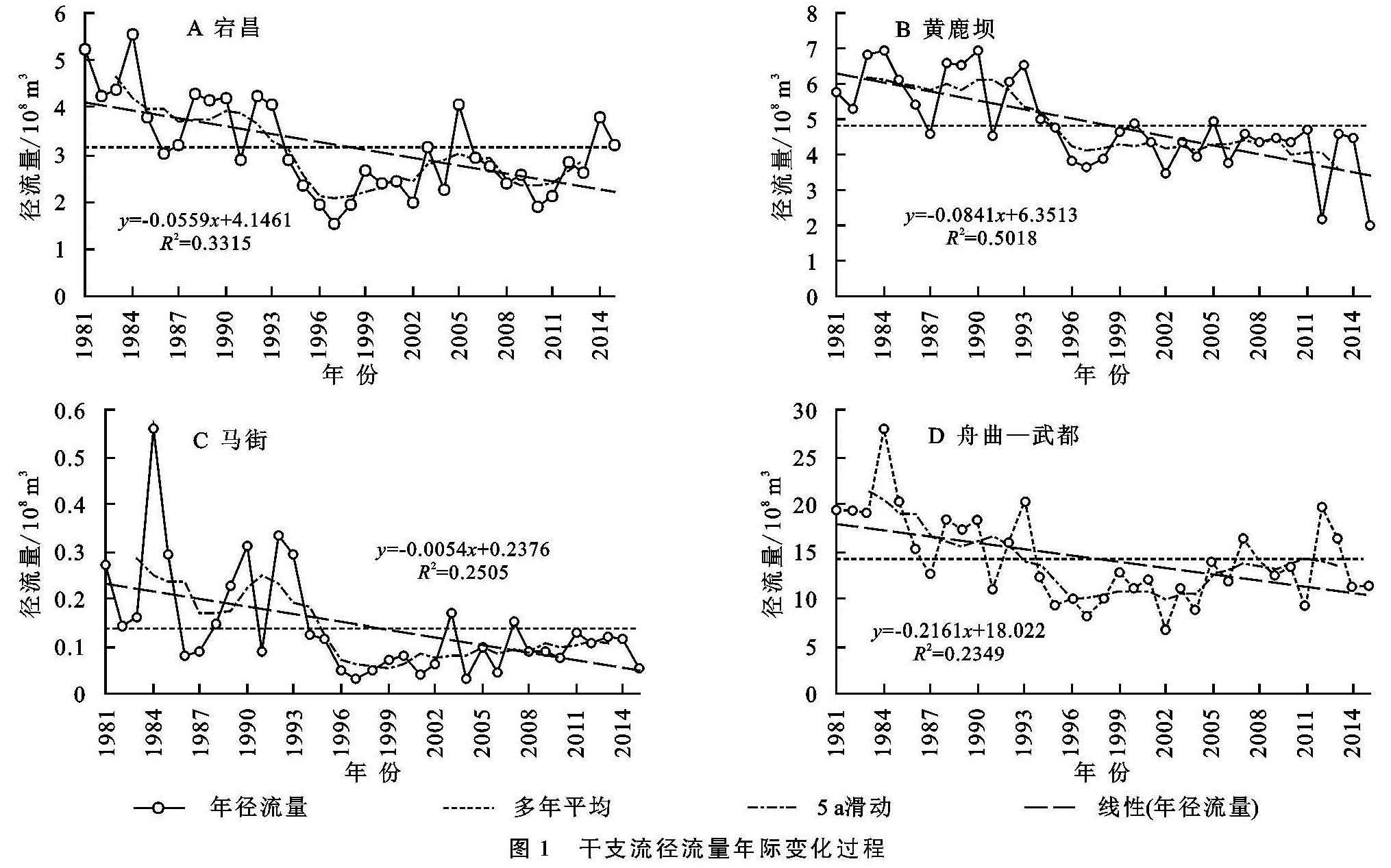
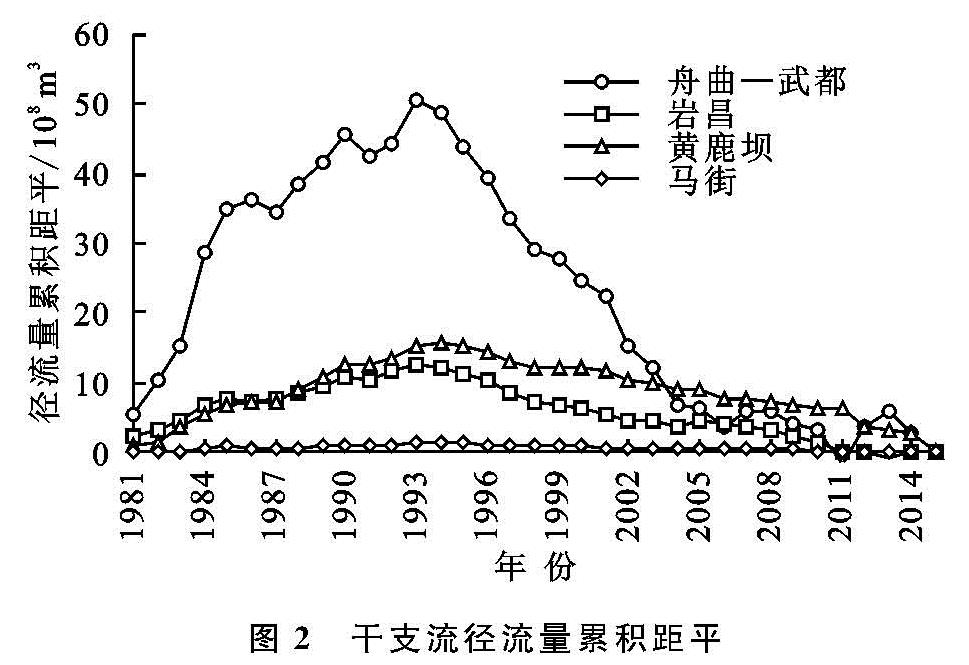
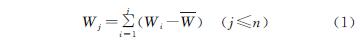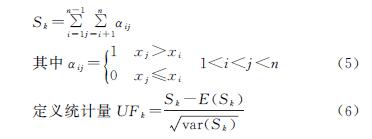3.1 干支流径流量年际变化及趋势
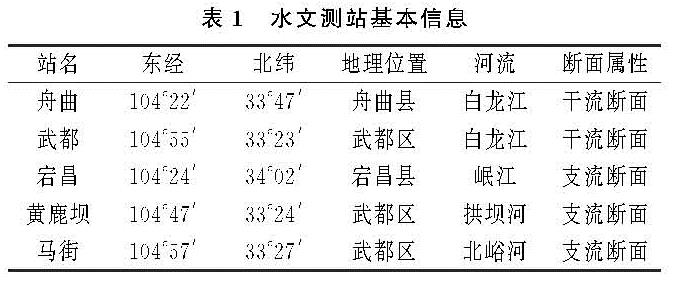
舟曲—武都区间白龙江干流多年平均径流量为14.13亿m3/a,该区间上的3条支流,岷江宕昌站、拱坝河黄鹿坝站、北峪河马街站多年平均径流量依次为3.14亿m3/a,4.84亿m3/a,0.14亿m3/a,干流区间入流6.01亿m3/a,占比分别为22.22%,34.22%,0.99%,42.56%,区间入流量最大,北峪河支流径流量最小,不足1%。径流量与不同站点的集水面积大小及气候条件、地形地貌有关,降雨量、集水面积、坡度越大,其径流量也相应越大。