2.1 气温突变变化特征分析
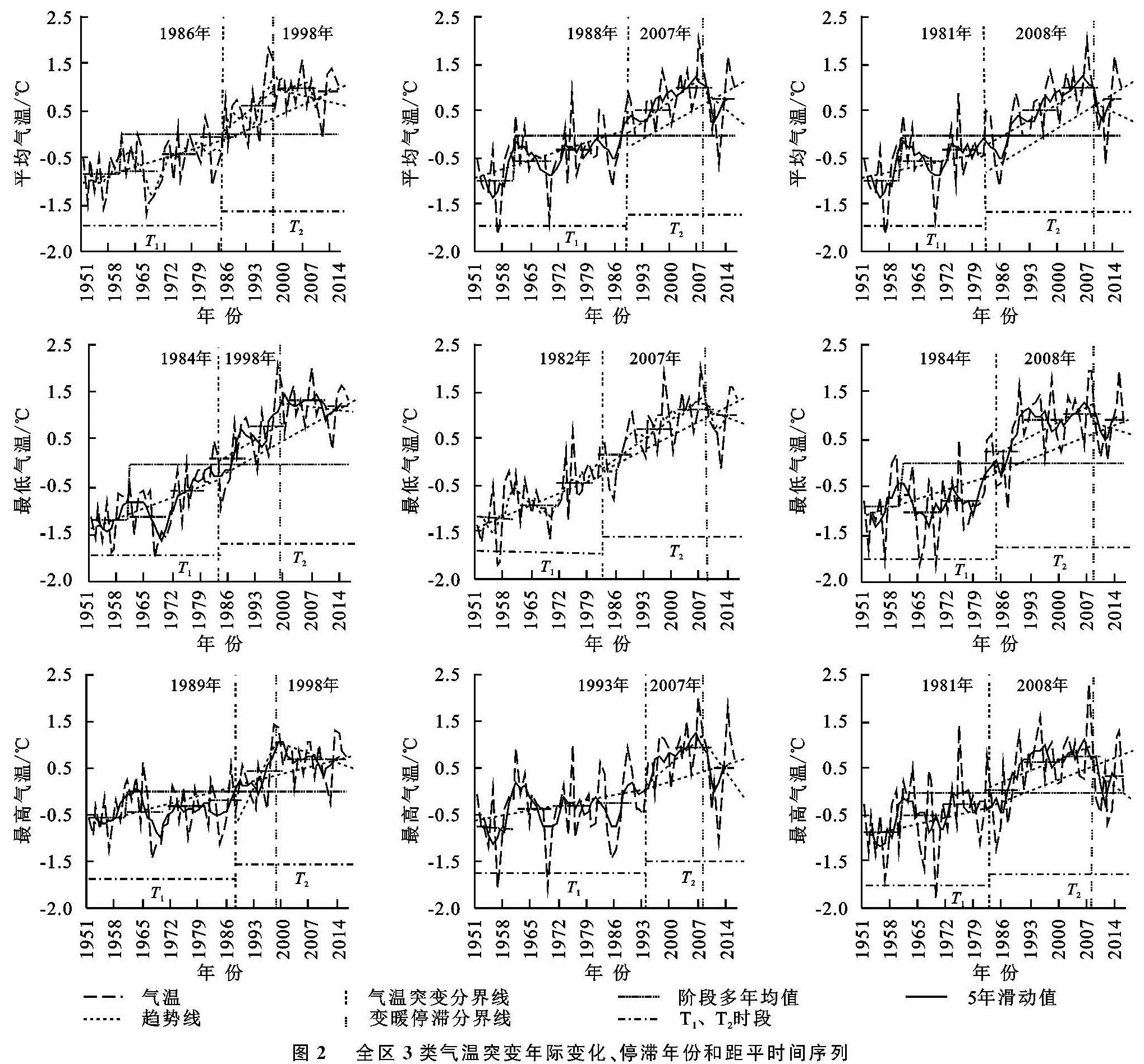
采用Mann-Kendall非参数统计法对全区3类气温进行突变年份分析,为叙述方便,将各分区3类气温1951年—突变年、突变年—2016年分别用T1,T2表示,3类气温的年平均值分别用:平均气温、最高气温、最低气温等简称表示(图2)。
整体上,全区3类气温突变时间普遍集中于1980s,其中中部区最高气温突变最晚(1993年)。同一分区,3类气温的突变时间较为接近,最低气温整体突变最早,平均气温次之,最高气温最晚; 同类气温,除中部区最低气温(1982年)外,中部区突变最晚(1982—1993年),西部区次之(1984—1989年),东部区最早(1981—1984年)。变异系数指离散程度大小,T1时段,除东部区最低气温外,全区最低气温整体升温最快,变化程度最剧烈; 平均气温升温速率次之,变化剧烈程度较弱; 最高气温升温速率最慢,变化剧烈程度最弱; 空间上,平均气温、最低气温升温速率均由西向东依次减小,最高气温与之规律相反,平均气温、最高气温变化剧烈程度自东向西依次减弱,最低气温则自西向东依次减弱。T2时段,除东部区最低气温外,其他区最低气温升温速率最快,平均气温次之,最高气温最慢,相应地,3类气温变化剧烈程度最低气温>平均气温>最高气温; 空间上,平均气温升温速率按东、西、中部依次减小,最高气温升温速率自东向西依次减小,平均气温、最高气温变化剧烈程度自东向西依次减弱,最低气温则由中部向西、东部区减小/减弱。
