资助项目:广西科技厅重点研发项目(桂科AB17292051); 广西气象局重点项目(桂气科2019Z04)
第一作者:莫建飞(1978—),男(壮族),广西象州人,硕士,高级工程师,主要从事生态遥感监测与评估应用研究。E-mail:mojfei@163.com 通信作者:莫伟华(1968—),女,广西宾阳人,硕士,正研级高级工程师,主要从事生态气象和环境遥感研究。E-mail:mwh-0419@163.com
(1.广西壮族自治区气象科学研究所/国家卫星气象中心遥感应用试验基地, 南宁 530022; 2.广西壮族自治区生态气象和卫星遥感中心, 南宁 530022)
(1.Guangxi Institute of Meteorological Sciences/ Remote Sensing Application and Validation Base of National Satellite Meteorological Center, Nanning 530022, China; 2.Guangxi Ecological Meteorology and Satellite Remote Sensing Center, Nanning 530022, China)
karst ecosystem; evaluation of soil and water loss sensitivity; key indicators; spatial principal component analysis; 3S technology
为了能更合理地评价岩溶地区水土流失敏感性,以岩溶生态系统为研究对象,以修正通用土壤流失模型(RUSLE)为蓝本,通过引入石漠化因子,对RUSLE进行修正; 通过计算土壤侵蚀量、划分土壤侵蚀强度、水土流失关键因子影响评估,构建广西岩溶生态系统水土流失敏感性评估指标体系; 在此基础上,对比分析了空间叠加分析法、层次分析法、空间主成分分析法3种水土流失敏感性评价方法,利用遥感数据对多种评估结果进行验证与对比,选取最优评价方法对广西岩溶生态系统水土流失敏感性进行了评估。结果 表明:引入石漠化因子后的修正通用土壤流失模型(RUSLE)可以较合理地评价广西岩溶生态系统土壤流失空间分布状况; 广西岩溶生态系统水土流失敏感性因子作用大小顺序为:气象>石漠化>植被>土壤>地形>人类活动,土壤流失影响率与大多数敏感性因子和土壤侵蚀强度均呈一致变化趋势; 3种水土流失敏感性评价方法对比以主成分分析法(PCAEI)评估结果最优,层次分析法和加权综合评价法(AHPEI)次之,因子叠加分析法(CMSEI)较差。广西岩溶生态系统水土流失敏感性以轻度、中度、高度敏感区为主,水土流失敏感性整体中度偏重,水土流失敏感性强度由东部向西部、由南部向北部逐渐增强,敏感区主要分布在河池市、百色市,不敏感区主要分布在桂林市、崇左市。
In order to evaluate the sensitivity of soil and water loss in karst more reasonably, the soil loss model of karst ecosystem was established based on the modified RUSLE model, into which karst rocky desertification correction factor was introduced. Based on the ratio of soil erosion amount to soil erosion area under different levels of intensity, the assessment model of impact of key factors of soil and water loss in karst ecosystem was established, and the key indicators of soil and water loss sensitivity in karst ecosystem in Guangxi were analyzed. With the support of 3S technology, an assessment indicator system of soil and water loss sensitivity in karst ecosystem in Guangxi was established. Spatial superposition analysis method, analytic hierarchy process and spatial principal component analysis method were used to establish the assessment models of soil and water loss sensitivity in karst ecosystem in Guangxi. The remote sensing monitoring data of soil and water loss were used to verify and compare the evaluation models, and the optimal model was chosen to analyze the spatial differentiation characteristics of soil and water loss sensitivity in karst ecosystem in Guangxi. The results show that the key indicators of soil and water loss sensitivity in karst ecosystem in Guangxi follow the order meteorology>rocky desertification>vegetation>soil>topography>human activities; the PCAEI model is the best, followed by the AHPEI model and the CMSEI model comes to the next. From the grade of sensitivity, the sensitive areas to soil and water loss were mainly mild, moderate and highly sensitive areas. On the whole, the risk of soil and water loss sensitivity in karst ecosystem in Guangxi was severe. From the perspective of spatial distribution, the intensity of soil and water loss sensitivity gradually increased from the east to the west and from the south to the north in the karst areas, and sensitive areas mainly distributed in Hechi City and Baise City, while insensitive areas mainly distributed in Guilin City and Chongzuo City.
