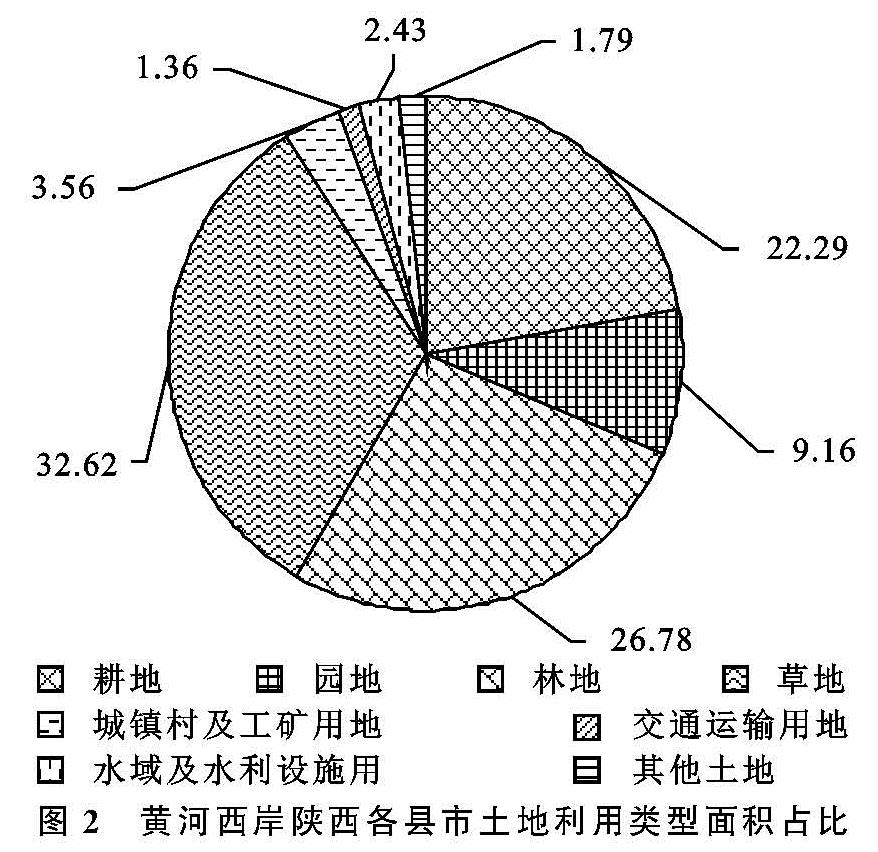
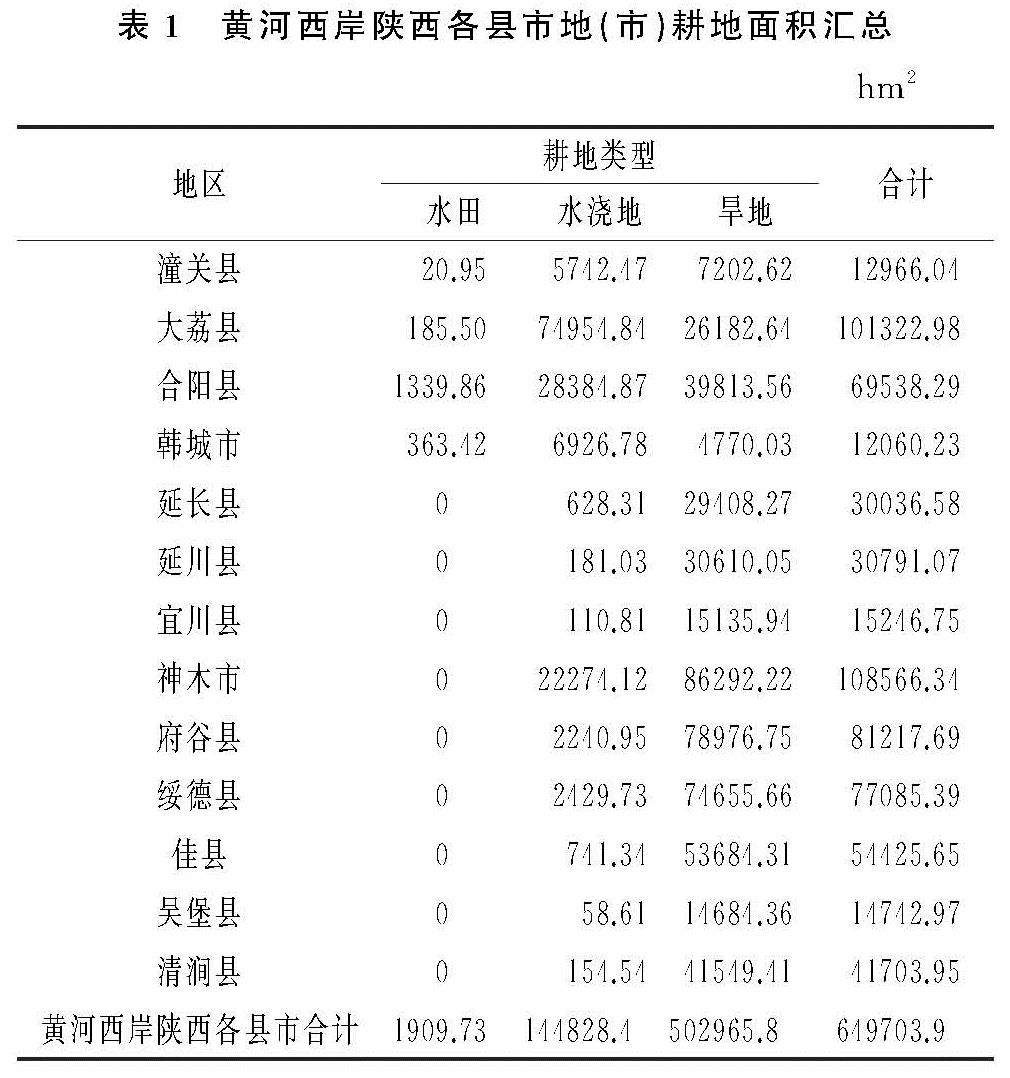
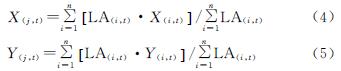2.1.2 数量变化情况
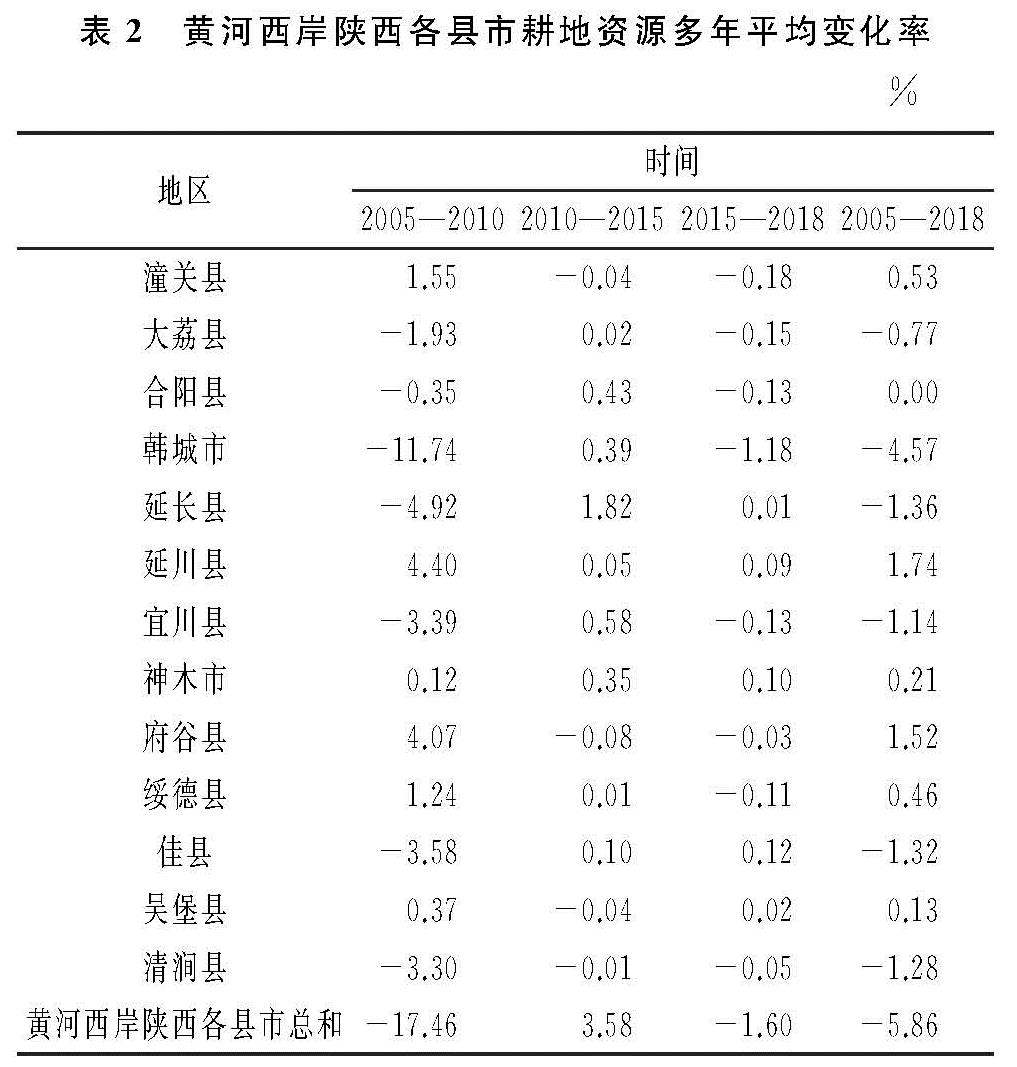
利用动态度模型法分别计算黄河西岸陕西各县市在2005—2010年、2010—2015年、2015—2018年以及2005—2018年4个时间段内的耕地资源平均变化率(表2)。
在2005—2010年黄河西岸陕西各县市耕地资源数量呈显著下降变化,2010—2015年耕地数量呈增加趋势,2015—2018年耕地资源数量略有下降。耕地面积的减少主要发生在2005—2010年期间,在此期间,大荔县、合阳县、韩城市、延长县、宜川县、佳县和清涧县的耕地资源均有不同程度的下降,其中,韩城市下降率最高,达到11.74%,这是因为《陕西省城镇体系规划2006—2020》明晰了韩城市作为县域中心城市的地位和作用,规划到2020年将韩城市建设成中等城市(区),在一定程度上加快了韩城市的耕地向建设用地转变速度。