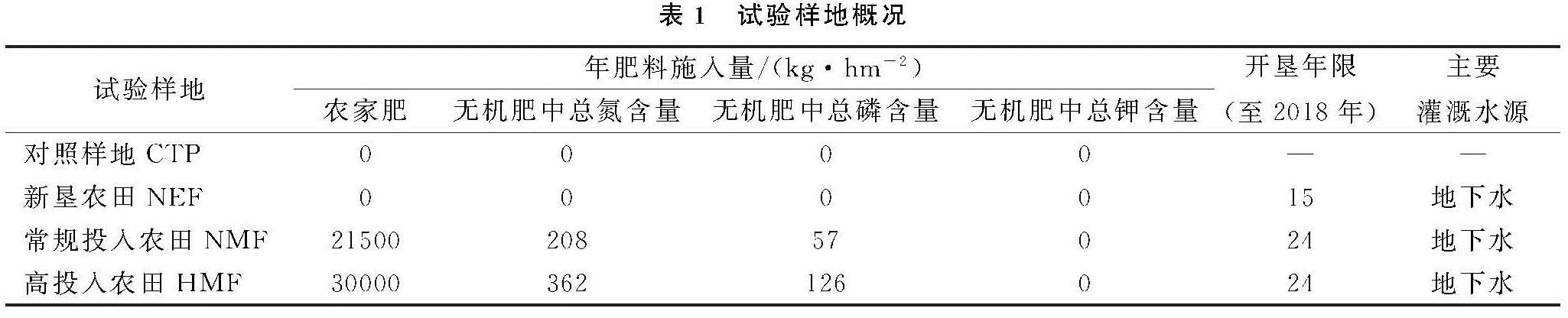
土壤有机质是土壤肥力的重要方面,其质量和数量直接或间接影响土壤潜在的生产力,是土壤养分的重要来源[21]。土壤有机质的稳定水平取决于农田有机碳投入和输出间的平衡,不同肥力投入导致耕地土壤变化的差异,影响土壤理化性质,改变土壤肥力,并且直接影响土壤有机质的分解及转化[22-23]。本研究中,在绿洲不同施肥处理下,土壤有机质的含量有明显的差异(p<0.05),且在2006—2018年,都表现为土壤表层有机质含量:HMF>NMF>NEF>CTP,高肥力投入显著增加了土壤有机质含量,这与陈文婷[24]和徐华清[25]的研究结果一致。新垦农田没有养分投入,但有种植农作物,可能是农作物的枯枝落叶增加了土壤有机质含量,所以新垦农田有机质较未开垦对照样地含量高。
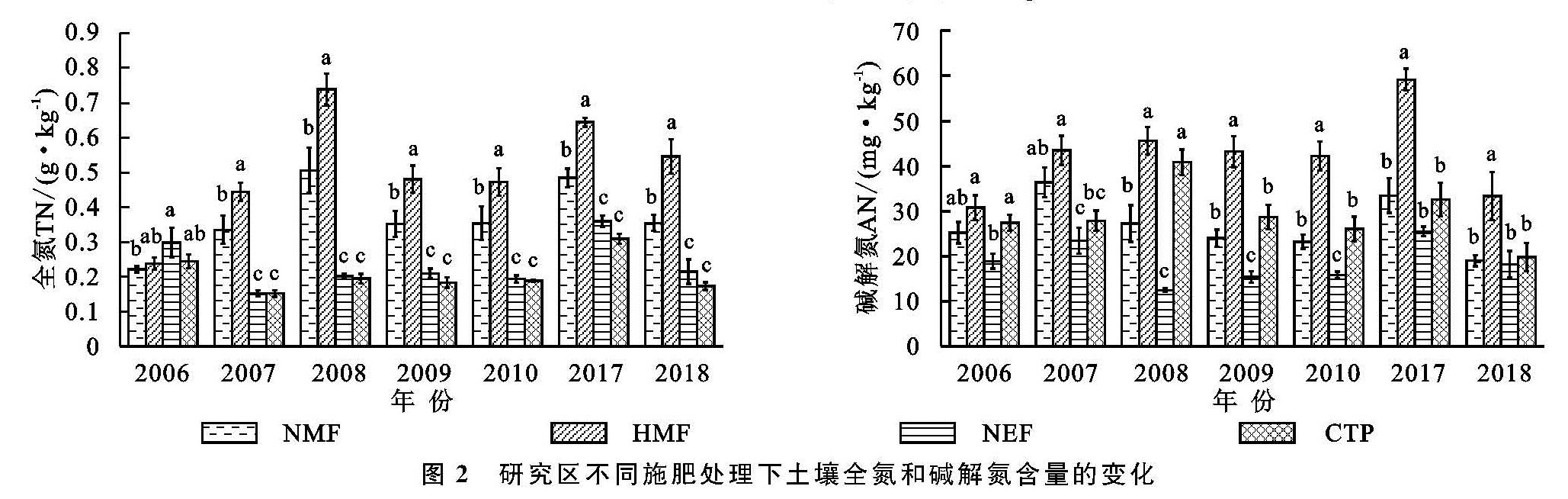
土壤氮素是植物吸收的大量元素之一,是衡量土壤养分最重要的指标[26]。磷是土壤中植物生长和发育所必需的营养元素,构成植物体内的许多重要化合物[27]。本研究中,在绿洲农田不同施肥处理下,土壤全氮、碱解氮、有效磷的含量有明显的差异,高投入农田的年肥料总氮、总磷含量施入量最高,土壤全氮、碱解氮、有效磷的含量显著高于其他3块样地(p<0.05),常规投入农田全氮含量显著高于无施肥样地和未开垦对照样地(p<0.05)。