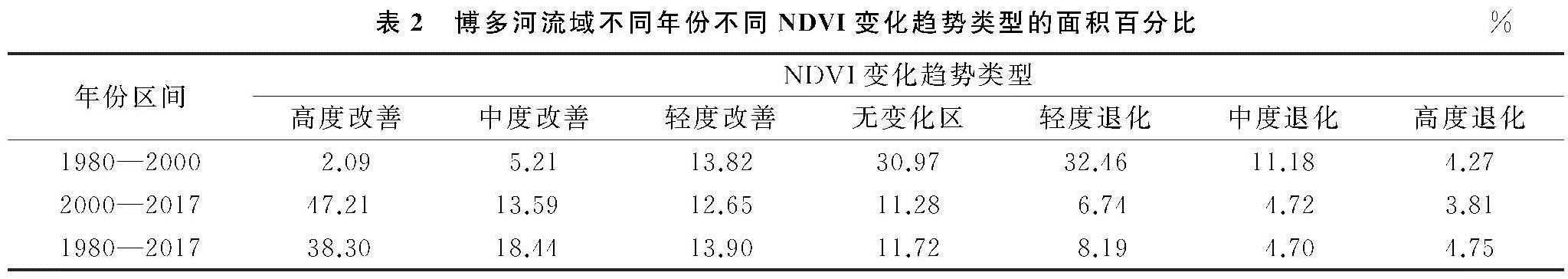
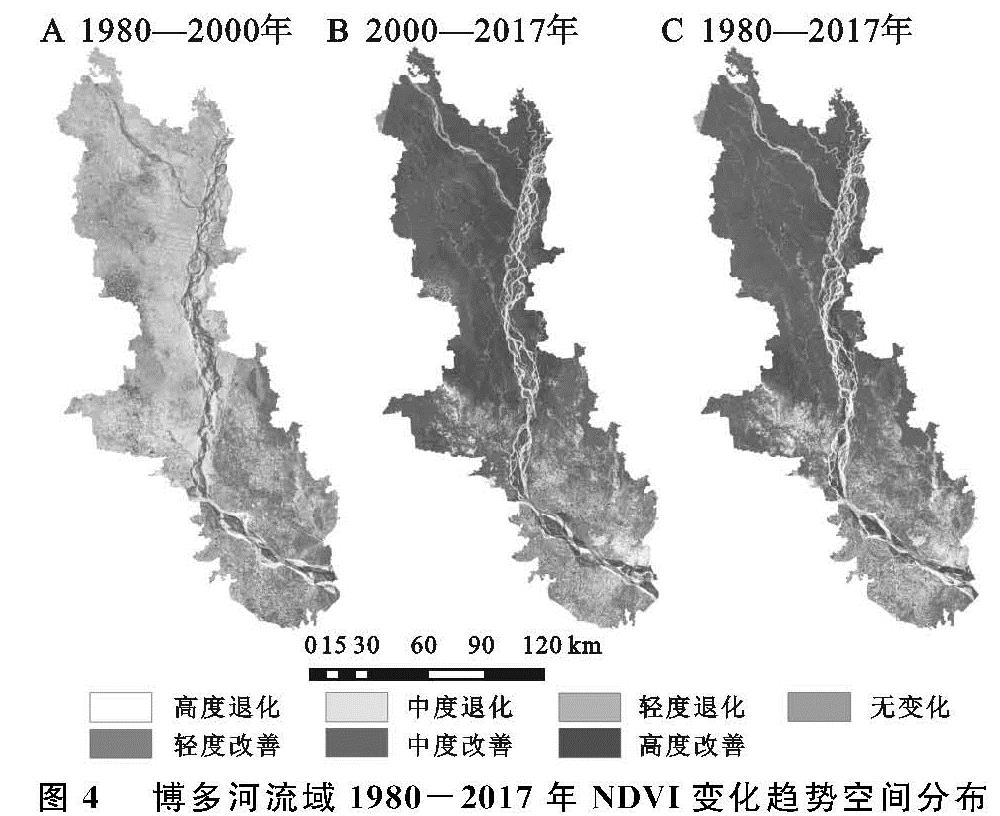
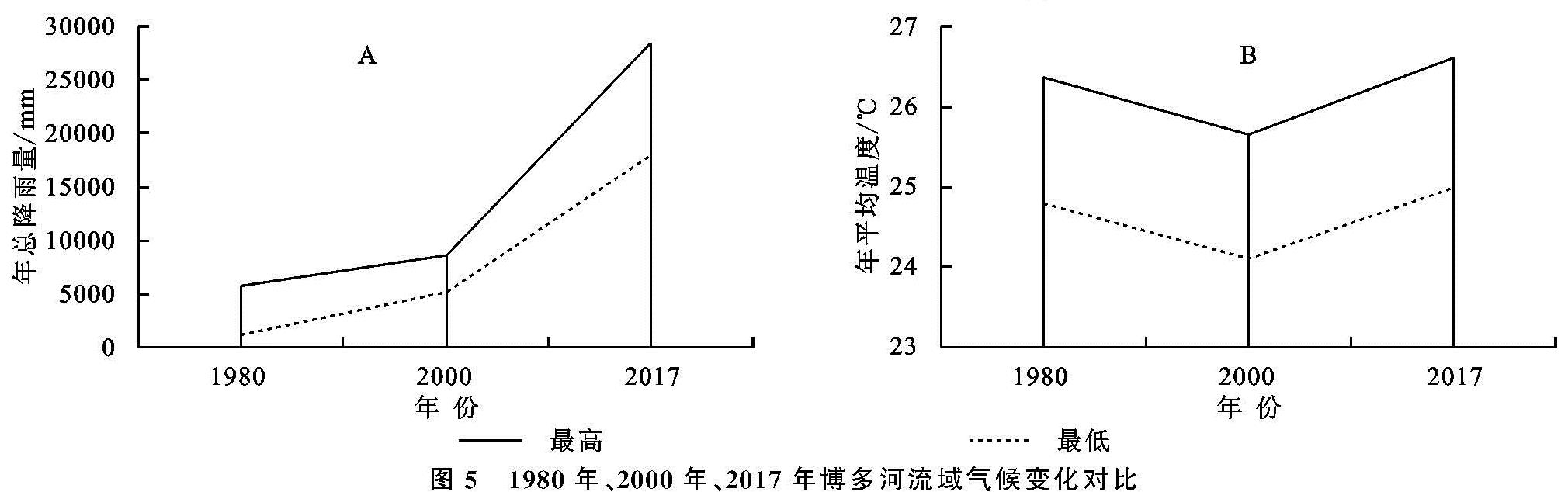
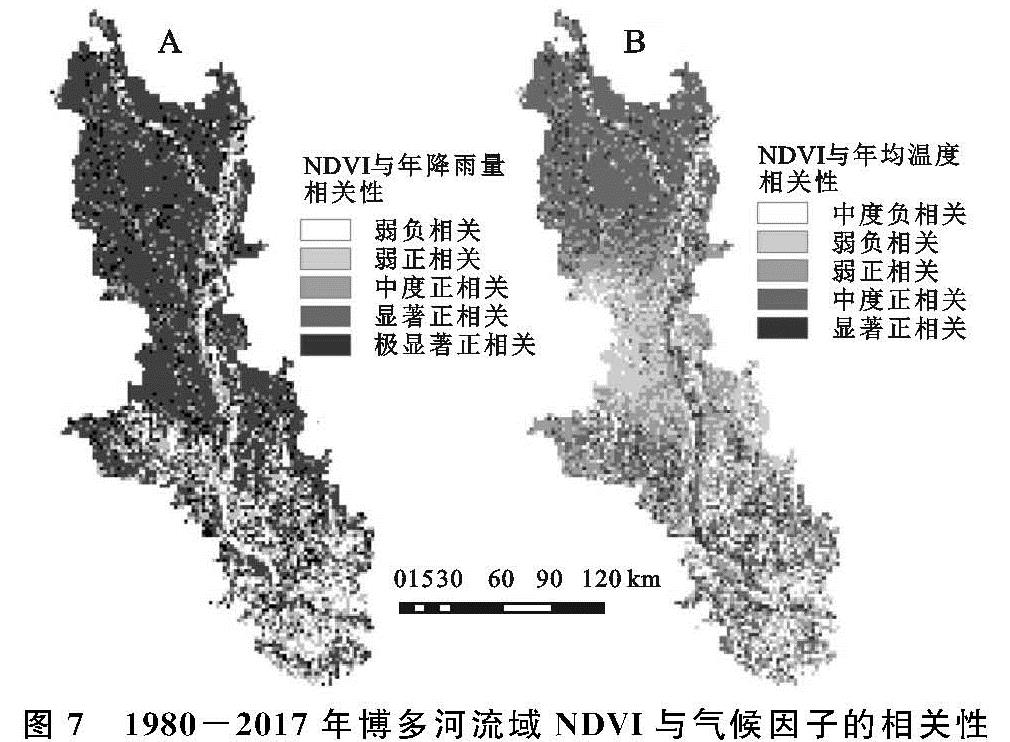
地表植被是陆地生态系统的核心组成部分,不仅能够促进地球生态系统平衡、能量流动、水循环以及气候变化[1-2],而且对于生态系统之间的能量传输和物质交换起着重要作用[3]。同时,它也是生态环境变化的敏感因子,是监测生态环境变化的一种重要的工具[4]。温度和降水等气候因子作为植物生长发育的必要环境因素,对植被的生长和物候等具有重要影响[5],气候变化必然也影响植物的生长状态[6]。因此,植被常常被视为全球环境变化的重要指示器[7]。植被覆盖变化严重受制于气候变化和人类活动的共同影响[8],其中,气温和降水是影响植被生长的主要自然因素[9]。