各站年径流量整体呈现下降趋势,其中1981—1993年径流量均值大于多年平均水平,为丰水期,1994—2015年径流量均值小于多年平均值,为枯水期,具体见图1; 各站累积距平曲线均呈现先上升后下降趋势,以1993年为分界点,1993年前高于多年均值,1993年后低于多年均值,具体见图2。各站径流量线性倾向变化率不同,舟曲—武都区间干流线性倾向变化率最大,为-2.16亿m3/10 a,35 a减少量达到7.56亿m3,其次黄鹿坝站为-0.84亿m3/10 a,宕昌站为-0.56亿m3/10 a,马街变化率最小,仅为-0.05亿m3/10 a,35 a减少量达到0.18亿m3。相比区间干流减少量,支流拱坝河占比38.89%,支流岷江占比25.93%,北峪河占比2%,区间入流占比32.8%,可见支流拱坝河和区间入流对于区间干流的变化有明显影响。白龙江流域自20世纪50年代以来,特别是90年代以来,由于气候变化和大肆砍伐森林等人类活动的影响,降雨量总体上呈现显著下降趋势,并且降水是白龙江流域径流的主要补给来源,舟曲—武都区间降雨量的显著减少趋势是导致径流显著性下降的主要原因,径流变化趋势与降雨量总体趋势相一致。