2.2 气温突变对第1类影响因子变化的响应
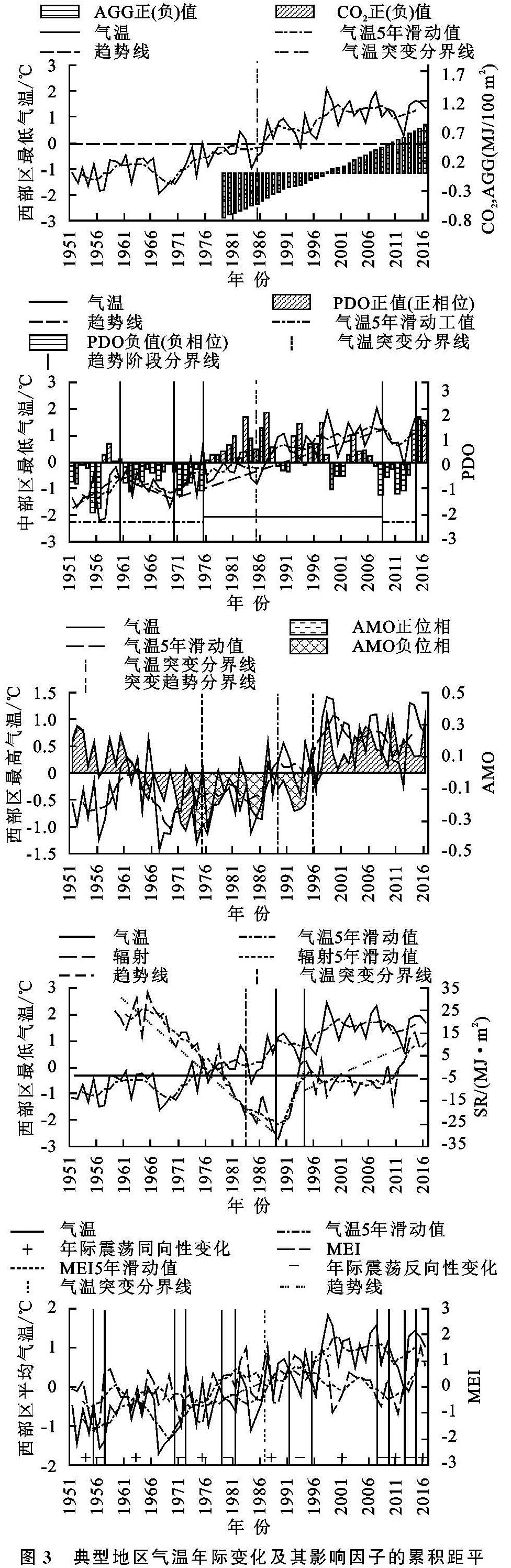
全区3类气温与AGG含(CO2)、PDO和AMO、太阳总辐射(SR)、MEI等(1951年—各分区3类气温突变年)的相关系数空间分布情况见表1,图3为代表性分区气温与AGG(含CO2),PDO,AMO,SR,MEI的累积距平年际序列变化情况,限于篇幅,以能代表普遍规律且相关性较好(p<0.05)的分区示例给出。
工业革命以来,人类活动不断排放CO2等温室气体,大气CO2福射强迫增加是造成全球变暖的主要原因[23]。由表1可知,全区最低气温与AGG,CO2相关性(0.782,0.714)最好,最高气温与AGG相关性(0.671,0.630)次之,平均气温与AGG相关性(0.623,0.685)相对较差; 空间上,除全区最低气温与二者和最高气温与CO2相关性外,其他类型气温与二者相关性均由西东、中部依次减弱。由图3可知,1979年以来AGG[0.234~0.391 W/(m2·10 a)]、CO2辐射强迫[0.258~0.308 W/(m2·10 a)]呈上升趋势,气温变化与之具有趋势同向性,并在AGG(含CO2)持续上升3~14 a后,全区3类气温发生突变。
太平洋年代际振荡(PDO)是北太平洋地区气候变化的一个主要模态,对于中国的气候变化起重要作用[24]。由表1可知,全区最低气温与PDO的相关性最好(0.301),平均气温(0.276)次之,最高气温(0.123)最差,除全区最高气温与PDO相关性外,中部其他类型气温与PDO相关性最好,西部次之,东部最差。