资助项目:国家自然科学基金“基于空间异质性和不确定性的城市扩展元胞自动机模型构建——以武汉城市圈为例”(41571384)
第一作者:周晓艳(1974—),女,湖北荆州人,副教授,博士研究生,主要从事城市地理与国土空间规划研究。E-mail:zhouxiaoyan@whu.edu.cn 通信作者:王诗琪(1997—),女,湖北武汉人,硕士研究生,研究方向为城市地理与区域发展。E-mail:sqwang@whu.edu.cn
(武汉大学 资源与环境科学学院, 武汉 430079)
(School of Resources and Environmental Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430079, China)
urban expansion; ecosystem service value; hot spot analysis; geographically and temporally weighted regression; the Yangtze River Economic Belt
城镇化进程是我国改革开放以来意义最重大的发展过程之一[1]。1978—2017年,我国城镇化水平从17.86%大幅增长至58.52%[2],但城镇空间扩张对社会经济和生态环境产生了重要影响。城镇扩张过程作为土地利用变化的关键驱动力,不仅会侵占生态、生产空间,而且会破坏地区生态安全格局、削弱资源环境承载力[3]。在新型城镇化建设背景下,如何实现城市发展与生态保护协同并进,同时从区域角度协调城市间发展关系,实现区域整体可持续发展是当前的重要研究热点[4]。
区域的景观具有重要的生态系统服务价值[5],城镇扩张驱动下的土地利用变化使得区域的景观格局发生变化,从而对生态系统服务价值产生重大影响[6-7]。我国区域发展面临着生态系统服务供给不足与生态系统服务价值损失之间的冲突问题[8],这将阻碍我国可持续发展战略的实施。已有针对城镇扩张与生态系统服务的相关研究较为丰富,研究内容主要包括城镇扩张背景下生态系统服务价值时空演变特征与分异机制[9-11],基于城镇扩张模拟的生态系统服务价值评估与预测[4,12],城镇扩张与土地利用变化对生态系统服务价值的影响等[13-14]。然而,地理时空分析不仅要考虑区域化过程变量的空间异质性,也要考虑其时间非平稳性,当前的相关研究缺乏对两者的综合考虑。本研究将时空地理加权回归(GTWR)纳入城镇扩张对生态系统服务价值影响的分析中,能更全面地揭示研究区域生态系统服务价值对城镇扩张的时空响应特征,从而为制定区域差异化的生态保护措施提供理论支撑。
自十三五规划以来,长江经济带发展战略成为我国三大区域发展战略之一。然而,在快速城镇化的过程中,土地利用低效和生态环境恶化等问题将限制长江经济带的可持续发展[15-16]。在“共抓大保护,不搞大开发”的重要理念下,如何权衡社会经济发展与生态环境保护成为长江经济带发展亟待解决的问题[17]。本文在现有研究基础上,对2000—2015年长江经济带128个研究单元的城镇扩张强度与生态系统服务价值进行测算,采用热点分析探索其时空演变格局,并通过时空地理加权回归模型探究长江经济带各研究单元城镇扩张对生态系统服务价值量变化的时空影响特征,以期为构建长江经济带的生态安全格局、实施差异化生态保护管理以及制定生态补偿措施提供理论依据。
长江经济带位于长江流域,地理坐标为东经96°24'—124°3',北纬19°55'—35°44',横跨我国东、中、西部,规划范围包括上海市、江苏省、浙江省、安徽省、江西省、湖北省、湖南省、重庆市、四川省、贵州省、云南省共11个省级行政区,面积约205万km2,截至2015年,年末常住人口总数约6亿人,地区生产总值约30.52万亿元,分别占我国国土面积、总人口数及国内生产总值的21.35%,42.75%,44.31%。长江经济带是我国海岸经济带以外最具发展潜力的综合经济带,自然资源丰富,工业基础雄厚,内河航道优越,经济发达,人才资源集聚,同时具有无与伦比的国家安全价值,是我国综合实力最强、战略支撑作用最大的区域之一[16-17]。
