资助项目:伊犁师范大学植物生态学重点学科科研项目“基于饱和修正NDVI的伊犁河谷草地退化影响因素量化研究”(YLUPE201801)
第一作者:付秀东(1998—),男,新疆阿勒泰市人,本科,地理科学专业。E-mail:764375674@qq.com 通信作者:闫俊杰(1984—)男,河南林州人,博士,副教授,主要从事遥感生态应用研究。E-mail:yan3550@sina.com
(伊犁师范大学 资源与生态研究所, 新疆 伊宁 835000)
(Institute of Resources and Ecology, Yili Normal University, Yining, Xinjiang 835000, China)
water use efficiency; influencing factors; MODIS; grassland; Ili River Valley
水分利用效率(Water Use Efficiency,WUE)是表征生态系统碳水耦合的重要指标,研究退化草地WUE的时空变化,对探明草地退化的环境效应具有重要意义。选择草地退化严重的伊犁河谷为研究区,基于MODIS NDVI(Normalized Difference Vegetation Index)、GPP(Gross Primary Productivity)、ET(Evapotranspiration)以及气象数据,并借助于GIS空间分析技术及趋势分析等方法,对2000—2014年伊犁河谷草地生态系统WUE时空变化和其影响因素进行了研究。结果 表明:(1)伊犁河谷草地WUE,ET及GPP均呈现明显的海拔分异,但WUE高值区域并未出现在干旱的荒漠区,而是主要分布在GPP为高值(GPP>650 g C/m2)且ET相对较高(300~500 mm)的区域;(2)近15年伊犁河谷草地ET及GPP总体呈降低趋势,WUE则总体呈增加趋势; 空间上,全区79.20%区域WUE有所增加,ET和GPP发生减少的比例则分别为92.31%和78.10%;(3)研究区WUE增加主要是由于ET减少程度高于GPP,但ET变化与GPP关系紧密,WUE的变化并不由单一的GPP或ET变化所主导,而是两者变化综合作用的结果;(4)近15年伊犁河谷降水的减少导致植被覆盖降低和ET减少,进而影响WUE的变化。WUE变化具有明显的空间异质性,15年内全区平均WUE增加6.61%,降水的减少是导致伊犁河谷WUE增加的主要气候因子。
Water use efficiency(WUE)is an important index indicating the coupling of carbon and water in the ecosystem. Study on the spatiotemporal variation of WUE in degraded grassland is of great significance for verifying the environmental effects of grassland degradation. Ili River Valley, labeled with serious grassland degradation, was selected as the study area. Based on data of MODIS NDVI(Normalized Difference Vegetation Index), GPP(Gross Primary Productivity), ET(Evapotranspiration)and meteorological factors, and with the help of GIS technology and the method of trend analysis, the spatiotemporal variation of WUE in the grassland ecosystem of Ili River Valley in 2000—2014 and its influencing factors were studied. The results showed that:(1)WUE, ET and GPP in the grassland of Ili River Valley all showed obvious differentiation along the altitude; areas with high WUE did not appear in arid desert area, but mainly distributed in area with high GPP(GPP>650 g C/m2)and relatively high ET(300~500 mm);(2)in the past 15 years, ET and GPP in the grassland of Ili River Valley decreased, while WUE increased; spatially, WUE increased in 79.20% of the grassland; the proportions of areas with decreased ET and GPP were 92.31% and 78.10%, respectively;(3)the increase of WUE in the study area was mainly due to the fact that the decrease of ET was higher than that of GPP; however, the change of ET was closely related to that of GPP; the change of WUE was not resulted from the single change in GPP or ET, but from the comprehensive interaction of changes in the both;(4)in the past 15 years, the decrease of precipitation in Ili River Valley was the main reason for the decrease of vegetation coverage, which affected the variations of WUE further. Variations of WUE in the grassland of Ili River Valley showed obvious regional characteristics. WUE increased by 6.61% on average within 15 years. The decrease of precipitation was the main climate factor that leaded to the increase of WUE in Ili River Valley.
