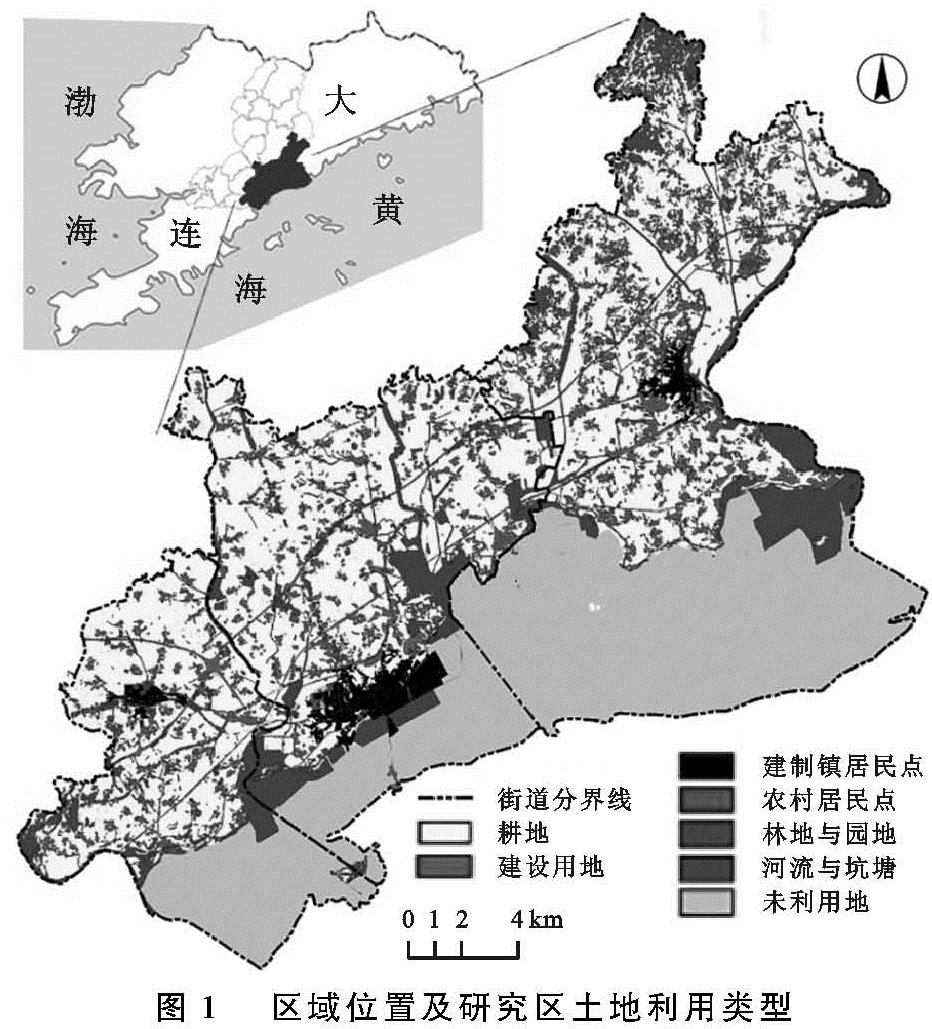
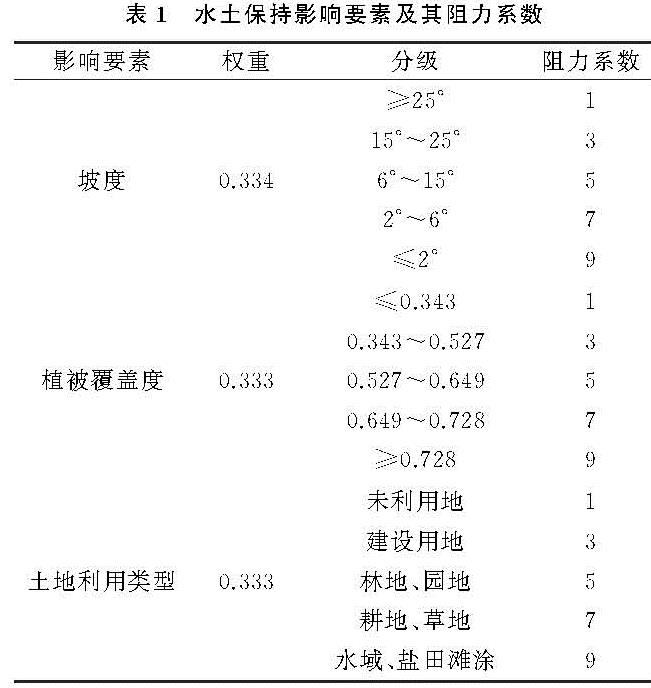
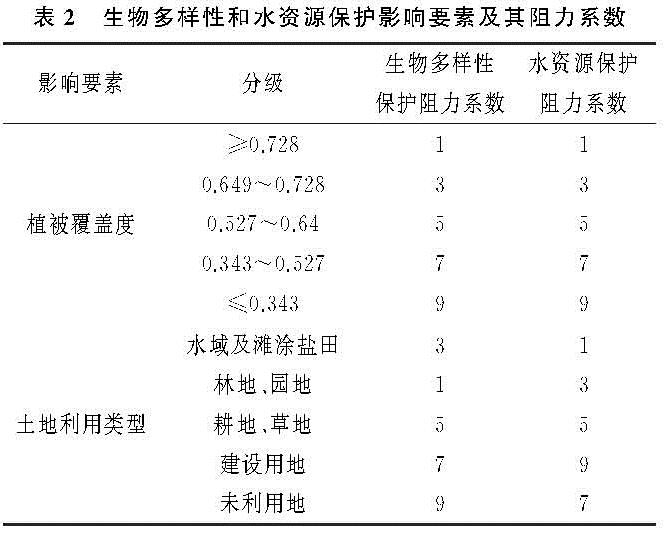
3.1 研究区单因子景观安全格局分析
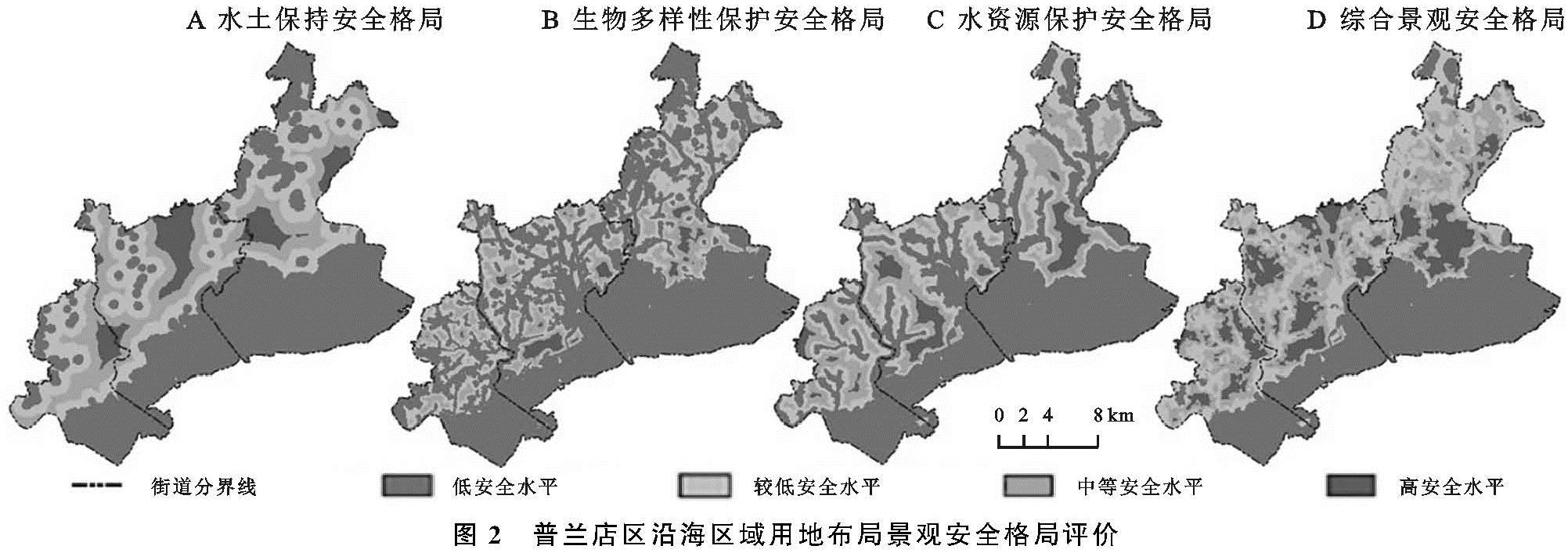
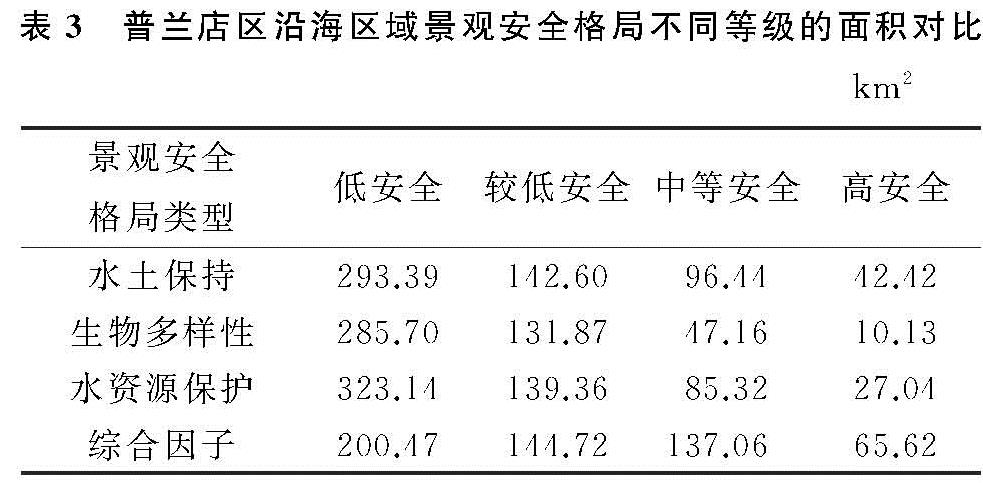
依据景观安全格局理论与方法,以阻力值发生明显突变处作为阈值,本文采用自然断点法将最小累计阻力值重新分为4类,得出研究区的水土保持、生物多样性保护和水资源保护的单因子景观安全格局和综合景观安全格局,其结果见图2和表3。
单因子水土保持安全格局从低到高4个等级分区分别占区域总面积的51.04%,24.81%,16.77%,7.38%。从图2A可知,水土保持低安全水平区域集中在南部及东南大片的盐田与滩涂,以及城子坦街道北部和西部山区、皮口街道中南部、杨树房街道西部等呈块状或带状集聚,坡度相对较大、植被覆盖度小、岩石风化大的区域。除了盐田滩涂外,这些区域大多为沿海丘陵区、具有一定坡度,植被覆盖度低,土地利用类型为抗侵蚀力较弱的耕地、草地、园地及建设用地等,水土流失非常容易发生。较低安全水平区域处于低安全水平区的外层,主要分布在城子坦街道东北部、皮口街道西北部和杨树房街道北部,水土流失容易发生。中等安全水平区集中在城子坦街道中部、皮口街道西北部和中南部、杨树房中北部,地势相对平坦,不易发生水土流失等地质灾害,比较适合农村居民点用地布局。高安全水平区域主要分布在沿海平原区的城子坦街道中部、皮口中南部和中东部,是比较理想的农村居民点的栖息地。为提升整体水土保持安全水平,丘陵山区继续采取封山育林、荒山造林、退耕还林等措施提高植被覆盖度,改善地表径流,减少水土流失。