本文采用长江经济带地级市及以上城市行政辖区为研究单元。为统一研究尺度,将湖北省内毗邻的仙桃市、天门市和潜江市这3个省直辖县级行政单元合并为“仙天潜地区”,最终得到128个研究单元。
研究数据主要包括长江经济带行政区划数据与土地利用遥感监测数据,数据皆来源于中国科学院资源环境数据中心(http:∥www.resdc.cn/),其中行政区划数据采用2015年全国省级与市级行政区划矢量数据。土地利用数据采用长江经济带2000年、2005年、2010年和2015年共4期数据,分辨率为1 km,包括6个一级分类和25个二级分类。借鉴谢高地等[18-19]建立的中国生态系统单位面积生态服务价值当量框架及其应用研究[20-21],将25个二级土地利用类型进行重分类,得到农田、林地、草地、水域、湿地、未利用地和建设用地共7个用地类型。
参考已有研究[22-23],构建城镇扩张强度指数,见公式(1):
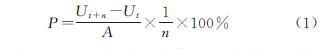 )
)
式中:P为t至t+n时段内研究单元的城镇扩张强度; Ut,Ut+n分别为研究时段初期与末期的城镇用地面积; n为研究时段长度; A为研究单元总面积。
谢高地等[19,24]在Costanza等的研究基础上,利用专家知识法,构建并修正了中国生态系统单位面积生态服务价值当量表,将生态系统服务分为供给服务、调节服务、支持服务、文化服务4个一级类型和9个二级类型。1个标准当量因子的定义为1 hm2全国农田年平均自然粮食产量的价值,考虑到人为因素干扰难以消除,在实际计算中可用单位面积农田粮食生产的净利润作为标准当量因子[21]。根据《中国粮食发展报告》计算得到2000—2015年全国单位面积粮食生产净利润为1 837.46元/hm2,全国粮食平均单产为4 856.97 kg/hm2,考虑到粮食生产能力的空间差异性,通过国家统计局数据计算长江经济带15 a间粮食平均单产为5 058.57 kg/hm2,基于此对全国单位面积粮食生产净利润进行修正,得到15 a间长江经济带标准生态系统服务当量因子价值量为1 913.72元/hm2,并构建长江经济带单位面积生态系统服务价值量表(表1)。
表1 长江经济带单位面积生态系统服务价值量元/(hm2·a)
基于各研究单元土地利用数据与生态系统服务价值量表,计算出研究单元的各项生态系统服务价值量,并构建生态系统服务价值量下降率与变化率指标,公式[25]如下:

式中:ESVi,ESVj,ESV分别为研究单元第i类用地的生态系统服务价值、第j项生态系统服务类型的价值以及生态系统总服务价值; Ai为研究单元第i类用地面积; VCij为表1中第i类用地第j项服务的价值系数; D与C分别为研究单元价值量下降率与变化率; ESVt+n和ESVt分别表示t+n时刻与t时刻研究单元的生态系统服务价值量。
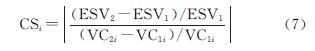
式中:CSi为第i种土地利用类型的敏感性指数; ESV1和ESV2分别为调整前后的生态系统服务总价值量; VC1i和VC2i分别为调整前后第i种土地利用类型的价值系数。若CSi>1,表明ESV对价值系数具有弹性; 若CSi<1,则说明ESV对价值系数缺乏弹性,计算过程是可靠的。
Getis-Ord G*指数可分析研究单元属性的空间分布格局,公式[26-27]如下:

式中:Xj为第j个研究单元的属性值; n=128; Wij(d)为以距离d为规则的空间权重; E(Gi*),var(Gi*)分别为Gi*的期望与方差,当Z值显著大于0时,表示第i个研究单元周围都是高值,为热点区,反之则为冷点区。
时空地理加权回归(GTWR)模型在地理加权回归(GWR)模型的基础上引入时间因子,既解决了截面数据样本数量有限性的问题,还考虑了时间与空间非平稳性,能有效估计因子参数,模型如下[28-29]:
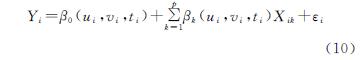
式中:(ui,vi,ti)为第i个样本单元的时空坐标; X,Y分别为解释变量与被解释变量; p为解释变量个数; β0(ui,vi,ti)为截距项; βk(ui,vi,ti)为第k个解释变量的估计系数; εi为模型残差。本文对GTWR模型的实现主要基于ArcGIS 10.2软件,采用Huang等[30]制作的GTWR插件,带宽采用AICc优化设置,时空距离参数比值为1。
2000—2015年,长江经济带城镇范围不断扩张,年平均扩张强度为0.02%,其中2000—2005年扩张强度最大,每年约0.03%。在各省市中,长江经济带下游地区的城镇扩张强度较大,其中上海市、江苏省、浙江省、安徽省的城镇年扩张强度分别为0.21%,0.12%,0.11%,0.05%; 中游江西省、湖北省、湖南省城镇扩张的强度较低,每年0.01%~0.02%; 上游重庆市城镇年扩张强度约0.02%,其他省份的年扩张强度则均不足0.01%。
为了深入探究长江经济带各研究单元城镇扩张的空间分布格局,对各时段内研究单元的城镇扩张强度指数进行热点分析(图1)。结合城镇扩张强度指数计算结果与热点分析结果,2000—2005年,长江经济带城镇扩张的热点区域主要集中在下游长三角的东南部,其中浙江省嘉兴市与宁波市城镇年扩张强度最大,分别为0.83%,0.62%,冷点区则不显著。2005—2010年,城镇扩张的热点区向长三角中部与北部转移,其中江苏省镇江市与南京市城镇扩张最为显著,年扩张强度分别为0.65%,0.30%,冷点区仍不显著。2010—2015年,城镇扩张的热点区覆盖长三角的大部分地区,浙江省嘉兴市与江苏省无锡市年扩张强度最大,分别为0.27%,0.22%,冷点区主要分布在长江中游和上游部分地区,其中岳阳等地区的年扩张强度几乎为0。计算2000—2015年各地区的年城镇扩张强度,其热点区仍然集中在长三角地区,冷点区分布在长江经济带上游与中游部分地区。
敏感性指数能验证ESV对价值系数的依赖性,另一方面也能反映各地类对生态系统服务总价值的影响[25]。将2000—2015年长江经济带各用地类型价值指数VC分别调整50%,根据公式(7)计算其CS值,结果见表2。总体而言,2000—2015年长江经济带各土地利用类型敏感性指数均小于1,说明生态系统服务价值量对于各地类价值系数不敏感,生态系统服务价值量的计算是合理的。其中,林地的敏感性指数相对较大,稳定在0.69,说明林地对于长江经济带整体的生态系统服务价值具有重要的作用。
基于生态系统服务价值当量表,计算出2000—2015年长江经济带各类生态系统服务价值量见表3。在2010—2015年,长江经济带的平均生态系统总服务价值量为73 186.25亿元,其中供给服务、调节服务、支持服务与文化服务分别占比为11.21%,52.59%,29.31%,6.89%。在15 a间,供给服务与支持服务价值量始终呈下降的趋势,而调节服务、文化服务和总服务价值量则在2000—2010年增加,在2010—2015年开始显著下降。总体而言,15 a间长江经济带生态系统的总服务价值量下降了0.27%,其中供给服务、调节服务和支持服务的价值量分别下降了0.71%,0.09%,0.53%,而文化服务则增加了0.12%。
