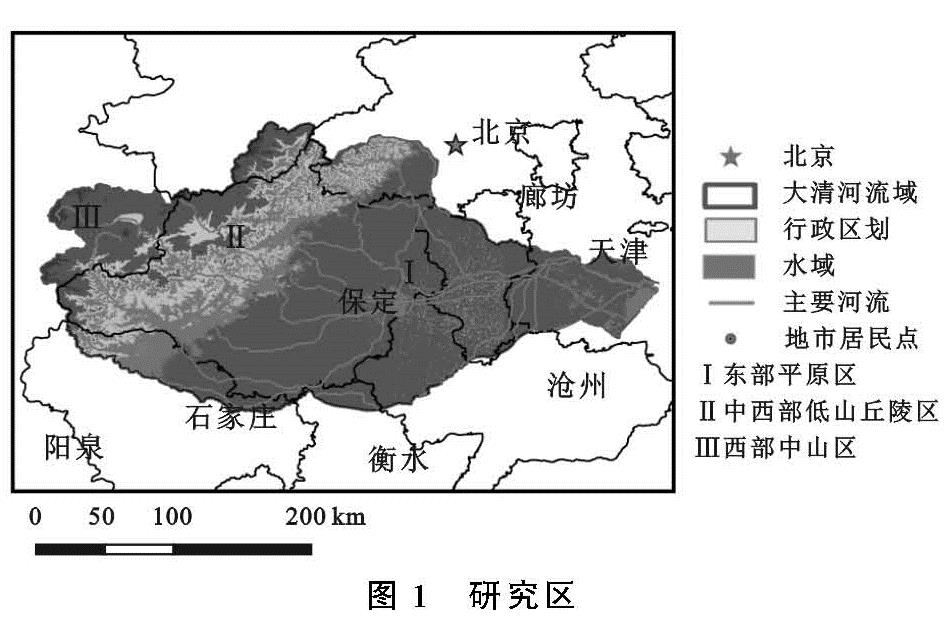
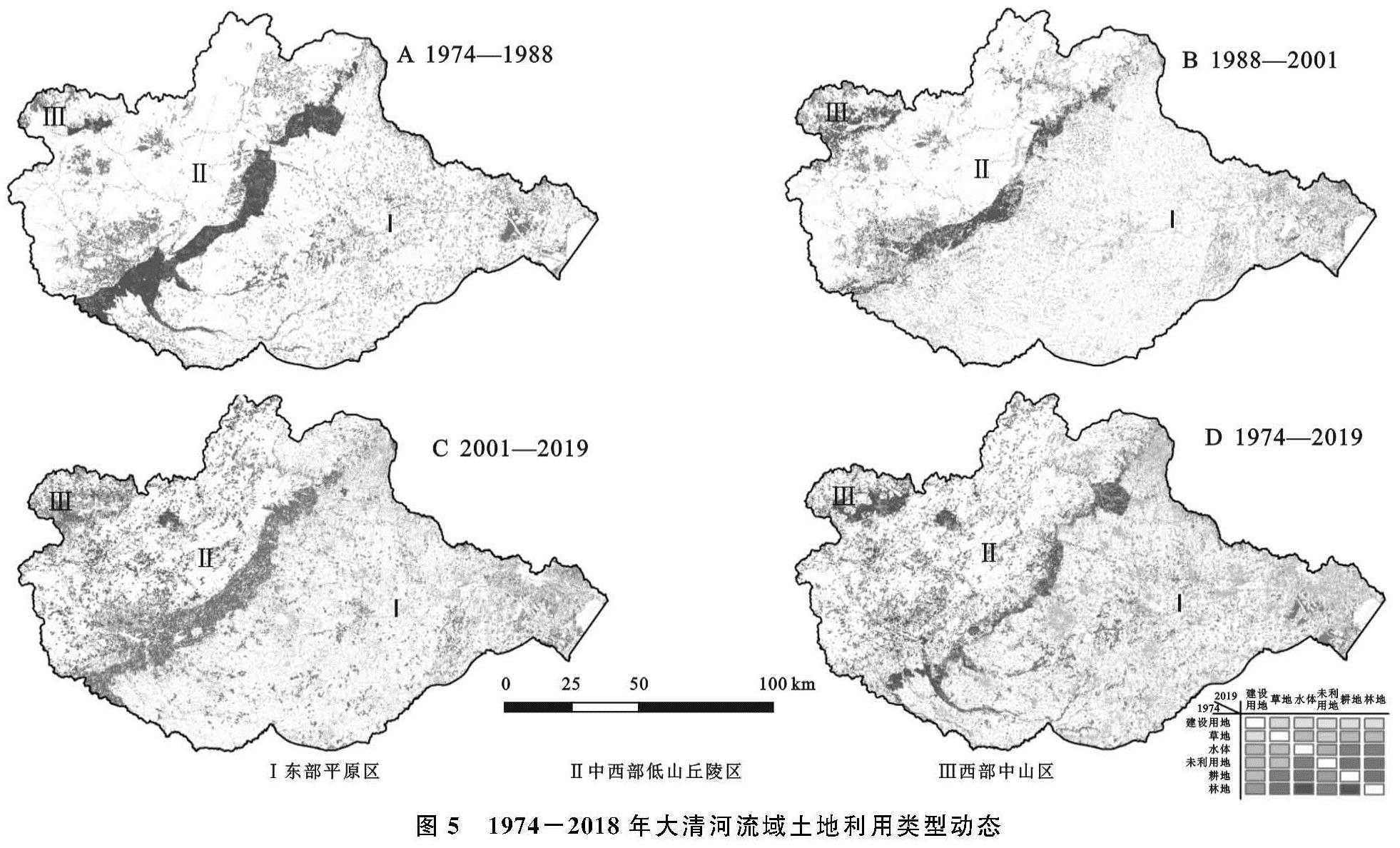
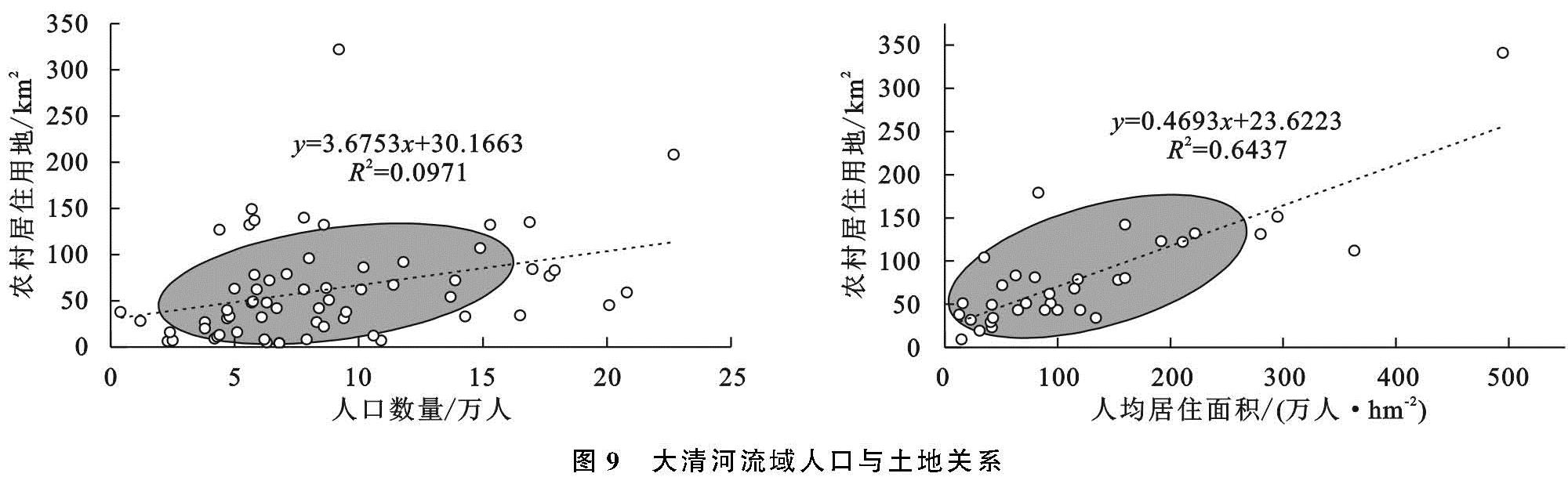
3.1.1 土地利用类型现状与研究阶段划分
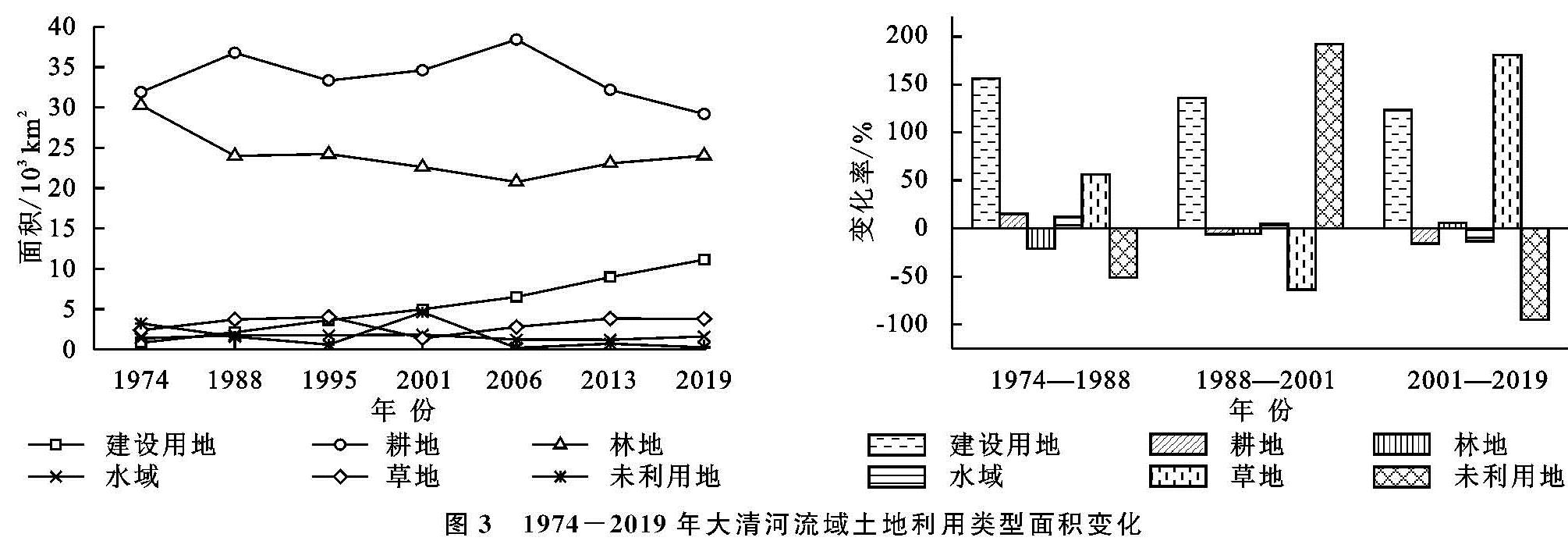
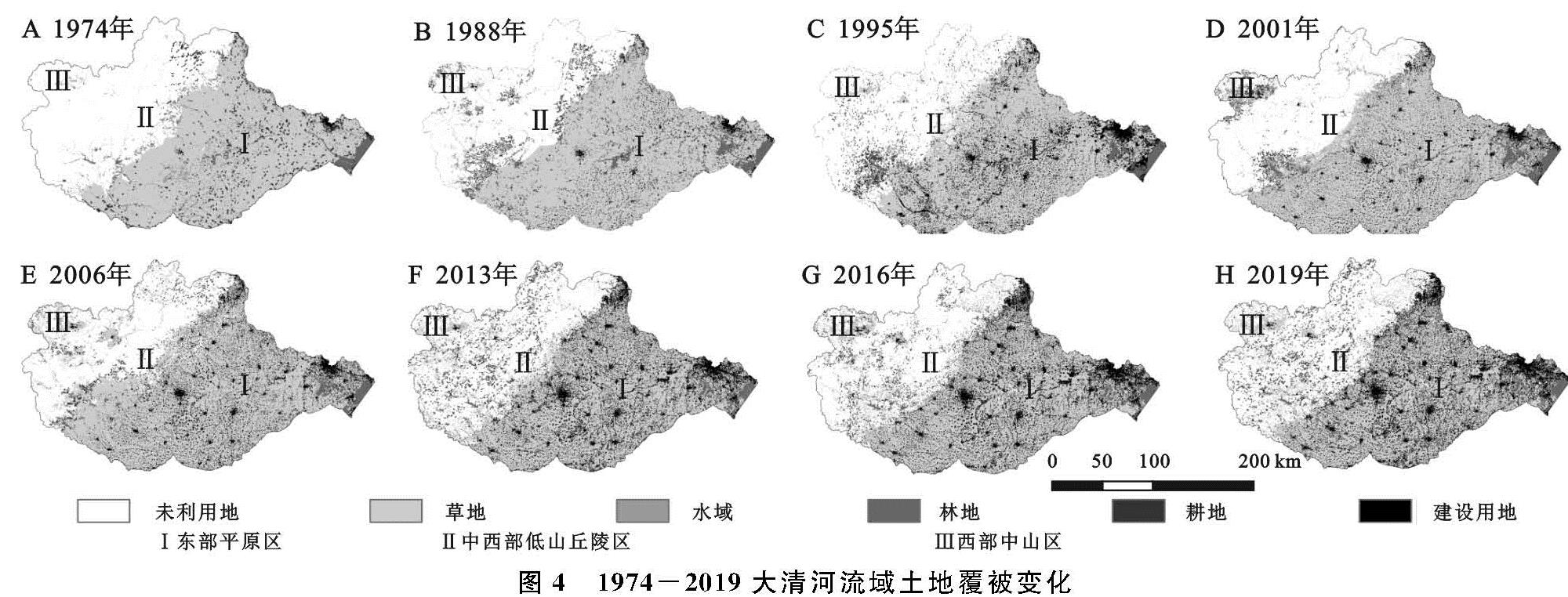
如图3—4所示,2019年,大清河流域建设用地在平原地区分布广泛,呈现“棋盘式”分布,在西部、中西部地区多呈不规则聚集分布,可达11 117 km2。
耕地呈现先增后减趋势,分布在东部、中部平原以及中西部居民点周围,面积为29 175 km2; 水体面积受降水、蒸发以及下垫面等的综合影响,最终面积约为1 580 km2; 草地面积多年来基本稳定,多分布在耕地、林地周围,面积约为3 781 km2; 林地主要分布在西部山区、中西部低山丘陵区,受前期垦荒与后期保护的双重影响,面积为23 999 km2; 未利用地区多分布于东部、中部地区的居民点周围,面积约为227 km2。
