森林土壤作为森林涵养水源的主体,其持水量可占总体涵养水量的85%以上,在调节水分循环方面发挥着重要作用[1-2]。森林土壤的水文物理性质是森林水源涵养功能的重要评价指标,其主要体现在涵蓄降雨、阻延径流和防洪减灾等方面[3]。森林土壤的水文物理性质普遍存在时空异质性和环境异质性[4],其影响因素主要包括地形地貌、土壤特征、降雨差异和植被类型。对于人工林生态系统而言,营林措施会改变林分空间结构和环境因子,造成土壤涵养水源能力发生改变[5]。因此,探究人工林土壤的水文物理效应对于森林涵养水源功能的提升与调控手段具有重要意义。
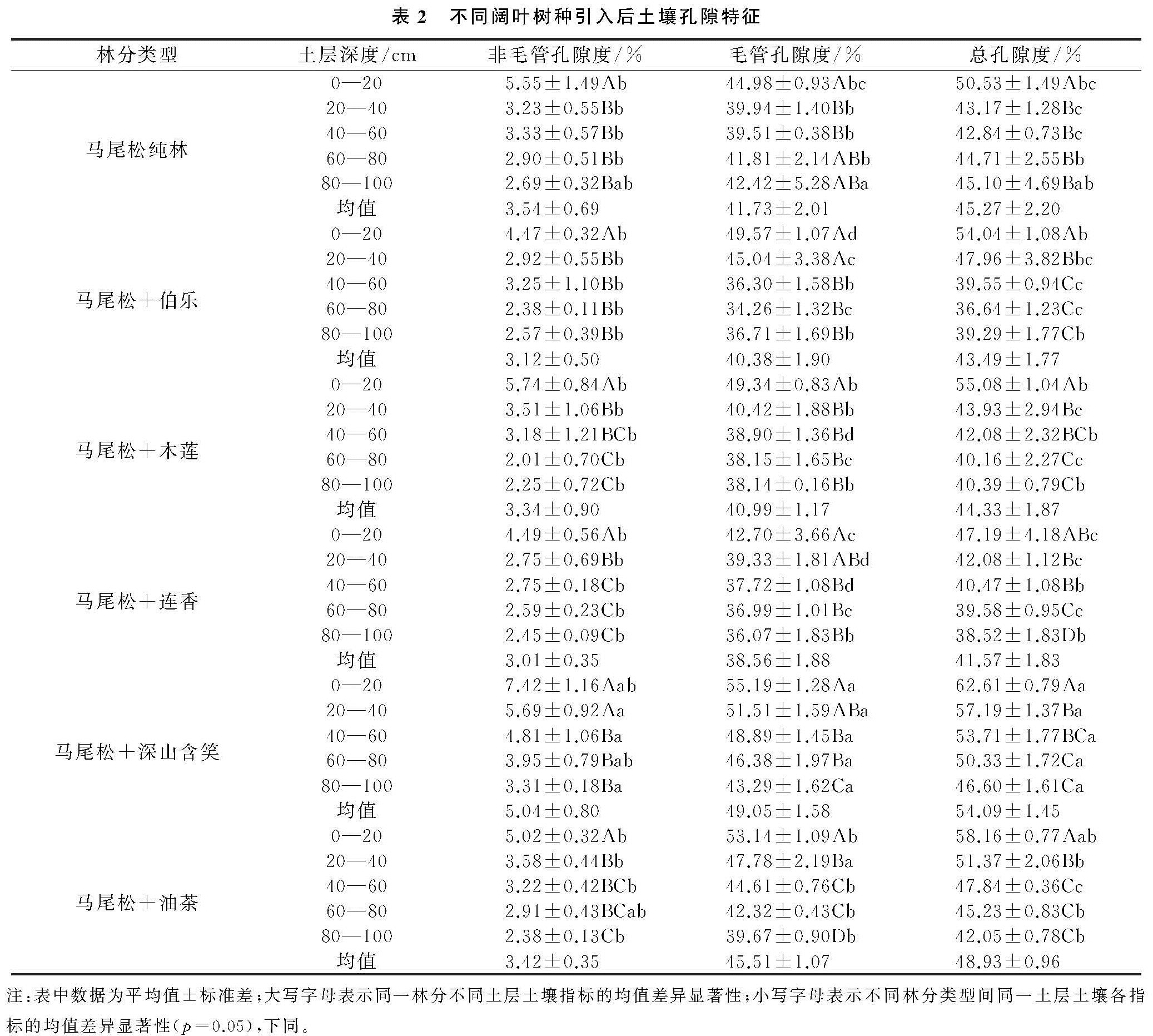
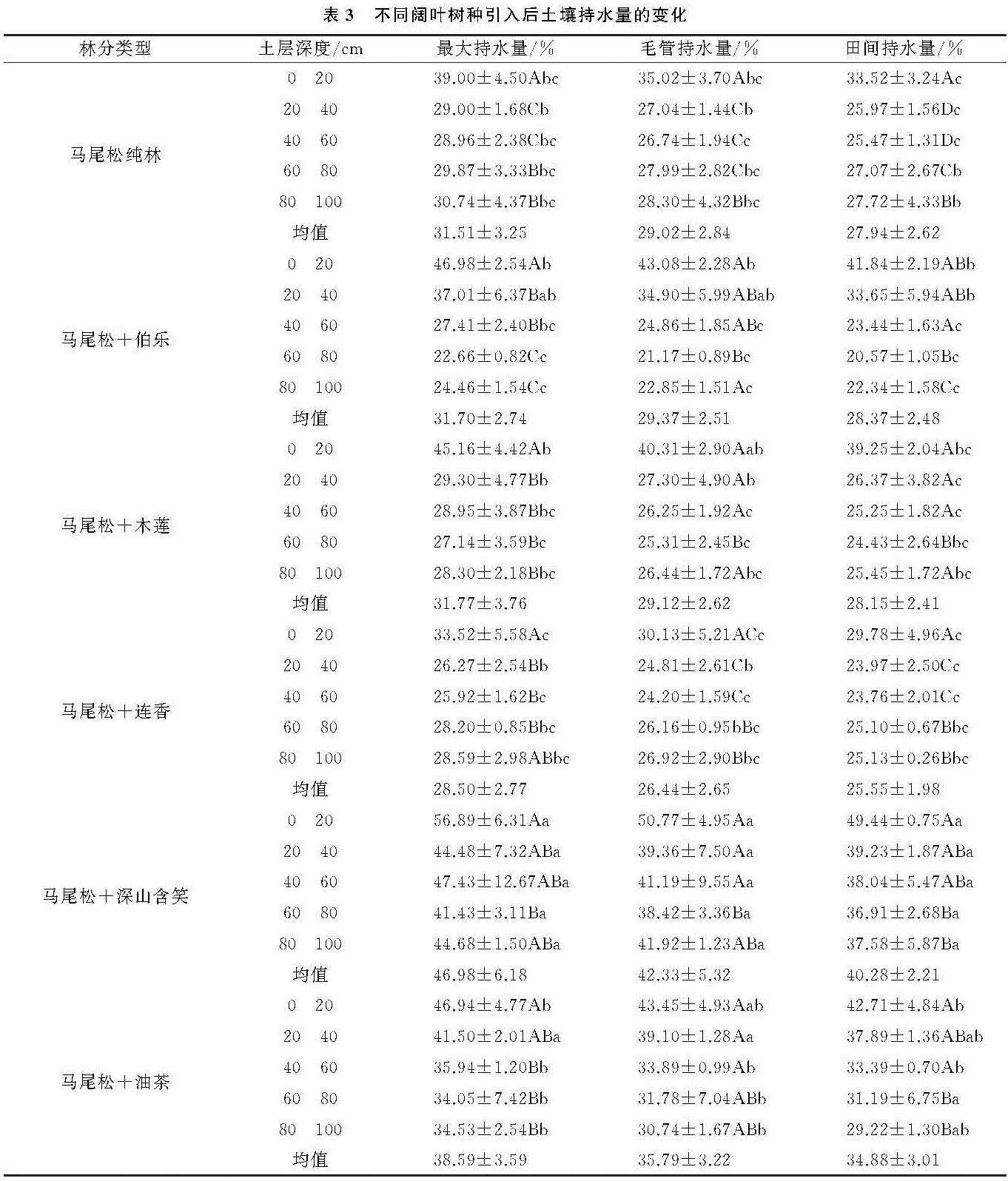
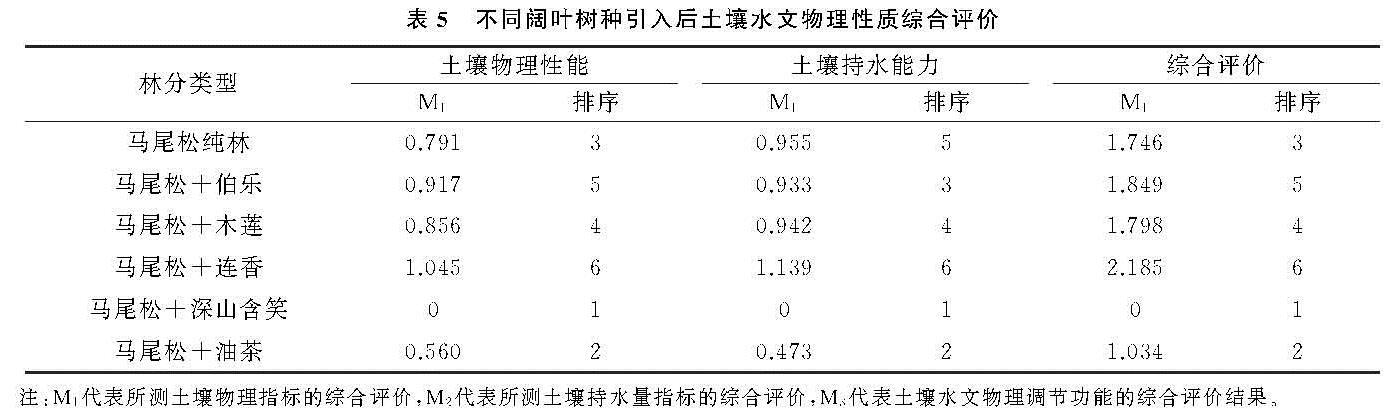
