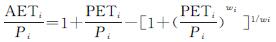3.1 2000-2015年哈长城市群土地覆被变化
对哈长城市群2000—2015年3个时期遥感影像进行处理,将土地覆被类型划分为建设用地、林地、草地、耕地、湿地和裸地(图1)。
研究区内的建设用地面积在15 a间持续增加,共增加1 462 km2,总体趋势表现为先快后慢。15 a间林地面积增加了1 527 km2,总体趋势持续增加,2010—2015年增加幅度大于2000—2010年。草地面积先增后减,共减少661 km2。2015年哈长城市群耕地面积占总面积的50.46%,15 a间耕地面积持续减少,共减少1 611 km2。湿地面积在2000—2015年先减后增,2000—2010年减少54 km2,2010—2015年有所恢复,增加117 km2,15 a间共增加63 km2。裸地包括采矿场、裸土、沙漠等,其面积在2000—2010年减少1 031 km2,2010—2015年增加了251 km2。
表1 2000-2015年哈长城市群土地覆被类型变化
3.2 生态系统服务的时空格局
哈长城市群2000—2015年土壤保持量空间分布格局见图2,具体而言,哈长城市群土壤保持量的多年平均值为21 107.53 t/km2,最低值在2015年(19 844.65 t/km2),最高值在2000年(21 934.19 t/km2)。从空间分布来看,哈长城市群的土壤保持能力呈东高西低态势,高值地区多分布在东南部; 2000—2010年土壤保持能力有所降低,降低的区域主要分布在黑龙江省的牡丹江市和哈尔滨市部分地区; 2000—2010年土壤保持能力增加的区域主要分布在吉林省的吉林市、长春市和辽源市部分地区。2010—2015年土壤保持能力有所降低,降低的区域主要分布在东南部的延边朝鲜族自治州、吉林市和长春市等。
