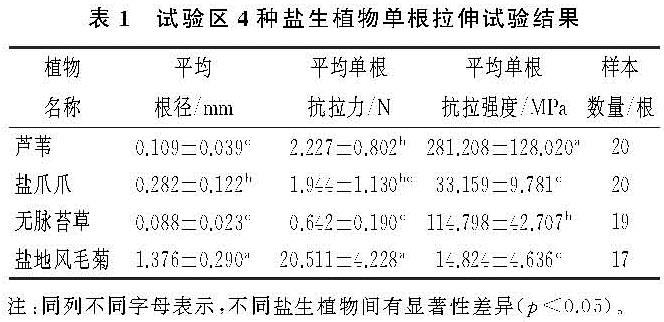
3.1 单根抗拉力和抗拉强度与根径之间的关系
由表1所示可知,区内4种盐生植物平均根径由大至小依次为盐地风毛菊(1.376 mm)、盐爪爪(0.282 mm)、芦苇(0.109 mm)、无脉苔草(0.088 mm),盐地风毛菊平均根径显著大于其他3种盐生植物(p<0.05),盐爪爪平均根径显著大于芦苇和无脉苔草(p<0.05),而无脉苔草和芦苇未表现出显著性差异。4种盐生植物平均单根抗拉力由大至小依次为盐地风毛菊(20.511 N)、芦苇(2.227 N)、盐爪爪(1.944 N)、无脉苔草(0.642 N); 其中,盐地风毛菊平均单根抗拉力显著高于其他3种(p<0.05),即分别为芦苇、盐爪爪、无脉苔草平均单根抗拉力的9.210,10.550,37.843倍。芦苇单根其平均抗拉力显著高于苔草(p<0.05),盐爪爪与无脉苔草之间无明显差异。区内4种盐生植物其平均单根抗拉强度由大至小依次为芦苇(281.208 MPa)、无脉苔草(114.798 MPa)、盐爪爪(33.159 MPa)、盐地风毛菊(14.824 MPa),其中,芦苇单根抗拉强度为无脉苔草2.45倍,盐爪爪8.48倍,盐地风毛菊18.97倍,芦苇单根抗拉强度与盐爪爪、无脉苔草、盐地风毛菊之间的差异显著(p<0.05),无脉苔草的平均单根抗拉强度显著大于盐爪爪与盐地风毛菊(p<0.05),而盐爪爪与盐地风毛菊之间未表现出显著性差异。