生物多样性保护安全格局从低到高4个等级的安全水平区域面积分别占区域总面积的67.09%,22.94%,8.21%和1.76%。低安全水平区域主要位于东部城子坦街道、碧流河社区和金山村、西部杨树房社区和清水河村、南部盐田和滩涂、北部城子坦街道郑沟村和下吴村、中部皮口街道的大岭和赞子河村等区域。这些区域除了南部盐田和滩涂外,水涵养林、水土保持林、沿海护路林和护岸林等植被覆盖率高、生态环境优越,是生物生存与繁衍的栖息地,生物多样性也丰富。但随着新农村建设和城镇一体化发展,该区生态环境因人类高强度活动极易遭到破坏,进而影响到生物多样性。生物多样性的较低安全水平区域为低安全水平区的生物栖息地提供了缓冲区,集中在城子坦街道中东部、皮口街道的西北部和杨树房街道北部。中度安全和高安全区域集中分布在城子坦街道中南部、皮口街道东南部和中南部、杨树房街道中北部,该区域以农用地和建设用地为主要土地利用类型,比较满足人类生产生活需要的栖息地标准,因此可以作为农村居民点的布局。
水资源保护安全格局从低到高4个等级的安全水平区域面积分别占区域总面积的56.21%,24.24%,14.84%和4.71%。低安全水平区域集中分布在研究区的东部、南部和西南部、皮口街道中南部和西部以及街道行政分界处,因碧流河、清水河和大沙河自北向南穿过研究区最终汇入黄海,也是街道的行政分界线。该区域均处于河流下游,水体面积占其“源”地的20.59%,且生物多样性丰富,但河流洪涝引发的自然灾害,不适应人类活动景观的分布与建设。水资源安全保护较低安全水平区域以低安全水平为中心,向外依次为中等安全水平和高安全水平区域。