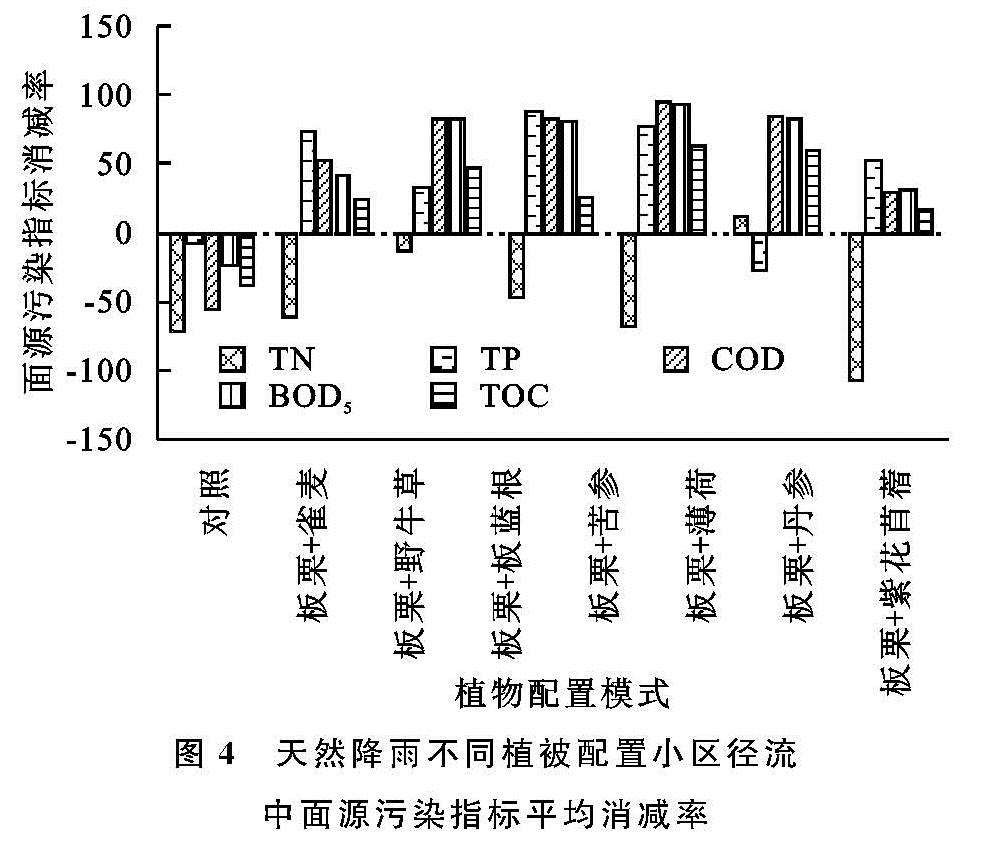
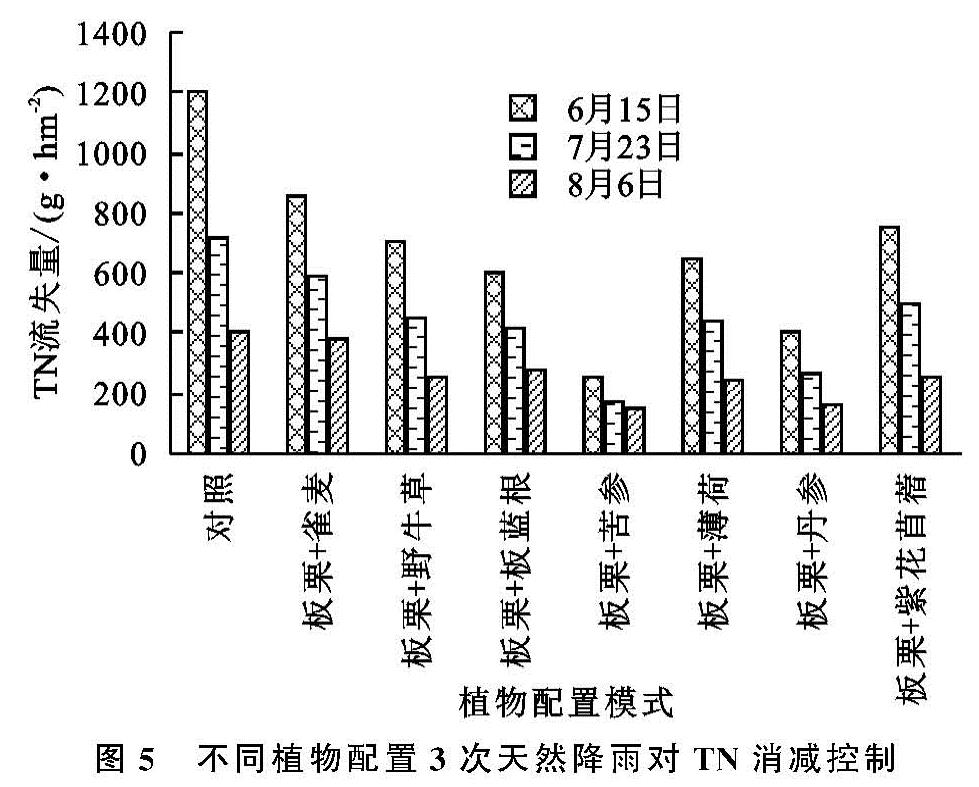
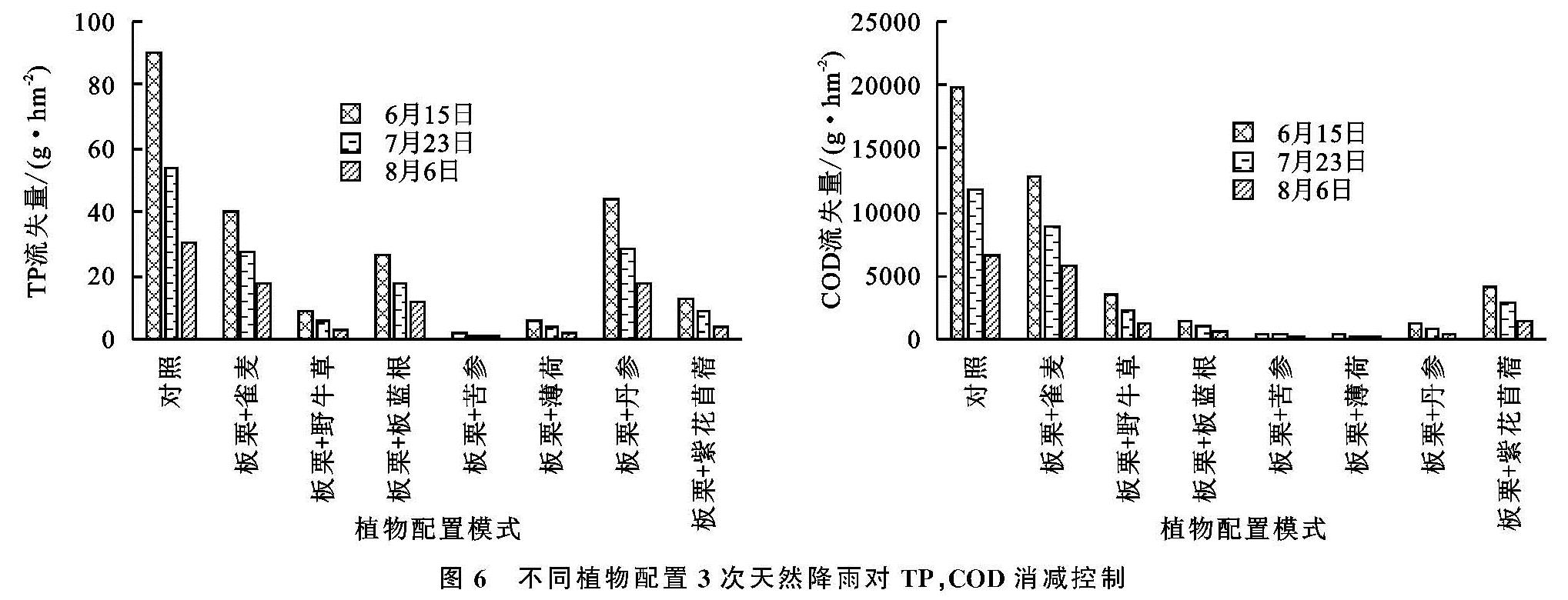
伴随农业生产过程中农药、化肥的广泛应用,造成其面源污染日益加剧,从而导致一系列危害性问题,例如水体水华现象、农产品质量不达标等,给人们的身体健康形成了严重的危害。当前得到广泛认可的生物防治方法之一是构建植物篱。该方法不但能够降低水流以及土壤养分的流失速度,而且还能够使水稳性土壤团粒构造得到改善 [1],尤其是应用在陡坡地当中,其成效更为显著 [2]。Zhao等研究不同植物在降水强度存在差异化,土壤水分含有量以及坡度差异化条件下的径流特点,从而得出,植被能够使产流时间得到延长,使径流系数得到缩减 [3]。黄欠如等研究发现由香根草(Vetiveria zizanioides)植被所构成的植物篱在我国南部区域应用较多,尤其是在红壤陡坡地区,其对径流以及泥沙的阻拦率依次为29%~72%,56.25%~97.4%[4-5]。