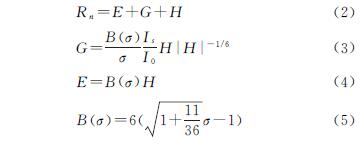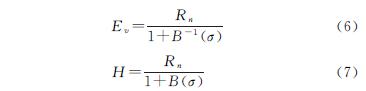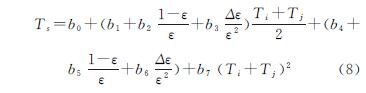2.1 MEP模型反演结果验证
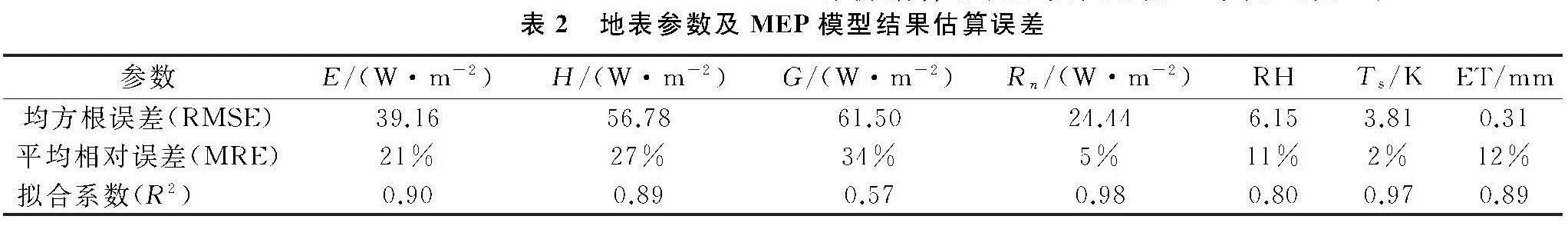
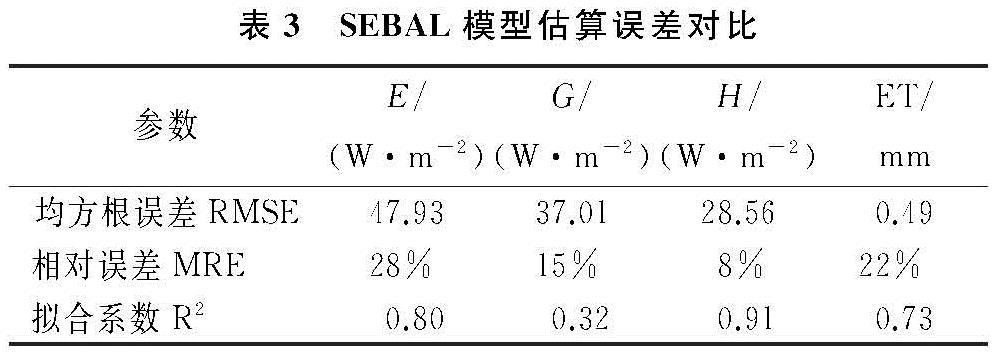
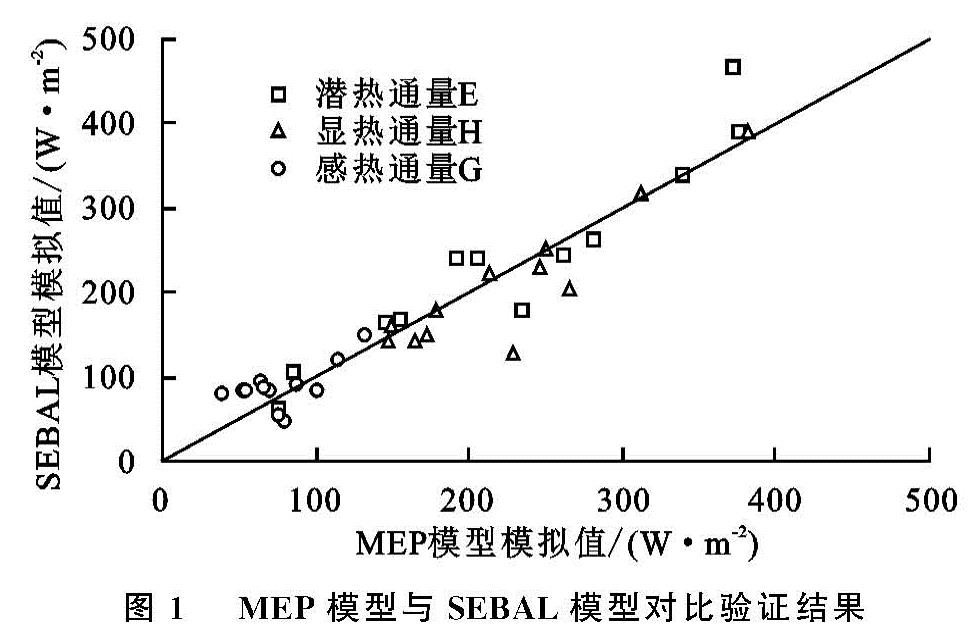
利用2016年5—10月沙丘和草甸两个观测站的涡度相关数据以及气象观测数据与MEP模型估算结果、SEBAL模型估算结果、地表参数进行对比。为了更好地评价两种模型,本文选用统计学中均方根误差(RMSE)、相对误差(MRE)与拟合系数(R2)作为评价指标,对比结果见表2与表3,图1。
由表2与表3得到,MEP模型反演G值的均方根误差与相对误差最大分别为61.50 W/m2,34%,G的拟合系数最小为0.57; SEBAL模型反演E值的均方根误差最大为47.93 W/m2,G的相对误差最大为15%,拟合系数最低为0.32; 地表参数验证结果相对较好,Rn的模拟结果误差较小,其拟合系数最高为0.98,Ts的平均相对误差最小为2%。由图1看出:SEBAL模型与MEP模型之间反演结果整体误差较小,其中MEP模型的H值偏高,G的误差相对较小,个别日期的E值有着较大的差异。
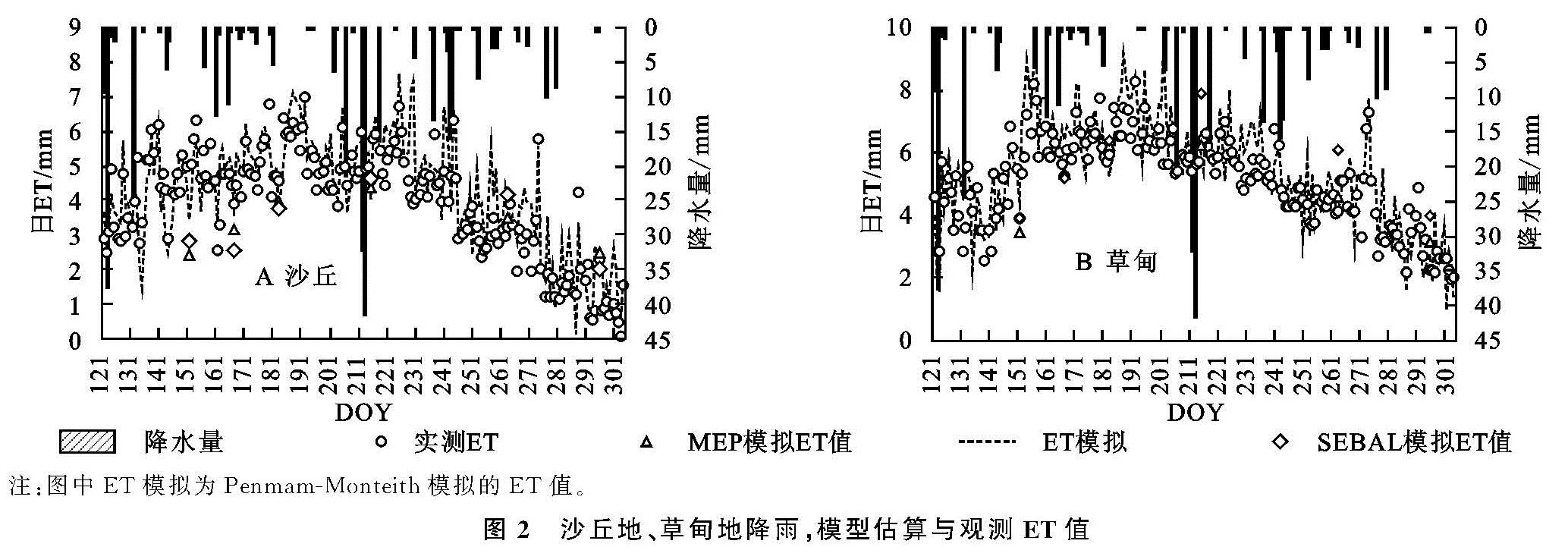
利用沙丘和草甸观测数据,通过MEP模型分别反演了两点的日ET,使用实测ET数据、遥感估算的ET数据以及Penmam-Monteith模拟ET之间进行对比,对比结果见图2。
