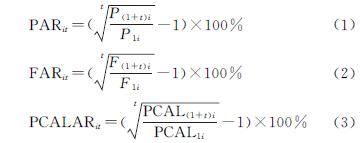3.1 农村人口变化的时空特征
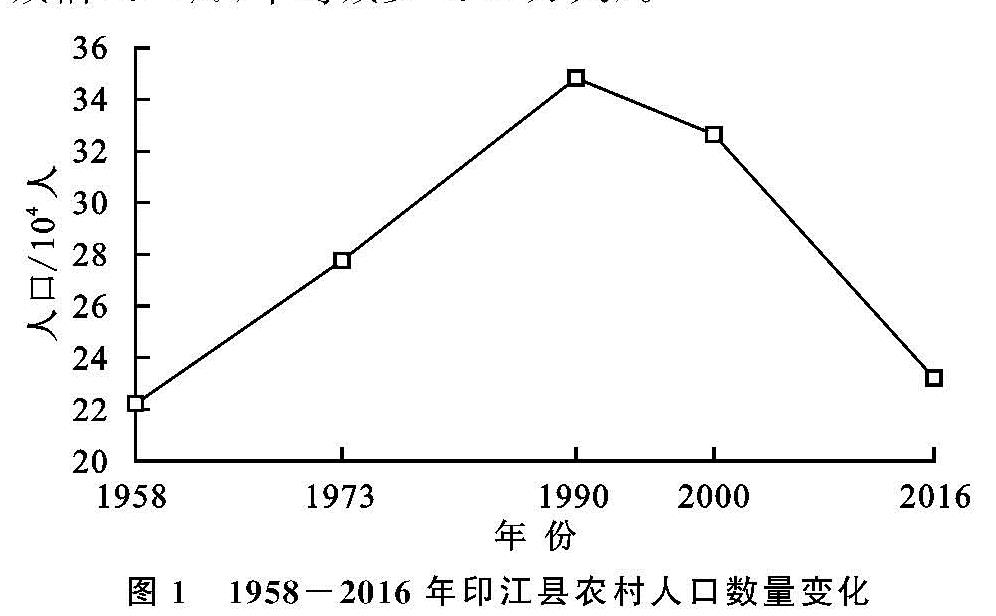
农村人口变化的时序特征。从图1可知,印江县农村人口时序变化经历了3个阶段。1958—1990年为增长期(年均增长1.42%,年均增加0.31万人)。农村人口在1990年达到顶峰后进入下降期,其中1990—2000年为低速下降期(年均减幅0.65%,年均减少0.22万人),2000—2016年为快速下降期(年均减幅2.11%,年均减少0.68万人)。
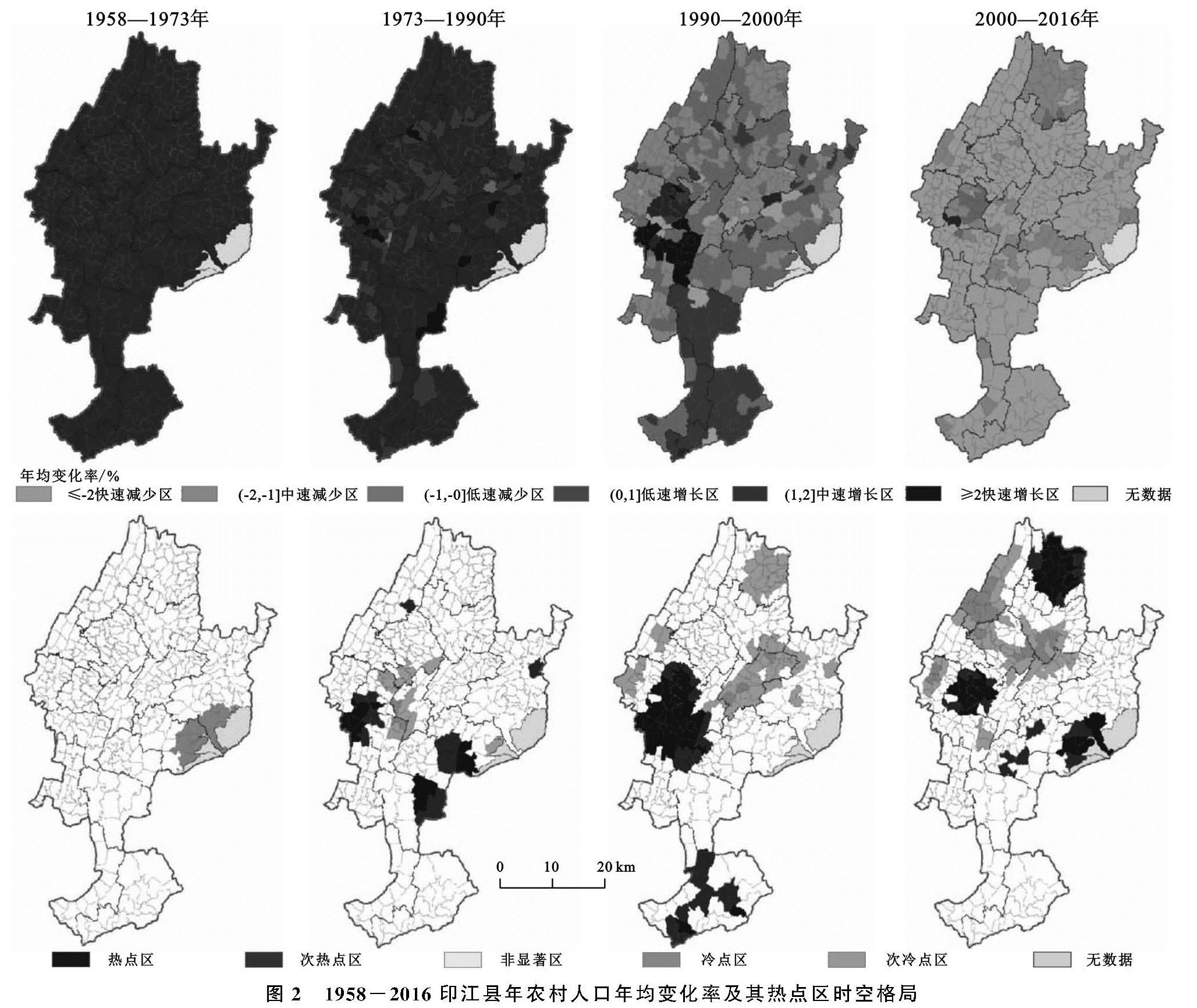
农村人口变化的空间特征。从图2可知,1990年前印江县各村人口以增长型为主,快速增长区主要以点状分布于峨岭街道、龙津街道、缠溪镇、板溪镇、木黄镇、紫薇镇的镇政府所在的村。中速增长区广泛分布于全县。低速增长区呈条带分布于中部。1990—2000年,快速增长区主要在以县城为中心的峨岭街道呈面状分布; 中速增长区集中在龙津街道,低速增长区集中在缠溪镇和洋溪镇。其余为人口减少区。2000—2016年,仅峨岭街道的村人口增长; 北部和东南部人口中速减少,其余地区人口年均降幅均大于2%,尤其是天堂镇、板溪镇和中兴街道的村人口减少最快,全县进入人口快速减少阶段。
3.2 耕地变化的时空特征
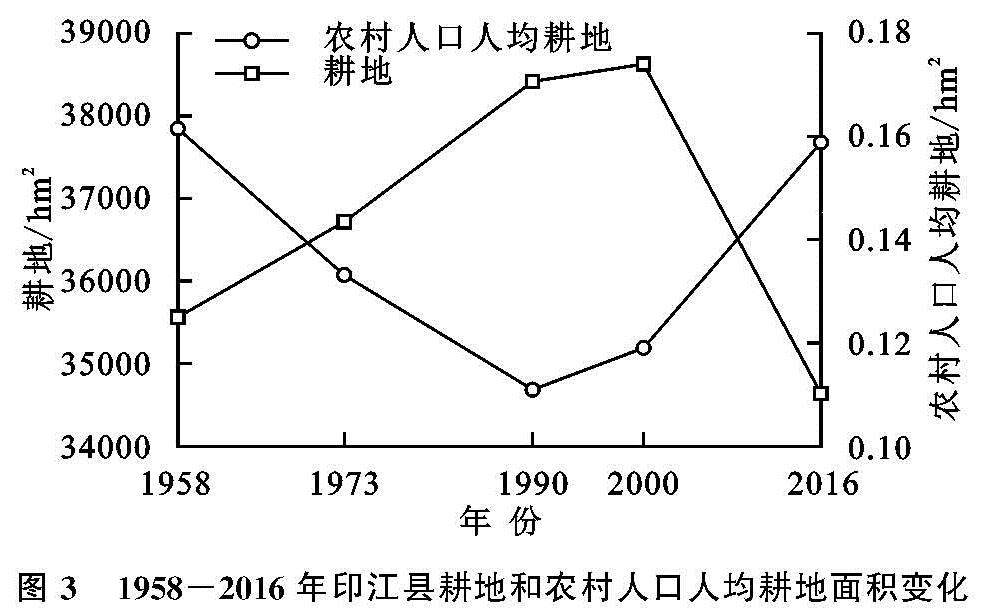