由图3看出,1951—2016年PDO发生了3次明显的正负位相交替,全区3类气温也相应发生了明显的升降趋势转折变化,1951—1959年PDO由负位相转变为正位相时,3类气温呈上升趋势,1959—1969年PDO整体处于负位相,气温呈持续下降趋势,1969—2008年PDO由负位相转为正位相且持续上升6~18 a(0.482/10 a),3类气温呈持续上升趋势并普遍于该阶段发生突变。
图2 全区3类气温突变年际变化、停滞年份和距平时间序列
AMO指发生在北大西洋区域空间上具有海盆尺度,时间上具有多年尺度的海表温度准周期性暖冷异常变化,在欧亚大陆的表面气温及全球其他区域气候演变中发挥了重要作用[25]。由表1可知,除中部3类气温外,其他分区最高气温与AMO相关性最好(0.354),平均气温(0.324)次之,最低气温(0.278)最差; 除最低气温与AMO的相关性外,最低气温、最高气温均与AMO的相关性均由自西向东部依次减弱。由图3可知,全区气温与AMO逐年变化具有相似性,AMO分别在1963年与1995年发生了两次明显的正负位相交替,在1951—1974年呈下降趋势(-0.24/10 a),1974—1998年AMO处于负位相且持续上升(0.143/10 a)7~19 a时,3类气温发生突变。