岩溶(喀斯特)生态系统具有特殊的生态功能定位,其与黄土、沙漠、高寒并列为我国的四大生态环境敏感脆弱区,水土流失是该地区最重要的生态环境问题。由水土流失所导致生态环境恶化对社会经济、生存环境和生态安全会产生诸多不利影响,严重制约了该地区经济持续稳定发展。因此,了解水土流失在岩溶生态系统发生的潜在可能性、关键影响因子及其时空分布格局,对国家和政府划定生态保护修复区、制定水土保持措施及政策、促进生态环境可持续发展具有重要意义。
合理的土壤侵蚀模型及代表性强的土壤侵蚀敏感性的因子,是实现水土流失敏感性客观准确评价的基础。目前国内外发展成熟的土壤侵蚀模型主要有经验统计模型[1]、物理成因模型[2-11]和分布式模型[12-13]。修正通用土壤流失模型(RUSLE)在岩溶地区的适用性已被验证[14-15],但由于岩溶生态区水土流失机理较复杂,土壤侵蚀的敏感性因子的区域适用性仍需深入研究。已有研究普遍证实强降水是引发岩溶地区水土流失的主要外营力[16-17],植被覆盖度与水土流失具有较高的相关性[18]。坡度也是影响岩溶生态区水土流失速率的重要因子,在相同坡体长度下水土流失速率与坡度呈正比[19]。岩溶生态区的原状土壤可蚀性低于其他常见土壤也是其水土流失的重要原因[20]。此外,不合理的土地开发利用方式导致的岩溶区水土资源空间调配失衡也会造成严重的水土流失[21-23]。石漠化是岩溶区的重要生态景观,水土流失会导致土壤生产力下降、土层变薄、加速土地石漠化,而石漠化加剧又会加重水土流失,形成恶性循环,但目前有关岩溶地区水土流失研究中鲜有考虑石漠化演变的影响。
目前,针对区域水土流失敏感性评估并没有普适性的评价方法,较常用的是GIS叠加分析法[24-31]和层次分析法[32-34]。但这些方法由于采用的敏感性指标不同所得的评估结果也存在较大差异。罗俊等[35]以碳酸盐岩区岩性的差异为主导指标,采用层次分析法评价了桂西北喀斯特地区水土流失敏感性,结果表明广西喀斯特地区以高度敏感和极敏感为主。凡非得等[36]利用降雨侵蚀力、地形起伏度、土壤类型、植被类型及土壤允许流失量为评价指标,选择GIS叠加分析方法对西南喀斯特区水土流失敏感性进行评价,结果表明广西喀斯特区水土流失以高度、轻度和极敏感区为主。因此,合理的评估方法对水土流失敏感性评价同样重要,但目前鲜见针对岩溶地区水土流失敏感性评价方法的适用性研究报道。
广西地处我国南疆,岩溶地貌分布广泛、石漠化现象突出。岩溶总面积833.4万hm2,占广西土地总面积35.1%,属亚热带季风气候,雨热同期,降水量丰沛,石漠化范围广,重度石漠化面积比例达13%。针对现有岩溶区土壤侵蚀敏感性指标研究中对石漠化演变考量较少,以及敏感性评估方法适用性比较研究不足的现状,本文以广西岩溶生态系统为研究对象,以修正通用土壤流失模型(RUSLE)为蓝本,通过引入石漠化因子,对RUSLE进行修正; 通过计算土壤侵蚀量、划分土壤侵蚀强度、分析水土流失关键影响因子,构建广西岩溶生态系统水土流失敏感性评估指标体系; 在此基础上,对比分析空间叠加分析法、层次分析法、空间主成分分析法3种水土流失敏感性评价方法,利用遥感数据对多种评估结果进行验证与对比,选取最优评价方法对广西岩溶生态系统水土流失敏感性进行评估,为岩溶区精准的生态保护空间定位提供技术支撑和水土流失的防治提供参考依据。
广西岩溶地区分布在北纬21°57'—26°06',东经105°02'—111°43',主要包括西江流域中上游的河池市、百色市、桂林市、崇左市、南宁市等老、少、边、山穷地区。地貌以峰丛洼地、峰林谷地、孤峰、残丘等类型为主,发育典型、分布广阔,占我国西南地区岩溶土地总面积的18.9%。地势由桂西北向桂东南倾斜,大部分出于云贵高原斜坡过渡地带,海拔为10~1 000多米。气候属亚热带季风气候,雨热同期,降水量时空分布不均。年平均气温17~23℃,年降雨1 100~1 500 mm,大雨、暴雨频率高,多集中在5—9月,大暴雨极易引发石漠化植被稀少地区的水土流失。土壤以石灰岩土为主,分为黑色、棕色、黄色和红色4类石灰土。黑色石灰土面积零星分布于石灰岩山地上部的岩缝和坡麓低洼地; 棕色石灰土多分布于石山下坡和山弄槽谷; 黄色石灰土多在海拔较高的石灰岩山地上; 红色石灰土主要分布在桂东北溶蚀平原区。植被类型较复杂,主要有热带雨林性常绿阔叶林、中亚热带典型常绿阔叶林、南亚热带季雨林化常绿阔叶林。总人口约占广西总人口的一半左右,经济发展相对落后,是广西重要生态保护、生态恢复治理和生态扶贫攻坚地区。