耕地变化的时序特征。从图3可知,1958—2016年印江县耕地面积呈现出先迅速增长后缓慢减少的趋势。在“以粮为纲”、开垦荒地等政策的影响下,1990年之前耕地迅速增长(年均增长0.24%,年均增加85.88 hm2),1990—2000年为缓慢增长期(年均增长0.05%,年均增加20.97 hm2)。之后,由于国家退耕还林等生态建设的实施、建设用地的增加、人口外出耕地撂荒等原因,耕地在2000年到达拐点后开始下降。2000—2016年耕地年均减幅0.68%,年均减少262.23 hm2。
耕地变化的空间特征。从图4可知,1990年前有3个区域耕地增长明显。快速增长区位于北部、西部的刀坝镇、天堂镇、沙坡子镇、板溪镇的村,中速增长区位于中东部合水镇、木黄镇,低速增长区位于南部杨柳镇、洋溪镇的村。耕地减少区以低山河谷区和梵净山中山区为主,主要分布于中南部的罗场乡、缠溪镇,东南部的紫薇镇的村。1990年后分为两个时段,1990—2000年快速增长区集中分布于中部和南部,点状分布于西部的村域; 耕地减少区在各乡镇均有分布。2000—2016年,耕地增长区主要集中于中东部区的村域; 耕地减少区分布于西北部、中部和南部的村域,其中快速减少区主要分布于以县城为中心的峨岭街道和中兴街道的村。
3.3 农村人口人均耕地变化的时空特征