中等安全和高安全区域集中分布在城子坦街道中南部、皮口街道中南部、杨树房街道西北部,该区域以建设用地和农用地为主要土地利用类型,比较适应农村居民点的布局。随水资源保护安全等级的提高,造成水资源安全能力的逐渐减弱。此外,研究区城子坦街道东部碧流河、皮口街道中部赞子河、穿越皮口街道与杨树房街道的清水河、杨树房街道西部大沙河和大高屯水库等区域是研究区重要的饮用水水源地,禁止非法占用河道、采砂采矿等行为,严禁向水体及河道排污,实施农村生活污水处理工程以及推进农业生产清洁化,严格保证饮用水源的生态安全。
3.2 研究区综合景观安全格局分析
利用水土保持、生物多样性保护和水资源保护等3种安全格局按照同等重要性进行叠加并利用自然断点分析法重分类后,得到普兰店沿海区域农村居民点综合景观安全格局(图2D和表3)。结果表明,综合景观安全格局中高安全区与中等安全区面积合计为202.68 km2,面积比重为36.99%,主要分布于城子坦街道中南部和东北部、皮口街道中南部和东北部、杨树房街道东部等区域,这与该区域以建设用地和农用地有很大关联。低与较低安全区面积合计为345.18 km2,面积比重为63.01%,主要分布于南部沿海滩涂和盐田、城子坦街道东部和西北部、皮口街道西北部和中东部、杨树房街道西部等区域,该区域大都处于低山和低丘缓坡区或河谷地带,林地资源分布相对集中,生物多样性和水资源安全保护功能突出。这种分布态势与研究区地形地貌特征较为一致。
表3 普兰店区沿海区域景观安全格局不同等级的面积对比km2
3.3 研究区农村居民点用地布局优化方式及策略
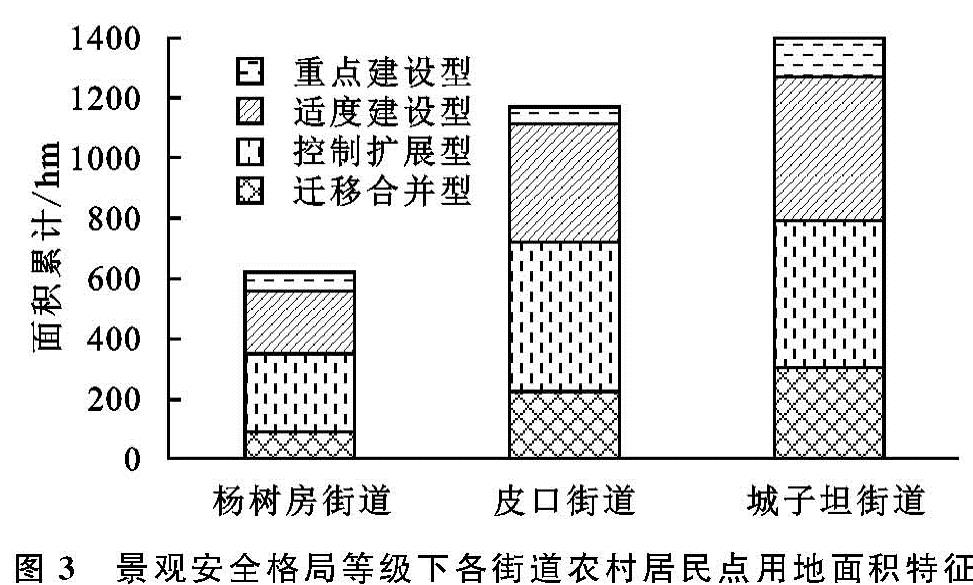