图3 1974-2019年大清河流域土地利用类型面积变化
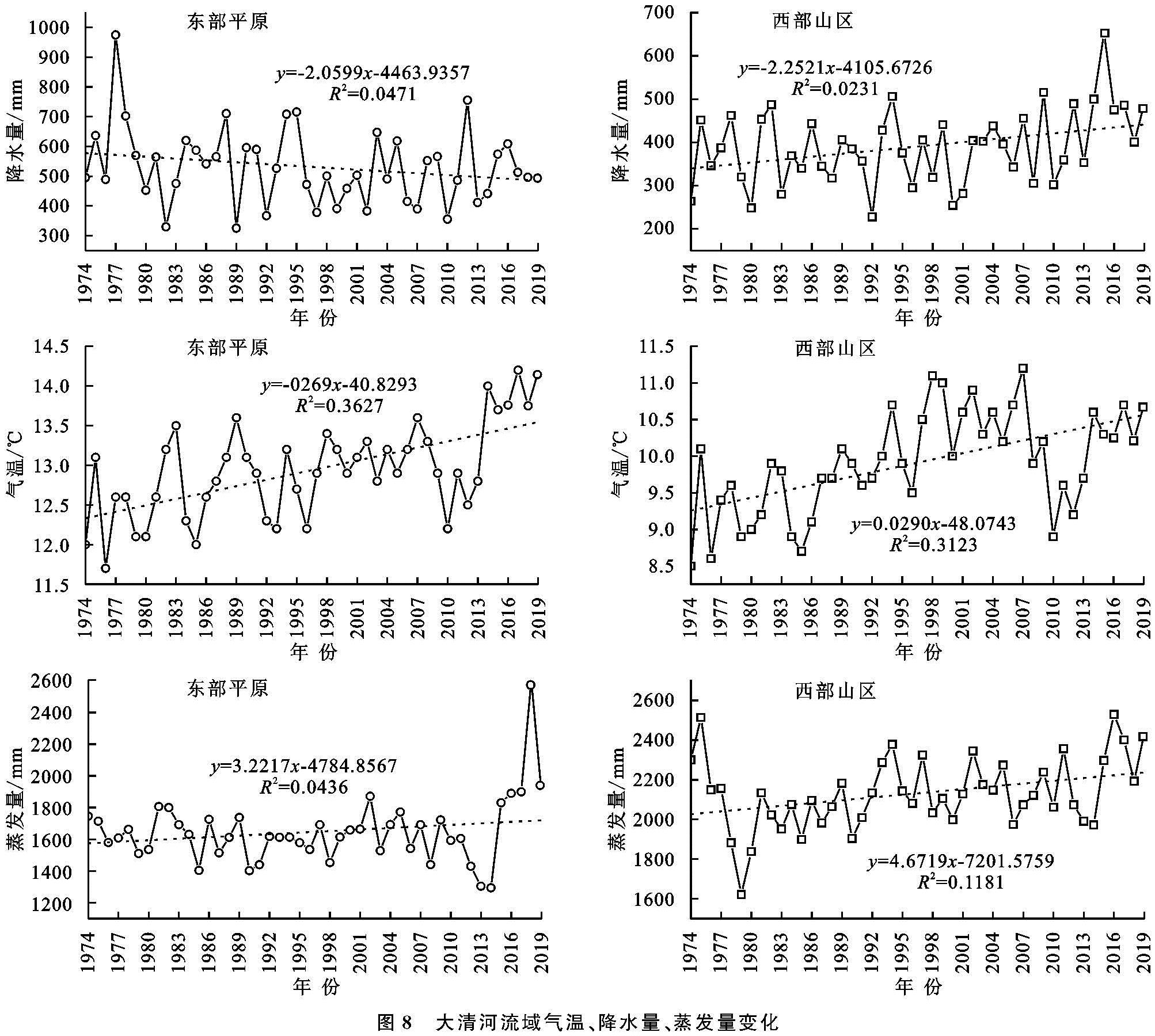
不同时期的土地政策对于土地资源分配具有重要影响以及强制约束力,1982—1986年“5个一号文件”的重要指导作用,使得粮食产量达历史最高,农村建设用地不断增大,标志着土地资源意识开始觉醒。1997年《关于进一步加强土地管理切实保护耕地的通知》、2000年《关于促进小城镇健康发展的若干意见》、《关于进一步做好退耕还林还草试点工作的若干意见》3个重要文件进一步规范了城镇土地利用,对于耕地保护、提高土地利用率具有重要意义,标志着对于土地的保护政策体系基本形成。2007年,“18亿亩耕地红线”的划定标志着对于土地保护体系的日趋完善。为提高研究区土地利用特征描述的科学性与合理性,将1974—2019年划分为三大阶段,即1974—1988年、1988—2001年、2001—2019年。