草地是陆地生态系统的重要组成部分,研究表明全球一半以上草地发生退化[1],草地退化的环境效应被广泛关注[2-3]。水分利用效率(Water Use Efficiency,WUE)代表了植物固定单位质量碳消耗的水分[4],由生态系统生产力和蒸散发(Evapotranspiration,ET)共同作用[5-6],是表征生态系统碳水耦合的重要指标[7],也是预测生态系统对环境变化响应的重要参数[8]。分析草地退化对生态系统WUE的影响,对从生态调节的角度来揭示草地退化的环境效应具有重要意义。
前人对植物个体或农田植被WUE特征及其影响因素进行了广泛研究[9-10]。遥感技术的发展促进了生态系统水平WUE研究的广泛开展[11-12]。基于遥感技术,Xia等[13]对全球陆地2000—2013年WUE分析表明非洲和大洋洲由北向南以及欧洲和南美洲由东向西,WUE有所增加,而Chen等[10]发现1999—2008年温带欧亚草原WUE整体呈增加趋势,但存在明显的空间分异; 邹杰等[14]对2000—2014年包括新疆在内的中亚地区WUE分析表明,该区域内主要生态系统的WUE均有所增加。对于WUE的影响因素,研究发现干旱是促使生态系统WUE变化的重要原因[15-16],适度干旱将激发植物通过自身调节提高对水分的利用效率[17]; 穆少杰等[18]发现,相对于温度,降水量的变化对WUE的影响更大。除气候影响因素外,Jin等[19]研究表明植被物候的改变也是生态系统WUE变化的重要影响因素。Zheng等[20]发现植被重建促进了黄土高原生态系统WUE的提高; 同时,Huang等[21]的研究发现高强度的放牧活动致使新疆覆盖水平较高的草地WUE发生明显降低(牧民更偏向于在覆盖度高的草地放牧)。可见除气候因素影响外,植被覆盖水平及物候等自身特性的改变也是影响生态系统WUE变化的重要原因。
位于我国天山西段的伊犁河谷,草地发育良好,是我国重要的优质牧场[22],但近15 a在气候变化和过渡放牧等干扰影响下,草地退化日趋严重[23]。基于此,本文利用遥感数据及气象数据,借助于GIS空间分析技术,对伊犁河谷草地WUE时空变化进行分析,探讨气候变化及草地退化对WUE影响,以期为草地退化环境效应的研究提供支持和参考。
伊犁河谷介于80°09'42″—84°56'50″E,42°14'16″—44°53'30″N,地处天山山脉西端(图1),北、南、东三面高山环绕,地形呈向西敞开的“V”字; 特殊的地形为西风带湿润水汽抬升凝结成雨提供了有利条件,河谷内降水充沛,造就了其“塞外江南”的美誉[24-25]。境内有巩乃斯河、喀什河、特克斯河以及伊犁河等主要河流。山脉和河流将整个河谷分割为伊犁河谷、特克斯谷地、巩乃斯谷地、喀什河谷丘陵和昭苏盆地5个地域单元,形成了独特的“山地—盆地—河谷平原”地形地貌[26]。河谷内年平均降水量200~800 mm,受到地形影响,山区降水是平原的3~5倍; 年平均日照时数达到2 700~3 000 h,年均气温2.9~9.1℃。河谷内草地植被发育良好,类型丰富,且垂直分异明显[27]。
本研究所用到的遥感数据包括MODIS的NDVI,ET以及总初等生产力(Gross Primary Productivity,GPP)成品数据,时间序列为2000—2014年。NDVI数据为MODIS MOD13Q1产品数据,该数据为16 d合成数据,其空间分辨率为250 m; GPP和ET数据分别为MODIS MOD17A3和MOD16A3产品数据,时间和空间分辨率分别为1 a和1 km。GPP和ET数据由蒙大拿大学密苏拉分校地球动态数值模拟研究组制作,数据经过全球多个区域地面通量数据的验证,被广泛应用于区域及全球尺度的相关研究[28-29]。草地空间分布数据是基于Landsat 8OIL近外、红和绿波段假彩色合成影像,利用目视解译方式获得其矢量数据,为便于数据处理,将矢量数据转换为栅格数据。