相应地,由图1可知区内4种盐生植物单根抗拉力随根径增加而增大,且单根抗拉力与根径符合指数函数关系。由图2所示可知,4种盐生植物单根抗拉强度随根径增大而减小,且单根抗拉强度与根径之间符合幂函数关系; 其中以盐爪爪为例,盐爪爪根径在0.35~0.6 mm比0.13~0.35 mm时单根抗拉力随根径增大的速率更大,同时其单根抗拉强度随着根径的增大其减小速率更缓慢,因此盐爪爪根径在0.35 mm时单根抗拉力学特性表现相对较好。该试验结果与刘昌义等[25]对西宁盆地细茎冰草(Agropyron trachycaulum)、霸王(Zygophyllum xanthoxylon)、白刺(Nitraria tangutorum)等5种草本和灌木根系单根拉伸试验结果,以及与李可等[26]对柠条锦鸡儿(Caragana korshinskii)和草地早熟禾(Poa pratensis)根系单根拉伸试验结果相一致。
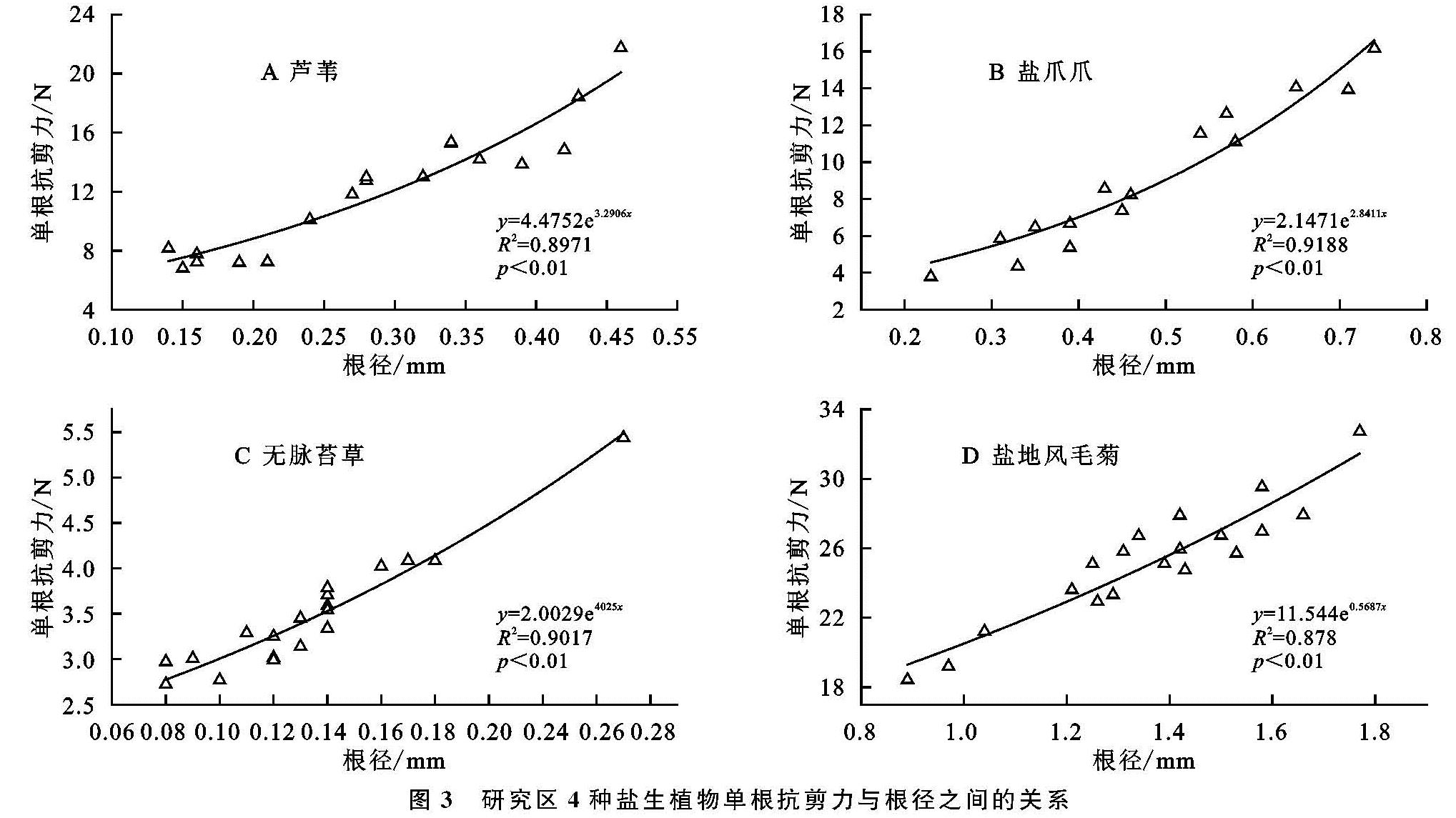
3.2 单根抗剪力、抗剪强度与根径之间的关系
由表2所示可知,区内4种盐生植物平均根径由大至小依次为盐地风毛菊(1.360 mm)、盐爪爪(0.475 mm)、芦苇(0.286 mm)、无脉苔草(0.132 mm),盐地风毛菊平均根径显著大于无脉苔草、盐爪爪、芦苇(p<0.05),盐爪爪平均根径显著大于芦苇和无脉苔草(p<0.05),而芦苇的平均根径显著大于无脉苔草(p<0.05)。4种盐生植物平均单根抗剪力由大至小依次为盐地风毛菊(25.243 N)、芦苇(12.035 N)、盐爪爪(9.073 N)、无脉苔草(3.484 N),其表现出的变化规律与平均单根抗拉力相一致。其中,盐地风毛菊的平均单根抗剪力显著大于其他3种盐生植物(p<0.05),芦苇的平均单根抗剪力显著大于盐爪爪和无脉苔草(p<0.05),盐爪爪显著大于无脉苔草(p<0.05)。进一步研究表明,同种盐生植物之间其单根抗剪力均大于单根抗拉力,表现在盐地风毛菊、芦苇、盐爪爪、无脉苔草单根抗剪力较抗拉力其增长幅度分别是23.0%,440.4%,367.7%,442.6%。
