资助项目:国家自然科学基金(71663017); 湖北民族大学博士启动金资助项目(4158002)
第一作者:刘恒(1995—),男,湖北钟祥人,硕士研究生,研究方向为资源环境评价与管理。E-mail:zxlh0601@163.com 通信作者:汤弟伟(1987—),男(土家族),湖北建始人,博士,讲师,主要从事资源环境评价与管理研究。E-mail:jstdw@163.com
(湖北民族大学 林学园艺学院, 湖北 恩施 445000)
(College of Forestry and Horticulture, Hubei Minzu University, Enshi, Hubei 445000, China)
net primary productivity; spatiotemporal dynamic; driving factors; Wuling Mountainous area
为了揭示武陵山区植被净初级生产力(NPP)时空动态特征和定量识别相关驱动因子及其影响力,基于2000—2015年MOD17A3数据集,采用变异系数、趋势分析和Hurst指数分析了该区植被NPP的时空动态特征及变化趋势,并利用相关分析、地理探测器从自然和人为两方面对驱动因子进行了解析。结果 表明:(1)2000—2015年,武陵山区植被NPP整体呈不显著下降趋势,年际波动性明显; 常绿针叶林和常绿阔叶林是生产能力最强的植被; 空间上呈现中部高、四周低的分布格局; 近16年表现出北增南减的变化特征,未来趋势以反持续为主,NPP可能增加。(2)驱动因子上,NPP与降水、气温均为正相关,气温为主要气象因子; NPP随着高程、坡度的增加均表现先增后减的趋势; 耕地转林地是土地利用变化引起NPP变化的主要地类转换。(3)因子影响力上,气温>降水>高程>土地利用>坡度,气温、降水和高程是主导因子,坡度和土地利用是重要因子,自然因素影响力强于人为因素。
To reveal the spatiotemporal dynamic characteristics of vegetation net primary productivity(NPP)in the Wuling Mountainous area and to quantitatively identify the relevant driving factors and their influence, based on the MOD17A3 dataset from 2000 to 2015, the coefficient of variation, trend analysis, and Hurst index were used to analyze the NPP spatiotemporal dynamic characteristics and changing trends, and driving factors were analyzed from natural and man-made aspects using correlation analysis and geo-detector. The results showed that:(1)between 2000 and 2015, the vegetation NPP in the Wuling Mountainous area showed no significant decline trend as a whole, with great inter-annual fluctuation; evergreen coniferous forest and evergreen broad-leaved forest were the most productive vegetation. The spatial distribution pattern of NPP was high in the middle and low in the surrounding area; the trend of NPP over the 16 years had increased in the north and decreased in the south, and the future trend will be the main anti-continuity, and the NPP will increase;(2)in terms of driving factors, NPP was positively correlated with annual precipitation and average annual temperature, and the temperature was the main climate factor; NPP increased first and then decreased with the increase of elevation and slope; the conversion of cultivated land to forestland was the main conversion of NPP caused by land-use change;(3)influence level of factor decreased in the order: temperature>precipitation>elevation>land-use>slope, temperature, precipitation, and elevation were the dominant factors, slope and land-use were the important factors, and the influence of natural factors was stronger than that of human factors.
