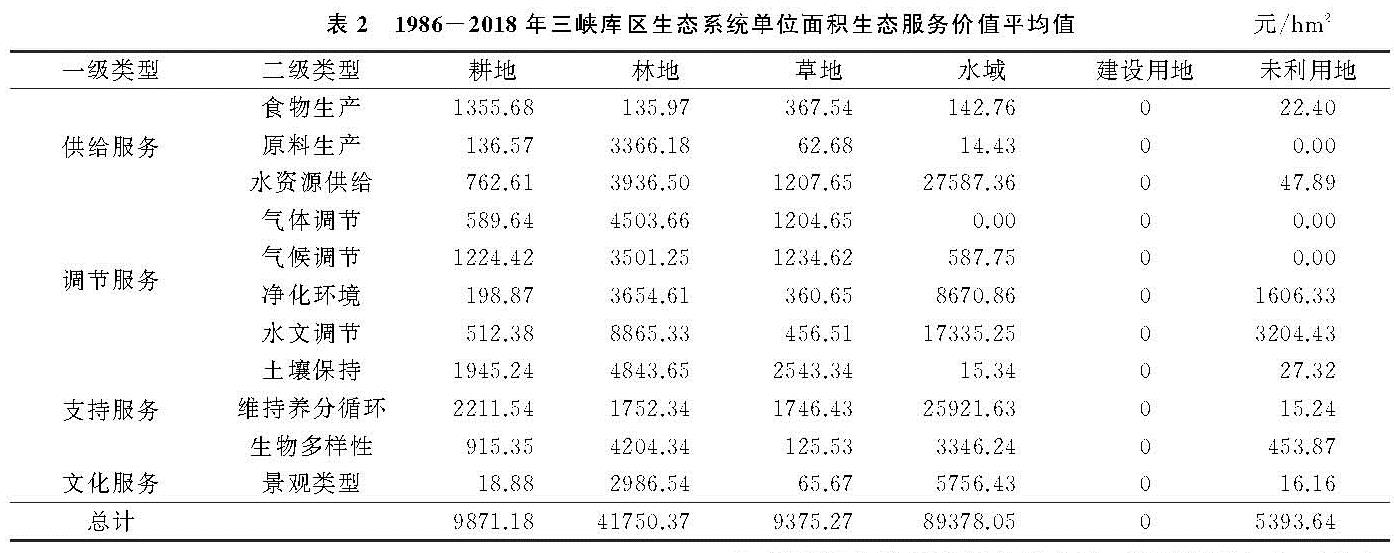
3.1 三峡库区土地利用类型结构分析
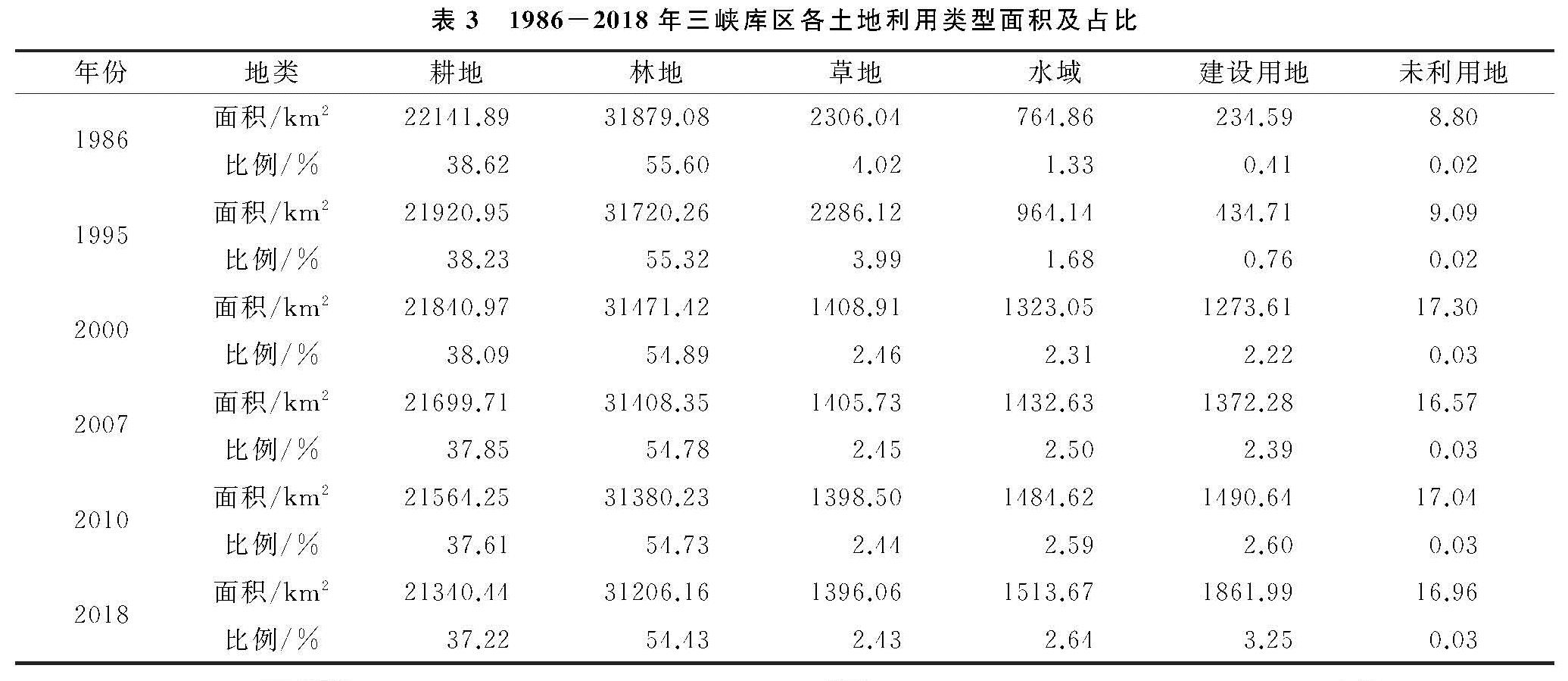
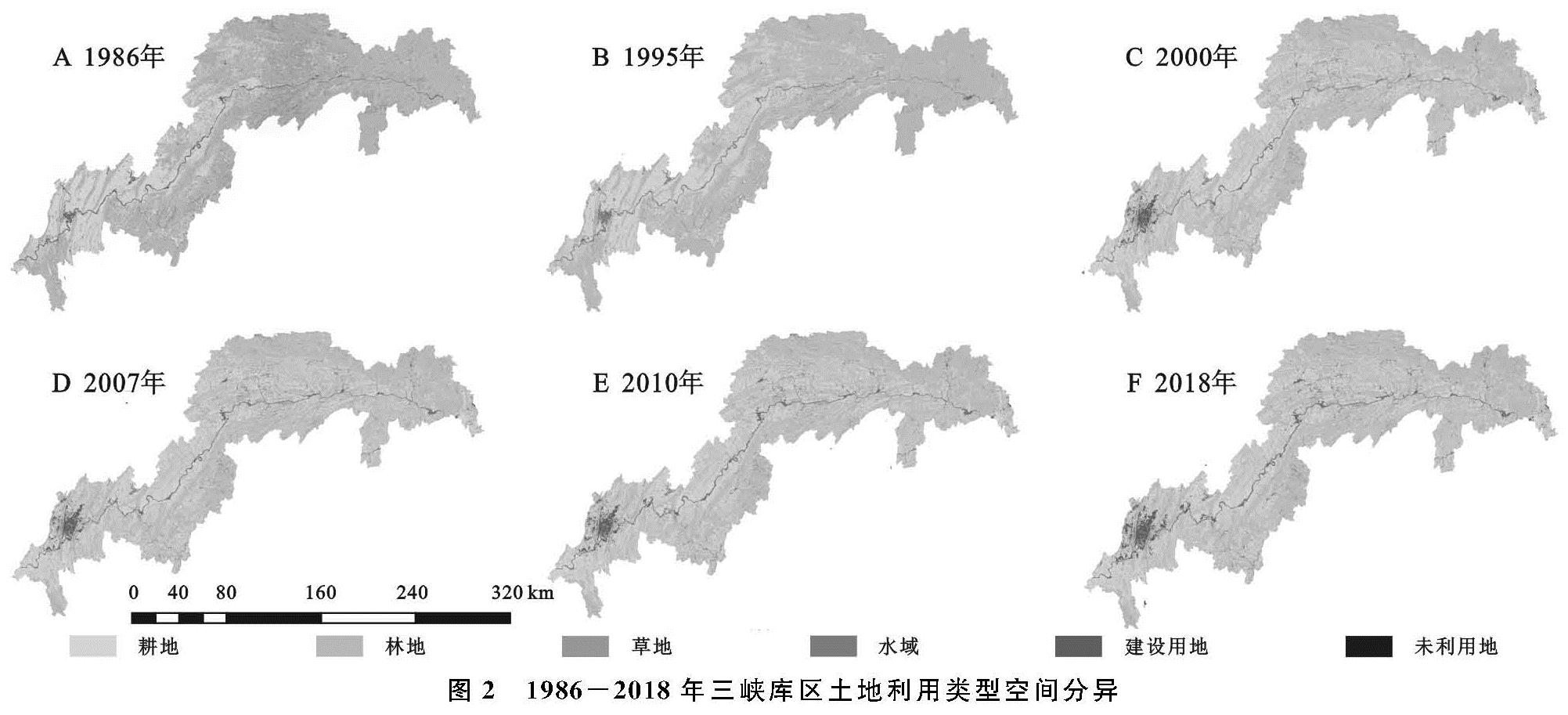
在RS和GIS的技术支撑下,对1986年、1995年、2000年、2007年、2010年和2018年三峡库区土地利用现状数据进行分类统计,进而得到各年对应各类土地利用类型面积和比例,结果见表3; 运用ArcGIS 10.1软件的制图功能,得到了三峡库区1986年、1995年、2000年、2007年、2010年和2018年6期的土地利用类型空间分异图(图2)。
表3 1986-2018年三峡库区各土地利用类型面积及占比
图2 1986-2018年三峡库区土地利用类型空间分异
通过表3和图2我们可以看出三峡库区1986—2018年土地利用的情况,总体来看,三峡库区土地利用的主要类型是林地和耕地,耕地在库区的中上游段分布居多。库区的下游段和重庆都市区的4条平行山脉(缙云山、中梁山、铜锣山和明月山)以林地为主要的土地利用方式; 草地零星地分布在三峡库区的部分区域; 建设用地规模随着时间地变化不断变大。在研究年限内,水域、建设用地和未利用地面积都呈现增多的状态; 草地、耕地和林地呈现减少的状态,三峡库区用地类型以林地与耕地为主。