从图中看出MEP模型估算ET和实测ET变化趋势基本一致,个别日期有所差异,遥感估算ET与实测ET以遥感反演ET值与观测ET以及Penmam-Monteith模拟ET之间误差较小,结果表明MEP模型能在不同的土地覆被类型模拟出精度较高的ET值。研究区ET总体波动较为平缓,表现为5—6月呈上升趋势,7—8月相对较高,9—10月处于下降趋势。沙丘的ET明显低于草甸,随着降水量的变化,沙丘的ET波动较为剧烈。降水对ET有着较大的影响,当有降雨事件发生的日期ET会随之降低,出现一个波谷,降雨事件结束之后ET会有明显升高,出现一个波峰。总体来说:在不同土地覆被类型下,MEP模型可以估算出相对精确的ET以及较为合理的变化趋势。
2.2 MEP和SEBAL模拟ET的时空分布特征
本文通过MEP模型与SEBAL模型分别反演出研究区瞬时潜热通量,通过日ET尺度扩展方法的到日ET值,日ET时空分布见附图13,附图14。
研究区日ET最大可以达到7 mm以上,主要集中在湖泊,湖泊相对较为稳定,日ET值在4~7 mm; 农田与草甸由于植被与农作物的影响日ET变化较为明显,尤其在6月、7月、8月,个别区域会有最大值出现,日ET保持在3~7 mm; 沙丘日ET一直处于较低水平,保持在1~3 mm。
SEBAL模型与MEP模型得到的ET空间分布图在5—7月差异较小,8—10月差异较大,二者差异较大的区域在半固定沙丘,误差在0.5~1 mm; 农田与草甸差异较小,误差在0.2~0.6 mm。主要原因有:(1)MEP模型以能量闭合为边界条件,而SEBAL模型会出现能量不闭合的情况,(2)输入参数不同,MEP模型所需参数少,只需要3个地表参数,而SEBAL模型输入参数多,参数的不同引起结果差异,(3)对于植被处理方法的不同:对于植被覆盖的地表MEP模型认为土壤热通量为零,直接计算显热通量,而SEBAL模型通过选取冷热点的方式估算显热通量,5—7月研究区处于春季,植被较少,8—10月研究区处于夏季植被生长茂盛,因此导致8—10月差异较大。