人均耕地变化的时序特征。1958—2016年印江县农村人口人均耕地面积呈现先减少后增加的态势。1990年以前农村人口人均耕地面积持续减少,从1958年的0.162 hm2/人下降到1990年的0.112 hm2/人,年均降幅达1.17%。1990年以后农村人口人均耕地面积呈增长趋势,其中2000—2016年增幅较大,年均增长1.82%,到2016年上升至0.157 hm2/人。
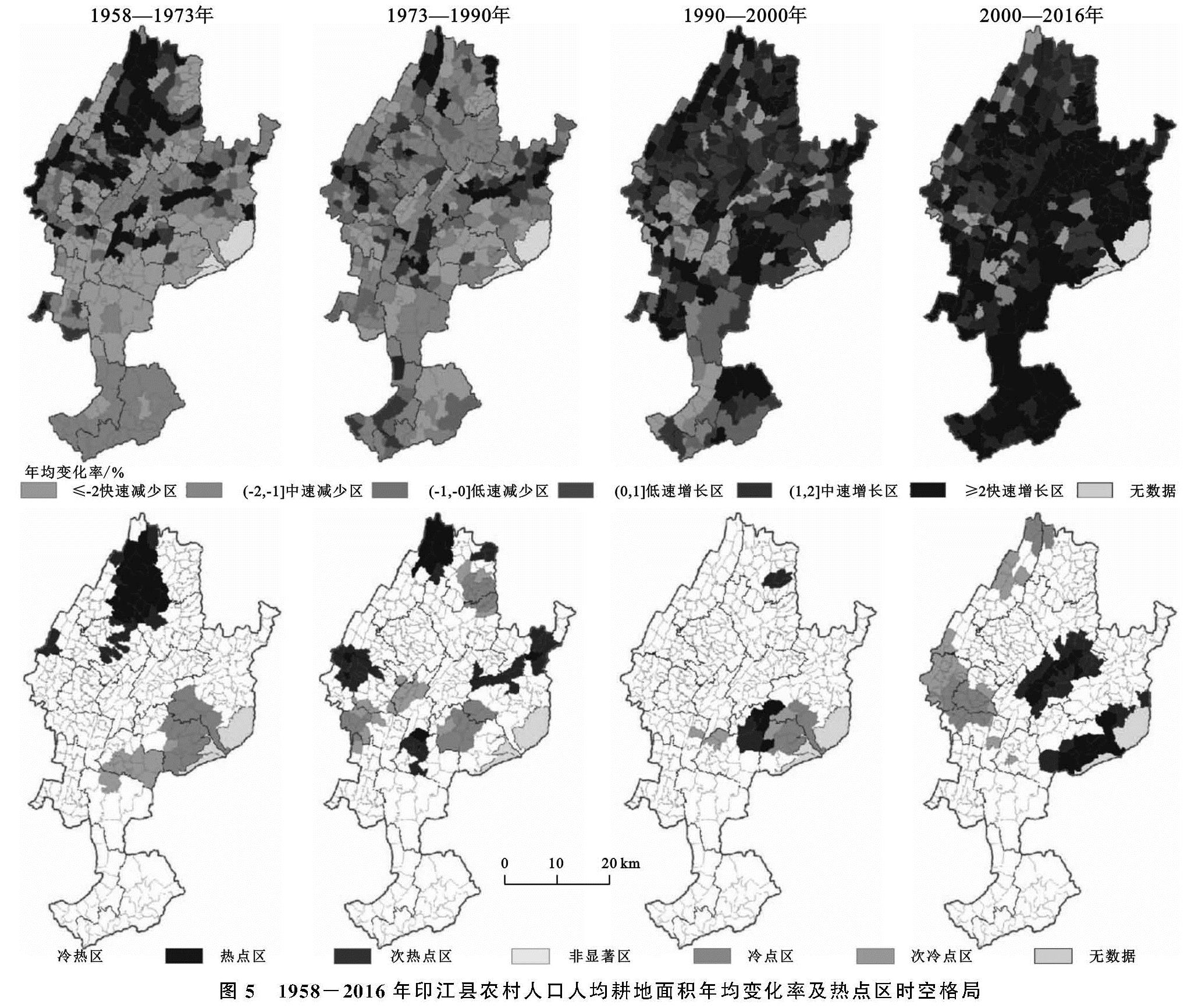
人均耕地变化的空间特征。从图5可知,1958—1973年人均耕地快速增长区主要分布于北部、西部的沙子坡镇、天堂镇、板溪镇的村。快速减少区主要分布于中南部缠溪镇、罗场乡,东南部紫薇镇的村域。1973—1990年全县以减少区为主,仅沙子坡镇、中兴街道、木黄镇、合水镇的部分村人均耕地面积增加。1990—2000年全县68.6%的村人均耕地面积增加,其中快速增长区主要分布在南部洋溪镇、中南部新寨镇,北部的杉树镇、刀坝镇的村域; 仅12.5%的村人均耕地快速减少,主要分布在县城中心的峨岭街道、龙津街道、以及罗场乡、杨柳镇的部分村。2000—2016年进入人均耕地全面增长阶段,全县68.9%的村为快速增长区,在全县均有分布; 仅4.2%的村为快速减少区,零星分布于全县。
图2 1958-2016印江县年农村人口年均变化率及其热点区时空格局
图3 1958-2016年印江县耕地和农村人口人均耕地面积变化
3.4 农村人口与耕地变化的耦合关系
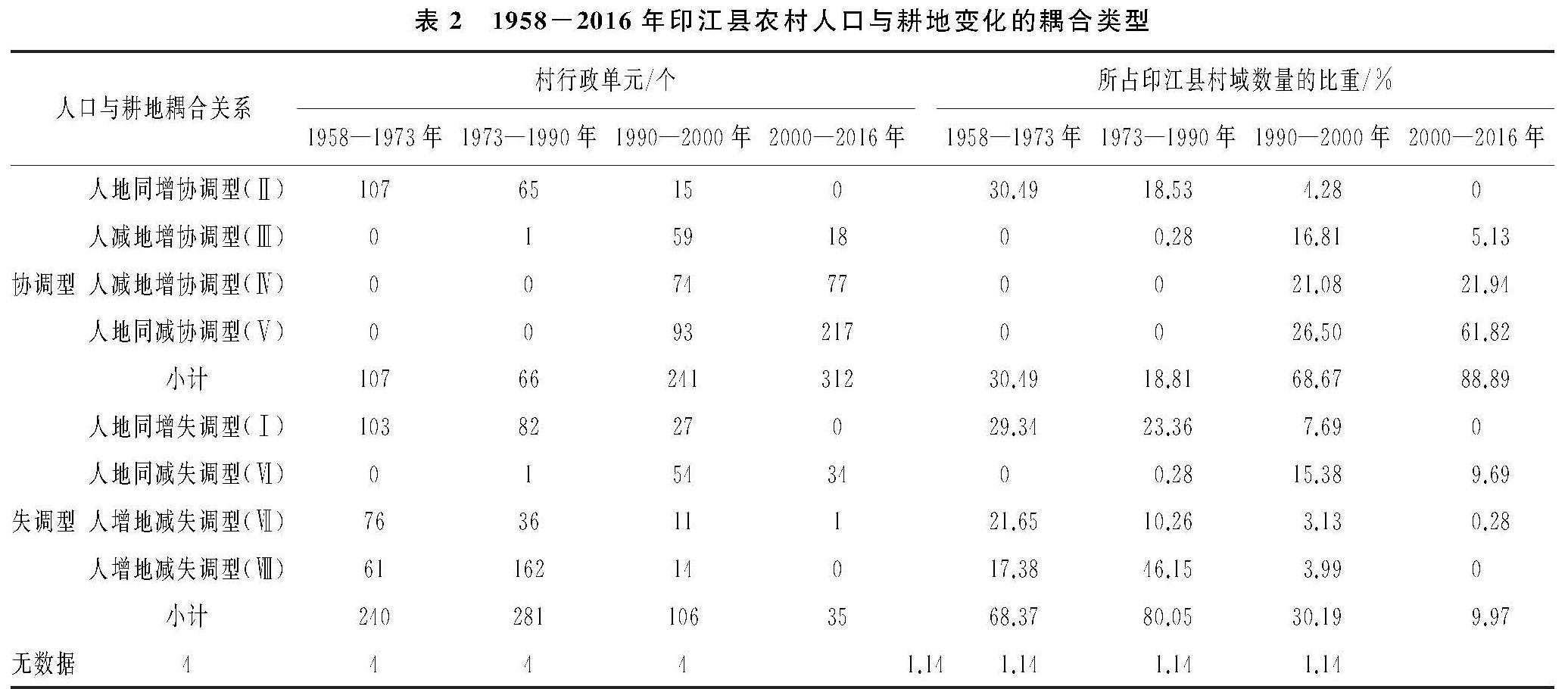