土壤中的氮素主要是受人类的生产活动,如耕作、施肥与灌溉等措施影响到氮素的循环与积累[28],本研究中,在绿洲不同施肥处理下,肥料的投入增加了土壤全氮、碱解氮含量,说明新疆绿洲农田在种植过程中要重视氮肥的施入[29]。
土壤速效钾含量对作物的生长具有重要作用,本研究中,在绿洲农田不同施肥处理下,土壤速效钾含量有明显的差异(p<0.05),在2006—2018年,总体上土壤速效钾含量:CTP(204.91 mg/kg)>HMF)(160.87 mg/kg)>NMF(155.40 mg/kg)>NEF(125.63 mg/kg)。根据土壤养分等级评定分析速效钾含量对应的水平等级(<100 mg/kg为严重缺钾; 100~125 mg/kg为缺钾; 125~155 mg/kg为适量; >155 mg/kg为富钾)来分析判断[30],本区域的不同施肥处理下,CTP,HMF样地、NMF样地速效钾为钾富集,NEF样地速效钾为钾适量。风沙土的钾元素比较充足,长期施肥提高了土壤速效钾含量,但长期不施肥土壤速效钾含量并没有显著降低,表明土壤中速效钾含量与土壤本身的钾含量有关[31-32]。
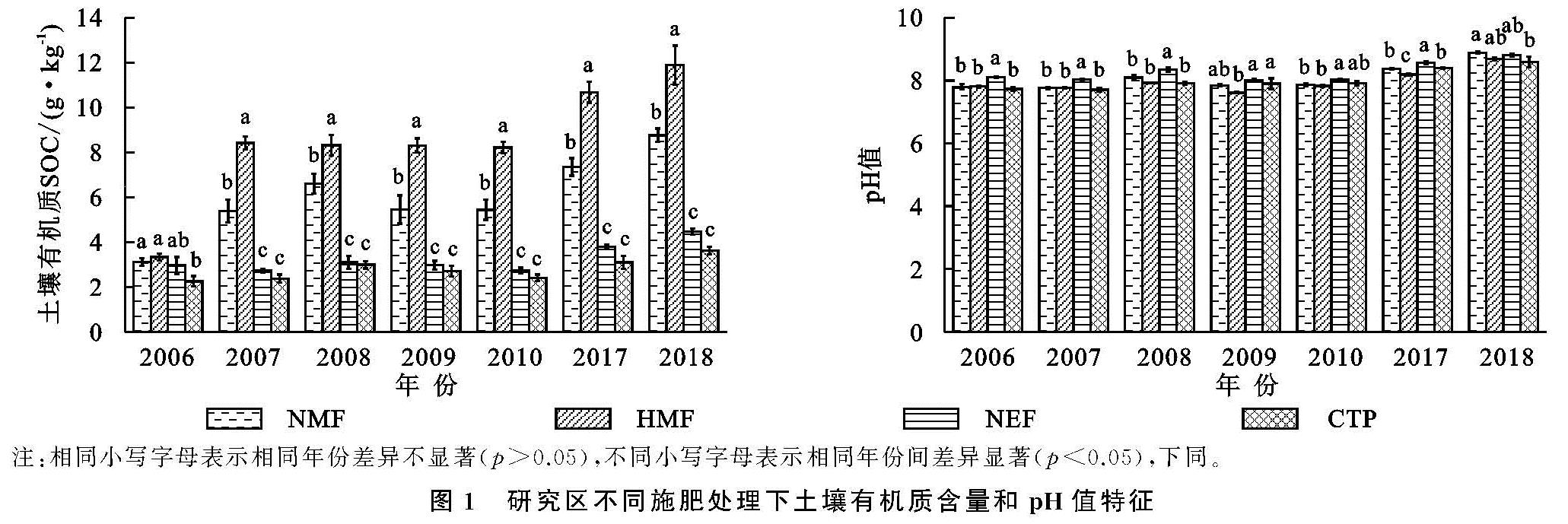