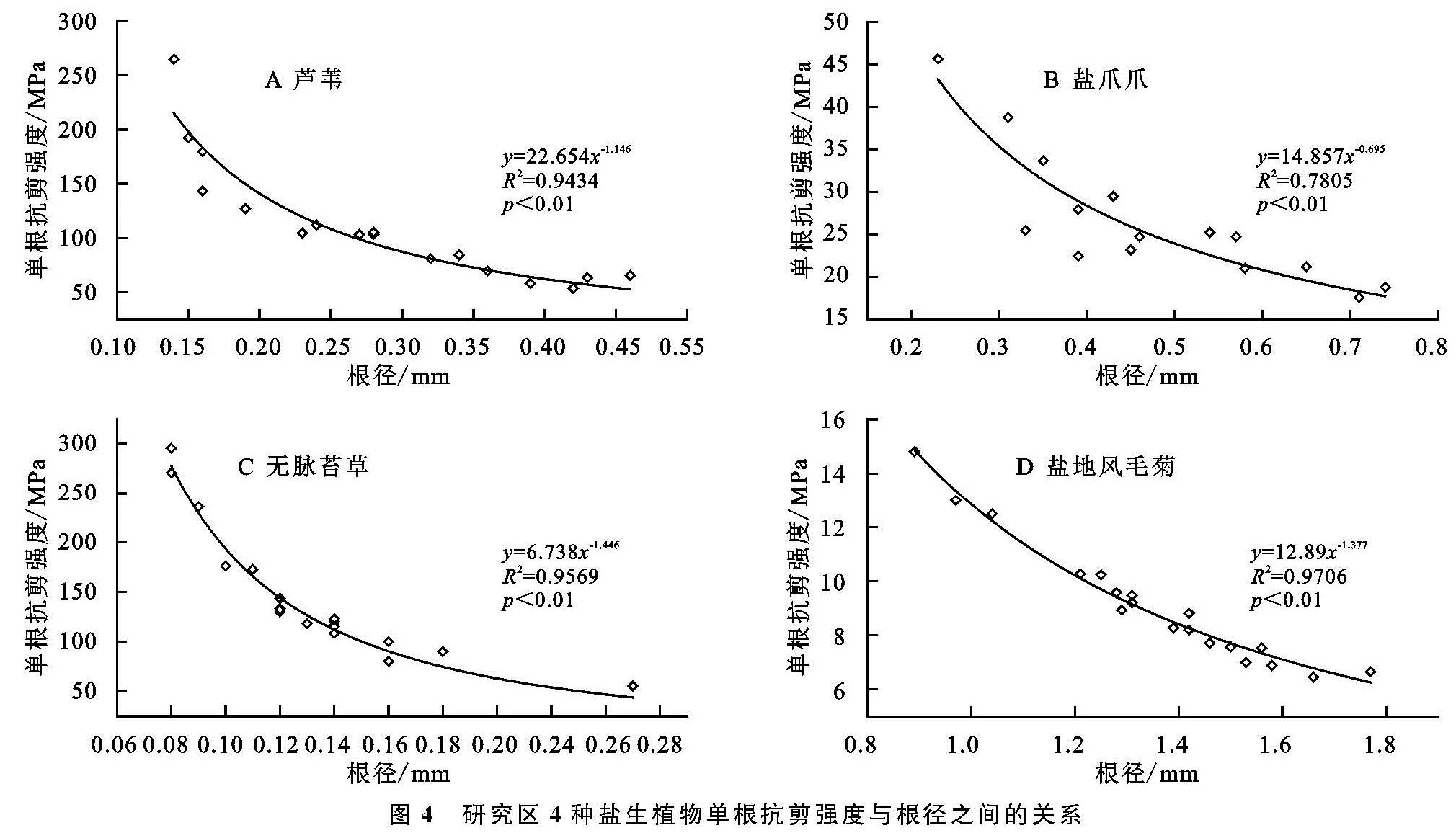
区内4种盐生植物其平均单根抗剪强度由大至小依次为无脉苔草(157.428 MPa)、芦苇(110.836 MPa)、盐爪爪(26.657 MPa)、盐地风毛菊(9.105 MPa),无脉苔草平均单根抗剪强度与芦苇、盐爪爪、盐地风毛菊间存在显著性差异(p<0.05),芦苇的平均单根抗剪强度显著大于盐爪爪和盐地风毛菊(p<0.05),而盐爪爪与盐地风毛菊之间无明显差异。其中,无脉苔草其抗剪强度为芦苇1.42倍、盐爪爪5.91倍、盐地风毛菊17.29倍; 此外,由图3所示还可知,区内4种盐生植物其单根抗剪力随根径增加而增大,且单根抗剪力与根径符合指数函数关系。另外,由图4所示可知,4种盐生植物其单根抗剪强度随根径增大而减小,且单根抗剪强度与根径之间符合幂函数关系; 其中以芦苇为例,芦苇根径在0.30~0.45 mm较0.15~0.30 mm时单根抗剪力随根径增大的速率更大,同时其单根抗剪强度随着根径的增大其减小速率更缓慢,因此芦苇根径在0.30 mm时单根抗剪力学性能相对较好。该结果与贺振昭等[27]对青海湖地区赖草(Leymus secalinus Tzvel)、紫花针茅(Stipa purpurea Griseb)等7种植物根系单根剪切试验结果,以及与李成凯等[28]对西宁盆地披碱草(Elymus dahuricus)、细茎冰草(Agropyron trachycaulum)、赖草(Leymus secalinus)等4种植物根系单根剪切试验结果相一致。