潼关县、延川县、神木市、府谷县、绥德县、吴堡县存在不同程度的耕地面积增加; 在2010—2015年黄河西岸陕西各县市耕地资源数量增加,表明耕地数量的减少趋势已经得到遏制,耕地数量保护政策发挥作用,其他各地(市)变化幅度不大,延长县耕地数量增长相对较大,为1.82%; 2015—2018年黄河西岸陕西各县市耕地资源数量稍有下降。各地(市)耕地数量比较平稳,韩城市相对有较大的减少,年平均减少率为1.18%。总的来说,2005—2018年,黄河西岸陕西各县市耕地资源数量表现下降趋势,且年平均下降率为5.86%。在2005—2010年、2010—2015年、2015—2018年为先下降、后上升、再下降的变化态势。
2.2 耕地质量变化特征
2.2.1 利用等耕地面积变化情况
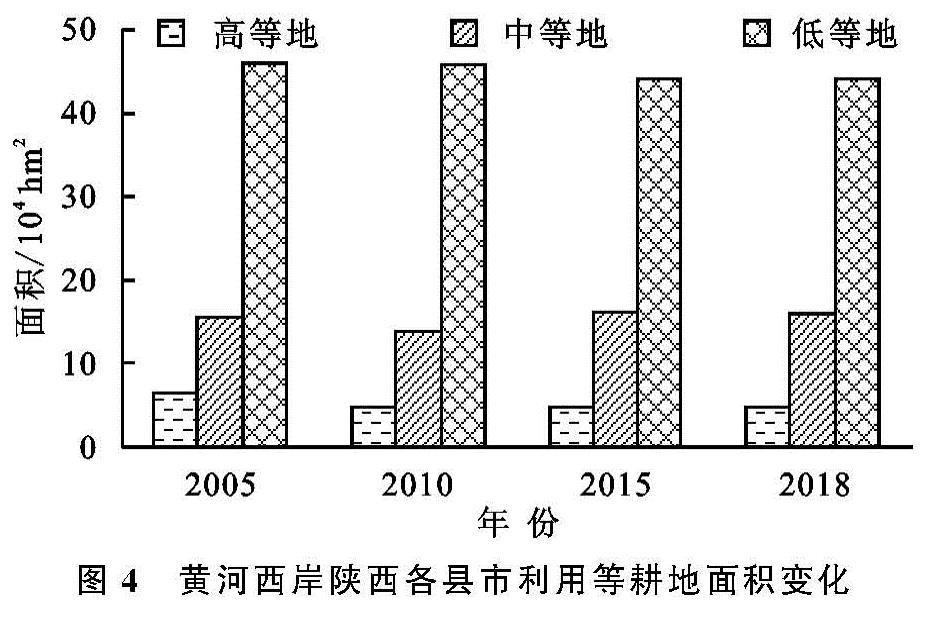
根据《中国耕地质量等级调查与评定(全国卷)》中对中国耕地质量等别类型的划分,分别把1—4等、5—8等、9—12等、13—15等耕地划分为优等、高等、中等和低等4个类型[28]。利用面积加权平均法对黄河西岸陕西各县市耕地利用等的面积变化情况结合优等、高等、中等、低等4个类型进行分析(图4)。
利用动态度模型法,结合黄河西岸陕西各县市耕地质量利用等别的优等、高等、中等、低等4个类型的耕地面积,分析其在2005—2010年、2010—2015年、2015—2018年、2005—2018年的平均变化率。由于在黄河西岸陕西各县市内不存在优等地,故本研究不对优等地做分析。