3.1.2 耕地与建设用地面积变化特征
根据流转面积的大小,该流域土地利用类型流转的主要方式包括以下几种变化形式,依次为:耕地转化为建设用地、林地转化为耕地、林地退化为草地、裸地转化为耕地、裸地转化为建设用地、草地转化为耕地。除了林地与草地的相互流转外,其余5种转化形式都与耕地与建设用地有关。由此可知,大清河流域土地利用变化的核心类型是耕地与建设用地。
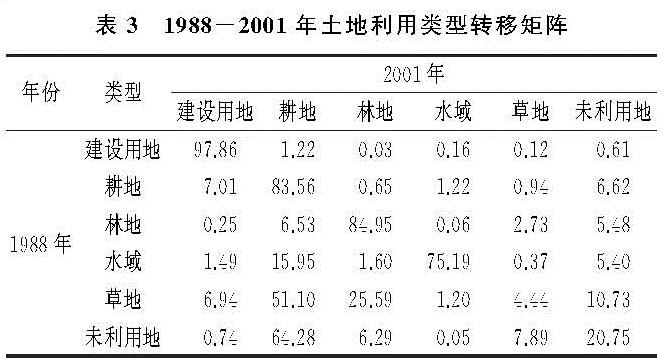
如表2所示,建设用地的转入类型在在前期主要以草地、未利用地为主,后又挤占大量耕地。1974—1988年,虽然增速较大,但主要是草地和未利用地转化为建设用地; 在1988年以后占用耕地现象频发。由此可知,在进行城市扩张的初期,为了保证粮食产量,先将未利用土地以及草地开发为建设用地,而后随着城镇化的加快,在有限的土地资源制约下,建设用地侵占耕地问题日益突出。