气象数据来自中国气象局气象数据中心,包括2000—2014年伊宁市、伊宁县、霍城、察布查尔、霍尔果斯、尼勒克、巩留、新源、昭苏、特克斯及巴音布鲁克11个气象站月平均气温和月累积降水量数据。利用Anusplina 4.2软件进行空间插值生成月气温和月降水量栅格数据。之后利用月气温和月降水量栅格数据,按照标准化降水蒸散发指数的计算步骤[30],逐像元计算,获得年SPEI空间分布数据,用SPEI指数来表征研究区干旱状况。
为保证多种数据的空间匹配,在数据计算和预处理过程中,将栅格化的草地空间分布数据、气温、降水和SPEI空间分布栅格数据以及NDVI,GPP和ET的像元大小统一设置或重采样为250 m。
2.2.1 单调趋势的Mann-Kendall非参数检验法 Mann-Kendall非参数检验方法特别适用于类型变量和顺序变量的趋势检验[31],广泛应用于水文、气象、植被及其他长时间序列数据趋势检验,其计算过程如下:
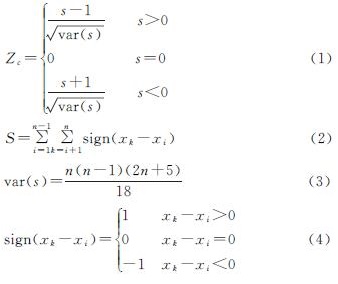
式中:xk,xi表示第k和第i个时间的ET,GPP或WUE值; sign为符号函数; n为时间序列长度。Zc为时间序列数据变化趋势检验统计量。若Zc>0,则时间序列变化趋势为上升,若Zc<0,则变化趋势为下降; α=0.05水平上; |Zc|=1.96,若|Zc|>1.96,则时间序列变化趋势在0.05水平上显著。
2.2.2 WUE计算方法 WUE通常利用固碳量与耗水量的比值来计算,但对固碳量和耗水量两个分量表达时所选指标常有不同[15]。净初级生产力(Net Primary Productivity,NPP)[4,10,13]和GPP[5,7,14,32]常用来表达固碳量,但也有用地表NPP和净生态系统生产力(Net Ecosystem Productivity,NEP)来表达[33]; 对耗水量的表达,ET是通用指标,但也有用降水量来表达[15]。为便于与国内相关研究[5,7,14,32]的对比,本文采用GPP与ET比值计算,详细公式为:
WUE=GPP/ET(5)
式中:WUE,GPP和ET分别为生态系统水分利用效率(g C/kg H2O),总初级生产力(g C/m2)和蒸散发(mm)。
基于2000—2014年伊犁河谷草地ET,GPP和WUE的年空间分布数据,计算其多年平均值,用其代表伊犁河谷草地ET,GPP和WUE空间分布,制作空间等级分布图(图2),依次分析其空间特征。
由图2A可知,伊犁河谷草地WUE海拔分异明显,WUE较高(>1.25 g C/kg H2O)的区域主要分布在乌孙山—昭苏盆地—那拉提山以及科古琴山—阿吾勒拉山的中山区,而WUE较低(<1.25 g C/kg H2O)的区域则主要分布河谷平原、低山丘陵以及河谷周围的高山区。具体来看,1.25 g C/kg H2O<WUE<1.50 g C/kg H2O分布面积比例最大,为43.88%,空间上主要分布在乌孙山、昭苏盆地—那拉提山以及科古琴山—阿吾勒拉山的中山区大部分区域; 1.00 g C/kg H2O<WUE<1.25 g C/kg H2O的面积比例为23.24%,主要分布于霍城县的低山丘陵、喀什河中游及特克斯河下游的两岸、以及—阿吾勒拉山的部分区域; WUE<1.00 g C/kg H2O的比例为17.09%,主要分布于河谷南部婆罗科努山—那拉提山高山区、河谷北部科古琴山—阿吾勒拉山高山区,以及伊犁河两岸河谷平原及部分的低山丘陵区; WUE>1.50 g C/kg H2O的面积比例为15.79%,主要分布在科古琴山山脉中部及昭苏盆地等区域。