3.4.1 农村人口与耕地变化的时空耦合特征 农村人口与耕地变化的时序耦合特征。1958—2016年印江县全县农村人口与耕地变化耦合类型由失调型向协调型转变。印江县1958—1973年与1973—1990年两个时段,均为人地同增失调型。1990年之后发生转变,1990—2000年为人减地增协调型,2000—2016年是人地同减协调型。
农村人口与耕地变化的空间耦合特征。从表2可知,印江县农村人口与耕地变化耦合类型的空间分布和村域数量比重。1958—1973年,以失调型村域为主,占全县村域总数的68.37%,数量由高到低分别是Ⅰ类>Ⅶ类>Ⅷ类。其中Ⅰ类主要集中在中部朗溪镇、合水镇,南部杨柳镇、洋溪镇及东北部木黄镇的村。Ⅶ类分布在县城周边的峨岭街道、龙津街道,中南部的罗场乡、缠溪镇,东部的紫薇镇及木黄镇南部村。Ⅷ类主要集中在西部的杉树镇、中部的朗溪镇、合水镇和罗场乡。协调型村域仅为Ⅱ类型,占全县村域总数的30.49%,主要集中在北部沙子坡镇、刀坝镇、天堂镇和中部板溪镇。1973—1990年,仍以失调型村域为主,村域数量增加,占全县村域总数的80.05%,数量从高到低分别是Ⅷ类>Ⅰ类>Ⅶ类>Ⅵ类。其中Ⅷ类增幅较快,较上一期增长2.67倍且全县均有分布,Ⅰ类和Ⅶ类数量减少。协调型仍以Ⅱ类为主,数量较上一期减少,占全县村域总数减少至18.81%,主要呈条带状分布于西北部和中东部。1990—2000年,以协调型村域为主,占全县村域总数的68.67%,涵盖了4种协调类型,数量从多到少依次为Ⅴ类>Ⅳ类>Ⅲ类>Ⅱ类。