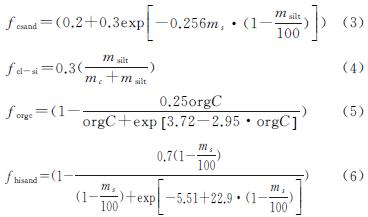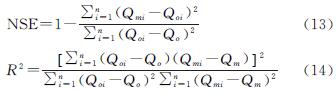2.1 延河流域SWAT模型的构建
2.1.1 SWAT模型土壤侵蚀子模块以及土壤保持量的获取 目前已有大量研究利用SWAT水文模型对黄土高原区域的产流产沙进行模拟[11-13],因此本研究选用SWAT模型,对延河流域土壤保持量进行模拟。该模型中产沙量的计算采用改进版通用水土流失方程(Modified Universal Soil Loss Equation,MUSLE),如式(1)所示。
Sed=11.8·(Qsurf·qpeak·areahru)0.56·Kusle·Cusle·Pusle·LSusle·CFRG(1)
式中:Sed为模拟产沙量; Qsurf为地表径流(mm H2O/hm2); qpeak为径流峰值(m3/s); areahru为HRU面积(hm2); Cusle为地表植被覆盖因子; Pusle为水土保持措施因子; Kusle为土壤可蚀性因子; LSusle为地形因子,包括坡长因子L和坡度因子S; CFRG为直径大于2 mm的粗碎块因子。
(1)土壤可蚀性因子(Kusle)可以表示土壤对侵蚀的敏感性,SWAT中计算Kusle因子的方法,具体公式如下式所示。
