2.1 微地形改造方法对年径流量及泥沙量的调控分析
大型露天矿排土场压实平台与松散边坡造成了人工堆垫地貌岩土侵蚀的特殊性,布设有效的工程与植物措施调控径流,减少水蚀至关重要[3]。因此,通过不同的微地形改造方法对胜利煤矿排土场平台进行治理,可有效调控径流及泥沙量。
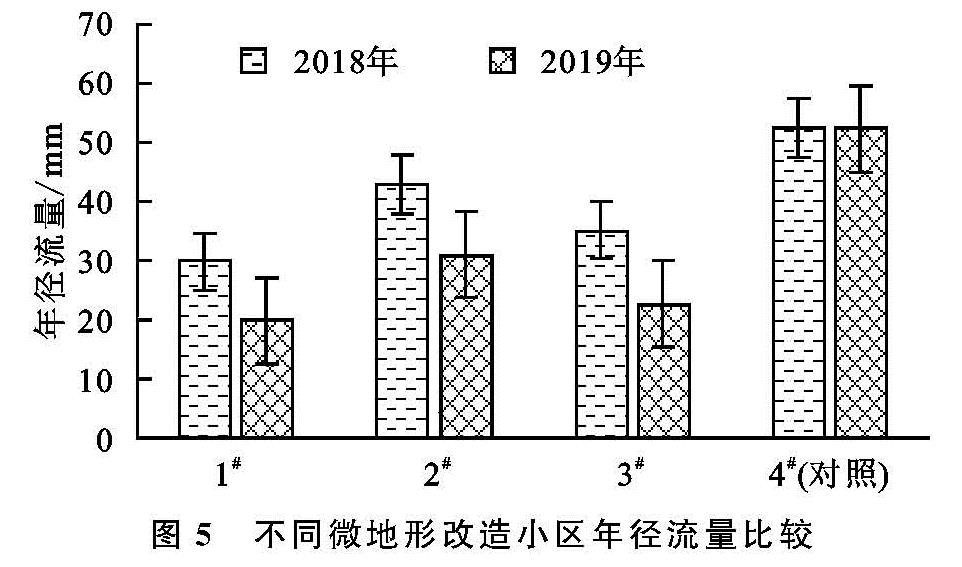
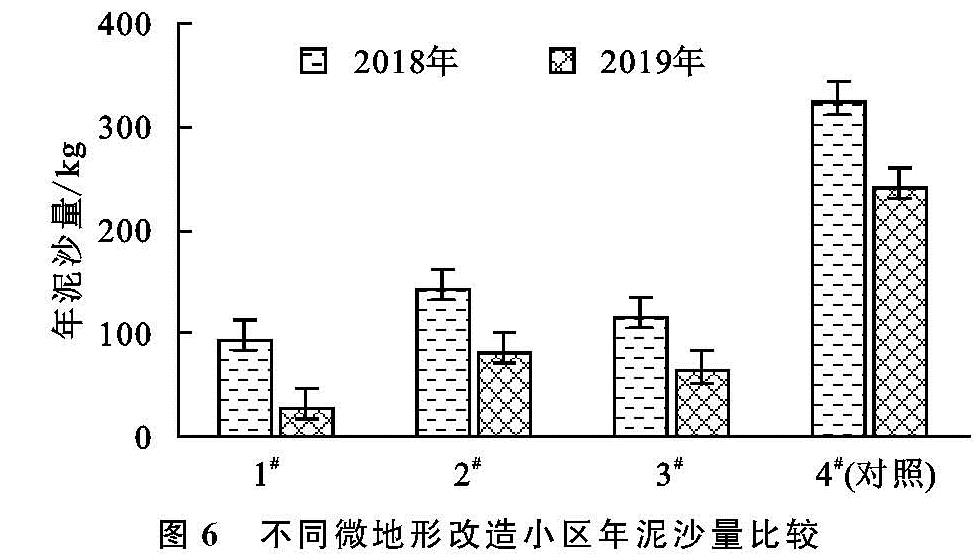
通过图5和图6的分析可知,在有效降雨情况下,对照小区(4#)的年径流量及年泥沙量均最大,4#小区2018年径流总量及泥沙量分别为52.43 mm和322.87 kg,2019年径流总量和泥沙量分别为52.35 mm和240.88 kg; 对照小区2 a内的径流量基本无变化,2019年较2018年仅减少了0.08 mm,但泥沙量减少了81.99 kg,这说明大型排土场压实平台易产流而不易起沙,这与杨娅双等[3]的研究结果一致。使用微地形改造方法的小区年径流量及泥沙量均小于对照小区(4#),2018年径流量及泥沙量由大到小的顺序为4#>2#>3#>1#; 2019年径流量及泥沙量由大到小的顺序为4#>2#>3#>1#。