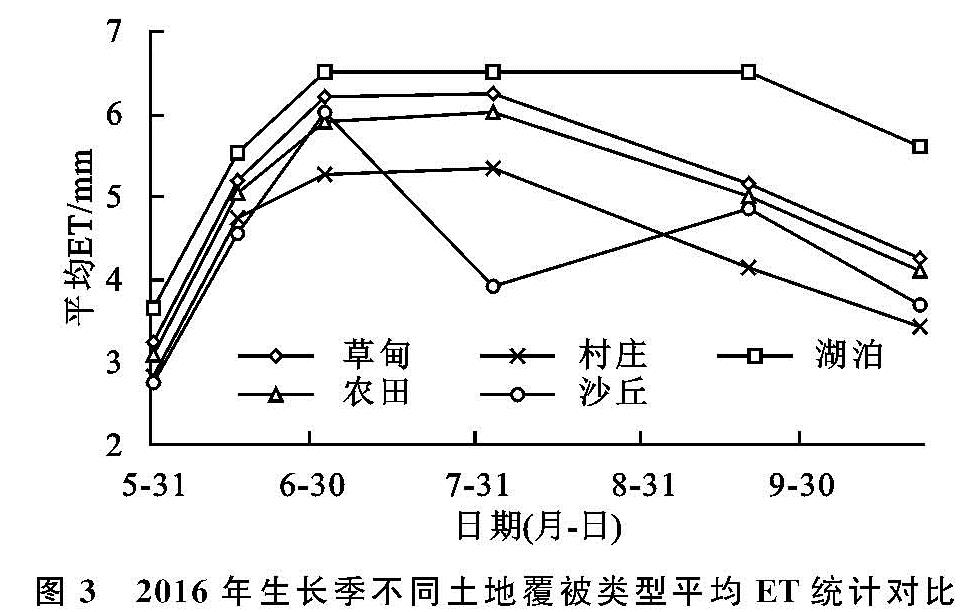
为进一步分析MEP模型与SEBAL模型的差异以及ET时空变化,按照不同土地覆被类型对ET时空分布图的ET平均值进行统计,得到各类土地覆被类型ET平均值变化曲线,见图3。
图3 2016年生长季不同土地覆被类型平均ET统计对比
随着时间的变化不同土地覆被类型下的ET值波动情况有所差异,但是整体呈现先增长后降低的变化趋势。5月所有土地覆被类型ET值均保持在较低水平,ET在2.5~4 mm; 6月—8月大部分区域的ET值均有较为明显的升高,而沙丘地由于水分补给不充足反而降低; 在9—10月ET呈现明显的下降趋势,10月除湖泊仍保持在相对较高的水平,其他区域ET值较低,ET空间分布情况与5月相似。湖泊、草甸、农田整体呈较高水平,受月份影响较为明显; 沙丘波动较为明显,受月份影响相对较小,沙丘类型不同,ET分布有较大差异,其中固定沙丘和半固定沙丘相似,而流动沙丘ET处于较低水平,尤其在6—8月差异较为明显; 村庄受人类活动影响较大,ET值分布相对较为集中并处于较低水平。
影响研究区ET时空分布的主要因素有:土壤类型不同,草甸地主要为黑钙土、栗钙土,沙丘地以砂土、壤砂土、壤土为主要的土壤类型,不同土壤类型下地表反照率有所差异,对太阳辐射的吸收也有差别[32],导致ET的不同; 植被类型不同,随着生长季的到来植被的蒸腾作用所占蒸散发总量的比重越来越大,不同植被类型蒸腾作用有着较大差异,导致ET的不同[33]; 土壤含水量以及供水条件不同,农田与草甸地的土壤含水量较高且水分供应充足,而沙丘地土壤含水量低,地下水埋深较深,除天然降水外,没有其他水源供给,因此沙丘ET要低于农田与草甸[34]。