Kusle=fcsand·fcl-si·forgc·fhisand(2)
式中:fcsand为沙土质地土壤侵蚀因子; fcl-si为黏壤土土壤侵蚀因子; forgc为土壤有机质因子; fhisand为高沙质土壤侵蚀因子。
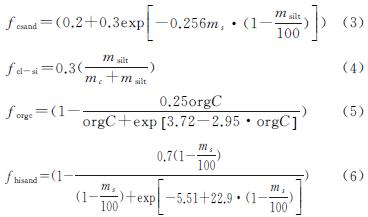
式中:ms,msilt,mc分别为砂粒、粉粒、黏粒的含量(%); orgC为有机碳含量(%)。
(2)植被覆盖因子(Cusle)是影响土壤侵蚀的最敏感因子,主要受到覆盖度、植被类型等的影响,SWAT模型中计算公式如下。
Cusle=exp([ln(0.8)-ln(Cusle,mn)]· exp[-0.00115·rsdsurf]+ln[Cusle,mn])(7)
式中:Cusle,mn为土地利用的最小植被覆盖度因子; rsdsurf为土壤表面残留物(kg/hm2)。
Cusle,mn因子可由已知的Cusle,aa因子用下式估计:
Cusle,mn=1.463ln[Cusle,aa]+0.1034(8)
式中:Cusle,mn为土地利用的最小植被覆盖度因子; Cusle,aa为土地利用年均植被覆盖因子。
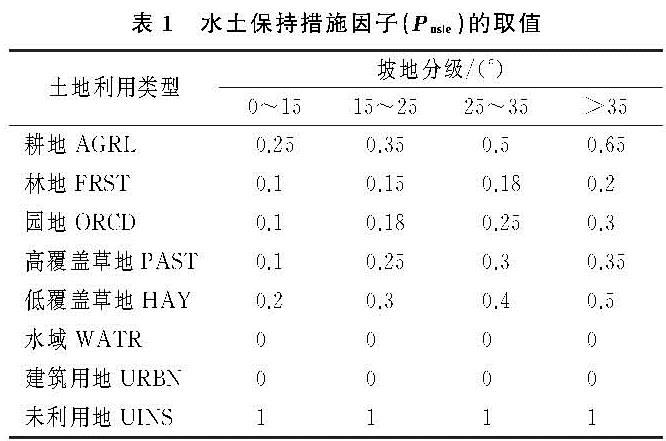