图1 研究区4种盐生植物单根抗拉力与根径之间的关系
图2 研究区4种盐生植物单根抗拉强度与根径之间的关系
3.3 根-土复合体试样中的根系特性
本项研究中,盐地风毛菊、芦苇、盐爪爪3种盐生植物根系多呈近似垂直分布,而无脉苔草根系则相对较细,且多在土体中呈水平或倾斜分布。区内4种盐生植物根—土复合体试样中含根数、含根量、根系质量计算结果见表3。待室内完成根—土复合体直剪试验后即对剪切后试样进行冲洗,从根—土复合体试样中清洗出分布于其中的根系,然后将洗净的根系晾干至根系表面未见水滴时,便对根径、根系鲜重、根数、含根量等指标进行统计[17]。
图3 研究区4种盐生植物单根抗剪力与根径之间的关系
图4 研究区4种盐生植物单根抗剪强度与根径之间的关系
表3 试验区4种盐生植物复合体中鲜根质量、含根量及含根数计算结果
由表3所示可知,区内4种盐生植物根—土复合体在地表以下0—10 cm深度处(即上层),土体含根量均大于10—20 cm处(即下层),4种盐生植物芦苇、盐爪爪、无脉苔草、盐地风毛菊其根—土复合体其上层含根量分别为0.016 g/cm3,0.007 g/cm3,0.063 g/cm3,0.005 g/cm3,下层含根量分别为0.010 g/cm3,0.003 g/cm3,0.011 g/cm3,0.001 g/cm3; 进一步研究表明,含根量由上层至下层其降低幅度分别为38%,57%,83%,80%,其中,无脉苔草试样由上层至下层含根量降低幅度是相对最大的,即分别为芦苇复合体试样降低幅度的2.20倍,盐爪爪试样降低幅度的1.44倍,盐地风毛菊试样降低幅度的1.03倍。
3.4 不同取样深度根-土复合体抗剪强度特征