从图5可以看出,在2005—2010年,黄河西岸陕西各县市的高等、中等、低等均呈下降变化,其中高等地有明显减少,这是由于在2005—2010年,为了发展经济、提高城镇化水平,不可避免地将耕地转为建设用地,而耕地利用等别为高等类型的耕地往往存在于区位等条件较好的地块,由此造成在此期间高等地面积大幅度减少; 在2010—2015年,高等地和中等地面积均增加,在此期间严格的耕地数量、质量占补平衡政策以及土地整治工程的结果; 在2015—2018年,3种类型的耕地利用等别面积浮动较平稳,证明近年来黄河西岸陕西各县市耕地资源在数量及质量上基本平稳。总的来说,在2005—2018年,高等地和低等地成不同水平减少,减少率分别为1.96%,0.31%,中等地面积略有增长,增长率为0.24%。
2.2.2 利用等别变化情况
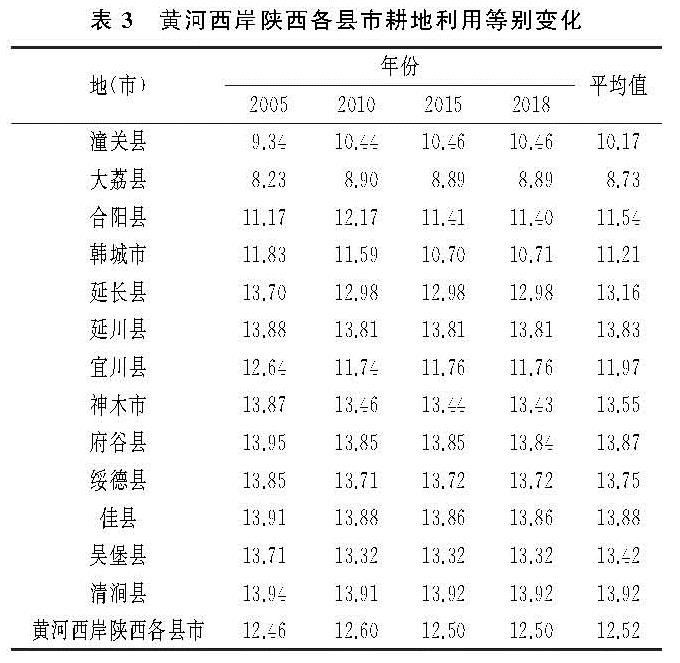
运用面积加权平均法计算黄河西岸陕西各县市各地(市)2005年、2010年、2015年、2018年耕地利用等别,并对4个时间点求平均值,分析其利用等别及其变化情况,计算结果见表3。
