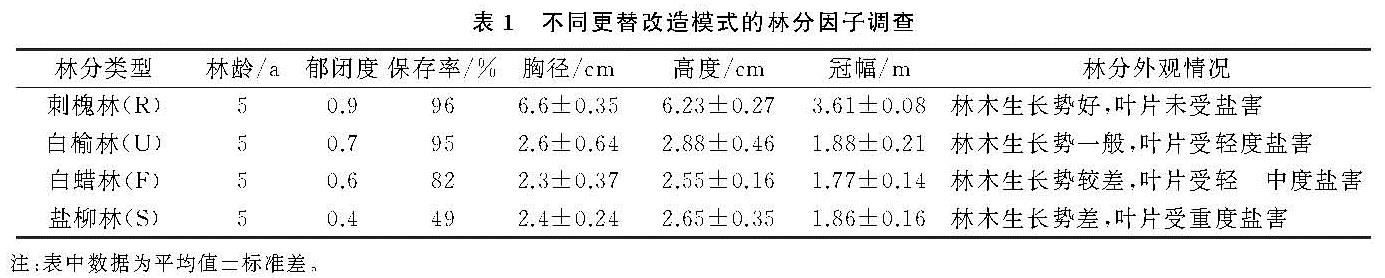
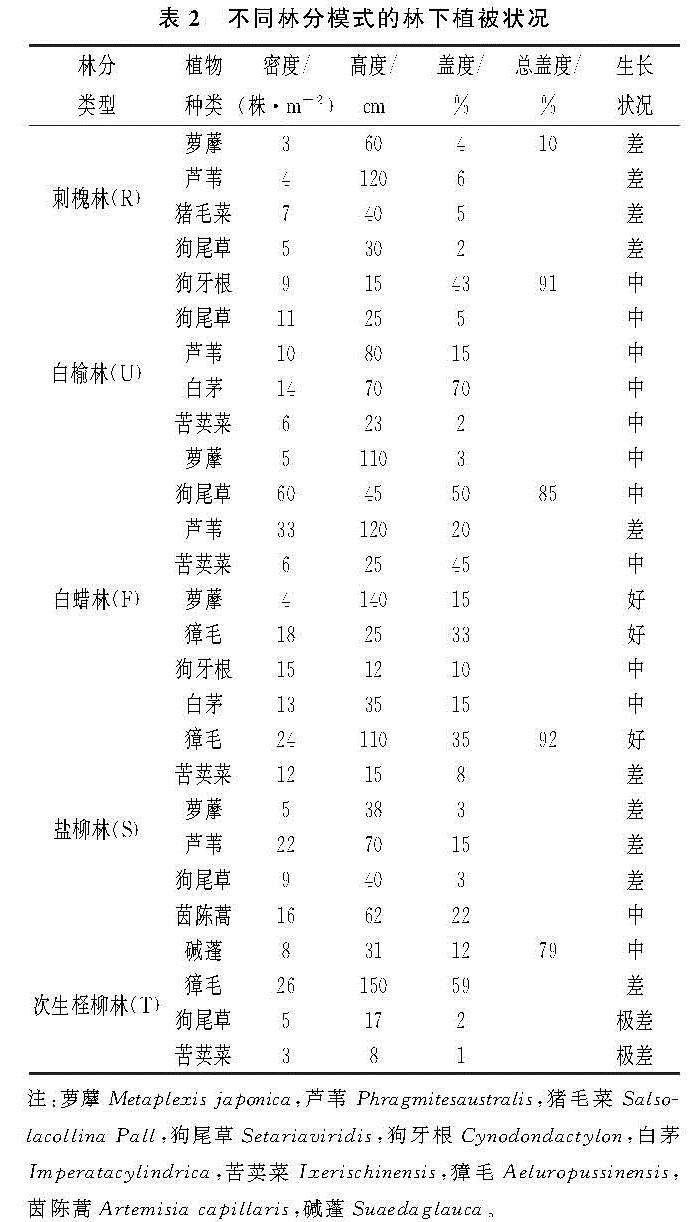
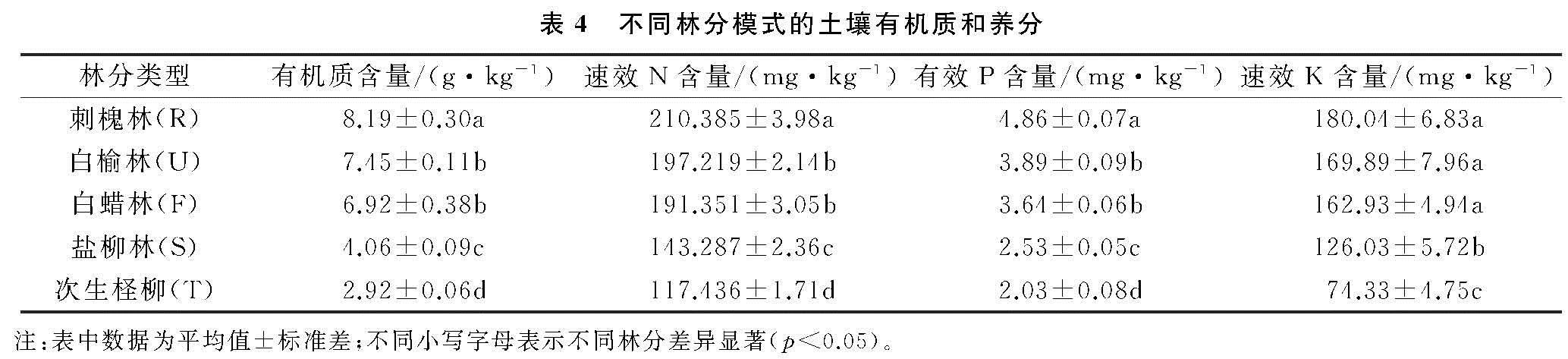
在黄河三角洲盐碱地退化林分的更替改造中,造林树种选择至关重要,是更替改造成败的重要因素之一[19]。乔艳辉等[20]在黄河三角洲人工衰退林分更替改造模式的分析与评价中提出,在衰退林分的更替改造中,首先应依据立地条件考虑选择在盐分、干旱等主要限制因子的表现上相当或者高于原有衰退林分的树种。针对次生柽柳林分由于受到人为干扰等因素的影响,林分出现退化成为残次林后,人工更替改造为刺槐、白榆、白蜡和盐柳4种林分模式,本研究分析了其更替改造5 a后的林分状况。分析表明,4种更替改造模式的林分状况因树种的不同而表现出较大的差异,尤其是林分郁闭度和保存率2个林分指标,以刺槐林分状况最好,白榆和白蜡次之,盐柳林分状况最差,这固然与树种的特性(树种不同,其生长速度不一样)有关,但主要原因是由于黄河三角洲地区