参考相关文献研究[5-8],景观安全格局越高的区域内农村居民点,其自然条件优势也相对较高。根据图2的研究区综合景观安全格局与图1的研究区农村居民点现状进行叠加,结合普兰店区空间发展规划,本文将农村居民点用地划分为重点建设型、适度建设型、控制扩展型和迁移合并型4种布局优化方式。研究区3个街道的农村居民点用地布局面积的统计结果,见图3。
(1)重点建设型。该区域的农村居民点用地处于综合景观安全格局中高安全水平状态,其用地优化方向为重点建设型。此类型农村居民点占总农村居民点用地规模的20.72%,面积共计654.55 hm2; 空间整体分布不均,主要集中在城子坦街道中南部的碧流河社区西北、大卢社区北部和东北部、金厂社区中部及东老滩社区中北部,皮口街道中南部和北部、新海社区北部、石固社区北部和东南部、三官村中部、大尹村西北部,杨树房街道中东部李家村中部和河西村东南部。其中城子坦街道农村居民点所占比重最大,占高安全水平区的农村居民总面积的48.30%。这些区域地势平坦、沿海冲积平原等自然条件优越,离国道和省道较近的便利交通,适合人类的生活生产活动,因而可作为农村居民点布局的重点建设区域。对于离建制镇比较近的重点建设农村居民点,采取政府引导、村民动员的组织模式,在依靠城镇现有的基础公共服务设施,促进区域内农村居民点城镇化发展。离建制镇较远的规模较大、连片的重点建设的农村居民点,在节约集约用地前提下建设现代化的农村社区,完善配套相应的基础公共服务设施,并接纳规模小、分布离散的迁移合并农村居民点,逐渐转变村民生活方式,推进农村人口城镇化。
(2)适度建设型。该区域的农村居民点用地处于中等安全水平状态,其用地优化方向为适度建设型。该类型农村居民点占总的农村居民点用地规模39.69%,面积共计1 254.22 hm2,主要分布在研究区中部和西北部,比较分散。