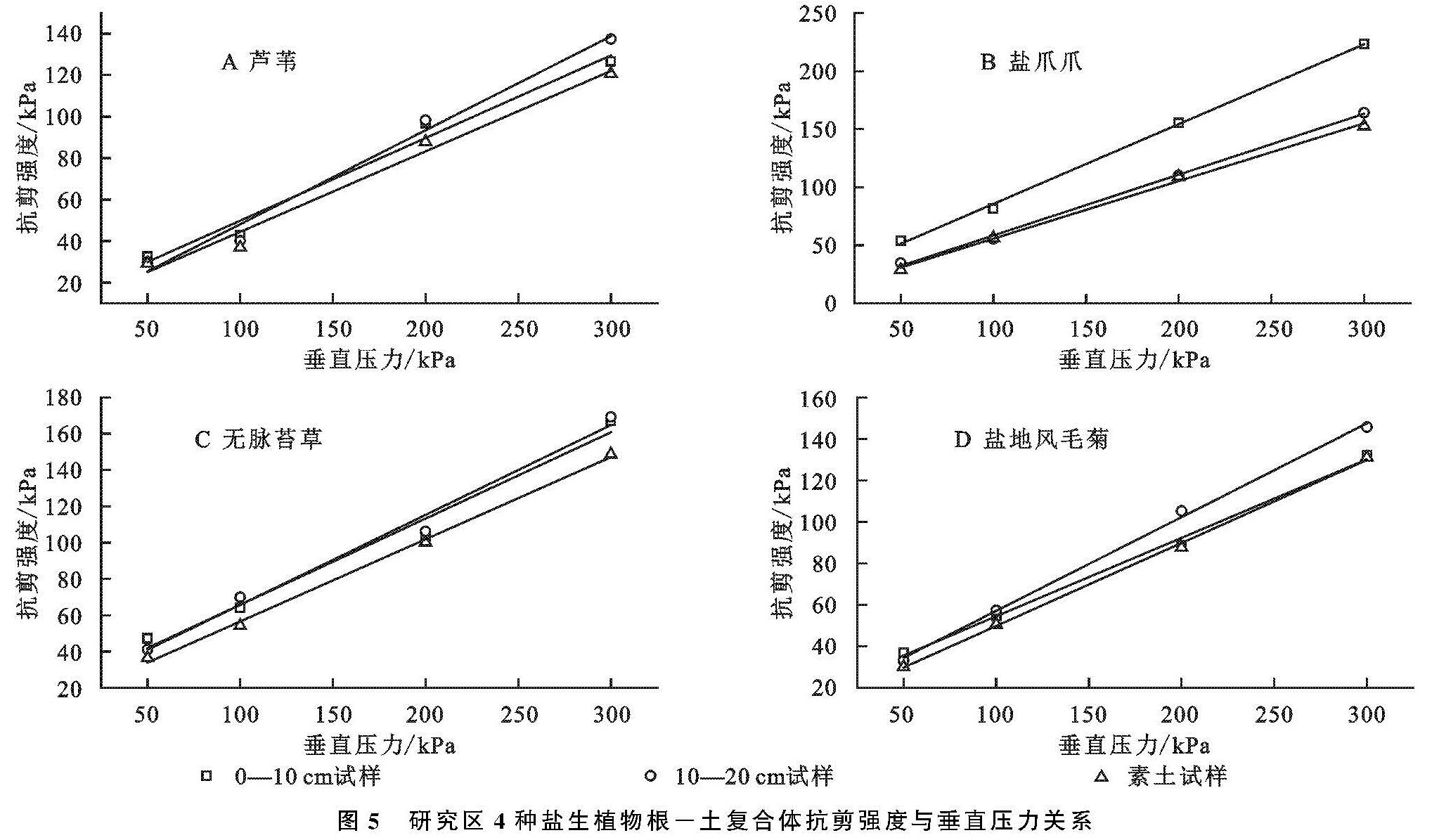
区内4种盐生植物根—土复合体原状试样和素土试样抗剪强度与垂直压力关系见图5。由该图可知,4种盐生植物根—土复合体及素土抗剪强度与垂直压力间呈线性相关关系,表现在随着垂直压力的增加,土体抗剪强度亦随之增强,这与摩尔—库伦准则相一致。此外,由该图还可知,区内4种植物根—土复合体抗剪强度与垂直压力关系曲线位于素土抗剪强度与垂直压力关系曲线上方,说明在四级垂直荷载作用下,素土抗剪强度均显著低于根—土复合体,其中芦苇、盐爪爪、无脉苔草、盐地风毛菊在地表以下0—10 cm深度处,其根—土复合体平均抗剪强度分别为75.675 kPa,128.575 kPa,95.450 kPa,78.150 kPa,地表10—20 cm深度处4种植物复合体平均抗剪强度分别为76.450 kPa,91.200 kPa,96.700 kPa,85.375 kPa。相应地,与4种盐生植物所对应的素土试样平均抗剪强度为69.650 kPa,86.725 kPa,84.875 kPa,74.850 kPa,与复合体试样相比较,素土抗剪强度降低幅度分别为8.9%,5.9%,12.2%,12.3%。
在地表以下0—10 cm,10—20 cm深度处,4种盐生植物根—土复合体平均抗剪强度均显著大于所对应素土,其主要原因是在0—10 cm深度处复合体含根量大于10—20 cm深度处,同时,反映出区内4种盐生植物根系对土体具有显著加筋作用,进而使得土体抗剪强度得到显著性提高[30]。本项研究,通过对比区内4种盐生植物根—土复合体与素土试样的抗剪强度可知,盐爪爪根—土复合体、无脉苔草根—土复合体抗剪切能力相对较强,表现在盐爪爪、无脉苔草其根—土复合体较芦苇、盐地风毛菊其抗剪强度平均增加幅度分别为44.4%,34.3%,25.3%,17.5%。