1#微地形改造小区年产流及产沙量最小,随着治理年限的增加,3#小区年产流产沙量小于2#微地形改造小区,说明单独阻拦板微地形改造方法(3#)要好于实施单独挡水围埂措施的2#小区; 实施微地形改造方法的小区年径流及泥沙量呈逐年减少趋势,1#,2#,3#小区2019年径流量较2018年分别减少了33%,28%,36%,泥沙量分别减少了71%,43%,45%。经过分析,第1年控制径流及泥沙量起主要作用的是微地形改造方法,随着治理年限的增加,在微地形改造方法的保护下小区植被生长较好,微地形改造与植被的综合作用发挥效果。综合年际变化分析结果,微地形改造方法对减少排土场平台水土流失起到了良好的效果,与对照小区相比,实施挡水围埂+阻拦板方法(1#)小区效果最好,次之为单独实施阻拦板小区(3#)。
2.2 微地形改造方法对削流率和减蚀率的影响
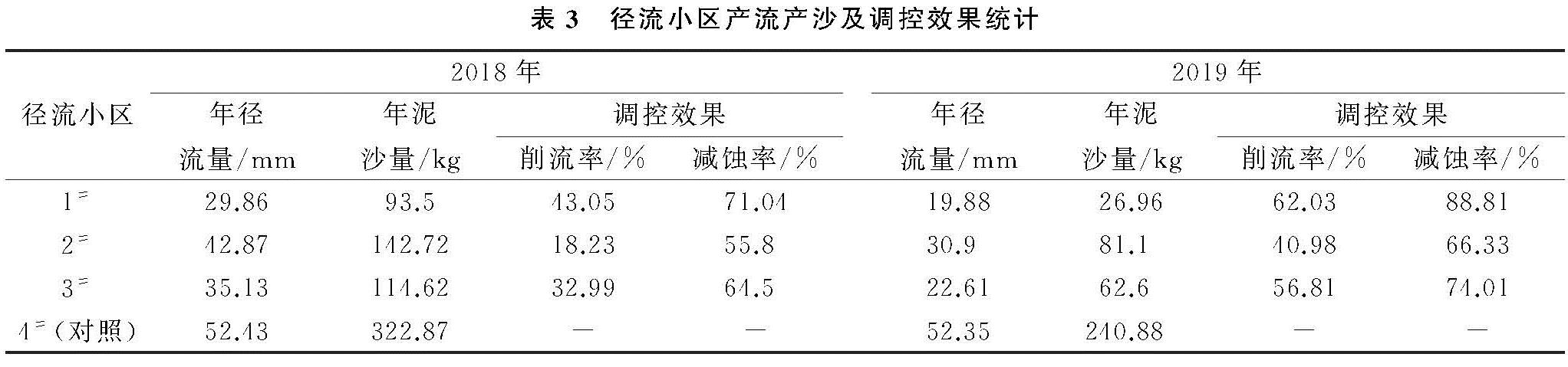
微地形改造方法对地表水文过程和土壤侵蚀过程有着十分显著的影响[21]。由表3看出,与对照小区相比,单独实施挡水围埂方法的小区(2#)削流率及减蚀率最小,2018年分别为18.23%和55.80%,2019年分别为40.98%和66.33%; 实施挡水围埂+阻拦板方法的小区(1#)削流率及减蚀率最大,2018年分别为43.05%和71.04%,2019年分别为62.03%和88.81%; 