研究数据主要包括遥感植被指数、气象、石漠化等级、土地覆被类型、地形等资料,所有数据采用GIS转换为栅格格式,空间分辨率为250 m,投影方式为CGCS2 000_GK_Zone_18。
NDVI为NASA官网下载的陆地标准数据产品MOD13Q1,即全球250 m分辨率植被指数16 d合成产品,数据年限为2000—2018年。利用MRT(ModisReprojection Tool)对数据进行格式转换、图像拼接、投影转换、质量检验、NDVI子集提取预处理。采用最大值合成法(MVC),将MO13Q1产品数据合成为月尺度的NDVI数据。
气象数据为广西气象信息中心提供的1961—2018年广西91个气象站点的日降水量,6,12,24 h共3个时段灾害性强降水过程的降水量。
石漠化等级数据来自广西气象科学研究所。该数据利用美国Landsat和中国HJ,GF卫星遥感数据,通过分析不同等级石漠化区的光谱和纹理特征,建立石漠化等级识别模型,共划分潜在、轻度、中度、重度4个石漠化等级[37]。本研究使用1988年、2018年两个时相的石漠化等级数据。
利用中国GF卫星遥感数据,研判滑坡、崩塌的形状、纹理、色调、地形、地貌等特征,并结合野外实地调查情况,建立水土流失遥感解译模型,从遥感影像计算出岩溶区水土流失遥感监测信息。
使用地球系统科学数据共享网提供的中国1:25万土地覆被类型数据。
基础地理信息数据为广西气象信息中心提供的1:25万广西行政边界、行政区点、喀斯特区边界数据。广西数字高程模型(DEM)数据来自地理空间数据云,空间分辨率为30 m。
在GIS技术的支持下,以修正通用土壤侵蚀模型RUSLE模型为蓝本,建立考虑岩溶区石漠化等级影响的土壤流失方程,模型基本表达式如下[38]:
A=R·K·LS·C·P·M(1)
式中:A是土壤侵蚀模数[t/(km2·a)]; R是降雨侵蚀力因子[MJ·mm/(hm2·h·a)]; K是土壤可蚀性因子[t·hm2·h/(hm2·MJ·mm)]; LS是坡长坡度因子,无量纲; C是植被措施因子,无量纲; P是水土保持控制措施因子,无量纲; M是石漠化修正因子,无量纲。R,K,LS,C,P等因子计算方法参见《生态保护红线划定指南》。
石漠化等级因子M是岩溶区土壤侵蚀程度严重、土层流失殆尽、无土无林、基岩大面积裸露、土地退化的表现形式。考虑到岩溶地区土壤瘠薄且分布不连续,为了合理评价岩溶地区土壤流失状况,在石漠化等级划分评价基础上,在侵蚀模型中引入石漠化修正因子,以修正土壤侵蚀模型的评价结果。本文基于岩溶区石漠化等级数据,确定石漠化等级修正因子的赋值。其中,潜在石漠化赋值0.7,轻度石漠化赋值0.6,中度石漠化赋值0.5,重度石漠化赋值0.4,极重度石漠化赋值0.3。
岩溶生态系统水土流失是自然条件与人为活动等多种因素综合影响的自然灾害。为表示岩溶生态系统土壤侵蚀因子对土壤流失的影响程度,建立岩溶生态系统水土流失关键因子影响评价模型,公式如下[39]:
μij=(Aij/A)/(Sij/S)(2)
式中:μij为土壤侵蚀影响因子第i等级对土壤侵蚀第j等级的影响率; Aij为土壤侵蚀因子第i等级在土壤侵蚀第j等级下的土壤侵蚀量; A为土壤侵蚀总量; Sij为土壤侵蚀因子第i等级在土壤侵蚀第j等级下的面积; S为土壤侵蚀总面积。
基于GIS空间叠加分析法,利用各因子连乘并开方,建立岩溶生态系统水土流失敏感性指数,公式如下[40]:
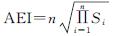 (3)
(3)
式中:AEI为水土流失敏感性指数; Si为水土流失第i因子敏感性等级值; n为因子个数。
基于层次分析法确定因子权重,采用加权综合评价法,建立岩溶生态系统水土流失敏感性指数,公式如下[41]:
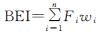 (4)
(4)
式中:BEI为水土流失敏感性指数; Fi为水土流失第i因子敏感性等级值; wi为第i因子权重值,由层次分析法确定; n为因子个数。
基于空间主成分分析法进行降维,将空间主成分与对应解释量的加权求和,建立岩溶生态系统水土流失敏感性指数,公式如下[42]:
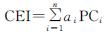 (5)
(5)
式中:CEI为水土流失敏感性指数; PCi为第i个主成分的解释量; ai为第i主成分解释量的贡献率。
基于GIS的信息量法,建立岩溶区水土流失敏感性评价验证模型,计算岩溶区水土流失敏感性评价信息量,公式如下[43]:
I(L,Xi)=ln(Ni/N)/(Si/S)(6)
式中:I(L,Xi)为因子Xi对水土流失发生事件(L)提供的信息量; N为研究区水土流失遥感监测单元总数; Ni为研究区内影响因子Xi在某二级指标水土流失遥感监测数; S为研究区单元总面积; Si为研究区内影响因子Xi在某二级指标的单元面积。水土流失敏感性评价信息量越大,说明水土流失敏感性区划结果与实际分布情况吻合度越较高。
基于岩溶区水土流失敏感性分区,采用加权综合评价法,建立研究区某区域的水土流失敏感性的危险性指数,公式如下[44]:
SEPDI=(M1+2M2+3M3+6M4+9M5)/(M1+M2+M3+M4+M5)(7)
式中:M1为不敏感区面积; M2为轻度敏感区面积; M3为中度敏感区面积; M4为高度敏感区面积; M5为极敏感区面积。SEPDI值为1~9,值越大表明该区域水土流失敏感性的危险度越大。
依据岩溶生态系统水土流失估算模型和各因子计算获取方法,计算广西岩溶生态系统水土流失总量,按照水利部颁布的《岩溶地区水土流失综合治理技术标准》(SL461—2009)进行水蚀强度分级。广西岩溶生态系统土壤侵蚀强度等级见图1。
广西岩溶生态系统平均土壤侵蚀模数为560.21 t/(km2·a),土壤侵蚀总量为3 691.06万 t/a。从侵蚀强度看,中度及以上土壤侵蚀量较大,土壤侵蚀模数分别为1 572.74万 t/a,826.49万 t/a,530.65万 t/a,394.08 t/a,所占岩溶区土壤侵蚀总量比例分别为42.61%,22.39%,14.38%,10.55%; 微度土壤侵蚀量最小,为14.74万t/a,仅占岩溶区土壤侵蚀总量比例为0.40%。从侵蚀面积上看,微度、轻度、中度土壤侵蚀面积较大,土壤侵蚀面积分别为15 539.25,24 595.13,19 877.68 km2,所占岩溶区总面积比例分别为23.58%,37.33%,30.17%; 剧烈土壤侵蚀面积最小,为433.44 km2,占岩溶区总面积比例为0.66%。
广西岩溶区水土流失的形成和发生是一个极其复杂的过程,从影响因素来看,是气象、地形、土壤、植被、石漠化、工程措施等多种因子综合作用的结果。气象因子根据广西不同时段极端降水事件[45]、降雨侵蚀力[46]的时空分布特征,将6,12,24 h极端降水量指标分5级:≤100 mm,100~150 mm,150~200 mm,200~250 mm,>250 mm; 将降雨侵蚀力指标分5级:≤5 000 MJ·mm/(hm2·h·a),5 000~6 000 MJ·mm/(hm2·h·a),6 000~7 000 MJ·mm/(hm2·h·a),7 000~8 000 MJ·mm/(hm2·h·a),>8 000 MJ·mm/(hm2·h·a)。地形、土壤、植被因子按照《生态保护红线划定指南》结合广西实际情况分级,其中,地形起伏度指标分5级:≤50 m,50~100 m,100~150 m,150~200 m,>200 m; 土壤可蚀性指标分5级:≤0.012,0.012~0.014,0.014~0.016,0.016~0.018,>0.018; 植被覆盖度指标分5级:≤0.2,0.2~0.4,0.4~0.6,0.6~0.7,>0.7。石漠化因子则根据广西石漠化等级数据划分为:潜在、轻度、中度、重度。人类活动因子根据土地利用方式划分为:林地、灌木林、草地、湿地、水田、旱地、园地、居住地、工矿用地、交通用地、裸地。采用岩溶生态系统水土流失关键因子影响评价模型,计算广西不同影响因子等级对不同土壤侵蚀强度的影响率(表1)。