区内4种盐生植物在地表以下0—10 cm,10—20 cm深度处,其根—土复合体黏聚力c值与相应素土黏聚力c值对比结果见图6。芦苇、盐爪爪、无脉苔草、盐地风毛菊4种植物地表以下0—10 cm,10—20 cm深度处,其根—土复合体黏聚力值c分别为4.87~12.27 kPa,6.75~16.91 kPa,16.34~18.19 kPa,11.96~16.96 kPa,4种植物根—土复合体试样对应素土黏聚力c值分别为3.92 kPa,6.12 kPa,11.32 kPa,9.76 kPa; 以上4种盐生植物与素土相比,黏聚力c值增幅分别为24.2%~213.0%,9.9%~176.3%,44.3%~60.7%,22.5%~71.0%。4种盐生植物根—土复合体试样黏聚力c值随着取样深度增加而逐渐降低,尤其是地表以下0—10 cm处根—土复合体与素土之间的黏聚力c值存在较大的差值,即分别为8.35 kPa,10.79 kPa,6.87 kPa,6.93 kPa,黏聚力c值的减小幅度分别为60.3%,60.0%,10.1%,29.5%。在地表以下0—10 cm深度处4种植物根—土复合体黏聚力c值相对较大,反映出区内植物根系在表层以下0—10 cm深度其所具有的浅层加筋作用相对更为显著。
3.5 相同取样深度根-土复合体抗剪强度特征
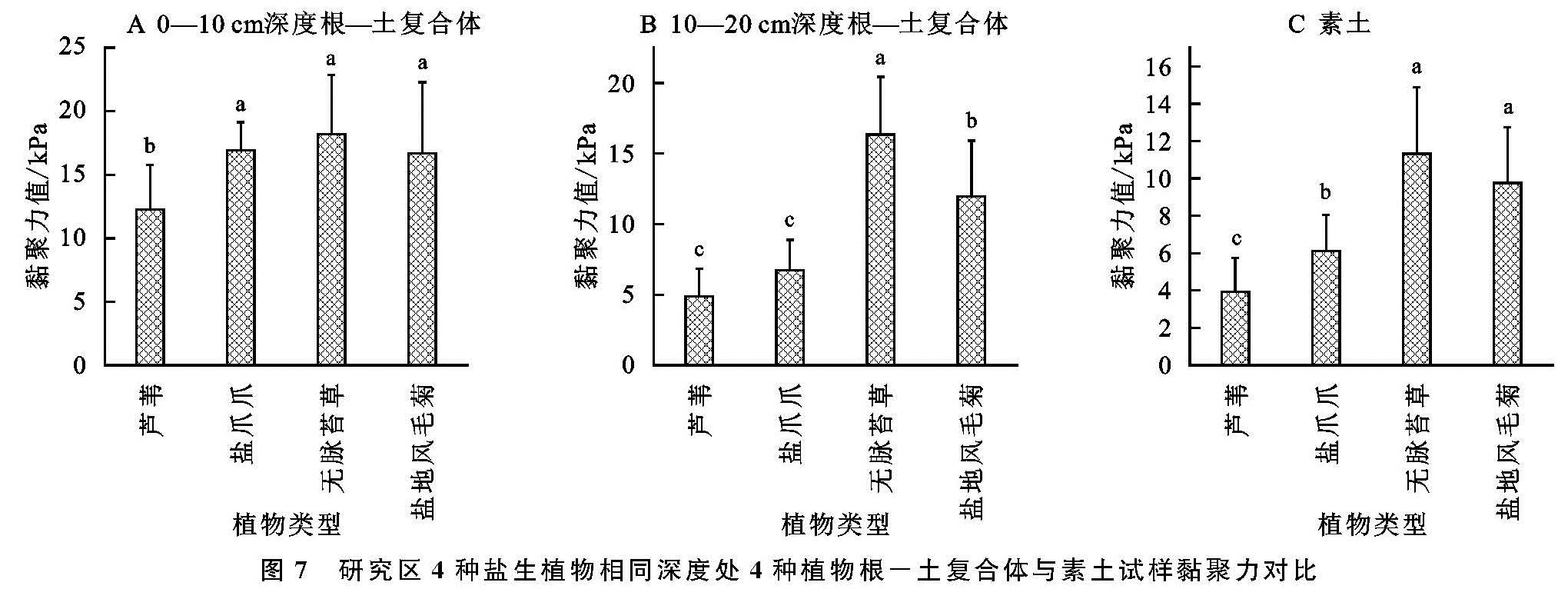