如表2—4所示,耕地的转入主要以草地、未利用地为主,同时也存在部分池塘、湿地退化为水田,将丘陵地区林地开垦为耕地。在1974—1988年,未利用地、草地的开垦比率较大,水田开垦比例在23.74%。如表3所示,1988年之后草地、未利用地的开垦比例开始下降,这是因为草地等类型土壤肥力较好、开垦难度较低。后期能继续开垦的草地面积已经很小。由于水田的经济效益明显好于旱地,使得湿地退化为水田、耕地现象严重[17]。
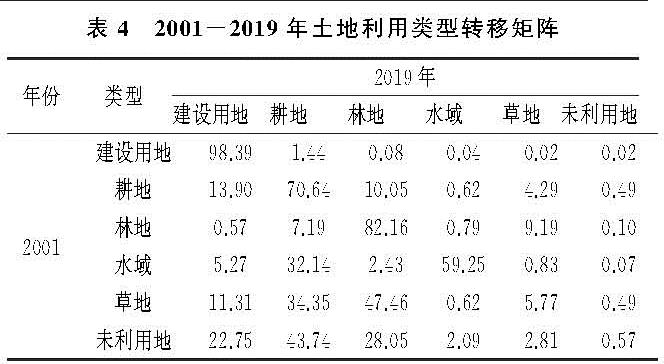
耕地的转出地类主要以建设用地、草地、林地、未利用地为主。在1974—1988年,耕地面积呈扩张趋势,几乎没有转出; 在1988年后,出现建设用地加速侵占耕地的趋势。如表4所示,在2001—2019年,建设用地侵占耕地面积已达13.90%。同时由于退耕还林还草的政策影响,分别有10.05%,4.29%的耕地流转为林地、草地。
1974—2019年,大清河流域土地利用类型变化动态如图5所示,该地域土地类型变化特征主要包含以下两个方面:
(1)建设用地呈现连续扩张趋势,且主要分布在东部、中部平原与西部的高山盆地,多以耕地或林地转化为建设用地。1974—2019年,在东部地区,共计有8 325 km2面积的耕地转化为建设用地; 从扩张规模与区域看,城市建设用地扩张规模大于农村、东部大于西部、平原大于山区; 从扩张速度看,建设用地增幅不断加大,在3个时期内建设用地扩张速度分别为:91.85 km2/a,220.30 km2/a,341.28 km2/a。建设用地对耕地的侵占呈现加剧趋势,围绕中心城区“摊大饼式”扩张问题突出。1988年之后,东部、中部平原地区加大了对草地、未利用的开发程度,分别有402 km2,1 053 km2的草地、未利用地成为建设用地。
(2)1974—1988年,耕地处于单向转入期且面积显著增加。耕地的扩张主要在中西部低山丘陵区,集中于保定市太行山东麓,将水土肥力较好的林地开垦为耕地,开垦面积达3 391 km2; 1988年之后,耕地变化由单向转化变为双向转化,耕地转入、转出程度剧烈,垦荒速度放缓。耕地的转入由初期的城镇周边变为边远地区、由大清河上游变为下游、由开垦旱地变为开垦水田、由大范围开垦变为小区域垦荒。