从气象因子看,气象条件对土壤侵蚀的影响表现为:6 h极端降水量影响率均值(4.63)>12 h极端降水量影响率均值(4.57)>24 h极端降水量影响率均值(4.50)>降雨侵蚀力影响率均值(4.35); 降水量各等级指标对土壤侵蚀的影响随土壤侵蚀强度均呈递增趋势,其中,极端降水量(>250 mm)和降雨侵蚀力[>8 000 MJ·mm/(hm2·h·a)]对土壤侵蚀量的总影响率最大,6,12,24 h极端降水量的总影响率分别为29.72,29.41,28.15,降雨侵蚀力的总影响率为28.12; 气象条件各等级指标对土壤侵蚀中度及以下的影响随降水量的增加基本不变,而强烈及以上的影响随降水量的增加呈递增趋势,其中,极端降水量(>250 mm)和降雨侵蚀力[>8 000 MJ·mm/(hm2·h·a)]的剧烈侵蚀对土壤侵蚀的影响最大,6,12,24 h极端降水量的影响率分别为17.00,16.84,15.77,降雨侵蚀力的影响率为15.55。
从地形因子看,地形起伏度对土壤侵蚀的影响表现为:地形起伏度各等级指标对土壤侵蚀的影响随土壤侵蚀强度均呈递增趋势,其中,地形起伏度(>200 m)对土壤侵蚀量的影响率最大,影响率合计为29.71; 地形起伏度各等级指标对土壤侵蚀各强度的影响随地形起伏度的增加呈增加趋势,其中,地形起伏度(>200 m)的剧烈侵蚀对土壤侵蚀的影响最大,影响率为17.17,地形起伏度(150~200 m)的剧烈侵蚀次之,影响率为13.89,地形起伏度(<150 m),影响率差别不大。
从土壤因子看,土壤可蚀性对土壤侵蚀的影响表现为:土壤可蚀性各等级指标对土壤侵蚀的影响随土壤侵蚀强度均呈递增趋势,其中,土壤可蚀性(>0.018)对土壤侵蚀量的影响率最大,影响率合计为27.29; 土壤可蚀性各等级指标对土壤侵蚀各强度的影响,除强烈侵蚀随土壤可蚀性的增加呈递减趋势,其余侵蚀等级呈增加趋势,其中,土壤可蚀性(>0.018)的剧烈侵蚀对土壤侵蚀的影响最大,影响率为14.59,土壤可蚀性(0.016~0.018)的剧烈侵蚀次之,影响率为14.36,土壤可蚀性(<0.016),影响率差别不大。
从植被因子看,植被覆盖度对土壤侵蚀的影响表现为:植被覆盖度各等级指标对土壤侵蚀的影响随土壤侵蚀强度均呈递增趋势,其中,植被覆盖度(≤0.2)对土壤侵蚀量的影响率最大,影响率合计为28.47; 植被覆盖度各等级指标对土壤侵蚀中度及以下的影响随植被覆盖的增加呈增加趋势,而强烈及以上的影响随植被覆盖度的增加呈递减趋势,其中,植被覆盖度(≤0.2)的剧烈侵蚀对土壤侵蚀的影响最大,影响率为14.68,植被覆盖度(0.2~0.4)的剧烈侵蚀次之,影响率为14.60,植被覆盖度(>0.4),影响率差别不大。
从石漠化因子看,石漠化等级对土壤侵蚀的影响表现为:1988年石漠化等级影响率均值(4.52)>2018年石漠化等级影响率均值(4.44); 1988年、2018年石漠化等级指标对土壤侵蚀的影响均随土壤侵蚀强度呈递增趋势,其中,1988年重度石漠化等级对土壤侵蚀量的影响率最大,影响率合计分别为27.33,2018年潜在石漠化等级对土壤侵蚀量的影响率最大,影响率合计分别为27.53; 1988年石漠化各等级指标对土壤侵蚀中度及以下的影响随石漠化强度的增加变化不大,而强烈及以上的影响随石漠化强度的增加呈递增趋势,其中,重度石漠化等级的剧烈侵蚀对土壤侵蚀的影响最大,影响率为14.66,2018年石漠化各等级指标对土壤侵蚀中度及以下的影响随石漠化强度的增加变化也不大,而强烈及以上的影响随石漠化强度的增加呈递减趋势,其中,潜在石漠化等级的剧烈侵蚀对土壤侵蚀的影响最大,影响率为14.78。
从人类活动因子看,土地利用方式对土壤侵蚀的影响表现为:工矿用地的剧烈侵蚀对土壤侵蚀的影响最大,影响率为15.85,灌木林的剧烈侵蚀次之,影响率为14.94,之后旱地、裸地的剧烈侵蚀,影响率分别为14.47,14.44。
从综合因子看,各影响因子指标对土壤侵蚀的影响表现为:因子影响率,气象(4.51)>石漠化(4.48)>植被(4.44)>土壤(4.36)>地形(4.18)>人类活动(4.12); 指标影响率,6 h极端降水量(>250 mm)影响率最大,为29.72,其次为地形起伏度(>200 m),为29.71,之后为12 h极端降水量(>250 mm),为29.00,地形起伏度(≤50 m)影响率最小,为20.55; 等级强度影响率,地形起伏度(>200 m)的剧烈侵蚀影响最大,为17.17,6 h极端降水量(>250 mm)的剧烈侵蚀次之,为17.00,之后为12 h极端降水量(>250 mm)的剧烈侵蚀,为16.84。