次之为单独实施阻栏板方法的小区(3#),2018年分别为32.99%和64.50%,2019年分别为56.81%和74.01%; 2018年和2019年削流率及减蚀率由高到低的顺序为1#>3#>2#。
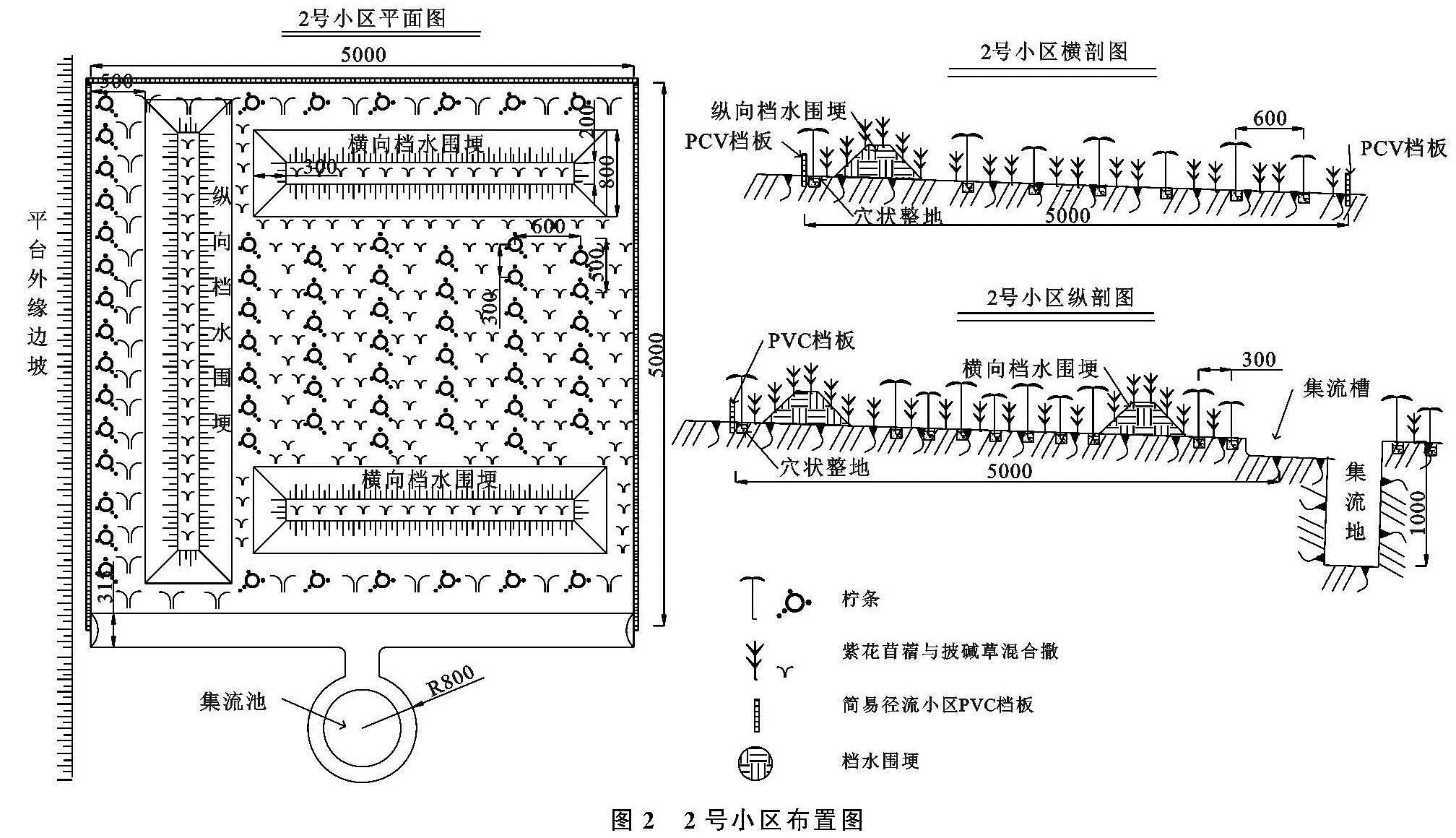
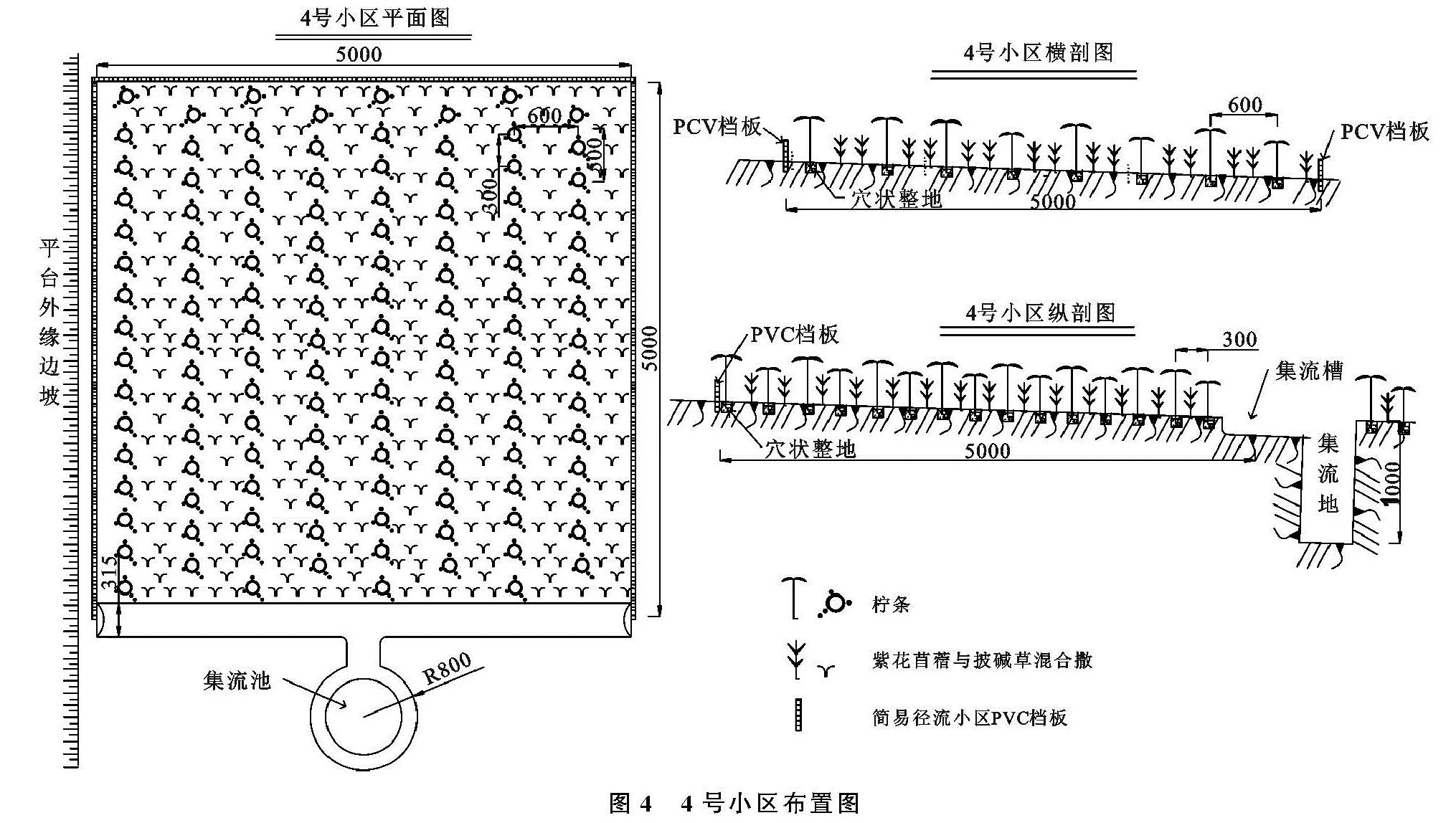
组合不同的微地形改造方法,塑造了不同形态的微地形及集水区,从而对相同条件下的微景观、土壤水文和植被恢复进程产生重要影响[22]。通过分析表明,挡水围埂+阻拦板方法的小区(1#)水沙控制效果最好,挡水围埂将小区分成较大的区块,埋入平台的阻拦板又将小区均匀分成更小区块,产流后阻拦板减缓了平台小区内表层土壤的横向位移,从而减缓径流对表土的冲刷; 挡水围埂阻拦了小区内纵向及横向径流和泥沙,双重作用下1#小区的水沙调控效果最好。3#小区虽然使用埋入平台的阻栏板划分了小区块,减缓或阻止了平台横向的水沙运输,但没有拦蓄纵向的产流,使得集流桶内的径流和泥沙量增加。2#小区仅使用挡土围埂对平台内的表层覆土进行了围挡,产流后对挡水围埂内部的水沙运移未进行调控,使其在3个微地形改造小区中水沙调控效果最差。