其中Ⅴ类主要在除南部以外的地区; Ⅳ类主要分布于西部沙子坡镇、中部朗溪镇、东部紫薇镇、罗场乡3个条带; Ⅲ类主要分布在板溪镇、新寨镇和紫薇镇的村。这一时期,失调型的区域减幅较大,占全县村域总数比重缩减至30.19%,4种失调型均有分布。其中Ⅵ类数量最多,主要分布于东部的木黄镇,中部的合水镇、朗溪镇、罗场乡,南部的杨柳镇。2000—2016年,以协调型村域为主,占全县村域总数的88.89%,数量从多到少依次是Ⅴ类>Ⅳ类>Ⅲ类,其中Ⅴ类在全县均有分布,Ⅳ类主要分布于中东部合水镇、木黄镇、紫薇镇,北部的板溪镇、天堂镇,南部的杨柳镇、洋溪镇。失调型仅占全县9.97%,为Ⅵ类主要以点状分布于峨岭街道、朗溪镇、中兴镇、沙子坡镇的个别村。
图4 1958-2016年印江县耕地面积年均变化率及热点区时空格局
3.4.2 槽谷区与非槽谷区农村人口与耕地变化的时空耦合对比 以地貌和行政村边界叠加划分印江县槽谷区和非槽谷区村域[28]。根据印江县地貌类型分区,将丘陵谷地区、低山河谷区和梵净山中山区村域合称为非槽谷区村,统计得出槽谷区村域共163个村,占全县村域总数的47.44%,非槽谷区村域共188个村,占全县村域总数53.56%。从图6可知,槽谷区和非槽谷区村域农村人口与耕地变化的耦合趋势基本一致。但是每种耦合类型在槽谷区和非槽谷区中所占比重有所差异。1958—1973年、1990—2000年、2000—2016年3个时段内,槽谷区失调型村域数量所占槽谷区村域总数的比重高于非槽谷区失调型村域数量所占非槽谷区村域总数的比重,而协调型耦合类型的数量比重则相反。