同时又出现,原先开垦的耕地又被建设用地挤占,这在中部的保定中心城区、北京房山区、天津的大港区表现明显; 2001年后,耕地变化程度加剧。中西部地区的早期开垦的耕地出现退耕还林还草现象,分别有3 477 km2,1 485 km2耕地重新变为林地、草地。在此时期,耕地的转入量小于耕地的转出量。
3.2 1974-2019大清河流域景观变化特征
3.2.1 类型水平变化特征
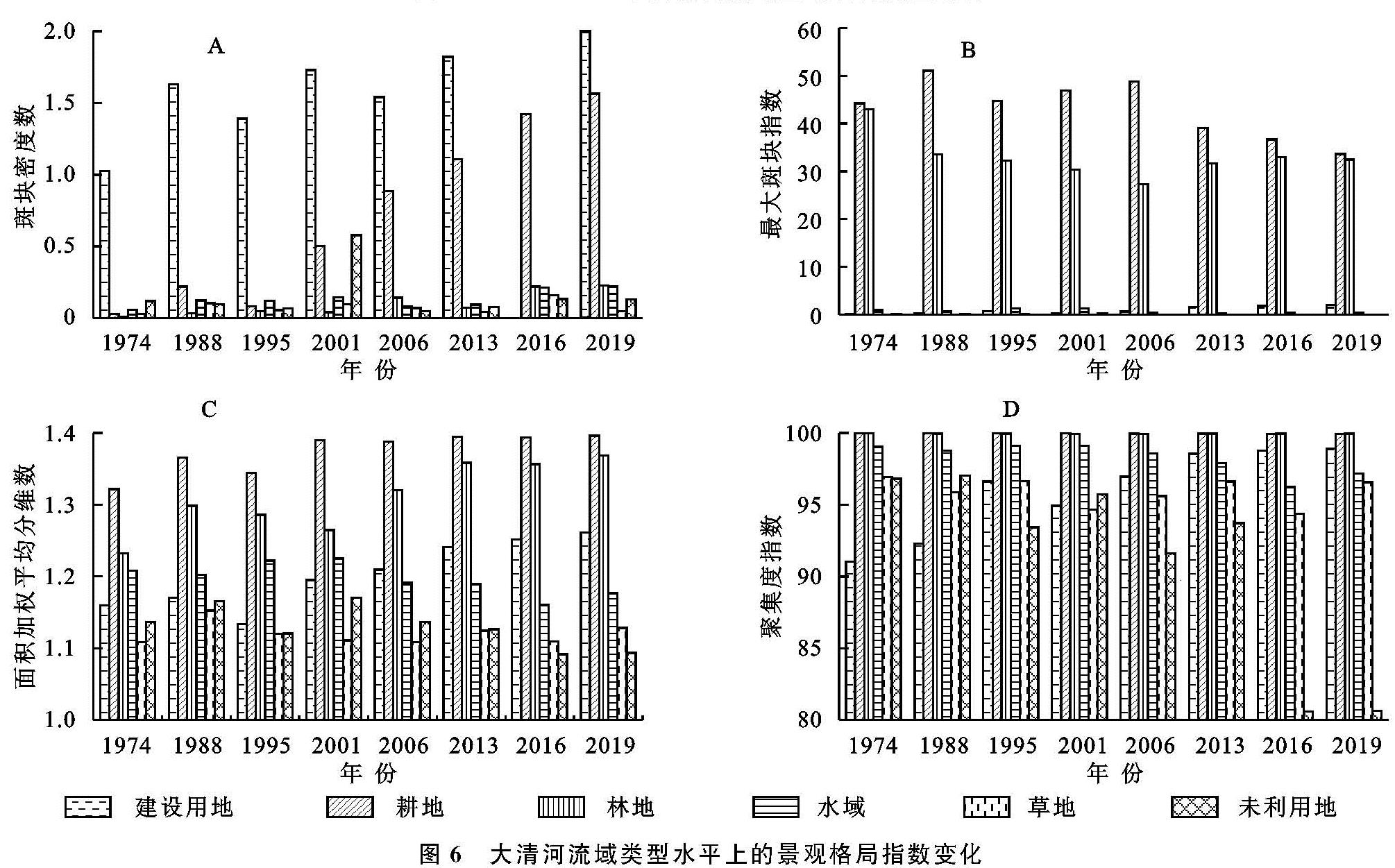
为了反映大清河流域不同土地类型的空间变化特征,分别计算1974—2019年大清河流域在类型水平的景观指数变化,结果如图6所示。
(1)斑块密度(PD)变化可以反映景观的破碎程度,建设用地的斑块密度最大,其次是林地。1995年、2006年建设用地斑块密度略有下降,在1974—2019年建设面积、林地的斑块密度逐渐增大,说明该种土地类型不断细碎化。(2)最大斑块指数(LPI)反映不同土地类型的聚合程度。