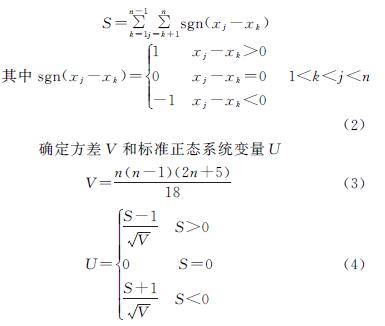
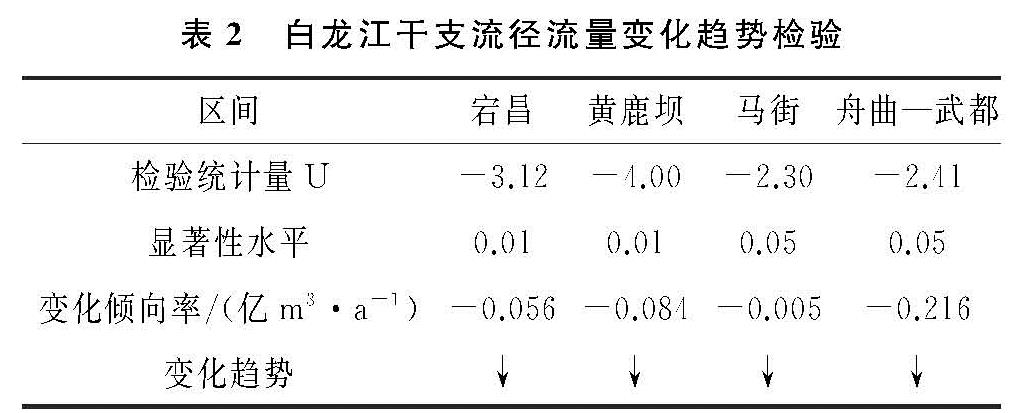
采用M-K法对各水文站的年径流系列进行趋势检验,将计算结果与显著性水平分别为0.1,0.05,0.01的置信区间临界值±1.28,±1.96,±2.58对比,可以看出宕昌、黄鹿坝检验统计量U均小于-2.58,达到了0.01的显著性水平,马街、舟曲—武都干流区间检验统计量U均小于-1.96,达到了0.05的显著性水平,且统计量U全部为负值,可见,年径流变化趋势呈现显著下降趋势,显著性水平均在0.05以上。对比图1中干支流径流量年际变化过程,计算结果与年际变化趋势一致。径流变化趋势检验结果见表2。
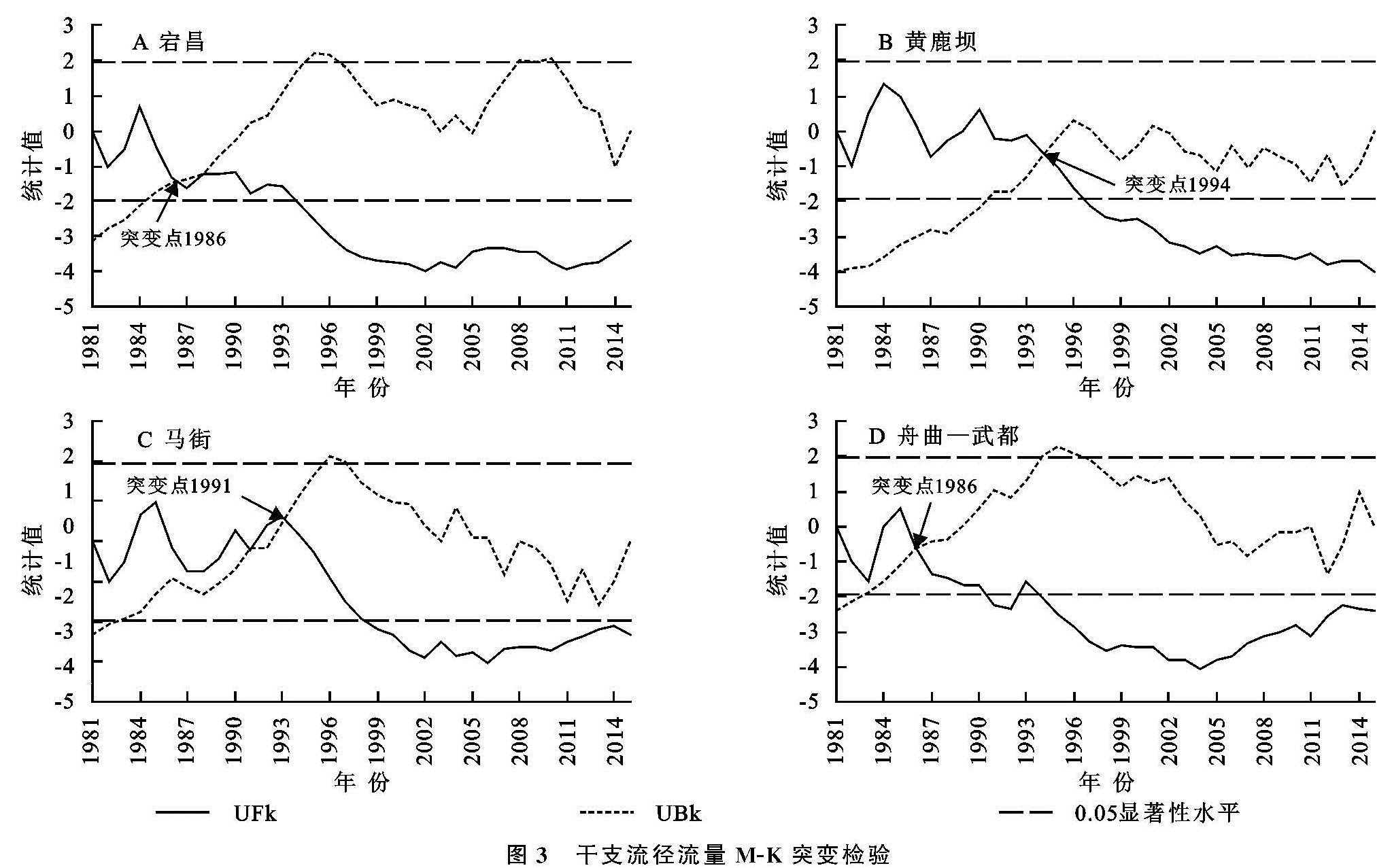
3.2 干支流径流量变化突变分析