2005年、2010年、2015年、2018年,黄河西岸陕西各县市的耕地平均利用等变化较平稳,且呈现自南向北逐渐降低的分异规律。耕地利用等别最高为潼关县和大荔县,潼关县和大荔县处于关中渭河平原区,自然资源匹配较好,土地平坦,土壤肥沃,光照充足,水热条件与水利化程度均较高; 其次较高的为合阳县、韩城市、宜川县,该地区为渭北黄土旱塬区土层深厚、富含钾质,加之光照充足,昼夜温差大,雨热同季,因此耕地利用等别相对陕北地区较高; 余下的地(市)耕地平均利用等为13等左右,由于分布在陕北黄土丘陵沟壑区和陕北长城沿线风沙区,土壤较贫瘠、热量较差,降水稀少,存在一定的生态脆弱性,耕地质量普遍较低。相比2005年耕地利用等别,2018年延长县、延川县、宜川县、神木市、府谷县、绥德县、佳县、吴堡县、清涧县十个区域上属于陕北地区的地(市)耕地利用等别均有提升,这是由于近些年来陕北地区积极开展土地整治工程,并进行生态建设,提高了部分低等地的耕地质量。韩城市的平均耕地利用等有所提高,因韩城市是承担2016年耕地保护与质量提升项目的试点县、市之一,开展了耕地质量提质建设工程,对耕地利用等提升具有积极作用。而潼关县、大荔县、合阳县耕地利用等有不同程度降低。潼关县和大荔县地处关中地区,近年来开展城市建设占用优质耕地,补充一般耕地,造成耕地质量有所下降。总体来看,耕地平均利用等在空间分布上按照分等指标区大致可分为关中渭河平原区>渭北黄土旱塬区>陕北长城沿线风沙区、陕北黄土丘陵沟壑区。