2.3 不同雨强下微地形改造方法的产流产沙量分析
本研究中小雨强的径流量和泥沙量是每年有效降雨中小雨强的径流总量和泥沙总量各自取平均值[6],中雨强及大雨强的径流量和泥沙量计算方法与小雨强相同。
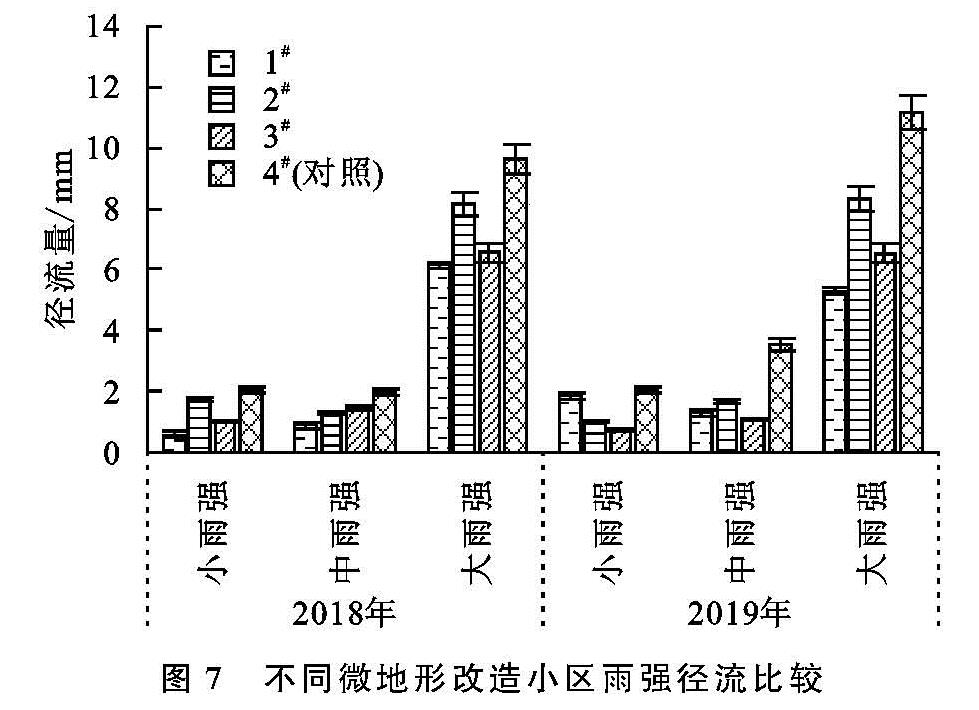
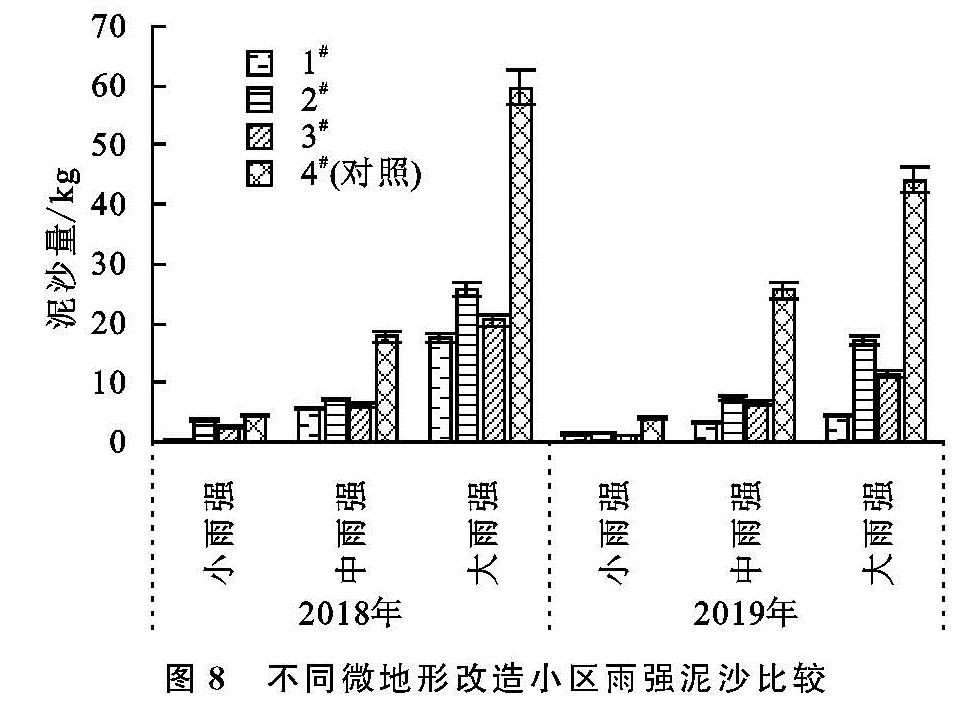
本文将2018年和2019年共24场有效降雨分为3种雨强类型:大雨强、中雨强及小雨强; 以便准确评价微地形改造方法对大型排土场平台次降雨条件下水沙调控效果。由图7和图8可以看出,从平台产流产沙情况来看,所有的24场有效降雨中,实施微地形改造方法的3个小区产流产沙量均小于对照小区(4#),说明排土场平台微地形改造方法对各类型的降雨均有好的调控效果。
由图7可知,小雨强下对照小区的年径流量最大,为2.07 mm; 挡水围埂+阻栏板微地形改造方法小区(1#)2 a的径流总量分别为0.57 mm和1.85 mm,比对照小区(4#)减少了72.6%和10.48%; 单独实施阻拦板的微地形改造方法的小区(3#)2 a的径流总量比对照小区分别减少了51.64%和65.58%; 2#小区2 a的径流总量比对照小区分别减少了16.51%和50.91%。