在近30 a的时间里,建设用地是三峡库区所有土地利用类型中变化幅度最大的,其面积由234.59 km2增长到了1 861.99 km2,增加了2.84%,并呈现不断增加的趋势; 其次是草地,面积由2 306.04 km2减少到1 396.06 km2,减少了1.59%; 第三是耕地,面积由22 141.89 km2减少到21 340.44 km2,减少了1.4%,并呈现逐年减少的趋势; 水域面积从764.86 km2增加到了1 513.67 km2,这是由于三峡大坝工程的建设和使用,导致库区水面面积不断增加; 林地面积由31 879.08 km2减少到31 206.16 km2; 未利用地占三峡库区总面积的比例本身比较小,变化不明显,但在总量上有一定的增幅,其具体变化过程分为4个阶段:先增加后减少,再次增加,再次减少。鉴于此,三峡库区的国土管理部门需要有针对性的制定相关耕地和林地的保护政策并切实推行,以保障库区的粮食和生态安全。
3.2 三峡库区土地利用变化速度分析
引入单一土地利用动态度及综合土地利用动态度对三峡库区土地利用变化速率进行分析,在利用1986年、1995年、2000年、2007年、2010年和2018年三峡库区土地利用现状分类数据的基础上,采用土地利用动态度的计算公式获得各土地利用类型的单一土地利用动态度及综合土地利用动态度,见表4。
从表4可以看出,三峡库区近30 a来建设用地的土地利用变化速度最快,在1995—2000年时段变化率最明显,增长率达到了38.596%; 耕地在2010—2018年时段变化最明显,减少率为0.259%; 林地、水域、草地和未利用地在1995—2000年时段变化最明显,林地减少率、水域增加率、草地减少率和未利用地增加率分别为0.157%,7.445%,7.674%,18.05%。
表4 三峡库区1986-2018年各类土地利用动态度