哈长城市群2000—2015年生态系统碳储量空间分布格局见图3,具体而言,生态系统碳储量多年平均值为11 866.53 t/km2,最低值在2010年(11 837.88 t/km2),最高值在2000年(11 888.90 t/km2)。从空间分布来看,哈长城市群生态系统碳储量呈东部高西部低的态势,但15 a来其空间分布无明显差异,其高值地区多分布在西北部和东南部分地区; 2000—2010年区域生态系统碳储量有所降低,降低到区域主要为大庆市和松原市。2010—2015年区域生态系统碳储量有所增加,增加区域主要分布在黑龙江省西部的大部分地区; 吉林省各区域有所增加,但不明显。
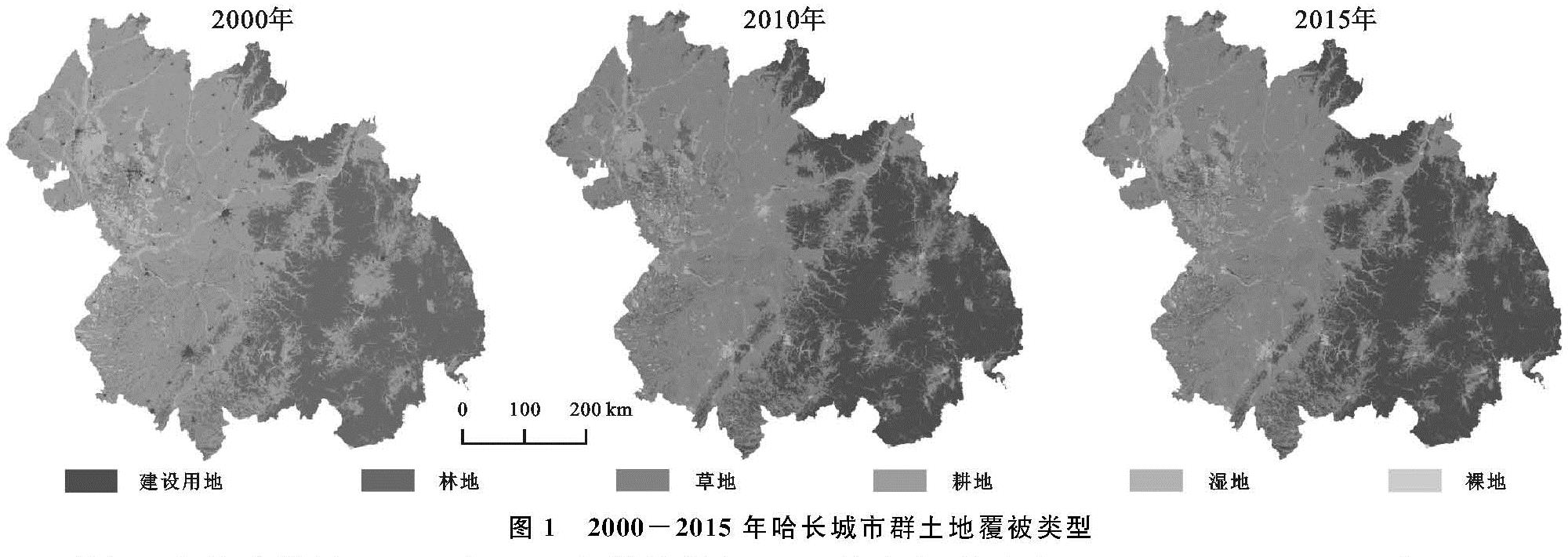
哈长城市群2000—2015年产水量空间分布格局见图4,具体而言,产水量多年平均值为118 055.46 m3/km2,最低值在2000年(92 952.47 m3/km2),最高值在2010年(133 045.84 m3/km2)。从空间分布来看,哈长城市群的产水量从东南部向西北部逐渐降低,高值区多分布在吉林省的东中部,黑龙江省的产水量相对于吉林省较低。由图4可知,2000—2010年的产水量呈增加趋势,增加的区域主要为吉林省大部分地区。2010—2015年的产水量略有降低,降低的区域主要为吉林省大部分地区,且降幅较明显; 2010—2015年增加的区域主要为黑龙江省大部分地区。
图2 2000-2015年哈长城市群土壤保持能力空间分布