ET的空间分布也呈现明显的海拔分异,但与WUE的海拔分异存在一定差异(图2A,图2B)。不同于WUE,ET低值(<300 mm)区域集中分布在巩乃斯河下游—伊犁河两岸、以及喀什河下游和特克斯河下游两岸平原区和低山区,该区域也是伊犁河谷最为干旱的荒漠区,而河谷周围的高山区ET相对较高(>400 mm); 此外,昭苏盆地—特克斯周围区域为WUE高值区域(>1.50 g C/kg H2O)而ET则相对较低(300 mm<ET<400 mm); 同时,阿吾勒拉山为ET的高值区域(>500 mm),而WUE则相对较低。具体来看,全区ET位于400~500 mm所占的面积比例最大,为41.74%,主要分布于研究区周边海拔较高的区域; 其次为ET>500 mm区域,其比例为19.01%,主要分布在河谷东部的阿吾勒山、昭苏—特克斯—那拉提的中山区以及乌孙山南麓; ET为200~300 mm和300~400 mm的面积比例分别为15.10%和17.56%,主要分布于科古琴山以南—乌孙山北部—特克斯河的冲积扇两岸; 而ET<200 mm面积比例最小,为6.59%,仅在霍城和巩留附近分布。
对于GPP,对比图2C与图2B和图1A可以看出,在河谷平原、低山以及中山区域,GPP的空间分异与ET较为一致,但在河谷周边的高山区域GPP的空间分异则与WUE较为一致。具体来看,伊犁河谷59.12%的区域GPP>500 g C/m2,空间上主要位于河谷的中山区域,该区域中,500 g C/m2<GPP<650 g C/m2和GPP>650 g C/m2的比例分别达到了31.98%和27.14%; 350 g C/m2<GPP<500 g C/m2与200 g C/m2<GPP<350 g C/m2的比例相当,分别为17.49%和15.16%,空间上主要分布在河谷周边的高山区及河谷中部的低山区域; GPP<200 g C/m2的比例最小,为8.23%,主要分布在河谷中部的平原区域。
综合图2A、图2B与图2C可以看出,昭苏盆地—特克斯的区域以及科古琴山的南部低山区,由于GPP高(>650 g C/m2)而ET相对较低(300 mm<ET<400 mm)成为伊犁河谷草地WUE高值(>1.50 g C/kg H2O)区域; 河谷周边的高山区域,由于GPP较低(<500 g C/m2)而ET较高(>400 mm),因而WUE较低(<1.00 g C/kg H2O); 而那拉提—阿吾勒拉山一带既是GPP高值(>650 g C/m2)区域,也是ET高值(ET>500 mm)区域,其WUE则并未达到最高; 同时,巩乃斯下游—伊犁河北岸的平原区及低山区,其GPP低(<350 g C/m2),ET也低(<300 mm),但WUE却并非最低; 伊犁河南岸平原区GPP最低(<200 g C/m2),ET也低(<300 mm),其WUE也低(<1.00 g C/kg H2O)。
由图3A可知,在空间上,伊犁河谷绝大部分区域草地WUE有所增加,根据统计结果,其比例为79.20%,但增大达到显著水平的面积有限,比例为16.61%,空间上主要分布在河谷北部、乌孙山及那拉提山的中山区域; WUE呈减少趋势的草地面积比例为20.79%,其中20.04%的区域呈非显著减少,空间上主要分布在河谷南部高山区域、乌孙山南麓喀什河下游两侧的低山和洪积冲积扇区。
从图3B可以看出,2000—2014年伊犁河谷草地ET减少区域占了绝大比例。根据统计结果,ET减少区域面积比例高达92.31%,而ET增加区域仅有零星分布。具体来看,ET呈显著减少的比例达到了48.21%,分布于巩乃斯河两岸、尼勒克和特克斯及科古琴山中山区; ET呈非显著减少的比例为44.10%,主要分布于冲积扇平原区以及那拉提—婆罗科努山—天山山脉高山区; ET呈显著增加的比例仅为0.35%; ET呈非显著增加的比例仅为7.34%,分布于河谷周边区域。
GPP总体变化趋势虽然与ET相同,但在空间上,GPP有所减少的区域明显少于ET(图3B和图3C)。根据统计,GPP呈减少趋势的比例为78.11%,其中,58.66%呈非显著减少,减少达到显著水平的比例仅为19.45%,空间上主要分布于特克斯河和巩乃斯河周边的低山和冲积平原区,以及乌孙山北麓的部分区域; GPP呈非显著增加的比例为20.34%,主要分布于研究区海拔较高的东部、南部和北部边缘区域,以及伊犁河出国境口的河谷平原区; GPP呈显著增加的比例仅为1.55%。