(3)水土保持措施因子(Pusle)是指采取水保措施后,土壤流失量相对于未采取任何措施时的比例,取值范围为0~1[14]。0表示不存在侵蚀现象的区域,1表示未采取水土保持措施的区域。SWAT模型中Pusle因子是采用Wischmeier和Smith给出的信息计算,为了使模拟结果更适合研究区,因此本文对Pusle因子进行了修改。SWAT模型中可对每一个HRU的Pusle因子进行修改,HRU中包含土地利用、坡度等信息,因此本文根据土地利用类型及坡度范围,并考虑前人在黄土高原的研究以及黄土高原上水保措施的实施,包括梯田、水平沟以及鱼鳞坑等的影响[15-16],最终确定表1中Pusle因子的取值。
(4)坡度坡长因子(LS)可以表示地形因子对土壤侵蚀的影响,SWAT模型中采用如下公式进行计算。

式中:Lhill为坡长(m); m为指数项; αhill为坡度。
m的计算公式如下:
m=0.6(1-exp[-35.835·slp])(10)
式中:slp为HRU的坡度。
slp与αhill的关系为:
slp=tanαhill(11)
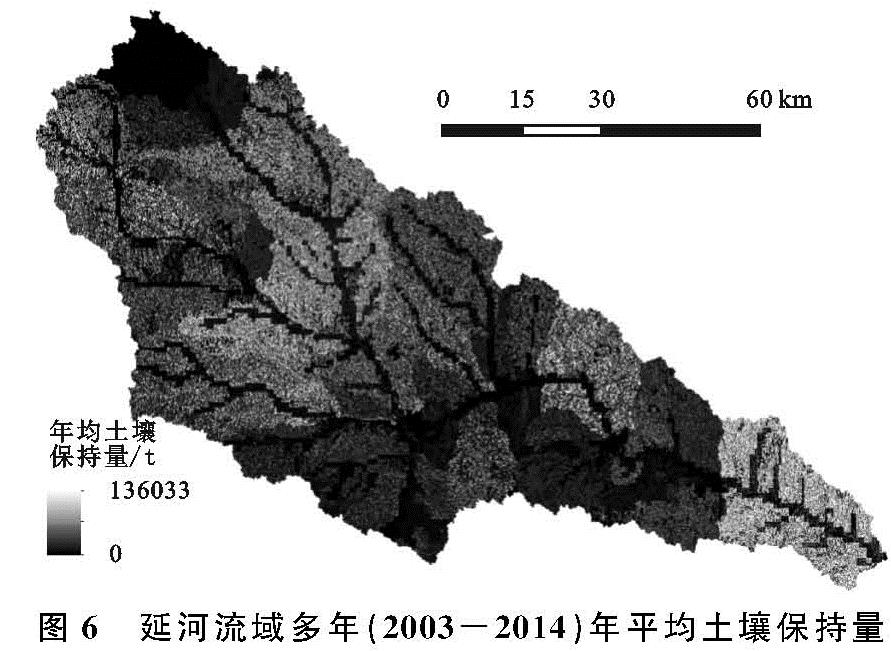
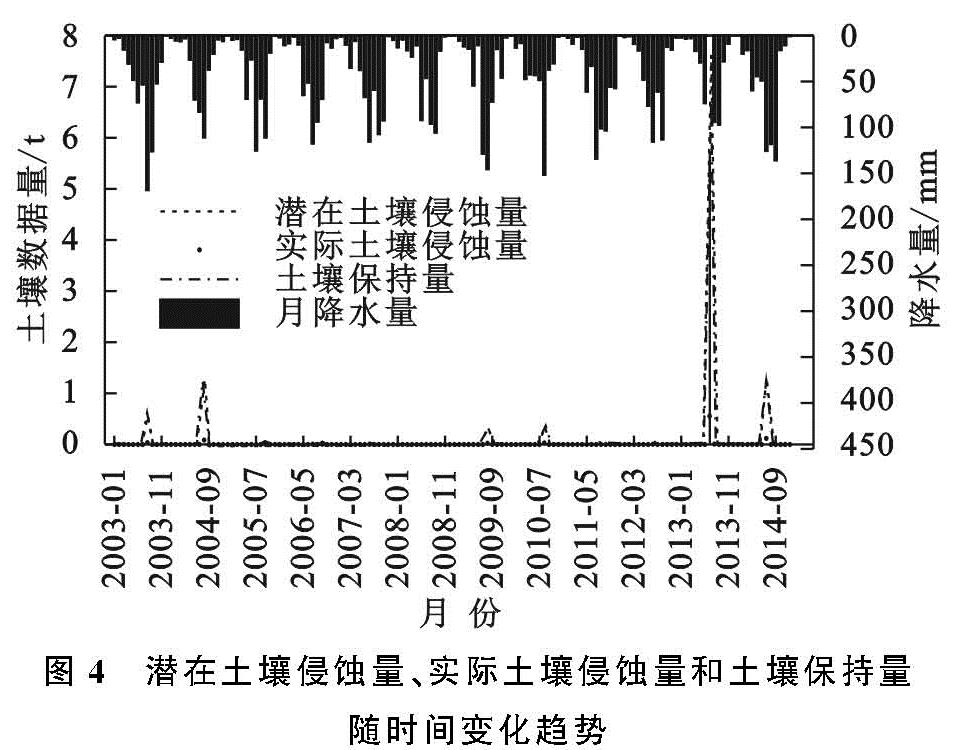
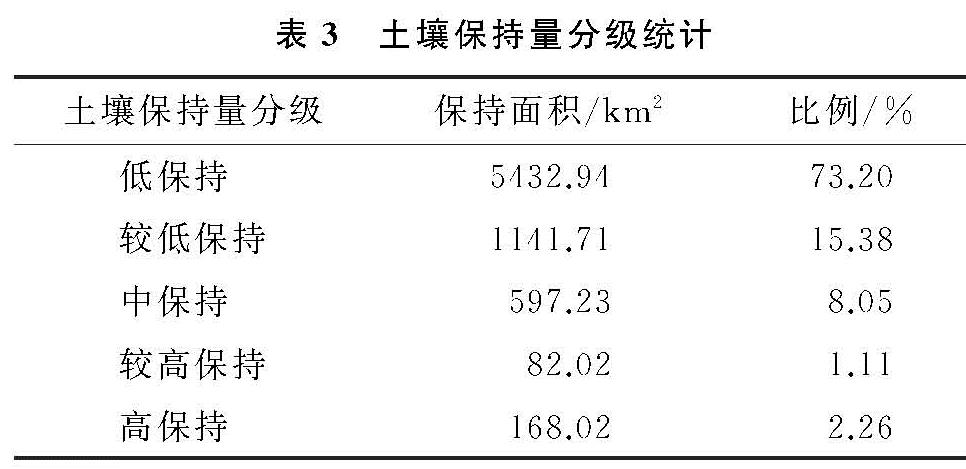