太阳辐射(SR)是指太阳以电磁波的形式向外传递能量,太阳向宇宙空间发射的电磁波和粒子流。由表1可知,全区3类气温与SR均呈负相关关系,全区最低气温与SR的相关性(-0.453)>平均气温(-0.308)>最高气温(-0.225); 空间上,除全区平均气温与SR的相关性由西向东依次减弱,最高气温、最低气温与SR的相关性均由西部向东、中部依次减弱。由图3来看,1959—1989年太阳总辐射呈快速下降趋势[-19.54 MJ/(m2·10 a)],气温与其具有趋势反向性,在此阶段3类气温普遍发生突变; 1989—1994年太阳总辐射急剧上升[7.50 MJ/(m2·10 a)],气温随之快速下降。
MEI基于热带太平洋上的海平面气压、地面纬向风、地面经向风、海表温度、海面气温和总云量6个要素综合地监测、诊断和判别厄尔尼诺(ENSO)事件的发生[31]。由表1可知,除中部3类气温外,西、东部平均气温与MEI相关性(0.345,0.201)>最高气温(0.305,0.198)>最低气温(0.246,0.123); 空间上,西部3类气温与MEI的相关性均最好,除平均气温外,其他类型气温均中部与MEI的相关性次之,东部最差。从图3上看,MEI整体呈上升趋势,全区3类气温与其变化趋势一致,且逐年变化以年际振荡同向性为主,但其间存在年际震荡反向性阶段(持续2~5 a)。在1976—1997年MEI呈持续快速上升(0.541/10 a)趋势,平均气温、最低气温、最高气温于该时段陆续发生突变。
表1 全区3类气温与第1类影响因子相关性的空间分布