土壤容重与孔隙度是土壤物理特性的重要指标,容重大小是土壤质地、结构和孔隙等物理性状的综合表现,而孔隙度能够反映土壤通透程度,其中毛管孔隙和非毛管孔隙分别使土壤具有储水性能和透水性能[6]。植被是土壤物理—水文效应的主要调节者[7],通常混交林比单一树种林分具有更高的土壤生态功能[8]。阔叶林地表枯落物含量分解速率通常大于针叶林,针阔混交林有利于凋落物的分解和养分释放,能够改善针叶林地力衰退并提高土壤水源涵养能力[9-10]。例如,针阔混交林能降低土壤容重并提高土壤孔隙度,从而直接影响土壤最大持水量,有效持水量和土壤渗透速率,其土壤拒水性显著低于纯林[11-13]。然而,不同树种间存在生物特性和林分结构差异[14-15],物质周转和养分归还能力对不同植被响应也有所不同,导致营造针—阔混交林对于土壤水文物理性质可能存在正效应或负效应[16]。因此,充分认知和定量评价不同类型针—阔林分的水文物理性质,对针叶林阔叶化经营和水资源的科学管理与应用具有重要意义。
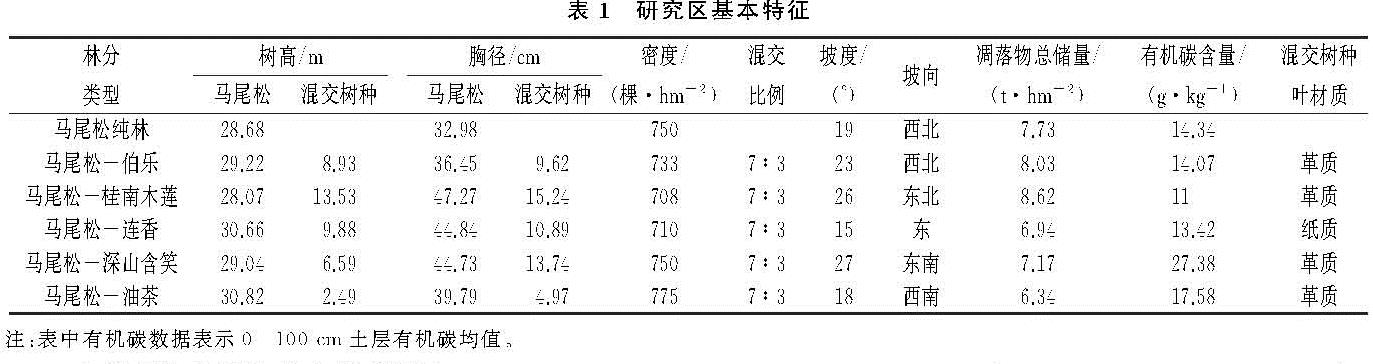
马尾松(Pinus massoniana)是中国特有乡土树种,其适应能力强,耐干旱,是南方荒山绿化造林的主要树种,面积高达1.13×107 hm2[17]。经过十多年的退耕还林治理,我国南方已形成以马尾松人工林为主的水土流失初步治理区,但马尾松纯林林分结构单一且生物多样性较差,其林下水土流失仍较为严重[18]。马尾松人工纯林所引起的土壤退化已成为中国南方最严重的退化生态问题之一[19-20]。如何通过林分改造提高马尾松人工林水源涵养功能成为当前亟需解决的问题。据报道,针叶人工林补植阔叶树种能显著改善土壤衰退现象[21],但其机理尚未得到充分认知,且不同阔叶树种间所带来的土壤水文物理效应差异尚未得到评估,因此,筛选适宜林分补植的阔叶树种显得尤为重要。基于此,本研究拟解决以下科学问题:(1)马尾松人工林土壤物理及水文效应如何响应不同阔叶树种的引入;(2)在马尾松人工林阔叶化改造中,如何选择树种以达到提升土壤蓄水保墒的目的。