研究区土地利用综合动态度最大的是1995—2000年时段,综合动态度为0.421,由此可知,在整个研究期内,三峡库区土地利用的变化速度最快的时期在1995—2000年时段,变化率为0.421%; 在这一时段水域、建设用地和未利用地都以较快的速度增长,而耕地、林地以及草地都以不同程度的变化速度减少,这是由于1997年重庆直辖,加快了三峡库区的发展。三峡库区在2010—2018年时段土地利用变化速度相对较快,变化率为0.175%,由此可见,建设用地和水域的增长速度加快,而其余类型的地类都以不同程度的速度减少。三峡库区在2007—2010年时段和在1986—1995年时段土地利用变化率分别为0.099%,0.077%,水域、建设用地和未利用地都以不同程度的变化速度增长,耕地、林地以及草地都以不同程度的变化速度减少; 三峡库区在2000—2007年时段的土地变化率为0.052%,水域和建设用地都以不同程度的变化速度增长,耕地、林地、草地以及未利用地都以不同程度的变化速度减少。
综上分析,水域和建设用地的土地利用变化率在5个时段均为正值,表明研究区近30 a来水域和建设用地的面积不断增加; 耕地、林地和草地的土地利用变化率在5个时段均为负值,表明其耕地、林地和草地的面积不断减少; 而未利用地的面积变化在这近30 a的5个时段中呈先增加后减少再增加又减少的趋势。在1995—2000年时段三峡库区土地利用变化率达到峰值,说明在该时段三峡库区城乡规划建设力度较大。
3.3 三峡库区土地利用程度分析
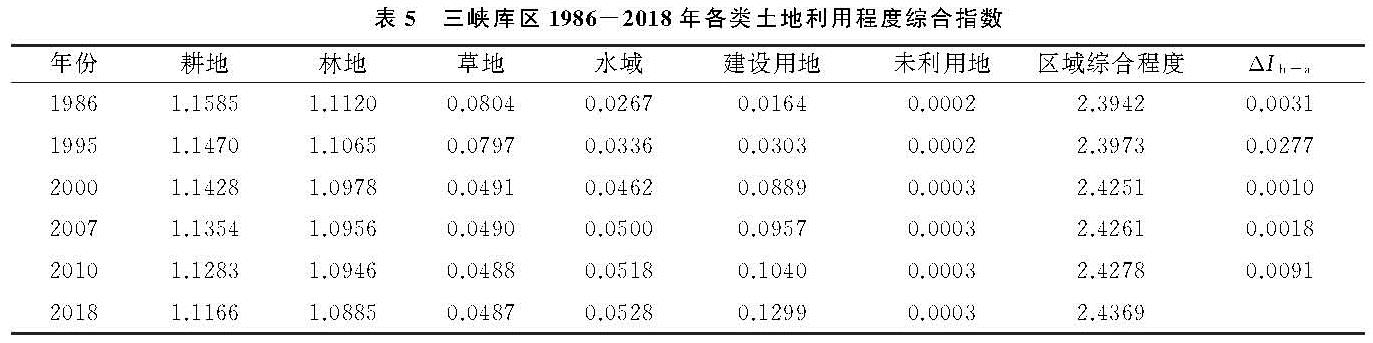