综上,AGG(含CO2)呈线性上升,气温变化与其具有趋势同向性,气温突变与AMO持续上升的时间具有一致性,且对PDO处于正位相且持续上升响应之间存在滞后现象,与太阳总辐射快速下降、MEI快上升趋势时间一致; 与MEI存在年际振荡同向性/反向性周期交替变化。
2.3 气温突变对第2类影响因子变化的响应
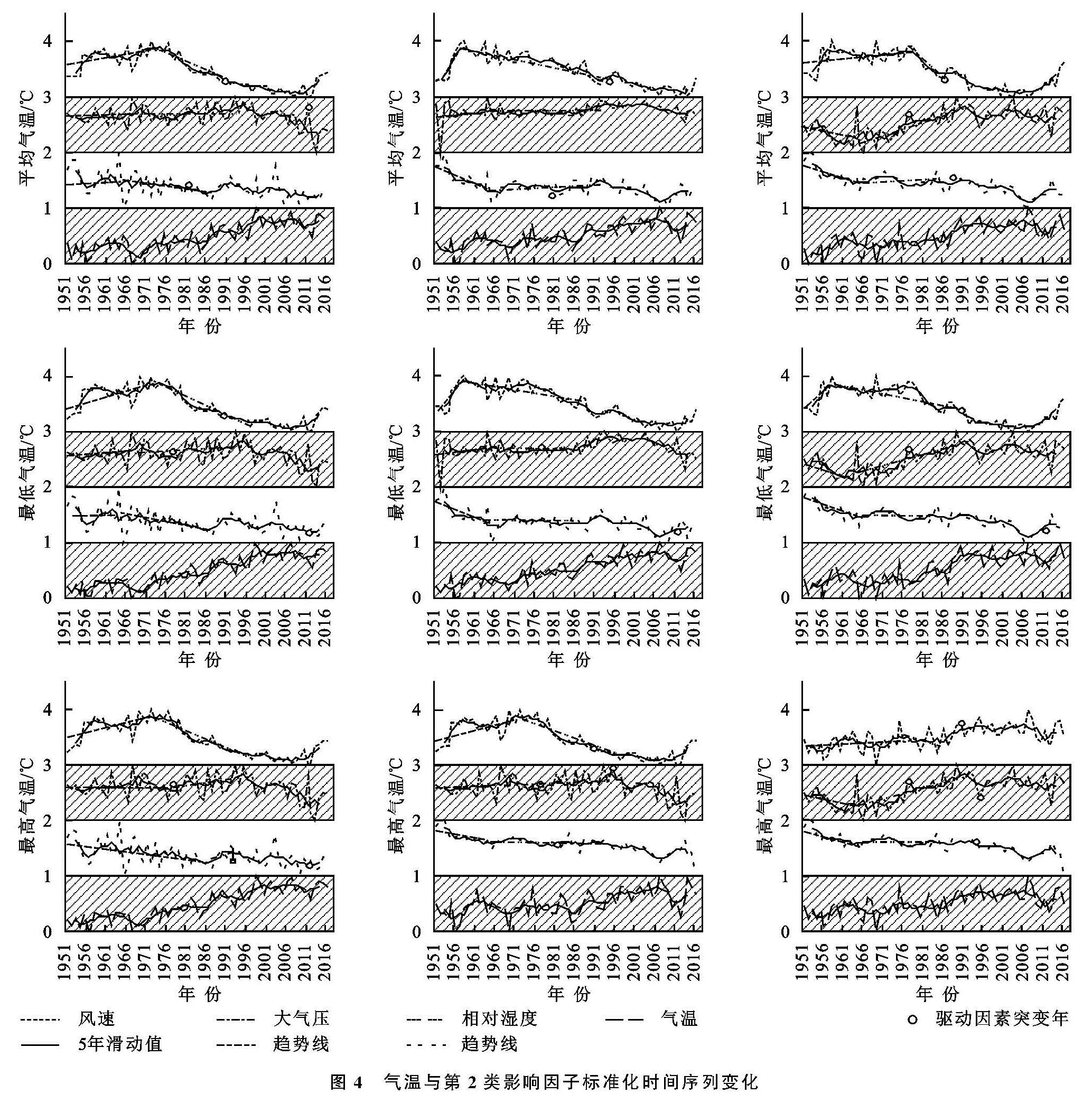
图4为气温与第2类影响因子标准化时间序列变化示意图,详细方法见
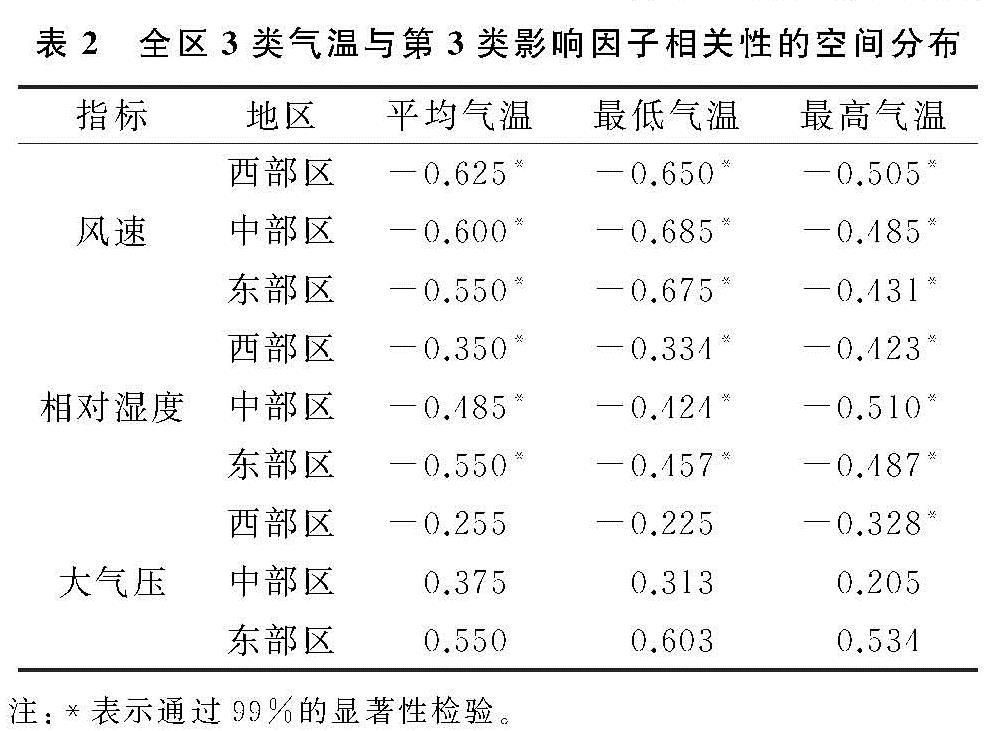
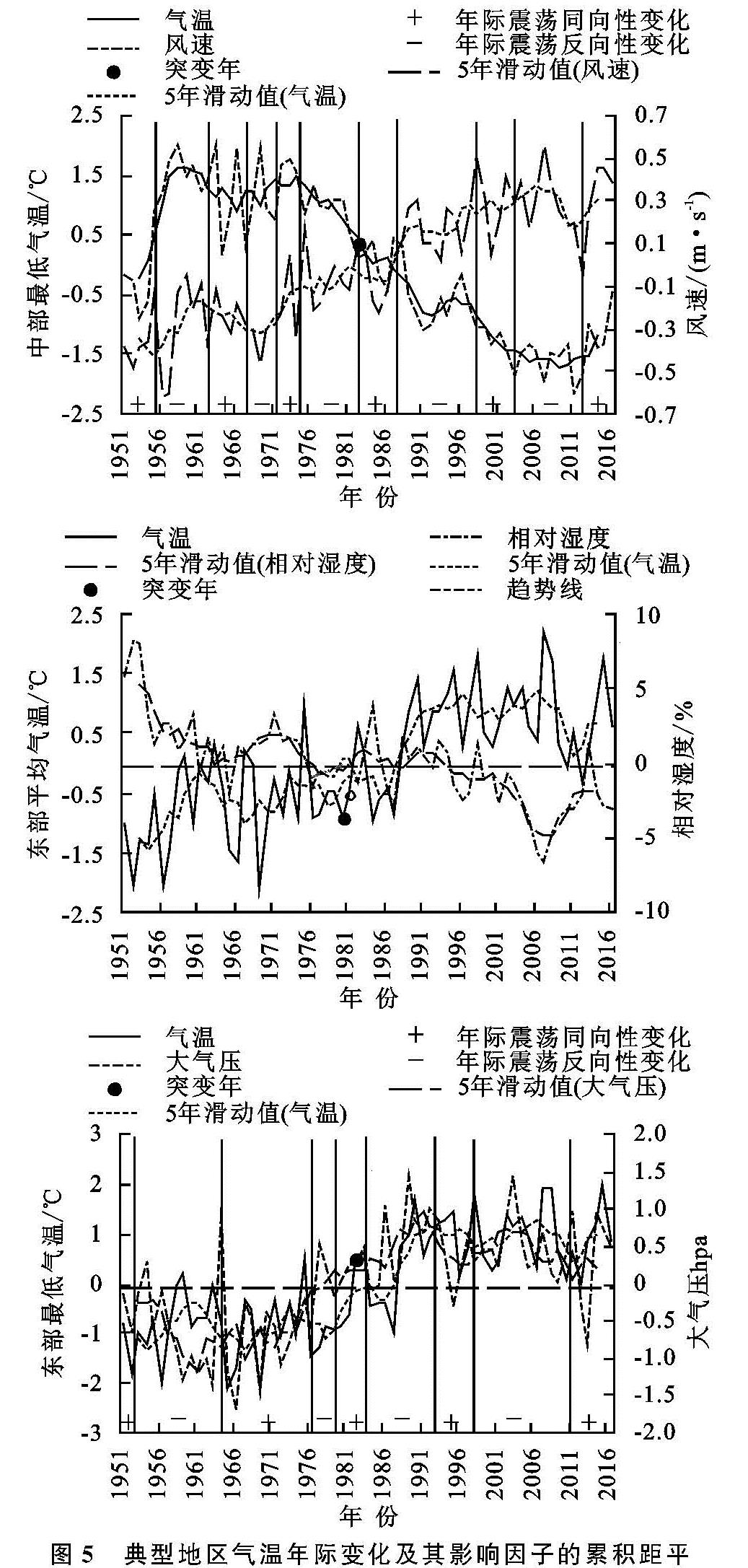
参考文献[31]。影响因子可能发生突变更早,且在气温突变后仍在一定阶段内保持这种趋势。全区3类气温与第2类影响因子的相关性空间分布见表2,气温及其影响因子累积距平的年际变化见图5,限于篇幅,以能代表普遍规律且相关性较好并通过99%显著性检验的分区示例给出。
由图4及图5可以看出,全区3类气温与风速存在5~20 a左右的年际振荡同向性/反向性交替周期性的变化。由表2可知,平均气温、最低气温、最高气温突变前与全区风速均呈极显著负相关关系,平均气温、最高气温与风速的相关性由东向西依次变好,
最低气温则由中部分别向东、西方向变差,最低气温与风速相关性整体(-0.685)>平均气温(-0.625)>最高气温(-0.505)。总得来说,气温上升与风速减小存在密切关系,风速在1951—1960年左右(1959—1977年)普遍呈持续上升趋势[0.01~1.16 m/(s·10 a)],其后至1986年左右(1981—1993年)为下降趋势(1981—1993年为全区各类气温突变时间范围,风速在此之后至2008年左右仍呈下降趋势,以下类似表述思路同此。