盐碱地土壤的次生盐渍化和干旱等因素的影响[21],刺槐树种的耐盐能力虽然不如白榆和白蜡,但其抗干旱的能力却强于这2个树种,在干旱、次生盐渍化相互交织的生境下,刺槐林分生长状况明显好于白榆和白蜡; 而盐柳树种在耐盐和耐干旱能力上都要差于刺槐、白榆和白蜡这3个树种,所以原本应该生长快的树种,其林分生长速度反而不如白榆和白蜡,这与乔艳辉等对衰退人工八里庄杨更替改造为白榆和盐柳2种模式林分的研究结果[20]相似。
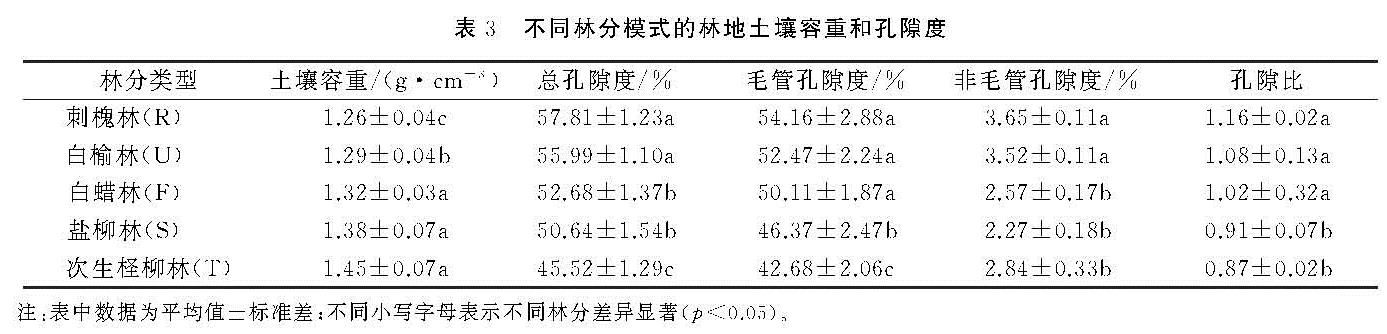
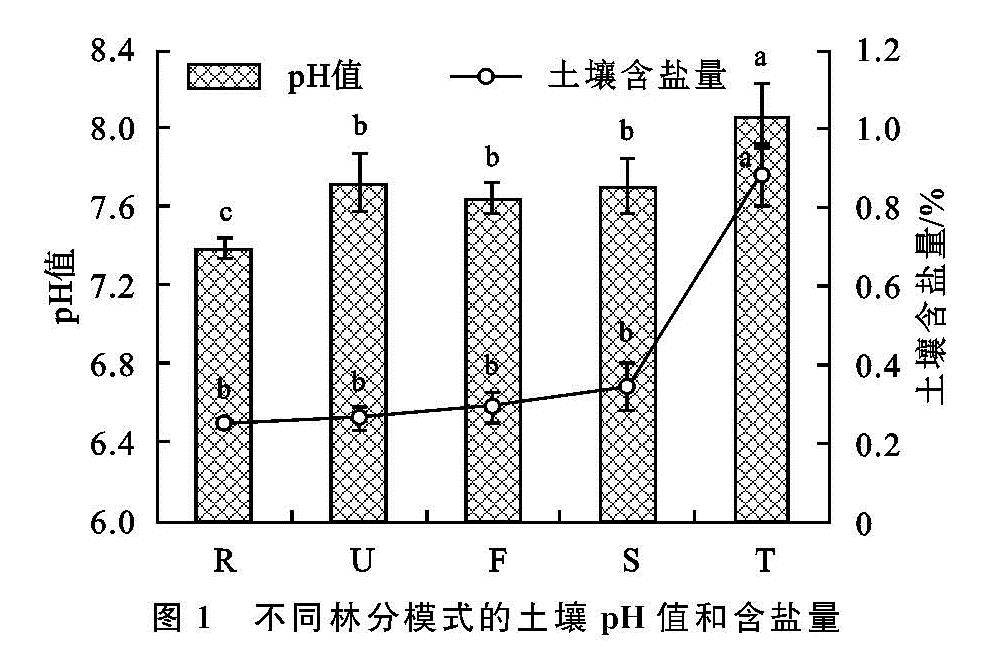
有关研究表明,在黄河三角洲盐碱地上造林之前实施的台田、条田整地和土壤淋溶洗盐等工程、水利措施,能有效地降低土壤表层含盐量,使得造林之初栽植的成活率得到保障,但在地下咸水埋深浅、矿化度高、蒸降比大等自然因素影响的条件下,造林地极易发生土壤次生盐渍化[15,22]。通过本研究对次生柽柳退化林分更替改造的4种模式的林分(生长)状况和土壤改良效应的分析来看,除了树种选择之外,造林栽植密度等也是需要考虑的重要因素之一。本研究的4种更替改造模式中,刺槐林栽植株行距为1.5 m×2 m,其他3种林分栽植株行距为2 m×3 m,由于刺槐林的密度较大,能及早郁闭,使得刺槐林分的土壤蒸发量减少,抑制了土壤返盐,林分状况得到改善,不仅提高了林分生长,而且在林地土壤的改良效应上效果亦明显突出。
虽然目前针对退化林分的改造已有很多的研究和实践,但针对不同成因、不同立地条件下的退化林分提出针对性强的改造技术和模式尚需要进一步加强和深入地提炼研究[19]。本研究仅是次生柽柳退化林更替改造为4种模式的林分在5 a时的效应分析与评价,而对退化防护林改造的研究是个连续的过程,随着时间推移,在黄河三角洲盐碱地恶劣条件下,这4种更替改造的林分效应的表现尚需进一步观察和研究。另外,退化林分的改造不仅涉及到技术因素,还涉及很多政策因素。本研究的对象是因工程建设和景观提升需要对退化的次生柽柳林皆伐更替为4种不同模式的林分筛选,在实际工作中,具体模式的应用还需要依据黄河三角洲地区盐碱地防护林是生态公益林的实际,处理好技术与政策的关系。