通过对研究区土地利用程度的计算和分析,能够进一步认识土地利用变化的发展程度[11],分析发现研究区土地利用是否处于发展状态。利用1986年、1995年、2000年、2007年、2010年和2018年三峡库区土地利用现状数据和土地利用程度的核算公式,本文得到了研究区各土地利用类型的土地利用程度和三峡库区近30 a的土地利用程度综合指数以及三峡库区近30 a来土地利用程度变化量,见表5。
表5 三峡库区1986-2018年各类土地利用程度综合指数
三峡库区在1986—2018年里耕地的土地利用程度是最高的,未利用地的土地利用程度是最低的; 水域和建设用地的土地利用程度在1986—2018年近30 a里呈现逐年上升的趋势,而耕地、林地和草地的土地利用程度在1986—2018年近30 a里呈现逐年下降的趋势。从总体来看,未利用地的土地利用程度在1986—2018年期间呈现上升的趋势,但其实际变化不明显,这是由于未利用地面积本身基数较小造成的。
研究区在1986—1995年的土地利用程度变化量为0.003 1,1995—2000年的土地利用程度变化量为0.027 7,2000—2007年的土地利用程度变化量为0.001,2007—2010年的土地利用程度变化量为0.001 8,2010—2018年的土地利用程度变化量为0.009 1,由于该5个时段的土地利用程度变化量都大于0,因而在这5个时段研究区都处于发展期。由于研究区1995—2000年的土地利用程度变化量是最大的,在一定程度上可以说是发展速度最快,这是由于1997年重庆直辖加速了三峡库区的发展。
3.4 生态系统服务价值时空演变分析