以2000—2016年为例,槽谷区协调型村域数量占槽谷区村域总数的86.50%,而非槽谷区协调型村域数量占非槽谷区村域总数的92.93%,表明非槽谷区人地和谐程度要好于槽谷区。
图5 1958-2016年印江县农村人口人均耕地面积年均变化率及热点区时空格局
表2 1958-2016年印江县农村人口与耕地变化的耦合类型
图6 1958-2016年印江县槽谷区、非槽谷区耕地与农村人口变化的耦合类型村域数量比例
3.5 农村人口与耕地变化的耦合关系的驱动因素
岩溶槽谷区农村人口与耕地变化的耦合关系受到自然、人文、政策等多方面的影响[28]。自然因素方面,受地形坡度、地形起伏度、离河流远近的水源条件、洪水等自然灾害方面的影响。人文和政策因素方面,1958年由于大跃进,印江县修建1 000多座炼铁炉大炼钢铁导致生态破坏[29]。同年,印江县成立45个人民公社,99%的农户加入人民公社,印江县农村人口的生产和生活几乎固定于乡村地域,对土地的依赖性强。1968—1973年印江县经历了建国后的人口生育高峰期,人口年增长率高达到30.22‰[29],是印江县的人口膨胀期,这段时间由于人口的迅速增长,对粮食的需求提高,导致耕地扩张。1979年国务院《政府工作报告》要求开垦荒地、以增加耕地面积。在大量开垦荒地和坡耕地的背景下,1979年印江县森林覆盖率降至15.6%[29],为建国以来的最低点,生态破坏严重。