中雨强时,挡水围埂+阻栏板微地形改造方法小区(1#)2 a的径流总量分别比对照小区(4#)减少了54.36%和62.97%,其他2个微地形改造方法的小区为24.10%~70.04%。大雨强时,挡水围埂+阻栏板微地形改造方法小区(1#)2 a的径流总量分别比对照小区(4#)减少了35.98%和52.57%,其他2个微地形改造方法的小区为15.21%~41.46%。通过分析可知,除1#小区外,其他两个微地形改造小区对小雨强的调节效果最好; 与对照相比,挡水围埂+阻栏板微地形改造方法(1#)小区2018年调控径流效果要好于其他2个微地形改造小区; 随着治理年限的增加,1#小区对大雨强的径流调控效果要好于其他小区。说明大雨强条件下,组合不同的微地形改造方法的拦水蓄水效果要好于其他单一的微地形改造方法。
由图8可知,小雨强下对照小区(4#)的泥沙量最大,为4.45 kg; 挡水围埂+阻栏板微地形改造方法小区(1#)2 a的泥沙总量分别为0.43 kg和1.40 kg,比对照小区(4#)减少了90.40%和66.80%; 单独实施阻拦板的微地形改造方法的小区(3#)2 a的泥沙总量比对照小区分别减少了45.35%和75.31%; 2#小区2 a的泥沙总量比对照小区分别减少了16.12%和63.38%。