植被净初级生产力(Net Primary Productivity,NPP)是指绿色植被在单位时间、单位面积由光合作用产生的有机物质总量中扣除自养呼吸后的剩余部分[1]。NPP不仅直接反映植被在自然环境状况下的生产能力[2],表征陆地生态系统的质量状况,而且是判定生态系统碳源/碳汇及区域生态支持能力的重要因子[3-4]。NPP受到光、热、水等自然条件的影响,其变化可用于表征全球气候变化和陆地生态系统响应,同时,NPP变化也与人类活动密切相关。由于植被及其影响因子的空间异质性,定量分析区域尺度NPP的时空动态特征及影响机制,对于科学评价区域生态系统质量和理解NPP对气候、土地利用变化等响应特征具有重要的理论和实践意义。
NPP的发展经历了“实测—统计模型—机理模型”3个阶段[5],基于多源遥感数据利用模型估算植被NPP进行相关研究成为当前主流[6]。估算模型可以分为气候相关模型、光能利用率模型和生态系统过程模型3类[7]。MODIS NPP产品MOD17A3是基于MODIS遥感参数、参考BIOME-BGC模型与光能利用率模型模拟的NPP数据[8],该数据集已在全球和区域研究中得到验证和应用[9-10]。国内学者利用MOD17A3数据也开展了相关研究:研究内容上,侧重于NPP的时空格局[11]、动力机制[12]及对气候变化的响应[13]; 研究尺度上,集中在全国[14]、省[13]、自然地带[15]及流域[16]等; 研究方法上,变异系数、趋势分析、Hurst指数等方法是探究NPP的时空特征及变化趋势的常用方法,相关性分析、地理探测器等方法用于驱动力分析。
武陵山区是指武陵山覆盖的区域,它是我国亚热带森林生态系统核心区、长江流域重要的水源涵养区和生态屏障,全国主体功能区规划将其划定为武陵山区生物多样性及水土保持生态功能区。目前该区存在地质灾害较多、土壤侵蚀严重、生物多样性受到威胁等问题。然而,关于该区NPP的研究鲜见报道,在较少研究中存在时间尺度短、仅考虑了NPP与地形因子的关系等问题,对于影响NPP的其他关键因子,如降水、气温、土地利用变化等,未作进一步解释。鉴于此,本文利用MOD17A3数据研究该区NPP的时空动态特征,并从自然和人为两方面对NPP的驱动因子进行综合分析,以期为该区的植被保护、资源管理及合理开发提供理论指导。
武陵山区地理位置为25°52'—31°24'N,107°4'—112°2'E(附图1),包含湖北、重庆、湖南、贵州4省市交界地区的71个县(市、区),国土面积约17.18万km2,是第二级阶梯向第三级阶梯的过渡带。该区为云贵高原的东部延伸地带,地势西北高—东南低,平均海拔为1 000 m左右。气候属亚热带向暖温带过渡类型气候,森林覆盖率高达53%,植被以常绿阔叶林和落叶阔叶林为主。由于自然条件的恶劣,加上人类不合理的活动,生态环境受到的威胁较多。
NPP数据为2000—2015年MOD17A3产品,空间分辨率为1 km。植被类型数据为MCD12Q1产品,空间分辨率为500 m,采用第4种分类方案。利用MRT对MODIS数据进行镶嵌、格式转换和重投影,在ArcGIS中进行单位换算、裁剪,并剔除无效值。质量控制数据(NPP_QC)表明研究区NPP反演结果中、高等级多年平均可信度为90.27%,考虑到武陵山区地形复杂、多云,数据质量整体能够接受。
研究区的气象(气温、降水)、土地利用和DEM数据均来源于中国科学院资源与环境数据中心(表1)。利用高程数据生成坡度数据,将土地利用数据重分类为耕地、草地、水域、林地、建设用地和未利用土地。除土地利用数据外,其他数据的分级均采用1/4倍标准差分级法[16]。该方法根据数据固有的数值特征和分布规律进行分级,不受人为干扰,分级结果更为客观。所有数据定义相同的空间参考、范围和分辨率,建立数据库。
变异系数能够反映地理数据的相对变化(波动)程度[17],用其来评估NPP在时间序列上的稳定性,计算公式为:
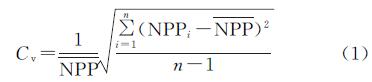
式中:Cv为变异系数; NPPi为i年NPP值; NPP^-为平均值; n为时间序列的长度。Cv值越大,表明NPP随时间序列波动大,反之则波动小。
Theil-Sen Median趋势分析结合Mann-Kendall检验,是判断长时序数据趋势的重要方法[18]。该方法不需要数据服从一定的分布,对数据误差具有较强的规避能力[19]。趋势分析的计算公式为:
β=median((NPPj-NPPi)/(j-i)), 2000≤i<j≤2015(2)