1984年后,随着家庭联产承包责任制的实施和《国务院关于农民进入集镇落户问题的通知》的颁布,至此在农业生产效率大幅提高和允许落户城镇的背景下,大量的农村人口逐渐向城镇转移[2]。特别是1990年贵州省开始有组织的向外输出农村剩余劳动力以来,印江县农村人口开始呈下降趋势。1999年开始实施的西部大开发战略推动印江县经济有所增长,农民对土地的依赖性逐渐减小,不再需要扩大耕地面积来提高粮食产量,耕地压力减弱[22]。
进入2000年以来,国家政策开始向恢复生态倾斜。2000年印江县作为贵州省试点开始实施退耕还林工程,2004年取消农业税,2005年印江县作为贵州省岩溶区石漠化综合治理工程试点县推进生态修复工作,坡耕地逐渐收缩。随着生态修复工程导致的坡耕地面积减少及农地边际化,劳动力成本上涨,当地农业劳动力逐渐减少。2009年贵州省实现基本普及九年义务教育、基本扫除青壮年文盲的“两基”目标,农村青壮劳动力外出务工人数进一步增加。2010年贵州省工业强省战略,城镇化和工业化迅速发展,耕地进一步减少。2014年以来贵州省实施精准扶贫政策,2016年印江县被列为国家重点生态功能区,生态移民搬迁、易地搬迁后导致农村人口大量外迁,一方面边远耕地撂荒之后转为林灌地,另一方面集中连片的林果地增加,耕地发生转型。国家和贵州省的土地利用政策、人口政策和社会经济发展模式及城镇化、工业化过程影响人口和耕地变化,最终驱动农村人口和耕地变化的时空耦合关系发生转变,人地关系矛盾逐渐缓和,农村人口和耕地变化的耦合关系逐渐由失调型向协调型转变。