中雨强时,挡水围埂+阻栏板微地形改造方法小区(1#)2 a的泥沙总量分别比对照小区(4#)减少了68.52%和86.71%,其他2个微地形改造方法的小区为59.61%~73.77%。大雨强时,挡水围埂+阻栏板微地形改造方法小区(1#)2 a的泥沙总量分别比对照小区(4#)减少了70.71%和89.59%,其他2个微地形改造方法的小区为56.88%~73.99%。通过分析可知,在小、中、大雨强时,实施微地形改造方法的3个小区泥沙量逐年减少; 与对照相比,挡水围埂+阻栏板微地形改造方法(1#)小区2018年在小雨强下调控泥沙效果要好于其他2个微地形改造小区; 随着治理年限的增加,1#小区对中、大雨强的泥沙调控效果要好于其他小区。说明中、大雨强条件下,组合不同的微地形改造方法的保土拦沙效果要好于其他单一的微地形改造方法。
2.4 微地形改造方法对植物群落多样性的影响
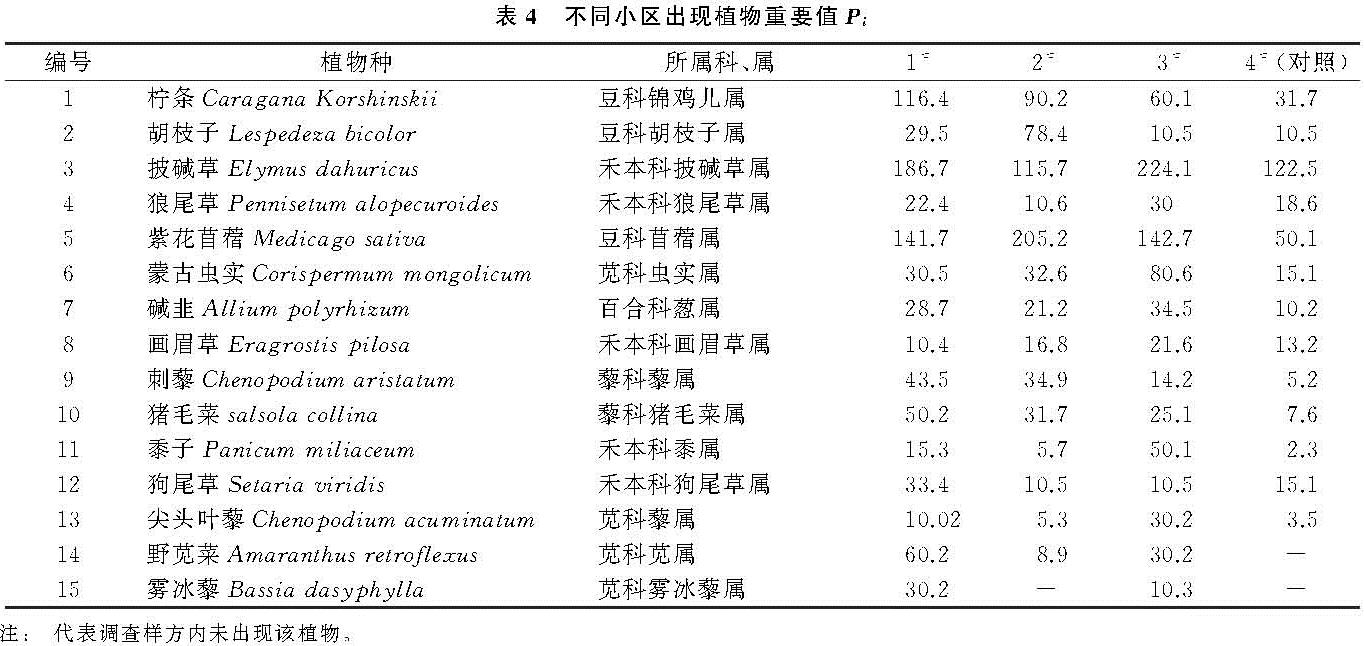
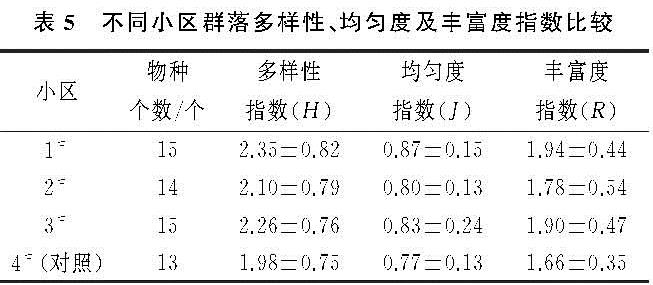
科学布设不同的微地形改造方法能充分发挥植被的恢复效果[17],进一步研究表明,微地形改造方法在植被恢复状况与对应的生态功能、水文特征和生物多样性方面都有非常紧密的联系[22]。