对2000—2015年各地区生态系统服务价值量的下降率进行热点分析见图2。供给服务价值量下降的热点区集中于长江经济带下游长三角地区,该区域范围内各研究单元的供给服务价值量均呈现显著下降特征,其中上海市、嘉兴市、苏州市、无锡市分别下降了14.32%,13.81%,13.02%,9.58%; 而供给服务价值量下降的冷点区主要集中在长江经济带上游部分地区。调节服务价值量下降的热点区集中在长三角东南部地区,其中上海市和嘉兴市分别显著降低了9.40%,5.61%; 冷点区集中在长江经济带中游湖北省与湖南省的部分地区。支持服务价值量下降的热点区也集聚在长三角地区,其中上海市、嘉兴市、苏州市分别降低了12.61%,12.32%,8.70%; 冷点区分布在长江经济带上游部分区域。文化服务价值量下降的热点区分布在浙江省与江西省部分地区,其中台州市和绍兴市分别显著降低了2.49%,2.09%; 冷点区则分布在中游湖北省与湖南省部分地区。生态系统服务总价值量下降的热点区集中在长三角地区,其中上海市、嘉兴市、镇江市总价值量分别降低了10.16%,8.00%,5.34%; 冷点区则集中在湖北省与湖南省部分地区。
考虑到长江经济带各地区的城镇扩张强度与生态系统服务价值量变化率的时空分布具有非平稳性的特征,采用GTWR模型从局部尺度来分析城镇扩张对价值量变化的影响。利用3个时段的面板数据分别以生态系统供给服务、调节服务、支持服务、文化服务与总服务的价值量变化率为被解释变量,城镇扩张强度为解释变量,进行OLS回归和GTWR回归,并对比其拟合结果。其中,文化服务的回归结果不满足F检验和t检验要求,说明城镇扩张对文化服务价值量变化的线性驱动作用并不显著。其他生态系统服务类型的回归参数见表4。
基于R2,RSS与AICc指数,对OLS与GTWR的回归结果进行对比。其中,GTWR模型的拟合度大于OLS的拟合度,而GTWR的残差平方和指数和AICc指数则显著低于OLS,说明采用GTWR模型能比OLS模型更有效地解释城镇扩张对生态系统服务价值量变化的影响作用及其时空异质性特征。
将局部样本的回归系数进行可视化,见图3。总体而言,大部分地区的回归系数为负数,说明随着城镇扩张强度的增大,各地区生态系统的供给服务、调节服务、支持服务及总服务价值量的变化率减小,城镇扩张对长江经济带大部分地区的生态系统服务价值具有显著的负面影响。对于不同的生态系统服务类型,回归系数的大小具有不同的空间分布特征,且在时间序列上发生变化。
对于生态系统供给服务价值而言,回归系数的绝对值较大的区域主要分布在长江经济带的上游和下游地区。在2000—2005年和2005—2010年,城镇扩张对长江经济带上游云南省与贵州省的南部地区和下游长三角地区的负面影响强度较大,主要源于城镇扩张减少了耕地与林地等能提供重要供给服务功能的用地,从而导致生态系统的供给服务价值量显著降低,而中游大部分地区受影响程度较小。2010—2015年,受城镇扩张负面影响较大的区域主要集中在长江经济带的上游地区和中游西部的少数地区,其耕地、林地及草地逐渐向建设用地和水域转化,供给服务价值量逐渐下降,而下游大部分地区受影响较小。
对于生态系统调节服务价值而言,回归系数绝对值较大的区域主要集中在长江经济带上游和中游地区。2000—2005年,长江经济带上游云南省和贵州省的南部地区以及中游湖南省的部分地区受城镇扩张的负面影响较大,主要源于城镇建设对林地、草地与水域的占用,而下游地区受城镇扩张的影响程度相对较小。2005—2010年,城镇扩张对长江经济带上游大部分地区的调节服务价值具有较强的负面影响,而云南省西部德宏傣族景颇族自治州等地区,受益于“三江”流域实施的天然林保护、退耕还林和石漠化治理等重要生态保护工程[31],其调节服务价值增加,回归系数为正。2010—2015年,由于澜沧江、金沙江等梯形水电站工程[32]的建设,云南西部部分地区水域面积增大,城镇扩张对该地区的调节服务价值具有正面影响,对长江经济带上游其他地区和中游西部部分地区仍具有较大的负面影响,对下游地区的负面影响较小。