近15 a伊犁河谷草地ET总体呈现极显著下降的趋势(Zc=-2.67,p<0.01)。在2000—2002年,ET逐渐增加,并在2002年达到最大值(453.66 mm),之后呈现波动式下降,在2014年达到最小值(335.97 mm)。GPP在研究时间范围内同样呈现降低的趋势,但其变化不显著(Zc=-1.5,p>0.05)。在年际波动上,GPP与ET的波动较为一致,最大值和最低值分别出现在2007年和2014年,分别为564.84 g C/m2,409.63 g C/m2。研究时段的15 a间,伊犁河谷草地WUE总体呈增加趋势,但变化趋势不显著(Zc=1.78,p>0.05)。2000—2007年时,WUE整体呈现上升的趋势,之后逐渐下降,在2010年达到最低值(1.19 g C/kg H2O)。在2011年、2012年,WUE逐渐上升,在2012年达到最大值(1.35 g C/kg H2O),之后再次下降。
对研究时段的前3 a(2000—2002年)及后3 a(2012—2014年)ET,GPP及WUE求平均值,并进行差值计算,得到其变化量。ET,GPP及WUE的在2000—2002年及2012—2014年的平均值分别为427.33 mm,524.86 g C/m2,1.21 g C/kg H2O及367.59 mm,480.48 g C/m2,1.29 g C/kg H2O,ET和GPP分别减小59.74 mm和44.38 g C/m2,减小13.98%和8.46%,WUE增加0.08 g C/kg H2O,增加6.61%。
图4为利用ET,GPP及WUE变化趋势Zc值空间分布数据进行叠加分析而得到的三者变化趋势交互关系图。由图4可见,伊犁河谷草地的绝大部分区域表现为GPP降低、ET降低而WUE增加,表明相对于GPP,ET减少速率更大,因此WUE才有所增加。研究表明干旱生态系统中,GPP高的季节或年份,其WUE也高[34],但伊犁河谷草地WUE的年际波动与GPP存在较大差异,两者相关系数为0.31(p=0.27)。同时WUE与ET的年际波动也存在较大差异,两者相关系数为-0.18(p=0.53)。相反,ET与GPP的年际波动一致性很高,两者相关系数高达0.88(p<0.001)(表1)。
WUE为GPP与ET比值,其变化由GPP和ET共同决定。但顾春杰研究表明,相对于ET,GPP是影响不同生态系统WUE的决定因素[35],而宫菲等人对宁夏陆地生态系统WUE与GPP和ET关系分析表明,该区WUE与ET呈极显著负相关(p<0.01),并指出生态恢复工程虽增加了生态系统的生产力,但也增加了水分消耗,致使生态系统WUE降低[36]。而本文中伊犁河谷草地WUE的增大虽然是因为GPP减少速率小于ET减小速率,但WUE与GPP及ET的相关性均不高,而GPP变化与ET却具有很高的相关性,这表明,不同于顾春杰及宫菲等人[35-36]的研究结果,单一的GPP或ET均不能构成伊犁河谷草地WUE变化的主导原因; 而同时,WUE的变化也不仅仅是GPP变化与ET变化的简单的累加,而是GPP和ET综合作用的结果。
用NDVI作为表征草地植被覆盖水平的指标,讨论植被变化对WUE的影响。
就NDVI与WUE的直接关系来看,由图5可知,2000—2014年伊犁河谷平均NDVI与平均WUE变化趋势相反,NDVI减小而WUE增加,根据表1,两者相关系数仅为-0.11(p=0.71),表明NDVI变化不是影响WUE的直接原因; 而空间上,绝大部分区域在NDVI减小的背景下WUE有所增大。