由图4可知当风速持续下降3~28 a,11~25 a,6~21 a,倾向率达到-0.53~-0.24 m/(s·10 a),-0.25~-0.24 m/(s·10 a),-0.39~-0.30 m/(s·10 a)时,平均气温、最低气温、最高气温分别发生突变。
由图4及图5可知,全区平均气温、最低气温、最高气温与相对湿度整体具有年际振荡反向性关系。由表2可知,全区3类气温与相对湿度均呈极显著负相关关系,除东部外,其他分区均最高气温与相对湿度相关性最好,平均气温次之,最低气温最差; 最高气温与相对湿度相关性中、东、西部依次减弱,其他气温与其相关性则均为东部(-0.334~-0.350)>中部(-0.424~-0.485)>西部(-0.457~-0.550)。整体上看,气温上升与相对湿度减小关系密切,且二者趋势峰(谷)值整体对应关系较好; 相对湿度在1951—1966年左右(1964—1988年)普遍呈下降趋势(-0.34~-0.56%/10 a),西部平均气温、西部最低气温与之相反; 其后至1986年左右(1981—1993年),全区相对湿度普遍呈下降趋势(-0.18~-0.11%/10 a),中部平均气温、西部最高气温与之相反。由图4可知当相对湿度持续下降16~22 a,16~20 a,11~29 a,倾向率达到-0.12~-0.11%/10 a,-0.14~-0.11%/10 a,-0.13~-0.12%/10 a时,3类气温发生突变。