2.2.3 区位指数变化情况
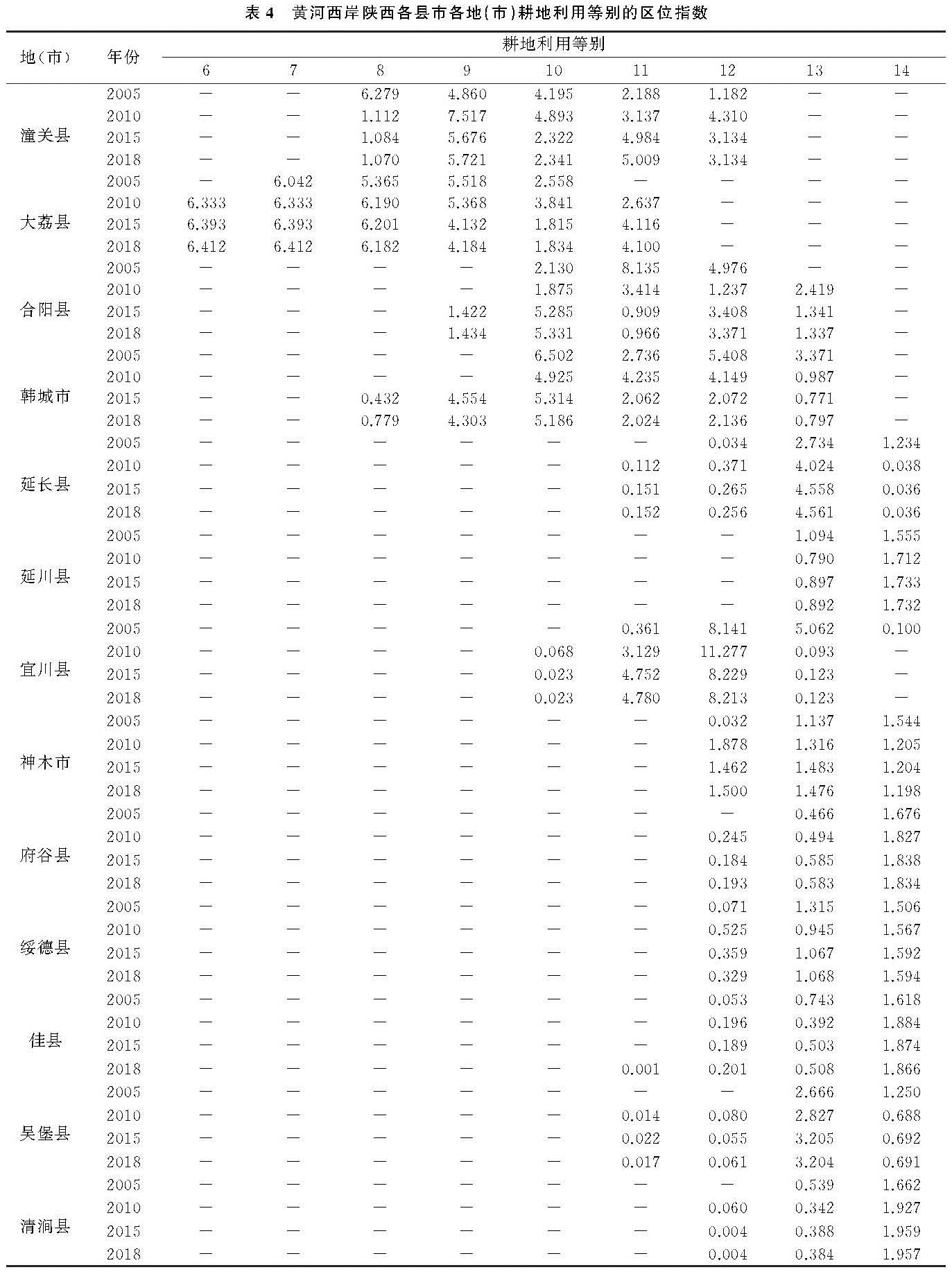
利用耕地质量区位指数分析法,分析黄河西岸陕西各县市在2005年、2010年、2015年、2018年的耕地质量聚集情况,计算结果见表4。
结果显示,中、高等地主要分布在黄河西岸陕西南部各县市,而北部县市中、低等地聚集程度较高。从时间推移来看,南部县市耕地质量有所下降,北部县市耕地质量提高。潼关县和大荔县的高等地和中等地的聚集程度较高,潼关县耕地利用等分布在8—12等,大荔县处于6—11等。这是由地理环境所致,关中平原的地势平坦、气候适宜,耕地质量较高。潼关县2005年8等地区位指数较高,2010年、2015年、2018年9等地区位指数最高,再次证明了潼关县耕地质量有所下降; 大荔县区位指数由2005年7—10等变为2010年、2015年、2018年的6—11等,高等地聚集程度较高,变化较平稳; 合阳县2005年利用等分布在10—12等,11等地区位指数最高,2015年、2018年10等地聚集度较高,但同时存在13等地; 韩城市通过耕地保护及提质工程,区位指数向高等地聚集,耕地质量提高。延长县、延川县、宜川县、神木市、府谷县、绥德县、佳县、吴堡县、清涧县位于陕北地区,由于自然条件的限制,耕地质量普遍不高,耕地利用等区位指数聚集在中、低等地。