据此,本研究于2019年8月中旬,对3个微地形改造小区及对照小区进行了植物群落学特征调查,供试的4个小区共出现15种植物,分属5科14属; 植物种类及植物重要值(Pi)见表4,物种多样性指数计算结果见表5。
物种多样性是生境中物种丰富度及分布均匀性的一个综合数量指标,可较好地反映群落的结构[23]。由表5看出,实施微地形改方法的3个小区物种个数、多样性指数(H')、均匀度指数(J)和丰富度指数均高于对照小区(4#)。3个微地形改造小区多样性指数最高的为挡水围埂+阻栏板的小区(1#),值为2.35; 其次为仅实施阻拦板的微地形改造小区(3#),值为2.26; 再次之为仅实施挡水围埂的微地形改造小区(2#)。群落均匀度指数反映的是群落植物分布的均匀程度,3个微地形改造小区均匀度指数最高的为1#小区,值为0.87; 其次为3#,2#,其值分别为0.83,0.80。物种丰富度指数表明群落物种丰富程度,3个微地形改造小区丰富度指数最高的为1#小区,值为1.94; 其次为3#,2#,其值分别为1.90,1.78。Shannon-Wiener多样性指数能客观反映植物群落内物种组成的变化情况,兼顾了物种丰富度和均匀度的不足,更能反映不同群落的多样性,因此,实施微地形改造方法的1#小区内植物群落表现出较高的物种多样性。