图3 2000-2015年哈长城市群生态系统碳储量空间分布
图4 2000-2015年哈长城市群产水量空间分布
3.3 不同土地覆被类型生态系统服务的差异
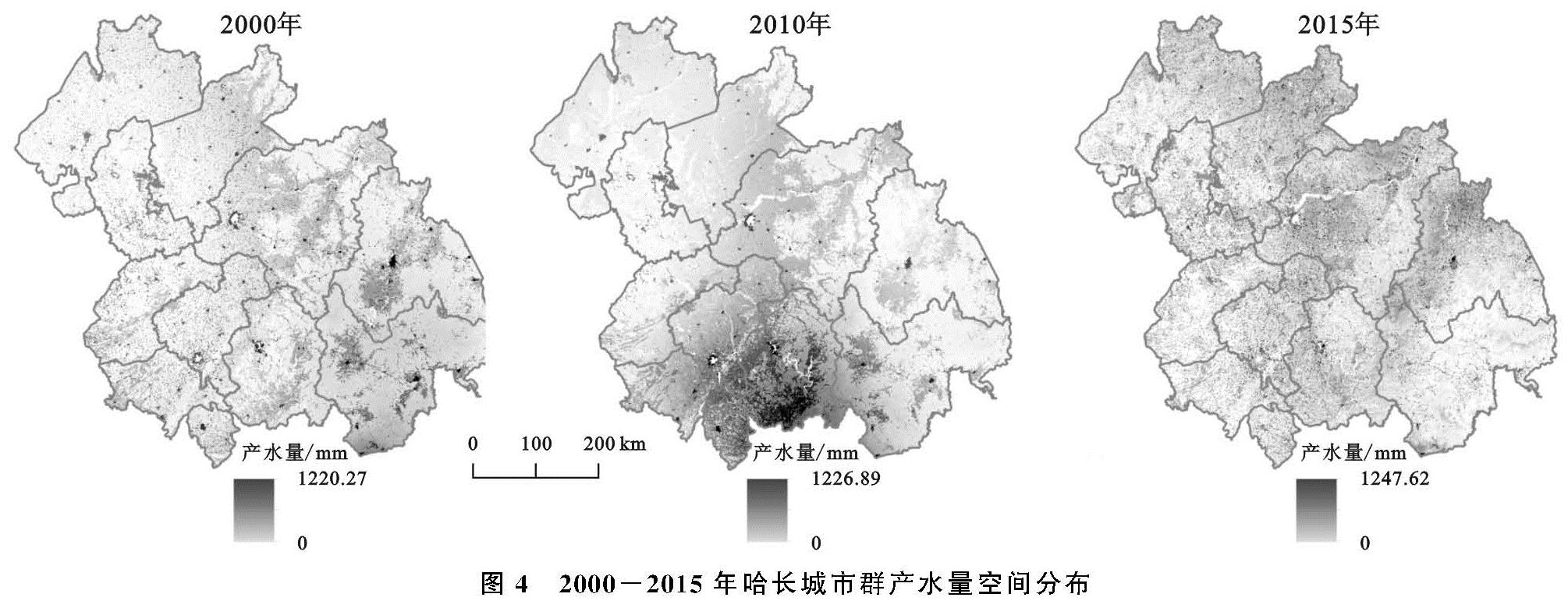
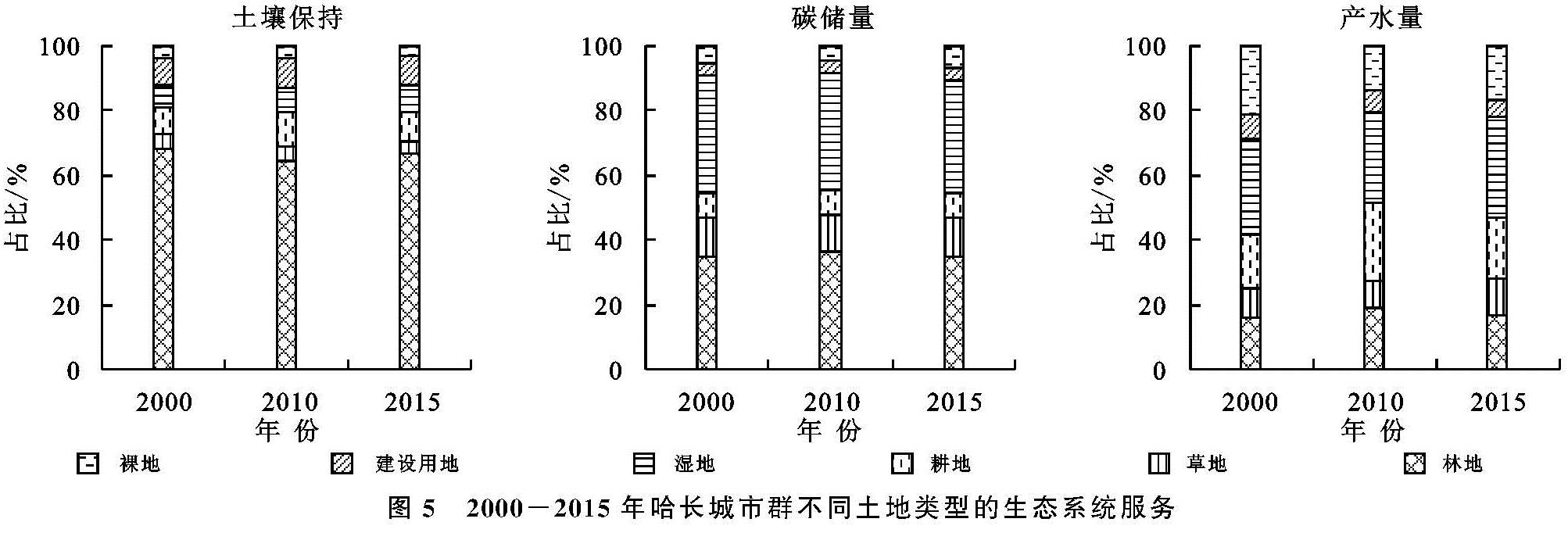
土地覆被对生态系统服务产生的影响,主要表现为同种土地覆被类型中不同生态系统服务间的差异和同一生态系统服务中不同土地覆被类型间的差异。本研究结合土地覆被数据,将哈长城市群3种生态系统服务的均值提取至各土地覆被类型,得出不同土地覆被类型下的生态系统服务(图5)。不同的土地覆被类型间,林地提供的土壤保持力最高,产水量最低; 草地和湿地提供的生态系统碳储量最高,土壤保持力最低; 耕地提供的产水量最高,生态系统碳储量最低; 建设用地提供的土壤保持力最高,生态系统碳储量最低; 裸地提供的产水量最高,土壤保持力最低。不同土地覆被类型提供的土壤保持能力从高至低依次为:林地>耕地>建设用地>湿地>草地>裸地; 生态系统碳储量:湿地>林地>草地>耕地>裸地>建设用地; 产水量:湿地>耕地>林地>裸地>草地>建设用地。
图5 2000-2015年哈长城市群不同土地类型的生态系统服务
3.4 生态系统服务的权衡与协同关系
3.4.1 生态系统服务关联关系
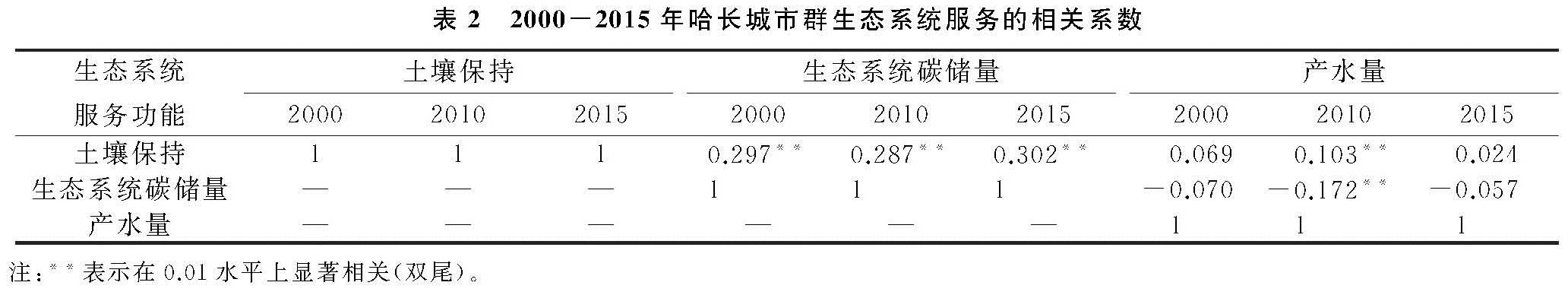
以30 m分辨率的栅格数据为基础,对哈长城市群土壤保持、生态系统碳储量和产水量3种生态系统服务进行样点采集,在研究区内获取均匀分布的点共29 205个,在SPSS软件支持下,对研究区3种生态系统服务做出相关性分析(表2)。