研究区4种盐生植物根—土复合体试样在相同位置处(地表以下0—10 cm,10—20 cm深度处)黏聚力c值对比结果见图7,由该图所示可知,位于地表以下0—10 cm深度处,4种植物根—土复合体黏聚力c值为12.27~18.19 kPa,与素土相比复合体黏聚力c值增幅为60.7%~213%,平均增幅为130.2%,黏聚力c值由大至小依次为无脉苔草、盐爪爪、盐地风毛菊、芦苇。相应地,在地表以下10—20 cm深度处,4种植物根—土复合体黏聚力c值为4.87~16.34 kPa,与素土相比黏聚力c值增幅为9.9%~44.3%,平均增幅为25.2%,黏聚力c值由大至小依次为无脉苔草、盐地风毛菊、盐爪爪、芦苇。由以上分析结果可知,区内在地表以下10—20 cm深度处4种植物根—土复合体黏聚力c值明显小于0—10 cm处,且4种植物根—土复合体在地表以下10—20 cm深度处黏聚力c值,略高于素土的黏聚力c值,这表明区内4种植物根—土复合体愈接近表层位置处,其黏聚力c值表现出愈大的规律,这主要归因于植物根系在表层位置处含根量相对较多,即表现在地表以下10—20 cm深度处,4种盐生植物含根量较0—10 cm处降低38%,57%,83%,80%。
图5 研究区4种盐生植物根-土复合体抗剪强度与垂直压力关系
图6 研究区2种不同深度4种盐生植物根-土复合体和素土黏聚力与深度之间的变化关系
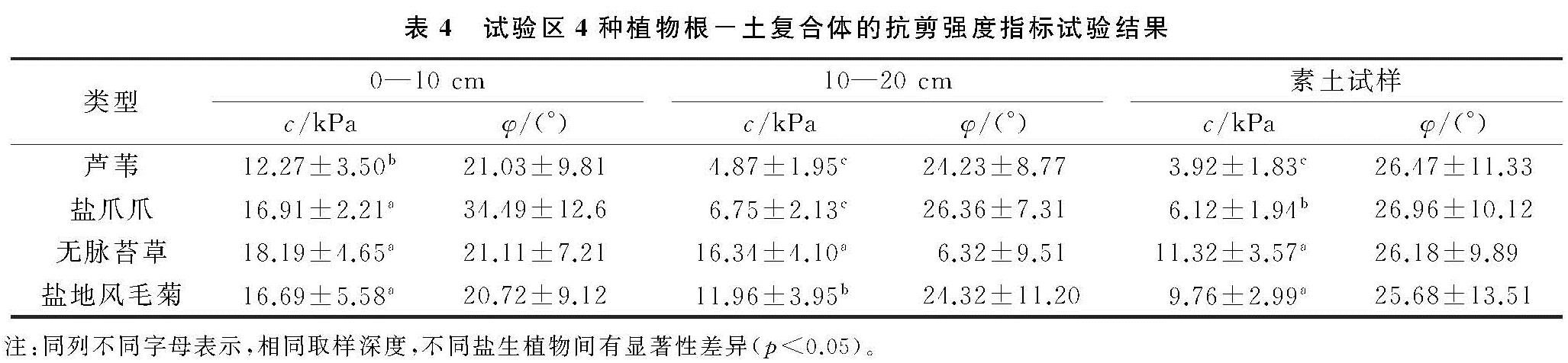
区内4种植物根—土复合体抗剪强度指标与取样深度之间变化关系见表4。由该表可知,随着4种植物根—土复合体取样深度增加,4种植物根—土复合体黏聚力c值呈逐渐降低的变化趋势,例如芦苇根—土复合体随着取样深度由地表以下0—10 cm增加至10—20 cm深度处时,其黏聚力c值则由12.27 kPa降低为4.87 kPa,降低幅度为60.3%; 相类似地,对于其他3种植物的黏聚力c值亦呈现出上述相类似的变化规律。