白龙江支流岷江上的宕昌站统计量UFk除1984年外,均小于0,呈现下降趋势,与M-K趋势检验结果一致,显著性水平0.01,在95%的置信水平条件下,年径流突变的临界年份为1986年。支流拱坝河上黄鹿坝站UFk除1983—1986年、1990年大于0,呈现上升趋势,其他年份均小于0,为下降趋势,显著性水平0.01,突变年份为1994年。支流北峪河上马街站UFk除1984—1985年、1992—1994年大于0,呈现上升趋势,其他年份均小于0,为下降趋势,显著性水平0.05,突变年份为1991年。舟曲—武都区间白龙江干流UFk除1985外,其他年份均小于0,为下降趋势,显著性水平0.05,突变年份为1986年,具体见图3。径流突变主要源于降雨等气象因素存在显著的变化,径流突变的临界年份前后均值变化明显,径流的形成除受流域气候因素的影响,还与下垫面等因素密切相关。各支流具有空间异质性,地形地貌、气象、地质、植被等各方面存在差异,地势西北高东南低,为典型的高、中山峡谷区,气候分布不均匀,自西北向东南由亚热带湿润气候过渡到高寒湿润气候,降水自上游至中游逐渐减小,多方面因素共同作用造成各支流突变年份并不完全一致。