岩溶生态系统水土流失在岩溶背景环境和人类活动的影响下,造成了土壤量流失和土壤质量下降。岩溶环境的脆弱性和人为的破坏性,决定了岩溶生态系统水土流失的敏感性。基于岩溶生态系统水土流失关键指标影响评价,从自然和人为因素,考虑选取降水量、地形起伏度、土壤可蚀性、植被覆盖度、石漠化演变趋势、土地利用方式等为评估指标,构建广西岩溶生态系统水土流失敏感性指标体系(表2)。
根据岩溶水土流失关键指标影响评价,将各因子对水土流失敏感性划分为不敏感、轻度敏感、中度敏感、高度敏感、极敏感,规定量值从1—9敏感性依次增加,获得广西岩溶生态系统水土流失敏感性指数值。从气象影响因子可知,水土流失量与高强度、大暴雨、特大暴雨等大侵蚀降水量密切关系,降水强度越高、降水总量越大,其水土流失量越大,水土流失敏感性越高。从石漠化影响因子可知,不同阶段石漠化等级对水土流失的敏感性呈现出较大差异。在石漠化形成初级,岩溶区还有土地覆盖,即“有土可流”,此时水土流失量随石漠化等级强度呈递增趋势。石漠化等级越高,水土流失敏感性越高。在石漠化扩张阶段,岩溶区已基本无土地覆盖,即“无土可流”,此时水土流失量随石漠化等级强度呈递减趋势。但这并不表明石漠化等级强度越高,水土流失敏感性越低。因此,可以采用石漠化演变趋势作为石漠化因子对水土流失敏感性评价指标。石漠化演变趋势变得越差,水土流失敏感性越高。基于GIS技术,将不同阶段的石漠化等级进行空间叠加,分析石漠化演变趋势,划分为变好、变较好、不变、变较差、变差5个等级,其中,变好:轻度变潜在、中度变潜在、重度变潜在; 变较好:中度变轻度、重度变轻度、重度变中度; 不变:潜在变潜在、轻度变轻度、中度变中度、重度变重度; 变较差:潜在变轻度、潜在变中度、轻度变中度; 变差:潜在变重度、轻度变重度、中度变重度。人类活动对水土流失的影响主要体现在土地利用方式的变化。土地利用方式越不合理越容易造成水土流失。根据土地利用方式对土壤侵蚀的影响率,将湿地、居住地划分为不敏感区; 林地、灌木林地为轻度敏感区; 草地和水田为中度敏感区; 旱地、园地为高度敏感区; 交通用地、工矿用地和裸地为极敏感区。
基于岩溶生态系统水土流失敏感性指标体系,耦合气象、地形、土壤、植被、土地利用方式等自然因素和人为因素对水土流失敏感性的相互影响作用,建立广西岩溶生态系统水土流失敏感性评估模型。
考虑选择降雨侵蚀力、土壤可蚀性、地形起伏度、植被覆盖度、土地利用方式,采用GIS叠加分析法,建立广西岩溶生态系统水土流失敏感性评估模型,公式如下:
CMSEI=(R1·K1·T1·C1·P1)5(8)
式中:CMSEI为水土流失敏感性指数; R1,K1,T1,C1,P1分别为降雨侵蚀力、土壤可蚀性、地形起伏度、植被覆盖度、土地利用方式敏感性等级值。
考虑选择极端降水事件、土壤可蚀性、地形起伏度、植被覆盖度、石漠化演变趋势、土地利用方式为评估指标,采用层次分析法,基于1—9标度法,通过两两对比判定水土流失敏感性指标的重要性,建立广西岩溶生态系统水土流失敏感性指标矩阵(表3)。
通过判断矩阵计算最大特征根λmax为6.120 5,特征向量为(2.345 7,0.395 2,0.620 6,0.936 8,1.537 2,0.276 0),CR=0.019(<0.1),满足一致性检验,归一化得权重为(0.382 9,0.064 5,0.101 4,0.153 4,0.253 1,0.044 7)。采用加权综合评价法,建立广西岩溶生态系统水土流失敏感性评估模型,公式如下:
AHPEI=0.3829R2+0.0645T1+0.1014K1+0.1534C1+0.2531M1+0.0447P1(9)
式中:AHPEI为水土流失敏感性指数; R2为极端降水量; M1为石漠化演变趋势。
同样考虑选择极端降水事件、土壤可蚀性、地形起伏度、植被覆盖度、石漠化演变趋势、土地利用方式为评估指标,采用空间主成分分析法进行指标集成(表4)。