当β>0时,植被NPP表现为上升趋势,小于0表现为下降趋势。
Mann-Kendall用于判断植被NPP变化趋势的显著性,计算公式为:
S=∑n-1j=1∑ni=j+1sgn(NPPj-NPPi)(3)
sgn(NPPj-NPPi)={1, NPPj-NPPi>0
0, NPPj-NPPi=0
-1, NPPj-NPPi<0(4)
Z={(S-1)/((var(S))1/2), S>0
0, S=0
(S+1)/((var(S))1/2), S<0
var(S)=(n(n-1)(2n+5))/(18)(5)
式中:sgn是符号函数。趋势检验的方法是[20]零假设H0:β=0,当|Zc|>Z1-α/2时,拒绝零假设。其中,Z1-α/2为标准正态方差; α为显著性检验水平。当|Zc|≥1.28,1.64,2.32,表示通过了信度为90%,95%,99%显著性检验,分别为无显著变化、显著变化和极显著变化。
Hurst指数用于定量描述NPP时间序列信息的长期依赖性,基本原理是[21]:
考虑一个NPP时间序列{NPP(τ)},对于任意正整数,定义均值序列:
NPP(τ)^-=1/τ∑τt=1NPP(τ) τ=1,2,…(6)
用X(t)表示累计离差:
X(t,τ)=∑tt=1[NPP(t)-NPP(τ)^-] 1≤t≤τ(7)
极差R(τ)定义为:
R(τ)=max1≤t≤τX(t,τ)-min1≤t≤τX(t,τ)τ=1,2,…(8)
标准差S(τ)定义为:
S(τ)=[1/τ∑τt=1(NPP(t)-NPP(τ))2]1/2 τ=1,2,…(9)
若存在R/S∝τH,说明NPP时间序列存在Hurst现象,H称为Hurst指数,其值用最小二乘法拟合获得。
H的值域为0~1,包括3种情形:(1)若H>0.5,说明时间序列过程具有持续性,H越接近于1,持续性越强;(2)若H=0.5,说明时间序列是随机性序列;(3)若H<0.5,说明时间序列过程具有反持续性,H越接近于0,反持续性越强。
地理探测器是探测空间分异性,揭示其背后驱动因子的一种方法[22]。本文选取分异及因子探测器来对武陵山区2000—2015年植被NPP的影响因子进行分析。因子分析用q值度量,值域为[0,1],q值越大表示某种因子对植被NPP的影响越大,反之则越小。具体原理见文献[22]。
2000—2015年,武陵山区植被NPP总量介于87.06~116.90 Tg C(1 Tg C=1012 g C,图1A),多年均值是101.89 Tg C; 年均NPP为507.12~680.96 g C/(m2·a)(图1B),多年均值是593.52 g C/(m2·a)。植被NPP年际变化大致可以分为3个阶段:2000—2002年,NPP急剧增加,在2002年增至最大; 2002—2011年,NPP波动下降,其中2004—2005年,2010—2011年表现为急剧下降,在2011年降至最低; 2011年以后,NPP波动上升。对比NPP总量与其均值偏离程度,2002年、2011年、2013年偏离度大,NPP变化明显,而2000—2001年,2005—2010年,2014—2015年这几个时间段偏离度小,NPP处于相对稳定状态。虽然研究期末相对于研究期初NPP增加,但从趋势线可以看出,研究期内NPP总的趋势为下降,但不显著。区域NPP主要集中于400~700 g C/(m2·a),所占比例在53.61%~90.24%变化,此外,NPP值大于400 g C/(m2·a)区域占比的多年均值为94.68%,反映出全区整体生产力水平较高。
不同植被类型的平均NPP差异显著,年际变化趋势与总趋势几乎一致(图2),多年均值排序为常绿针叶林[606.31 g C/(m2·a)]>常绿阔叶林[600.52 g C/(m2·a)]>落叶阔叶林[586.85 g C/(m2·a)]>一年生阔叶植被[541.31 g C/(m2·a)]>一年生草本植被[519.97 g C/(m2·a)]。常绿针叶林和常绿阔叶林植被NPP多年均值高于全区多年均值,是该区固碳、生产能力最强的植被类型。
武陵山区2000—2015年各地年均NPP变化范围为78.13~1 209.71 g C/(m2·a)(附图2A),空间差异显著,整体呈现中部高、四周低的空间格局。低值集中于贵州境内的沿河、务川、德江、松涛、印江、思南,湖南的新化、辰溪、涟源、洞口、邵阳、武冈,以及湖北的巴东、来凤、长阳和五峰等地,没有明显集中的高值区。分省来看,4省NPP均值排序为重庆[608.46 g C/(m2·a)]>湖南[594.78 g C/(m2·a)]>贵州[586.74 g C/(m2·a)]>湖北[586.14 g C/(m2·a)]。