该区域地势相对平坦,交通便利、农业资源与水文资源也丰富,基础公共服务设施相对完善,给农村的生活和生产提供了有力条件。在政府和村民共同参与、土地利用集约前提下,注重水资源保护、生物多样性保护和水土保持,合理规划村庄用地的建设,进一步完善日常生活的基础设施及配套农业生产,为农业产业化发展创造条件。
图3 景观安全格局等级下各街道农村居民点用地面积特征
(3)控制扩展型。该区域的农村居民点用地处于较低安全水平状态,其用地优化方向为控制扩展型。此类型农村居民点面积共计1 057.10 hm
2,占总的农村居民点用地规模33.46%,主要集中在城子坦街道中北部和中南部、皮口街道西北部和东北部、杨树房街道中北部。该区域农村居民点一部分是北部的低丘缓坡区,地质灾害易发区,农业生产条件受到限制多。另一部分是靠近河流或坑塘水面的农村居民点,为了保护水资源安全和生物多样性丰富,减少或者不再安排该区域内的建设用地报批。这类农村居民点建议控制其发展规模,不盲目向外扩展,通过整治废弃或闲置居民点,加强其内部的生态基础设施建设,保护生态环境,促进人与自然和谐相处。
(4)迁移合并型。该区域的农村居民点用地处于低安全水平状态,其用地优化方向为迁移合并型。此类型农村居民点面积共计193.74 hm2,占总农村居民点用地规模的6.13%,主要分布在城子坦街道东老滩南部、碧流河东南部和渔业村南部,皮口街道中东部和南部,杨树房街道西北和中南部。该区域农村居民点一部分为西北低丘区域坡度大的区域,交通不便,受地质灾害等因素影响的不适宜居住环境,通过就近迁移到交通便利、生活条件较好的重点建设区或适度发展区,也能够提升农村民的生产和生活水平。还有一部分位于南部入海口区域或河流的生态保护范围内的居民点,为保护水资源的良好生态环境,这些农村居民点直接迁入邻近适度建设型或重点建设型的居民点内。