研究中涉及潜在土壤侵蚀量(Sedq)、实际土壤侵蚀量(Seda)、土壤保持量(Sedc)3种数据量的计算。潜在土壤侵蚀量是指在假定没有地表植被覆盖和水土保持措施下的侵蚀量,即通过将SWAT源代码和数据库中的Cusle,Pusle因子修改为1得到的产沙量。实际土壤侵蚀量是指流域实际发生的侵蚀量,即由SWAT模型直接模拟得到的产沙量。土壤保持量是二者的差值,计算公式如下式所示。
Sedc=Sedq-Seda=11.8(Qsurf·qpeak·areahru)0.56·
Kusle·LSusle·CFRG·(1-Cusle·Pusle)(12)
2.1.2 数据库的构建
(1)土地利用数据库。研究中主要使用2005年、2010年的土地利用数据,将延河流域土地利用数据分为耕地、林地、园地、高覆盖草地、低覆盖草地、建设用地、水域和未利用地8类,模型在输入土地利用数据时,同时还需要输入土地利用索引表,方便将流域的土地利用类型与SWAT模型自带的植被生长模型库和农业管理数据库进行连接。因此,按照SWAT模型中土地利用的编码对各种土地利用重新进行编码,见表2,从而建立土地利用索引表。
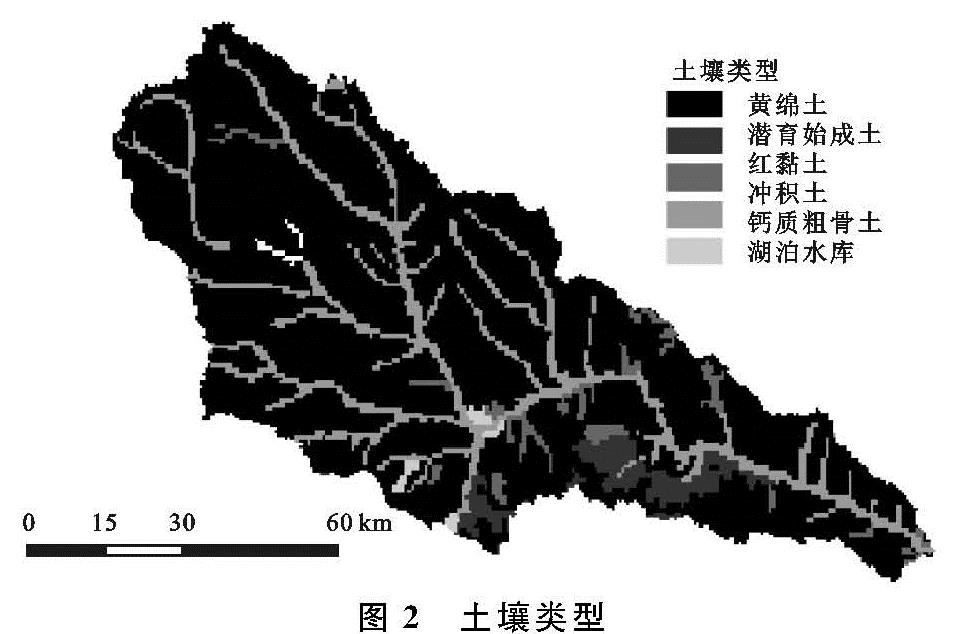
(2)土壤数据库。本文所使用的土壤数据来源于HWSD,流域的土壤类型主要包括黄绵土、冲积土、粗骨土、红黏土、潜育始成土等,见图2。通过在HWSD中获取各种土壤的部分参数以及利用SPCS软件计算部分土壤参数,建立土壤参数数据库,并根据各类土壤在SWAT中的编码,建立土壤参数索引表。