根据上文分析,伊犁河谷草地WUE增加主要是由于ET减小的程度高于GPP的减小程度。对于草地生态系统,植被覆盖的降低通常伴随着GPP的降低,根据表1,2000—2014年伊犁河谷NDVI与GPP的相关系数达到了0.86(p<0.001); 但更为重要的是,植被覆盖对ET具有重要的调节作用,植被覆盖降低不仅致使草地植被蒸腾量减少[37],还致使植被水源涵养的功能降低[38],使降水及冰雪融水等水分更容易形成地表径流而流失,减少可供蒸腾和蒸发的水量,从而使ET总量减少。同时图6中,伊犁河谷草地NDVI与ET年际波动高度一致性,两者相关系数也高达0.95(p<0.001),这进一步表明伊犁河谷草地植被覆盖降低促使ET逐渐减少。
Zhu等[39]基于通量监测的数据发现,在我国的温性草地、高寒草甸及温带落叶阔叶林,叶面积指数能通过调控ET中的蒸发和蒸腾两个分量的比例来影响生态系统的WUE。本文虽采用NDVI来反应植被覆盖,但由NDVI与ET却具有很高的相关性,同时,NDVI与WUE的相关性并不高,由此可见,伊犁河草地NDVI可以通过对ET的调节来影响WUE。
除植被覆盖外,气候因子对WUE的变化也具有重要影响[40-41]。伊犁河谷草地降水及SPEI总体均呈现降低的变化趋势,空间上,绝大部分区域在降水减少及气候变干旱(SPEI减小)的条件下WUE增大; 气温也呈降低趋势,但却存在明显的空间差异,有大面积区域在气温升高的条件下WUE增大,也有大面积区域在气温降低的条件下WUE增大。根据表1,WUE与降水和SPEI的相关系数分别达到了-0.49(p=0.06)和-0.58(p=0.03),而WUE与气温的相关系数为0.34(p=0.21)。可见相对于气温变化,WUE与降水和SPEI相关性更高。
降水是生态系统水分的最终来源,根据表1,ET与降水的相关系数达到了0.55(p=0.03),而ET与气温的相关系数仅为0.04(p=0.89)。由此可见,相对于气温,降水的减少是导致伊犁河谷ET减少的主要驱动因素,因而也是促使草地WUE的增大的重要驱动因素。关于降水与WUE关系的研究较少,但这些研究表明降水是控制WUE时空变化的主要因子[42],本文的研究结果支持该结论。同时,Hu等[43]的研究指明草地WUE之所受到降水的控制,原因可能是WUE和降水的关系主要由碳过程控制,而不是水过程,而本文中降水与NDVI的GPP的显著相关性也对该结论给予了支持,且NDVI降低所致使草地生态水源涵养功能的降低对ET减少的影响和伊犁河谷草WUE增加起到重要作用。
干旱是植被生长的重要抑制因子,但在一定范围内,随干旱程度增加,植物通过自身调节,使GPP减少低于ET减少[44],提高WUE。伊犁河谷草地WUE虽然与SPEI具有较高相关性,且全区绝大部分区域也是在干旱化的条件WUE有所增加,但这并不能证明干旱程度的加深就是致使伊犁河谷草地GPP减少程度低于ET减少程度的驱动因素,干旱对WUE的影响仍需深化研究。
(1)伊犁河谷草地WUE,ET和GPP均存在明显海拔分异; 海拔较低的河谷平原区为三者的共同低值区,而中山区域虽为三者的共同高值区域,但该区内WUE与GPP和ET却存在明显空间差异; 高山区域内GPP和WUE均较低,而ET则较高。
(2)2000—2014年伊犁河谷草地平均ET和GPP呈降低趋势,而平均WUE则呈增加趋势,但仅ET变化达到显著水平; 15 a内,全区平均ET和GPP减小13.98%和8.46%,WUE增加6.61%。空间上,全区有92.31%和78.10%的区域ET和GPP有所降低,其中48.21%的区域ET降低达到显著水平,而GPP的该比例明显小于ET,为19.45%; 全区79.20%的区域WUE有所增加,但达到显著水平的比例仅为16.60%。
(3)伊犁河谷草地WUE增加主要是由于GPP降低速率低于ET,但ET变化与GPP关系紧密,WUE的变化并不由单一的GPP或ET变化所主导,而是GPP和ET变化综合作用的结果。
(4)相对于气温,降水是影响伊犁河谷草地植被覆盖和ET的主要气候因子。在2000—2014年,伊犁河谷降水的降低是导致草地WUE升高的主要因素。