1#小区实施了挡水围埂+阻拦板的方法,组合的微地形改造方法拦蓄了平台内横向及纵向的径流,减缓径流流速,增加了地表入渗; 且埋入平台内部的阻拦板防治了表土与平台压实面分离,这些都可能为植物生长提供安全稳定的环境,有利于植被恢复,所以1#小区植物群落多样性指数、均匀度指数和丰富度指数最高; 3#小区仅实施阻栏板的微地形改造方法,细化小区内部空间,保证初始阶段植物种分布的均匀性; 虽然防治了表土与平台压实面分离,但是调查发现其纵向冲刷高于1#小区,这可能是其多样性指数低于1#小区原因。2#小区仅实施挡水围埂的微地形改造方法,对小区内调查发现,挡水围埂内部空地有0.01 m2~0.09 m2面积不等的秃斑; 物种数量少,有秃斑现象产生,故2#小区生物多样性低于3#小区。4#小区仅实施了覆土种植的方法,对平台内的横纵向径流未实施调控,平台压实面与表土分离,平台压实面开始裸露; 小区内出现0.16 m2~0.36 m2面积不等的“秃斑”,物种数量更少,秃斑面积较大,故4#小区植物群落多样性最低。结合2 a的调查表明,2018年各供试小区植物种类组成单一,主要为人工种植初期成活的植物种,无层次分化,仅为单层结构; 2019年,除对照小区外,其他3个微地形改造的小区物种种类都有增加,层次开始分化,微地形改造措施能充分发挥植被的恢复效果。