在GIS技术的支持下,结合三峡库区生态系统单位面积生态服务价值表,得到了1986—2018年三峡库区生态系统服务价值核算结果以及结构变化情况表(表6)。通过对表6分析可知,研究区1986—2018年生态系统服务价值总量由1 639.56亿元持续增长到1 662.01亿元,增长率1.37%; 单位面积生态系统服务价值由28 596.02元/hm2增长到28 987.57元/hm2。研究区各土地利用类型的生态系统服务价值占比大小依次为:林地>耕地>水域>草地>未利用地>建设用地; 研究期内耕地、林地和草地的生态系统服务价值持续减少,变化率分别为-3.62%,-2.11%,-39.45%; 水域和未利用地生态系统服务价值持续增加,变化率为97.91%,0.01%; 耕地生态系统服务价值减速逐渐降低; 林地、草地和水域生态服务价值呈现先增后减趋势; 未利用地生态服务价值逐年增加。
表6 1986-2018年三峡库区各地类生态系统服务价值结构及变化
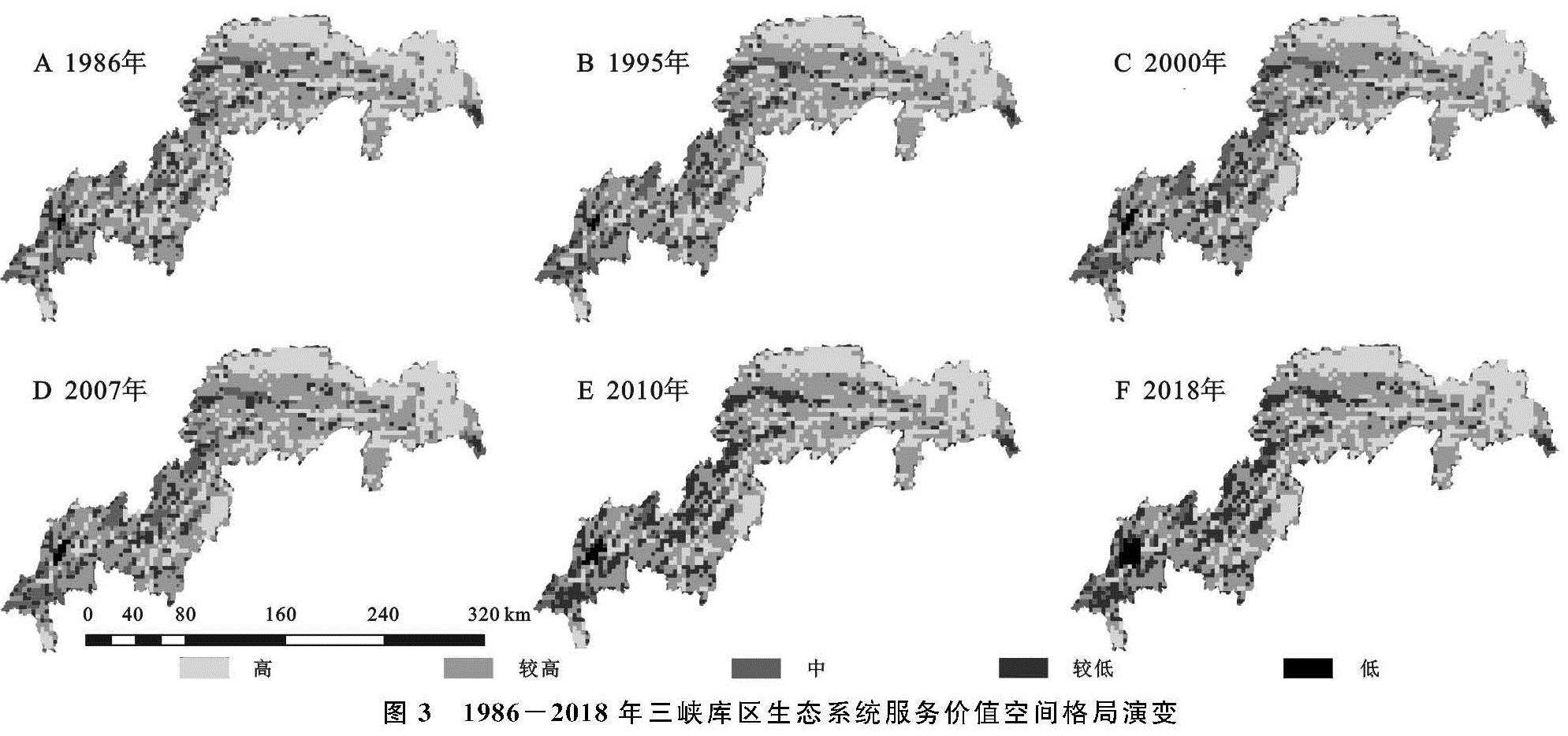
本文通过计算评价单元格单位面积生态系统服务价值,引入中心点赋值法,运用GIS软件进行生态系统服务价值空间插值,结合几何间隔分类,采用GIS自然间断点法,并充分考虑研究区的真实状况,将研究区生态系统服务价值评价单元的价值划分为低[0,2000)、较低[2000,4000)、中[4000,6000)、较高[6000,8000)、高[8000,∞)共5个价值等级,并得到研究区6期单位面积生态系统服务价值空间格局分布图(图3)。
图3 1986-2018年三峡库区生态系统服务价值空间格局演变