由于研究植被变化及其与气候因子的关系可以为应对全球变化提供重要的理论依据[10],近年来,开展植被覆盖研究揭示区域生态系统演化特征已成为全球变化研究的一个重要领域[11]。
归一化植被指数(Normal Difference Vegetation Index,NDVI)是植被要素的重要表征之一[12],能较好地反映植被生长活动的季节变化和年际变化,因此被广泛应用于全球或区域尺度上植被覆盖变化特征及其对气候的响应模式的研究上[13-14]。在之前的研究中,研究者们侧重于分析均态气温和降水与植被覆盖之间的相关性,结果表明气温一般有利于水资源丰富地区的植被生长,降水则通常对干旱地区或者干湿季差异明显地区的植被活动具有显著的胁迫性[15-17]。有学者在中国三江源地区的研究中发现气候条件的变化对植被生长产生负面影响[18]。并且气温是决定流域植被绿度的控制因素,植被对降水的响应相对较低[19]。此外,也有学者在不同区域开展了长时间序列植被指数的动态分析[20-21]、植被覆盖变化驱动因子分析[22]、气候变化及人类活动对植被覆盖的影响[23]等研究,取得了很多丰厚的研究成果。区域植被覆盖度与气候变化的响应成为全球变化科学研究的热点。
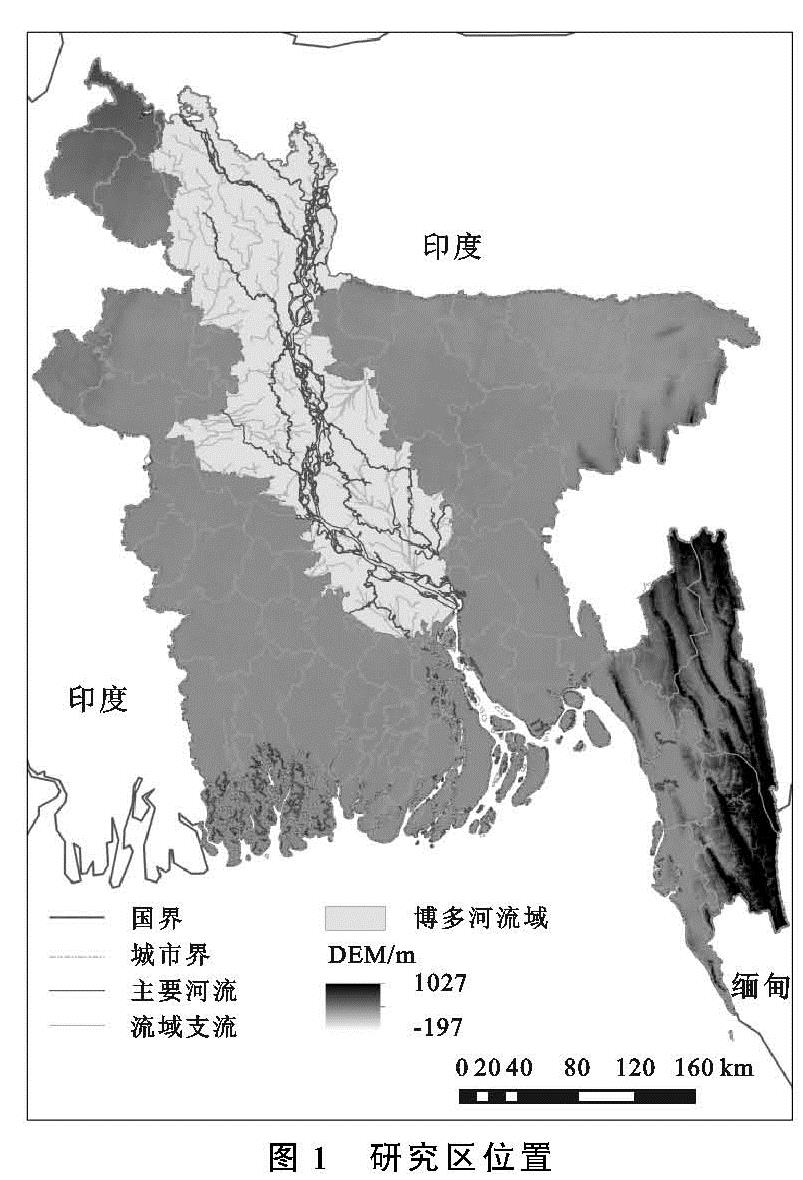
博多河流域位于孟加拉国境内,是该国社会经济发展的核心区和战略区,而孟加拉国是中国“一带一路”发展倡议沿线重要节点国家,研究沿线国家的植被—气候环境,对于恢复和建设区域生态安全具有重要的意义和价值。研究以孟加拉国博多河流域为研究区,基于1980年、2000年、2017年流域遥感影像数据和流域内各城市气温与降水数据,采用GIS软件和数理统计分析工具相结合的方法,分析1980—2017年近40 a间博多河流域NDVI变化情况和气候变化情况,并试图分析两者间的关联性,旨在为改善流域生态安全状况、丰富流域植被变化与气候变化的响应研究提供科学参考。