Donjadee等也对此展开了相关探讨,从而得出,当土地坡度超过30%时,该植物篱所发挥出的径流阻拦率能够达到31%~69%,泥沙阻拦率能够达到62%~86%[6]。李凯等也对此展开相关探索,重点区域分析了密云水库岸滨地区,从而得出在自然降水环境下,由柳树(Salix matsudana)+丁香(Syzygium aromaticum)+蒿(Artemisia)组成的植被结构可发挥最佳的减流效果,能够降低62.9%,其中减沙效果最佳植被组合是毛白杨(Populus tomentosa)+紫丁香(Syringa oblata)+葎草(Humulus scandens),可减沙78.18%,另外,在面源污染防治方面成效最为显著的植被组合为油松(Pinus tabulaeformis)+金叶榆(Ulmus pumila)小区[7]。如今,全球各国关于面源污染所进行的探索多数都是基于降水模拟或径流冲刷的方式而实施的,未在实地进行验证,在推广应用方面存在较多的问题,因此开展天然降雨条件下植物配置模式防控面源污染对于坡耕地氮磷流失生态阻控具有很大的实践意义。
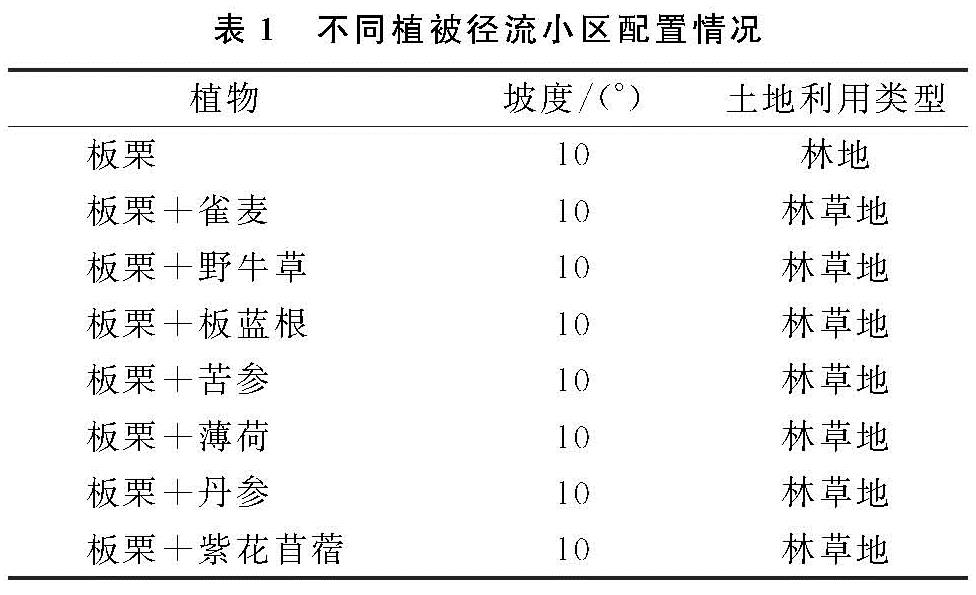
密云水库坐落在北京地区,是该地最重要的地表饮用水来源,也是北京市生态涵养区,保证密云水库水质安全关乎北京市经济绿色可持续发展和首都的社会安全稳定。该地区最大的面源污染源头就是水源保护区陡坡地,要从根本上解决农业面源污染问题,要注重农业面源污染的“源头控制”与“过程阻断”,技术层面上要从优化生产技术着手。利用植物篱的建立与应用,来降低与防控面源污染给当地水质造成的污染,同时这也是进行面源与水体污染治理与防控的良好手段与途径,所以探讨差异化植被配置给面源污染防控所产生的影响,从而构建最佳植被配置的植被缓冲带,从而为确保该水库水质发挥关键作用。为实现植被配置效果的最佳化,该文利用8个差异化植被配置野外规模化径流小区的构建,探索自然降水环境下差异化植被配置给面源污染所形成的制约作用,研究各种植被配置所产生的面源防控作用,从而为陡坡地区生态保护及防控植物配置方面发挥借鉴作用。