另外,在地表以下0—10 cm深度处,无脉苔草和盐爪爪根—土复合体黏聚力c值显著大于盐地风毛菊和芦苇(p<0.05),盐地风毛菊和芦苇黏聚力c值相对较小,即4种草本无脉苔草、盐爪爪、盐地风毛菊和芦苇其黏聚力c值分别为18.19 kPa,16.91 kPa,16.69 kPa,12.27 kPa; 相应地,在地表以下10—20 cm深度处,无脉苔草的平均黏聚力c值显著大于盐地风毛菊、盐爪爪、芦苇(p<0.05),盐地风毛菊的平均黏聚力c值显著大于盐爪爪和芦苇(p<0.05),盐爪爪与芦苇未表现出显著性差异。
图7 研究区4种盐生植物相同深度处4种植物根-土复合体与素土试样黏聚力对比
试验区地表以下10~20 cm深度处,4种盐生植物其平均黏聚力c值分别为16.34 kPa,11.96 kPa,6.75 kPa,4.87 kPa。由区内4种盐生植物在地表以下2种深度位置处的复合体黏聚力值及变化规律可知,区内增强土体抗剪强度作用相对较为显著的植物种分别为无脉苔草、盐地风毛菊,其黏聚力平均值分别是17.25 kPa,14.46 kPa; 另外,区内4种盐生植物根—土复合体内摩擦角与采样深度之间则未表现出显著性关系,二者间的关系尚有待于进一步深入研究。
表4 试验区4种植物根-土复合体的抗剪强度指标试验结果
综合表1,表2和图6所示可知,区内4种盐生植物其平均单根抗拉力与平均抗剪力的变化规律基本相一致,但4种盐生植物根—土复合体黏聚力值的变化未体现出一致性的规律。其次,通过综合分析区内4种盐生植物其单根抗拉、抗剪强度,以及复合体抗剪强度指标黏聚力c值的大小可知,在4种盐生植物中,无脉苔草相对具有更为显著的固土护坡效果,其次为芦苇、盐爪爪,而盐地风毛菊相对不及前3种。