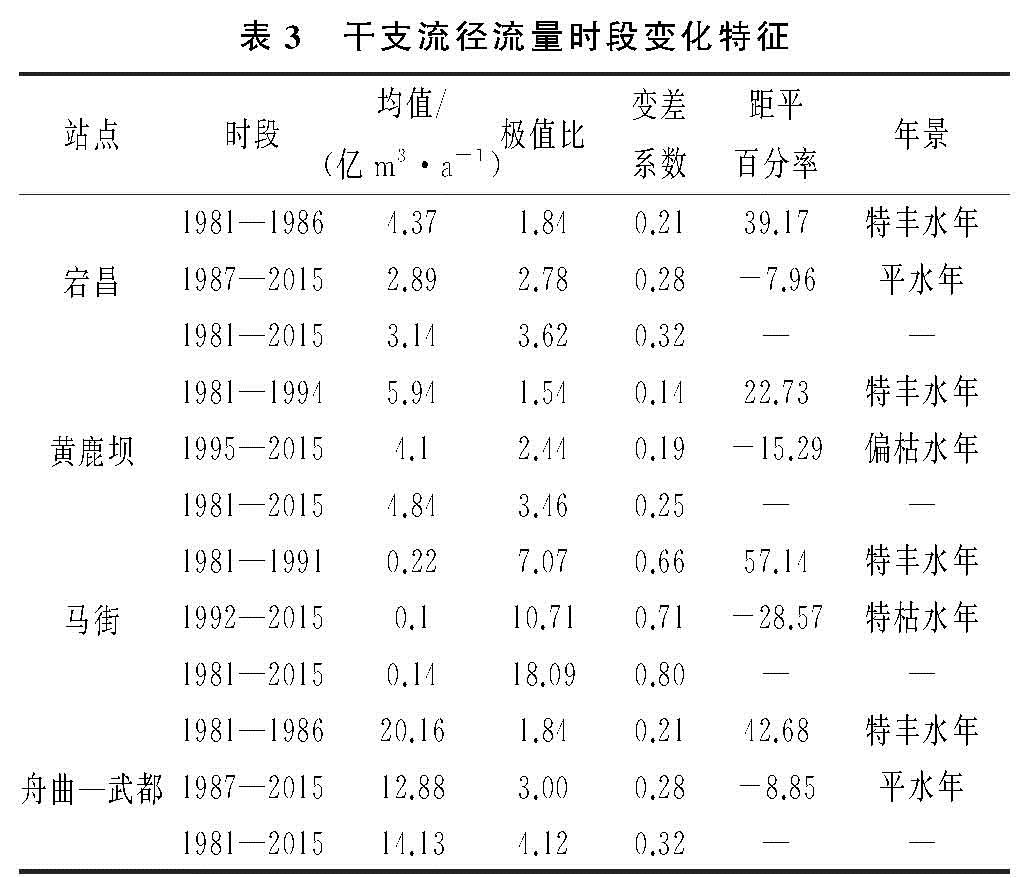
各站以突变点划分前后时段为基准期与变化期,统计不同时段的径流特征参数值,见表3。各站年径流量均呈下降趋势,宕昌站由基准期4.37亿m3/a降至变化期2.89亿m3/a,较基准期减少33.87%; 黄鹿坝站由基准期5.94亿m3/a降至变化期4.10亿m3/a,减少率30.98%; 马街站由基准期0.22亿m3/a降至变化期0.10亿m3/a,减少率54.55%; 舟曲—武都区间干流由基准期20.16亿m3/a降至变化期12.88亿m3/a,减少率36.11%,尽管年径流量最小,突变年份前后马街减少率最大,其次为舟曲—武都区间干流。各站各时期变差系数与极值比存在差异,表明各站径流年际波动变化明显。宕昌1986年前后由特丰水年变为平水年,黄鹿坝1994年前后由特丰水年变为偏枯水年,马街1991年前后由特丰水年变为特枯水年,舟曲—武都区间干流1986年前后由特丰水年变为平水年。突变年份前后各时期呈现不同的年景分布,与各支流的地形地貌、气象、植被覆盖等气候及下垫面条件差异有关。