2.3 耕地质量重心迁移特征
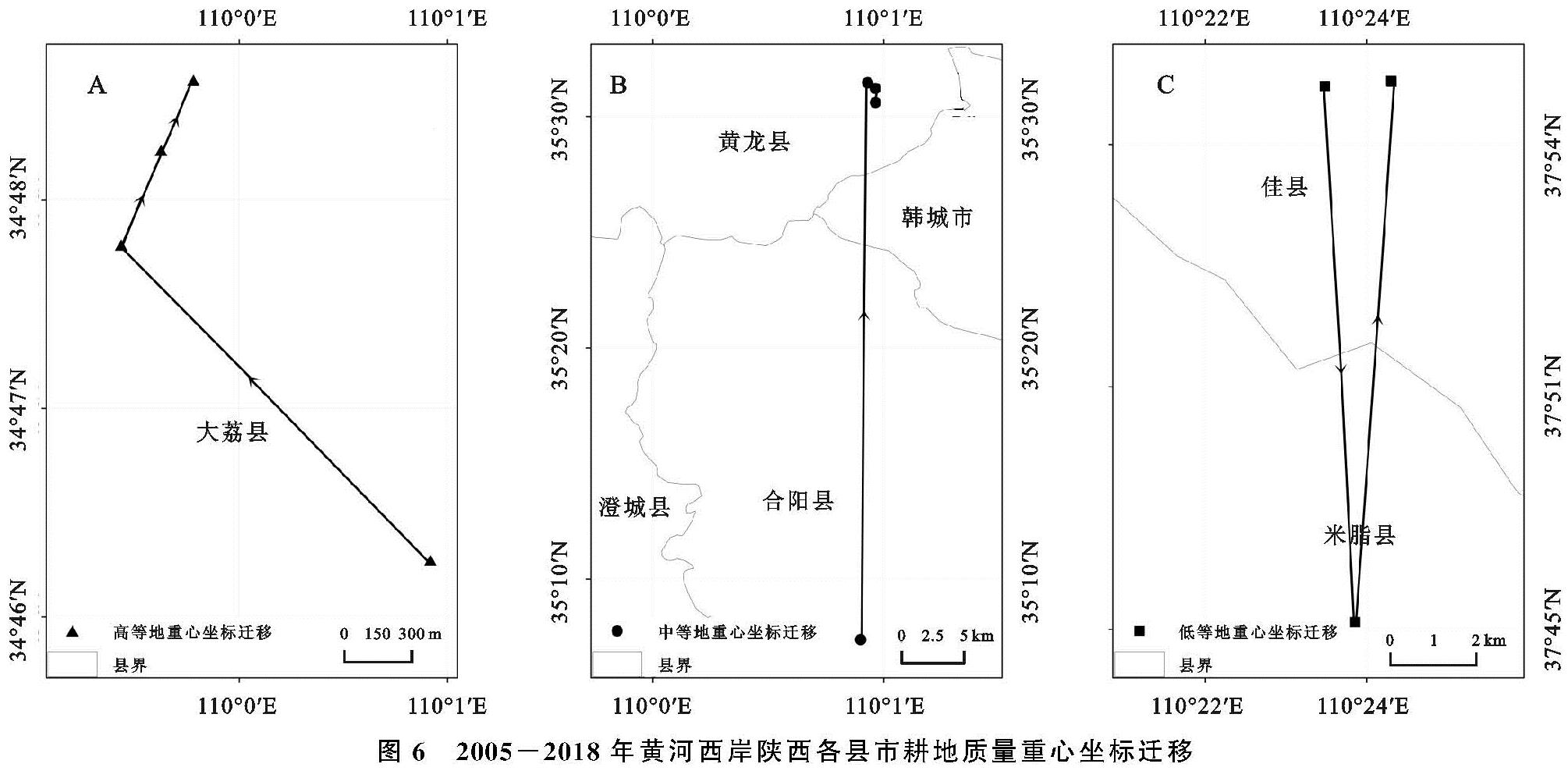
将重心迁移模型运用到耕地质量重心迁移中,并结合优、高、中、低的耕地利用等别,计算2005年、2010年、2015年以及2018年不同质量类型的耕地重心坐标,分析黄河西岸陕西各县市耕地质量利用等的重心迁移轨迹,见图6。
图中显示,2005年、2010年、2015年、2018年4个时期高等地和中等地耕地质量重心均向北迁移,低等地重心先向南,后向北迁移。高等地的重心在2005年、2010年、2015年、2018年4个时期均在大荔县,大荔县地处关中平原,自然条件有利于农业种植,耕地质量高。其中,2005—2010年,重心迁移幅度最大,经向向西移动0.012 4°,纬向向北移动0.012 6°,向西北方迁移。2010—2015年,迁移幅度有所减小,经向向东移动0.001 7°,纬向向北移动0.003 8°,向东北方移动。2015—2018年,重心迁移方向继续向东北方移动,经向移动0.001 3°,纬向移动0.002 8°。