空间主成分分析结果显示,按照结果选取前4个主成分即可达到主成分分析85%累计贡献率的统计要求,选取前5个主成分即可达到对整体评价的98.64%贡献,说明前5个主成分已经能够很好地反映岩溶区水土流失敏感性状况。进一步分析各主成分,第1主成分的贡献率为43.29%,在土壤可蚀性上的特征向量值较大,可以概括为土壤敏感性因子; 第2主成分的贡献为20.92%,在石漠化演变趋势上的特征向量值较大,概括为石漠化敏感性因子; 第3主成分的贡献率为19.18%,在地形起伏度上的特征向量值较大,概括为地形敏感性因子; 第4主成分的贡献率为9.47%,在土地利用方式上的特征向量值较大,概括为人为活动敏感性因子; 第5主成分的贡献率为5.78%,在极端降水事件上特征向量值较大,概括为气象敏感性因子。综合考虑各个主成分的贡献因子,地形、土壤、石漠化、气象、人为活动5个因子是影响岩溶区水土流失的主要因素,这与研究区的实际也是相符的。根据空间主成分分析结果,建立广西岩溶水土流失敏感性评估模型,公式如下:
PCAEI=0.4329PC1+0.2092PC2+0.1918PC3+0.0947PC4+0.0578PC5(10)
式中:PCAEI为水土流失敏感性指数; PC1,PC2,PC3,PC4,PC5分别为第1—5主成分。
根据岩溶生态系统水土流失敏感性评估模型,采用GIS技术,获得空间分辨率为250 m的广西岩溶生态系统敏感性综合指数分布,并利用自然断点法将广西岩溶生态系统水土流失敏感性划分为不敏感、轻度敏感、中度敏感、高度敏感和极敏感5级敏感区。为进一步验证评估模型研究结果的合理性,根据水土流失遥感监测数据,采用基于GIS的信息量法,计算广西岩溶区水土流失敏感性等级信息量(表5)。
验证对比结果显示,广西岩溶生态系统水土流失敏感性信息量均随敏感性等级强度的增强而增加; 进一步分析各敏感性等级强度信息量,CMSEI模型的高度及以上敏感性等级信息量为正值,而AHPEI模型和PCAEI模型的中度及以上敏感性等级信息量为正值,说明AHPEI模型和PCAEI模型的敏感性评价优于CMSEI模型; PCAEI模型的中度及以上敏感性等级信息量均大于AHPEI模型的中度及以上敏感性等级信息量,且PCAEI模型的极敏感信息量最大(0.85),而PCAEI模型的轻度与不敏感性等级信息量均小于AHPEI模型的轻度与不敏感性等级信息量,且PCAEI模型的不敏感性信息量最小(-2.27),说明PCAEI模型的不敏感性评价也优于AHPEI模型。因此,通过综合的对比分析,广西岩溶生态系统水土流失敏感性评估模型,PCAEI模型最优,其次为AHPEI模型,之后为CMSEI模型。
基于水土流失敏感性评估最优的PCAEI模型,统计广西岩溶区各地级市水土流失不同等级敏感区域面积及其比例,计算各地市水土流失敏感性SEPEI值(表6)。从敏感性等级看,广西岩溶生态系统水土流失敏感性主要以轻度、中度、高度敏感区为主,占岩溶区总面积的74.01%,其中,轻度敏感区面积比例最大,为29.07%,极敏感区面积比例最小,为10.56%; 从敏感性的危险性看,广西岩溶生态系统水土流失敏感性整体中度偏重,其中,河池市的敏感性的危险性最高,其次为百色市,之后为南宁市; 从空间分布格局看,极敏感区主要分布在河池市南部和西部、百色市东北部、南宁市北部,分别占总岩溶区总面积的5.68%,2.28%,0.84%,该区域极端降水强度大、地形起伏度大、土壤可蚀性强、植被覆盖度小、石漠化改善状况差,且受人类活动干扰较大; 高度敏感区主要分布在河池市南部、百色市南部、崇州市北部,分别占总岩溶区总面积的7.45%,4.87%,2.21%,该区域极端降水强度较大、地形起伏度较大、土壤可蚀性较强、植被覆盖度较小、石漠化改善状况较差,且受人类活动干扰大; 中度敏感区主要分布在河池市东南部和北部、百色市南部、崇左市北部,分别占岩溶区总面积的8.39%,5.42%,4.32%,该区域极端降水强度较大、地形起伏度较大,但石漠化演变趋势稳定、土壤可蚀性一般、人类活动干扰较小; 轻度敏感区主要分布在河池市东北部、崇左市中部、桂林市大部,分别占岩溶区总面积的5.95%,4.48%,4.47%,该区域极端降水强度较小、地形起伏度较小、土壤可蚀性较小,但植被覆盖度较高、石漠化演变趋势良好、受人类活动干扰较也较小; 不敏感区主要分布在崇左市南部、桂林市东北部、河池市东部,分别占岩溶区总面积的3.37%,2.76%,2.39%,该区域极端降水强度小、地形起伏度小、土壤可蚀性小、植被覆盖度高、石漠化改善状况最好。从总体看,广西岩溶生态系统水土流失敏感性强度由岩溶区的东部向西部、由南部向北部逐渐增强; 敏感区主要分布在河池市、百色市,分别占岩溶区总面积27.47%,15.71%(图2)。