耕地、林地的最大斑块指数远大于其他类型但数值逐渐降低,说明林地、耕地在大清河流域中的景观主导性正在降低。建设用地的最大斑块指数逐渐增大,即建设用地在空间上呈现聚合趋势。(3)面积加权平均分维数(FRAC_AM)表示土地利用类型分布的规则化程度。林地、耕地的平均分维数高于其他类型,由于耕地与林地面积较大,景观形状呈不规则分布,范围较为稳定,受人为干预较小。而建设用地多与人类活动有关,在景观特征上受人为扰动较大,其平均分维数显著增大。(4)聚集度指数(COHESION)表示不同土地类型在空间分布上的聚集性程度。由于水域之间较好的联通性,以及耕地与林地的巨大面积,因而耕地与林地、水域的聚集度指数均大于95%。由于建设用地集中连片式发展的特点,其集聚度指数呈增大趋势,而未利用地被耕地、建设用地等不断挤压、切割逐渐破碎,聚集度指数逐渐减小。
图5 1974-2018年大清河流域土地利用类型动态
3.2.2 景观水平变化特征
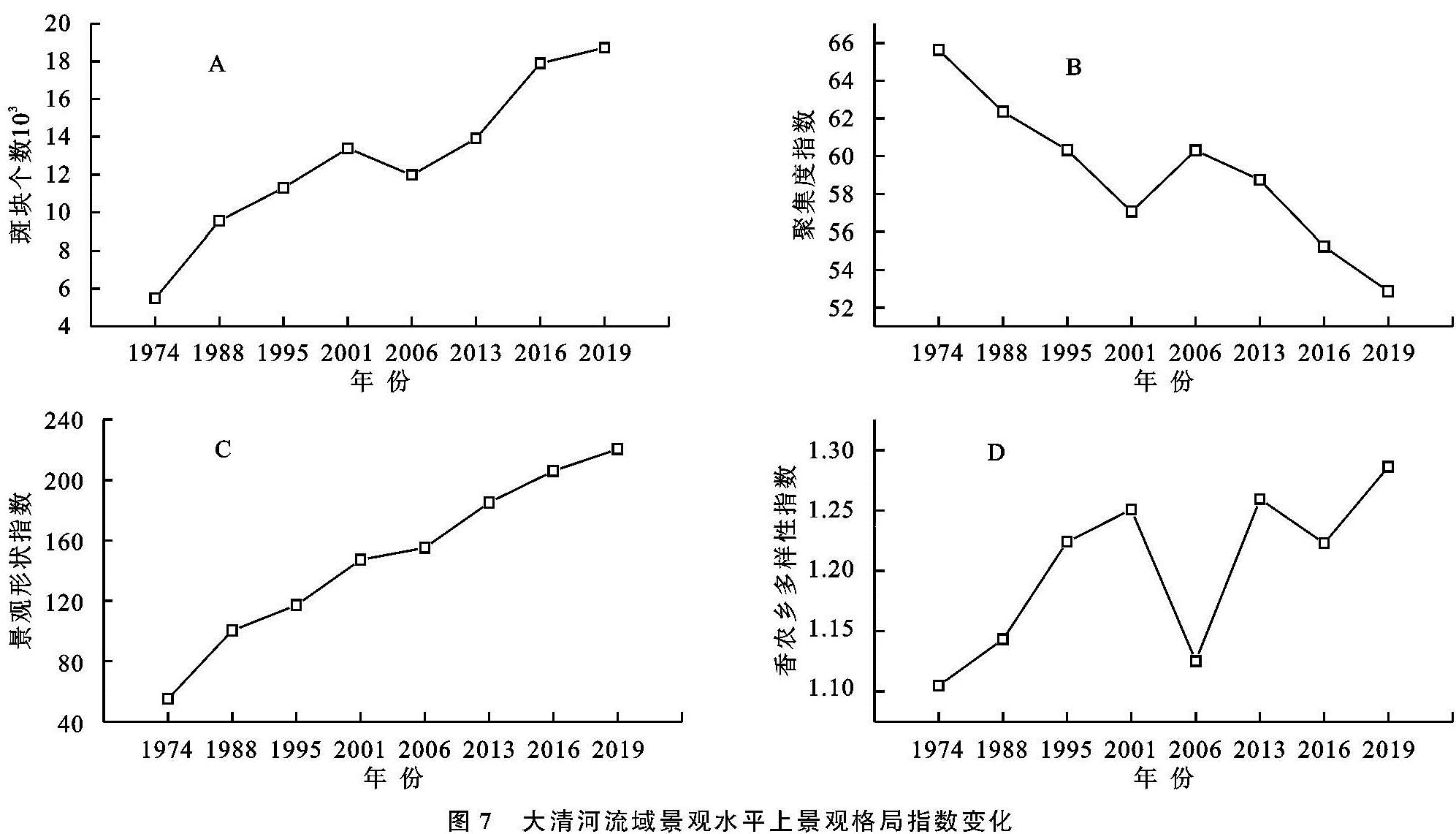
1974—2019年大清河流域景观水平上景观格局指数变化如图7所示。
从景观水平[18]角度看:
(1)1974—2019年大清河流域的斑块个数(NP)从54 835增加到187 133,增幅达到241%,持续增长的斑块个数证明该流域的景观破碎程度增大。(2)聚集度指数(CONTAG)在1974—2001年呈现减小趋势,后在2006年小幅上升后继续下降,说明空间格局逐渐聚集,耕地、林地等优势类型连接性的斑块数量则在进一步减小。(3)景观形状指数(LSI)逐渐增大,表明土地类型景观形状复杂程度不断增大,斑块不规则程度增大,对大面积耕种、动物迁徙等有一定负作用。(4)香农多样性指数(SHDI)在1974—2001年逐渐增大,在2006年减小为1.12后又继续增长,并在2019年达到最大值1.28,这是由于大清河流域土地利用种类越来越丰富,在该区域各种类型土地所占比例均衡化趋势明显,区域发展科学性增强,景观异质性增大。
综合来看,大清河流域景观总体破碎程度加大、景观连通性降低、斑块趋于复杂态势明显。该流域内的耕地、林地以及逐渐增加的建设用地出现均衡分布的趋势。