从图3可以看出,三峡库区单位面积生态系统服务价值主要以较高和高两个等级为主,其面积平均占比为53%,32.53%; 高和中等级面积比例呈现减少趋势; 低、较低和较高生态服务价值面积占比呈现增加趋势,所有等级的面积变化速率为先增后减; 东北部、东南部山地以及长江沿岸区域单位面积生态系统服务价值较高,主要为高级和较高等级分布区域,江津区、长寿区以及忠县是中等级生态系统价值的主要分布区,重庆主城区和渝西地区是较低和低级生态系统服务的集中区域。
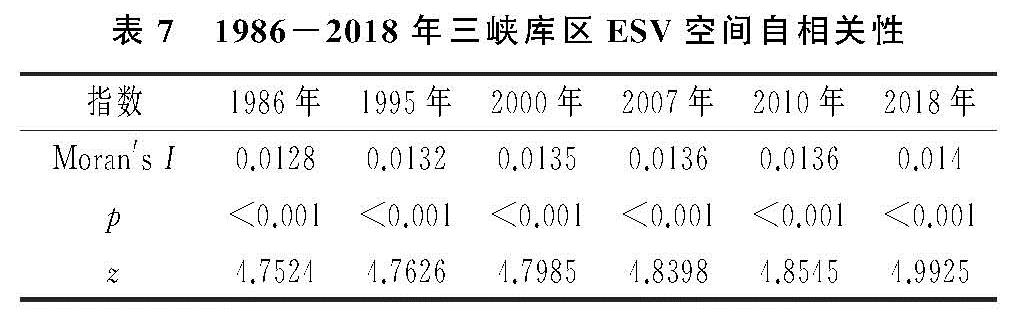
3.5 生态系统服务价值空间自相关分析
从表7空间自相关分析结果显示,研究区1986-2018年的6个时期的生态系统服务价值全局Moran's I值全部大于0,且p值全部低于0.001,说明三峡库区生态系统服务价值的空间分布呈现出一定的正向自相关性,同时在空间上呈现出显著的聚集性,其中高值区聚集明显,中低值区分区域相邻布局; 研究区1986-2018年6个时期的全局Moran's I指数总体上呈现上升的趋势,在1986年的值最低,为0.012 8,表明生态系统服务价值的空间自相关性持续增强,由于库区的建设与区域发展等因素促使三峡库区生态系统服务价值的空间聚集性持续加强。
表7 1986-2018年三峡库区ESV空间自相关性
3.6 土地利用程度对不同生态系统服务类型的影响分析
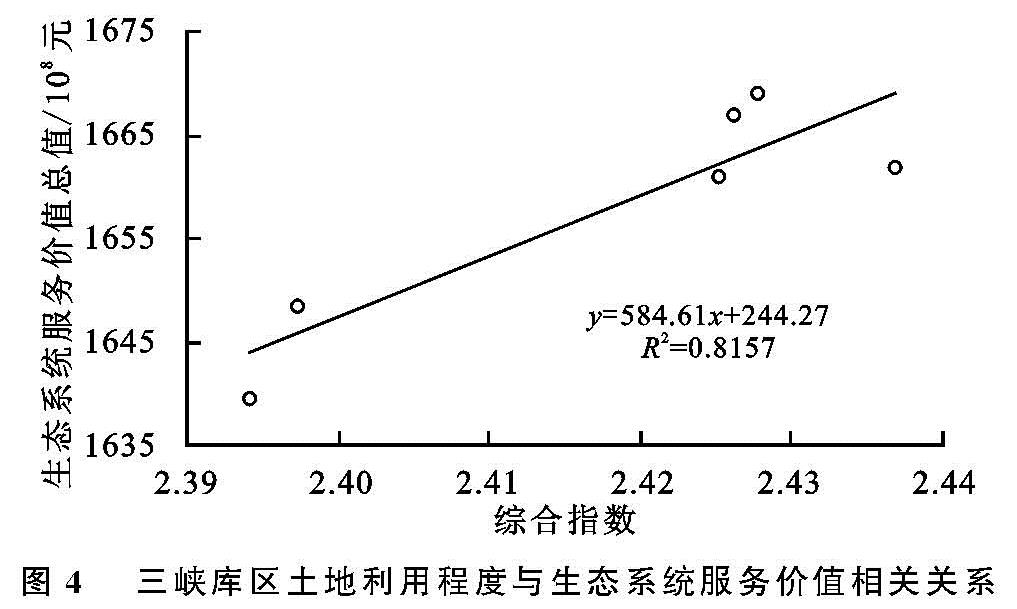