石漠化是岩溶区的重要生态景观,水土流失和石漠化发展存在着恶性循环,但目前有关岩溶地区水土流失研究中鲜有考虑石漠化演变的影响。李阳兵等[47]研究指出的岩溶区必须基于生态退化的现状来评价土壤侵蚀敏感性,凡非得等[36]也提出未来岩溶区应该结合石漠化及其变化过程数据来研究水土流失敏感性。本研究在水土流失敏感性因子中增加了石漠化等级变化作为影响因子,较充分考虑了石漠化等级变化对水土流失的影响:石漠化程度加剧,说明在自然或人为因素影响下,植被生态环境变差,水土流失敏感性较高; 石漠化程度变化较小或不变,说明自然或人为因素对岩溶生态系统影响较小,生态平衡维持得较好,但这种平衡是基于生态保护条件下,脆弱且容易打破,水土流失敏感性中等; 石漠化程度变轻,说明自然或人为因素对岩溶生态系统的作用是有利的,植被生态环境变好,水土流失不敏感。本研究发现,石漠化等级变化指标在6种水土流失敏感性因子中,作用大小仅次于气象因子。引入石漠化因子后的修正通用土壤流失模型(RUSLE)可以较合理地评价广西岩溶生态系统土壤流失空间分布状况,有效地改进了岩溶区不考虑石漠化或只考虑石漠化等级作为水土流失敏感性评估指标,解决了岩溶区水土流失“无土可流”问题,使岩溶生态系统水土流失敏感性评价更加合理。
本研究对比分析空间叠加分析法、层次分析法、空间主成分分析法3种水土流失敏感性评价方法,发现以极端降水、土壤可蚀性、地形起伏度、植被覆盖度、石漠化演变趋势、土地利用方式为评估指标的主成分分析法(PCAEI)评估结果最优。可能原因是PCAEI的气象评估指标考虑了极端降水事件对水土流失的影响,而岩溶区土壤浅薄且分布不连续,在地形起伏度较大、植被覆盖度较低的下垫面,高强度的极端降水对地表具有很强的冲刷能力,极易造成水土流失,这与蔡雄飞等[48]的结论是一致的。岩溶生态系统水土流失敏感性各关键指标的影响程度存在差异,采用空间主成分分析法将多个影响因子通过正交线性变换来选出少数重要指标进行多维数据集成的PCAEI法,改进了不考虑因子重要性的CMSEI法及采用专家打分法与层次分析法相结合主观性的AHPEI法,使岩溶生态水土流失敏感性评估更加适用与客观。此外,基于较高空间分辨率的石漠化等级评价数据,采用“3S”技术和空间主成分分析法开展岩溶生态系统水土流失敏感性评价,可以为区域生态保护空间精准定位提供技术支撑,对生态系统环境敏感性评估方法,具有较好的应用价值。进一步地研究采用更高分辨率的卫星遥感影像数据获取NDVI、石漠化数据,计算更高精度的植被覆盖、石漠化演变趋势数据,为岩溶区域更客观化、精准化、定量化的生态空间划定提供技术支撑,为岩溶区植被生态恢复及水土流失的防治提供参考依据。
(1)引入石漠化因子后的修正通用土壤流失模型(RUSLE)可以较合理地评价广西岩溶生态系统土壤流失空间分布状况。广西岩溶生态系统侵蚀强度以中度及以上为主,合计占比89.93%,其中中度侵蚀占比最大(42.61%),微度土壤侵蚀量占比最小(0.40%)。侵蚀面积以中度及以下为主,合计占比91.08%,其中轻度占比最大(37.33%),剧烈侵蚀面积占比最小(0.66%)。
(2)水土流失敏感性是自然因素与人为因素共同作用的结果,对比分析了气象、土壤、植被、石漠化、地形和人类活动共6种水土流失敏感性因子,作用大小顺序为:气象>石漠化>植被>土壤>地形>人类活动。水土流失影响率与大多数敏感性因子和土壤侵蚀强度均呈一致变化趋势,即随着敏感性因子或土壤侵蚀强度的增大,水土流失影响率增大。对比分析各种因子,6 h极端降水量(>250 mm)对各等级土壤侵蚀的综合影响率最大,地形起伏度(≤50 m)影响率最小。
(3)对比分析空间叠加分析法、层次分析法、空间主成分分析法3种水土流失敏感性评价方法,以极端降水、土壤可蚀性、地形起伏度、植被覆盖度、石漠化演变趋势、土地利用方式为评估指标的主成分分析法(PCAEI)评估结果最优,层次分析法和加权综合评价法(AHPEI)次之,因子叠加分析法(CMSEI)评估结果较差。
(4)利用优选的主成分分析法(PCAEI)分析水土流失敏感性空间分异特征,广西岩溶生态系统水土流失敏感性主要以轻度、中度、高度敏感区为主,水土流失敏感性整体中度偏重。水土流失敏感性强度由东部向西部、由南部向北部逐渐增强,敏感区主要分布在河池市、百色市,不敏感区主要分布在桂林市、崇左市。敏感区具有极端降水强度较大、地形起伏度较大、土壤可蚀性较强、植被覆盖度较小、石漠化改善状况较差及受人类活动干扰大的共同的特征。