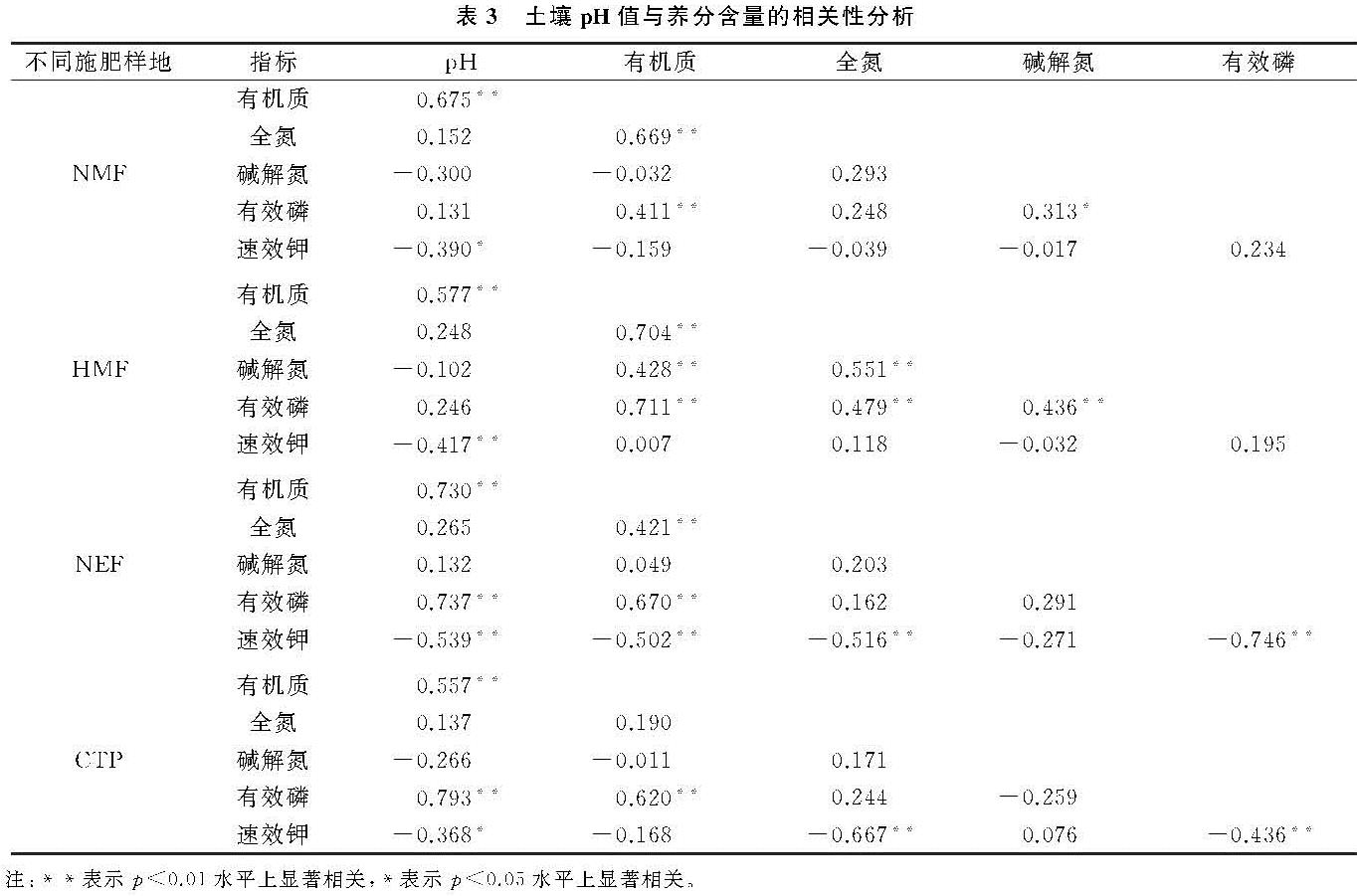
从长期不同量施肥下4块样地土壤养分的平均值来看,长期定位施肥对策勒绿洲农田土壤养分有积极影响,高投入农田土壤养分含量平均值最高,常规投入农田次之,开垦未投入农田和未开垦对照农田养分含量指标基本处于最低水平。张晓东等[33]对新疆玛河流域绿洲农田不同开垦年限下土壤养分的含量进行分析,发现长期的开垦(开垦年限>13 a)会使绿洲农田土壤退化,降低了土壤养分及有效养分含量。苏永中等[34]对临泽边缘绿洲沙地农田进行长期施肥定位试验,表明农田开垦和合理化施肥对绿洲土壤养分有积极影响。本研究中,肥料的投入对绿洲农田土壤养分产生积极影响,高肥料施入量的土壤养分指标含量也相对较高。土壤pH值是土壤重要的理化性质之一,它直接或间接影响土壤养分的存在状态和转化[35-36]。本研究中,随着处理年限的增加,土壤pH值有增加趋势,但相同年份,未开垦农田和两块施肥农田土壤pH值较低。可能是氮肥的施入降低了土壤pH值[37]。对4块样地土壤pH值和养分含量进行相关性分析,土壤pH值与速效钾含量呈显著或极显著的负相关性。研究过程中,施肥主要是有机肥和氮、磷肥,但施肥样地速效钾含量显著高于开垦未施肥样地。研究表明策勒绿洲开垦过程中施肥可以改善土壤盐碱化,降低土壤pH值从而促进土壤养分活化,增加土壤有效养分的吸收[38]。