(3)气象数据的准备。本文选用流域内及距离流域较近的11个传统气象站点1999—2014年的逐日气象资料输入到SWAT模型中,其中降水、最高温度、最低温度、相对湿度、风速可直接在中国气象数据共享网站获取,太阳辐射数据通过天气发生器模拟得到。
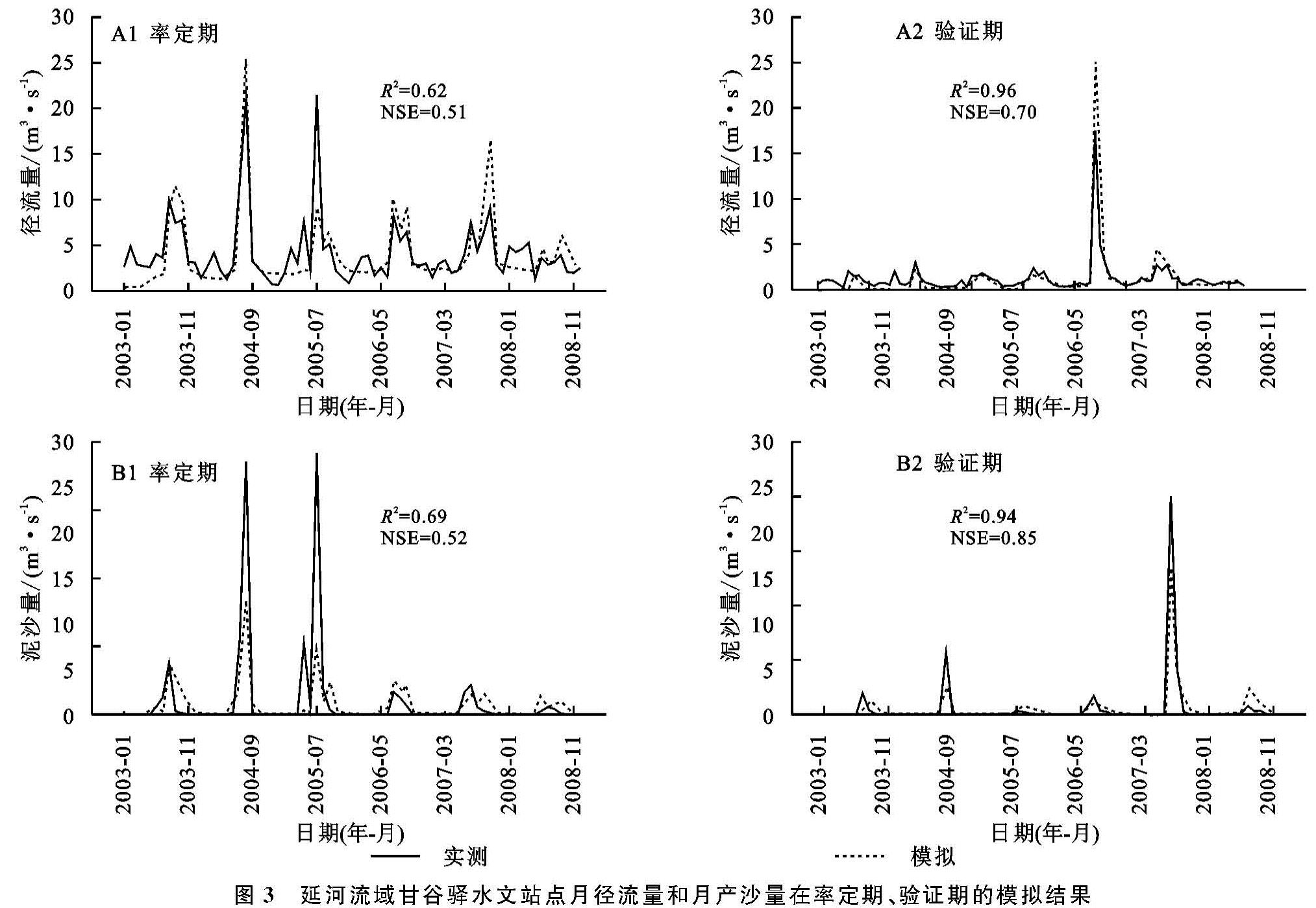
2.1.3 模型的建立 本研究使用ArcSWAT 2012版本,首先是子流域的划分,基于DEM生成河网,通过设定阈值(形成子流域的最小给水面积)为10 000 hm2,设置流域出水口点,将延河流域划分为41个子流域; 其次是水文响应单元(HRU)的划分,模型在划分子流域的基础上,通过叠加土地利用数据、土壤数据和坡度数据,获得各个子流域中具有相同土地利用类型、土壤类型和坡度的HRU。最后将气象数据等导入模型,对延河流域1999—2014年产沙量进行模拟。模型以1999—2002年作为预热期,利用2003—2008年甘谷驿水文实测值进行率定,利用2009—2014年的水文实测值进行验证。由于研究时间较长,土地利用会发生一定程度地变化,因此将预热期和率定期视为整体,选用2005年土地利用进行模拟; 在验证期时选用2010年土地利用进行模拟。