3.3干支流变化特征关系
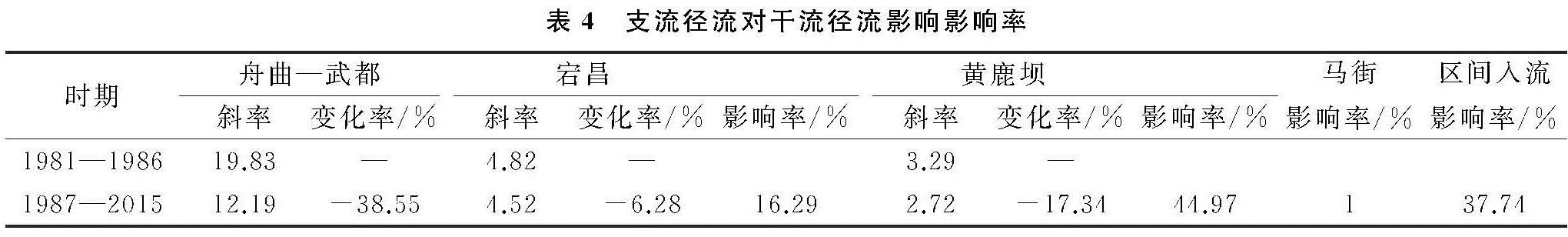
根据舟曲—武都区间干流M-K突变检验,突变点为1986年,以1986年为界,1981—1986年为基准期,1987—2015年为变化期,利用累积量斜率变化率(SCRCQ法)探讨舟曲—武都区间3条支流对于白龙江干流的影响,计算得到各支流和区间入流对舟曲—武都区间干流1986年前后出现变化的影响率大小,是变化期对比基准期斜率变化的反映,从各部分径流1986年前后变化率的角度得到各部分的影响率。具体见表4。
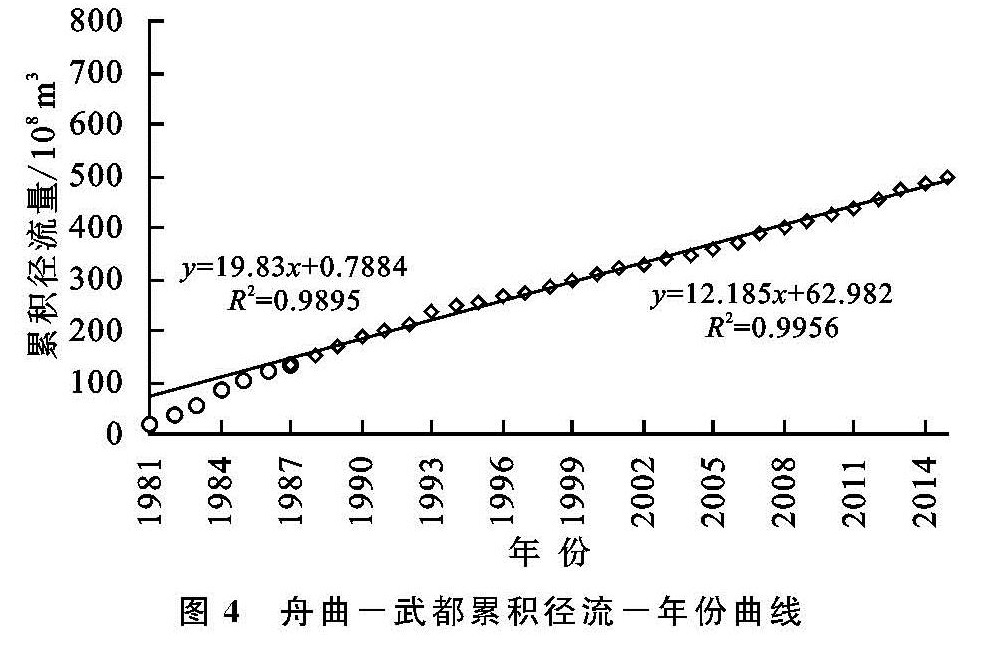
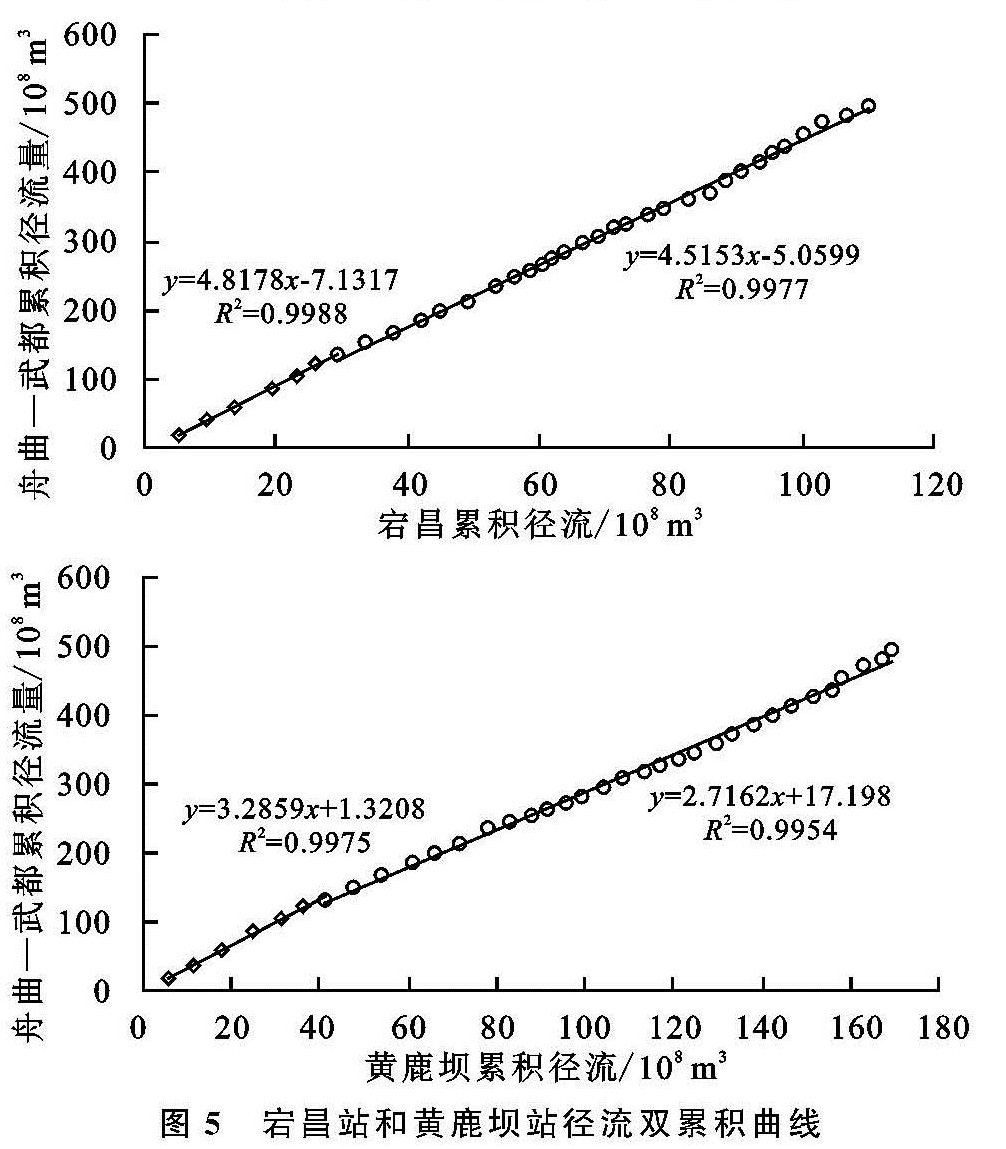