对于生态系统支持服务价值而言,长江经济带上游南部地区回归系数的绝对值较大。2000—2005年,由于耕地和林地、水域等生态用地被破坏,长江经济带上游云南省与贵州省的南部地区和下游北部地区的支持服务价值受城镇扩张的影响较大,中游地区受影响较小。2005—2010年,城镇扩张对支持服务影响较大的地区主要集中在贵州省南部。到了2010—2015年,受城镇扩张负面影响较大的地区主要分布在长江上、中游以南,该地区的耕地、林地、草地和湿地不断向水域和建设用地转化。
对于生态系统总服务价值而言,回归系数绝对值较大的区域主要集中在长江经济带的上游地区。2000—2005年,由于大量耕地和林地等生态用地被建设用地侵占,城镇扩张对总服务价值负面影响较强的地区主要分布在云南省与贵州省南部。2005—2010年,受城镇扩张负面作用较强的地区收缩至贵州省南部。到了2010—2015年,城镇扩张对长江经济带上游大部分地区都具有较强的负面影响,对云南省西部部分地区则具有正面影响,对中游和下游的大部分地区的负面影响较小。
本研究从不同的生态系统服务类型角度,分析了长江经济带各地区生态系统服务价值对城镇扩张的时空响应特征。在已有相关研究中,黄敏等[33]对全国范围的研究表明城镇化水平与生态系统服务价值显著负相关,虎陈霞等[14]对嘉兴市的研究表明建设用地与生态系统服务价值具有负相关关系。本文的研究结果则表明,总体上长江经济带城镇扩张对生态系统服务价值具有负面影响,但对不同的生态系统服务类型,不同地区有显著的时空异质性。因此,在进行长江经济带生态保护的差异化管理中,应重点加强城镇扩张对上游地区尤其是上游南部地区生态系统影响的管控,保持中游地区耕地和水域、湿地等生态用地的稳定以维持其生态系统服务功能,优化下游地区城镇发展格局以增强生态环境承载能力。
由于数据和研究尺度的局限性,本文也有以下不足。一方面,本文在进行空间分析时采用了地级市及以上城市尺度,但不同的评价与分析尺度上生态系统的格局与过程将呈现不同的特征[34]; 另一方面,城镇扩张不仅包括城镇用地扩张的强度,也包含城镇扩张的空间形态和空间差异指数等多方面内涵。在未来的研究中,可尝试利用更精细的数据从多视角多尺度进一步探究生态系统服务价值对城镇扩张的时空响应特征,以期为区域发展和生态环境保护差异化管理提供理论指导。
(1)2000—2015年,长江经济带城镇范围不断扩张,年平均城镇扩张强度为0.02%。在15 a间,城镇扩张的热点区主要分布在下游长三角地区,其中嘉兴、无锡、镇江、苏州、南京等城市的扩张强度最大; 而冷点区则主要分布在上游与中游部分地区。
(2)2000—2015年,长江经济带生态系统服务总价值量下降了0.27%,其中供给服务、调节服务和支持服务价值量分别降低了0.71%,0.09%,0.53%,且下降的热点区皆分布在长三角地区。长江经济带整体的文化服务价值量增加了0.12%,局部下降的热点区主要分布在江西省与浙江省部分地区。
(3)城镇扩张对长江经济带的文化服务价值量的影响不显著,但是对大部分地区生态系统的供给服务、调节服务、支持服务以及总服务的价值量均产生负面影响,且影响强度大小具有显著的时空异质性特征。长江经济带上游地区,尤其是上游南部地区的各类生态系统服务价值在各时段内受城镇扩张的影响强度较大; 中游西部部分地区的供给服务、调节服务和支持服务的价值量在部分时段内受城镇扩张的影响强度较大,总服务价值量受影响较小; 下游地区的供给服务和支持服务价值量在部分时段内受城镇扩张的影响较大,调节服务和总服务价值量受影响较小。