2.1.4 模型的参数敏感性分析、率定、验证以及不确定性分析 本文通过选用SWAT-CUP(SWAT-Calibration and Uncertainty Programs)中的SUFI-2算法对SWAT模型进行敏感性参数分析、率定、验证以及不确定分析。在该算法中,采用判定系数(Cofficient of determination,R2)和纳什效率(Nash-Sutcliffe efficiency coefficient,NSE)对模型进行适用性评价,其中R2可评价模拟值与实测值变化趋势的一致性,NSE可反映模拟值与实测值之间的拟合程度[17]。
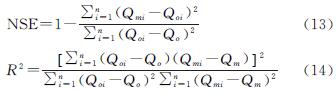
式中:Qmi为模拟值; Qoi为实测值; Qm为模拟均值; Qo为实测均值。
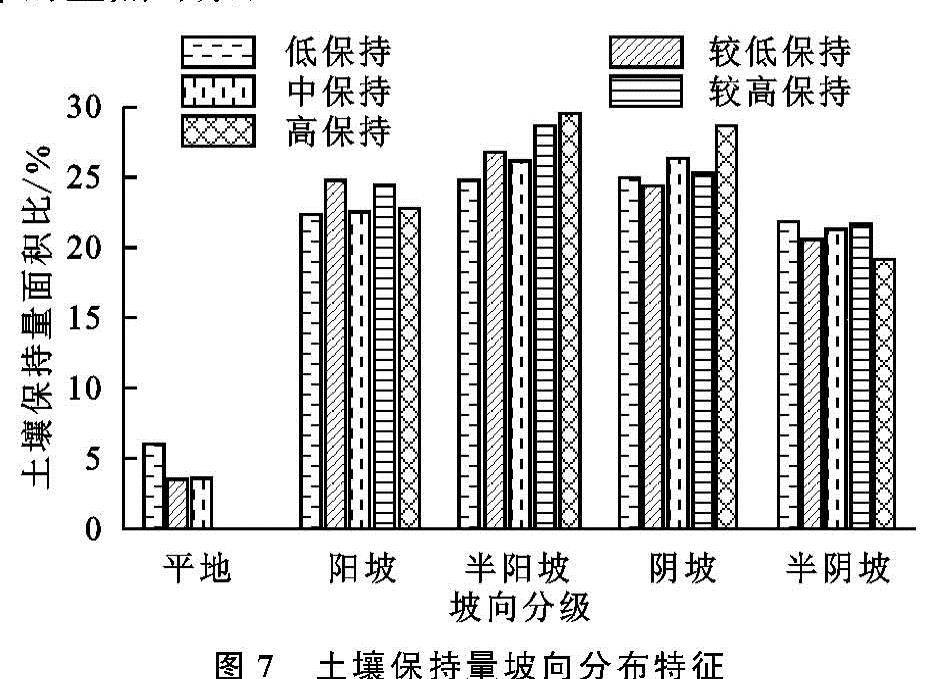
2.2 地形因子的获取
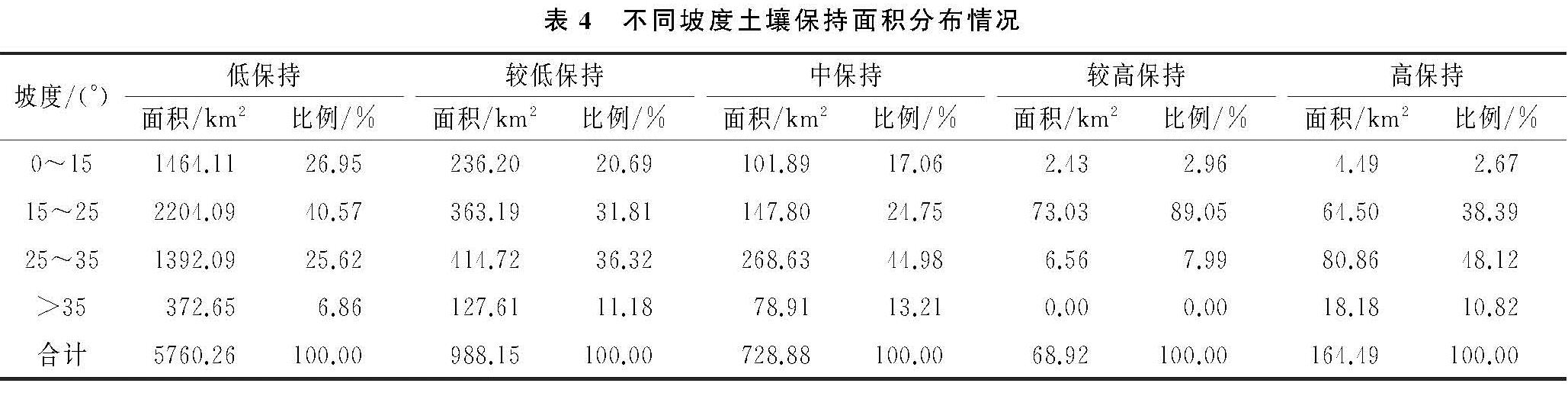
本文选用的地形因子包括:坡度、坡向和高程,其中坡度由DEM直接获取,将其分为0°~15°,15°~25°,25°~35°以及>35°共4个等级,获得坡度分级图; 坡向由DEM直接获取,将其分为平地、阳坡、半阳坡、半阴坡及阴坡5类,获得坡向分级图; 高程由DEM直接获取,通过设置50 m的高程间隔,分为26个等级,获得高程分级图。