为了定量验证并进一步分析土地利用与生态系统服务价值的相关关系,本文计算出了研究区1986年、1995年、2000年、2007年、2010年以及2018年6个时期的土地利用程度综合指数分别为2.394 2,2.397 3,2.425 1,2.426 1,2.427 8,2.436 9,再核算研究区土地利用程度综合指数与生态系统服务价值的相关系数,同时在Origin 2017软件中生成二者关系的散点图,并进行线性拟合,结果见图4。
图4 三峡库区土地利用程度与生态系统服务价值相关关系
研究区土地利用程度综合指数与生态系统服务价值的相关系数为0.815 7,表示二者关系为强相关,且拟合曲线显示研究区生态系统服务价值随土地利用程度的增加呈上升趋势(图4),说明二者存在显著的正相关关系。
土地利用程度的加深表明人类对土地的劳动及资本投入增加,同时表明人类对生态系统干扰也越多。研究区土地利用程度的增加主要是由于库区社会经济的快速发展,催生了对大量建设用地的需求,而建设用地的主要来源是耕地和林地,使得这两种地类有所减少,但由于“天保工程”,“退耕还林”等生态保护政策的有效实施,又使得林地和耕地在大量转化为建设用地的同时有一定的补偿来源。另一方面,由于库区的三次蓄水,使得库区水平面有所上升,水域面积增加较为显著。在生态系统服务价值的构成中,林地和耕地的价值始终低于水域的价值,林地和耕地的减少导致生态系统服务价值的降低要低于水域增加的价值,最终使得研究区生态系统服务价值增加。
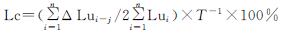 (2)
(2) (3)
(3)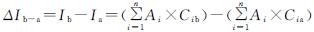 (5)
(5)
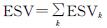 (7)
(7)