由图4及图5可知,气温与大气压存在年际振荡同向性/反向性交替周期变化(3~20 a)。除最高气温外,其他气温与大气压相关性自西向东依次增强; 西部最高气温与大气压相关性最好(-0.328),平均气温次之(-0.255),最低气温(-0.225)最差; 中部平均气温与大气压相关性最好(0.375),最低气温次之(0.313),最高气温较差(0.205); 东部最低气温与大气压相关性最好(0.603),平均气温次之(0.550),最高气温较差(0.534)。整体上看,除西部最高气温外,西、中部大气压在1951—1968年左右(1965—1978年)普遍呈持续上升趋势(0.12~0.24 hPa/10 a),东部在1951—1966年普遍呈下降趋势(-0.35~-0.42 hPa/10 a); 其后至1986年左右(1981—1993年)大气压持续增加。由图4可知当大气压持续增加17~24 a,17~20 a,17~25 a,倾向率达到0.10~0.17 hPa/10 a,0.11~0.42 hPa/10 a,0.11~0.42 hPa/10 a时,3类气温发生突变。
整体上看,1980s~1990s,随AGG(含CO2)持续增大、AMO持续上升、PDO处于正位相阶段且呈上升趋势、太阳总辐射快速下降、MEI快速上升、全区风速和相对湿度持续下降、大气压持续上升,全区气温发生突变,突变是各影响因子共同作用的结果。