根据舟曲—武都区间的白龙江干流累积径流量—年份曲线(图4),基准期斜率为19.83,变化期斜率12.19,变化期较基准期的变化率-38.55%。依据舟曲—武都干流累积径流量—支流各站累积径流量曲线(图5),支流岷江宕昌站基准期斜率由4.82变为变化期斜率4.52,变化率-6.28%,对舟曲—武都干流径流变化影响率为16.29%; 支流拱坝河黄鹿坝站基准期斜率由3.29变为变化期斜率2.72,变化率-17.34%,对舟曲—武都干流径流变化影响率为44.97%; 支流北峪河为一条径流量较小的支流,多年平均径流量仅为0.14亿m3/a,占舟曲—武都干流多年径流量的0.99%,比重不足1%,对于舟曲—武都区间干流影响十分有限,这里考虑其影响率为1%; 与三条支流影响率做差,剩余的干流区间入流影响率为37.74%。可见,对于舟曲—武都区间白龙江干流径流变化,拱坝河支流变化影响最大,其次是干流区间入流变化、岷江支流变化,最后是北峪河小支流的影响。影响率大小除与各支流的径流量大小有关,也与其径流变化率相关,北峪河马街站径流量占比不足1%,影响率最小,虽然区间入流径流量大于拱坝河黄鹿坝径流量,但因拱坝河径流变化率较大,其影响率最大。