总的来说,2005—2018年期间,高等地重心向东北方向迁移,经度移动0.009 4°,纬度迁移0.019 2°; 中等地由2005年所在的合阳县经过2010年、2015年、2018年迁移至黄龙县,主要处于关中平原与陕北黄土高原地过渡地带,在2005—2010年迁移距离最大,经向向东移动0.005 0°,纬向向北移动0.401 1°。2010—2015年以及2015—2018年迁移幅度均较小。总体来说,2005—2018年中等地重心向东北方移动,经度迁移0.010 6°,纬度迁移0.397 0°; 低等地重心在2005年处于佳县,2010年迁移至米脂县,位于陕北地区。2015年、2018年再次转移至佳县,迁移主要发生在2005—2010年和2010—2015年内,2015—2018年期间重心迁移量微小,2005—2018年重心向东北方移动,经度迁移0.013 6°,纬度迁移0.001 1°。耕地质量的重心迁移是相对于整个研究区而言,由于近年来耕地占补平衡以及土地整治工程,耕地重心处于不断迁移中,迁移幅度相对不大,且中等地重心坐标迁移量>低等地重心坐标迁移量>高等地重心坐标迁移量。
表4 黄河西岸陕西各县市各地(市)耕地利用等别的区位指数
图6 2005-2018年黄河西岸陕西各县市耕地质量重心坐标迁移
 (2)
(2)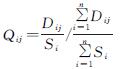 (3)
(3)