其中哈长城市群的土壤保持与生态系统碳储量及土壤保持与产水量的相关系数均大于0,表征土壤保持与二者间均是协同关系; 生态系统碳储量与产水量的相关系数小于0,表明这组服务间呈现权衡关系。15 a来,随着哈长城市群植被覆盖度的增多,使土壤的抗冲蚀能力显著增强,即土壤保持能力显著提高; 植被覆盖度的增多同时促使其蒸腾耗水的需求不断提高,使得降水日渐成为主导土壤保持能力和产水量的首要因子。
表2 2000-2015年哈长城市群生态系统服务的相关系数
3.4.2 生态系统服务权衡协同度
在行政区范围内设置采样间隔点的距离为5 km,在研究区各市域内共获取77 412个均匀分布的点,基于哈长城市群的行政区划图,对哈长城市群2000—2015年生态系统服务变化量的栅格图进行样点采集,以估算3种生态系统服务间的权衡协同度(图6)。协同作用是哈长城市群3种生态系统服务间的主导关系,其中土壤保持—生态系统碳储量间的协同程度最高。南部吉林省境内的辽源市、吉林市、四平市在生态系统服务间关联关系中,土壤保持—生态系统碳储量的协同度最为明显,分别为9.12,8.21,7.10,辽源市的土壤保持—产水量的协同度高于其他各市,协同度为3.76,其他服务间的协同程度较低,主要是南部地区以林地为主,随着地表植被状况的改善,土壤保持量与生态系统碳储量显著提高。北部黑龙江省境内各市多以权衡为主,协同程度较低,其中齐齐哈尔市、牡丹江市、哈尔滨市土壤保持—生态系统碳储量的权衡度分别为2.60,1.89,1.75,主要原因是随着城市化进程的加快及重工业的快速发展,地表植被遭到破坏,再加上降水相对较少,导致对土壤保持量和生态系统碳储量的急剧下降。
图6 2000-2015年哈长城市群生态系统服务间权衡协同度分布