NPP变异系数为0.04~0.68(附图2B),均值为0.09,处于较低水平,说明研究时段武陵山区NPP空间上总体趋于相对稳定,植被受自然和人类活动干扰小,植被生态系统处于良性循环。变异系数高值零散分布于湖北的巴东、秭归和湖南的怀化等地,其中巴东、秭归为三峡库区,实行大规模的植树造林和封山育林保障库区生态,使得该地NPP波动相对较大,NPP处于增加趋势,而怀化可能是城镇化建设导致。
武陵山区植被NPP趋势分析β值为-42.96~13.56(附图3A),呈增长、减少趋势的区域分别占区域总面积的44.13%,55.87%,表明武陵山区NPP空间上总体处于减少趋势,与3.1时间上变化趋势结论相同。而β平均值仅为-0.93,反映出减少趋势是微弱减少。由附图3B可知,该区NPP总体变化不显著,无显著变化占比为99.38%,其中无显著下降、无显著增加比例分别为56.90%,42.48%,与变异系数分析一致。增加区域集中于武陵山区北部,特别是湖北省境内,而减少区域集中于南部,变化幅度均较小。总体而言,武陵山区NPP呈微弱的减少和北增南减趋势,北部海拔高、生态环境脆弱,应继续加强生态管控和巩固现有保护成果; 而南部相对海拔低、适宜开展农业活动和城镇化建设,但考虑到整个区域的功能定位以及生态适宜性,应坚持保护优先的发展战略。
武陵山区2000—2015年NPP的Hurst指数值域为0.06~0.55(附图4),均值为0.29。将Hurst指数结果划分为强反持续(0<H≤0.25)、弱反持续(0.25<H<0.5)、不确定(H=0.5)和弱持续(0.5<H≤0.75)4个等级(附图5)。NPP反持续性趋势范围大于不确定和持续性趋势,其中弱反持续、强反持续比例分别为74.27%,25.72%,说明该区植被NPP未来变化趋势是反持续状态,即与过去的变化趋势相反。从NPP未来趋势的空间分布来看,强反持续集中于湖南境内的桑植、慈利、永顺、张家界、沅陵、古丈、安化等地,弱反持续广泛分布于各地。
为探究武陵山区植被NPP变化趋势的持续性,将趋势检验结果与Hurst指数分级结果叠加,共9种情形(附图6)。NPP呈现无显著下降—弱反持续、无显著下降—强反持续、无显著增加—弱反持续和无显著增加—强反持续的比例分别为41.59%,15.65%,32.70%,10.04%。处于无显著增加趋势的北部以弱反持续为主,表明NPP未来可能表现出减少的态势,应加强植被保护以防止其向减少趋势发展。无显著减少的南部也以弱反持续为主,NPP未来可能增加。2000—2015年,武陵山区植被NPP整体呈微弱减少但以反持续为主,由此推断该区未来NPP整体呈增加态势。
武陵山区2000—2015年年均气温的变化范围为14.96~16.61℃,多年均值是15.86℃,呈不显著上升趋势; 年降水量为1 082.56~1 644.72 mm,多年均值是1 350.18 mm,呈不显著下降趋势(图3)。从各地多年均值的空间分布来看,气温与降水均表现出明显的经纬度和垂直地带性分异规律:气温整体由东南向西北递减,而雪峰山、巫山、齐岳山及武陵山等高海拔山脉的存在导致局部地区气温较低,如湖北鹤峰、利川、五峰等(附图7); 受季风气候的影响,降水量总体从东向西递减且分布不均,湖北鹤峰、湖南城步降水较多,贵州境内则降水较少(附图8)。
植被生长与气温、降水等气象因子密切相关,本文通过植被NPP与年均气温、年降水量的偏相关分析和T显著性检验,定量识别NPP对气候变化的响应。武陵山区2000—2015年植被NPP与气温的偏相关系数为-0.66~0.94,均值为0.49,正相关、负相关的比例分别为98.94%,1.06%,表明植被NPP与气温总体为正相关。其中,极显著正相关占比为22.42%,主要分布于重庆境内的酉阳、秀山和湖南的桑植、龙山、永顺、张家界、保靖等地(附图9A),49.21%的区域相关性不显著。植被NPP与降水的偏相关系数为-0.72~0.94,均值为0.41,正相关的比例为95.16%,说明植被NPP与降水总体也为正相关。正相关中,13.36%的区域极显著,集中于湖北的鹤峰和湖南的石门、桑植、慈利、龙山、永顺、张家界等地(附图9B),贵州的湄潭、石阡也零散分布,另65.67%的区域相关性不显著。总体而言,研究区植被NPP与气温、降水两个气象因子主要表现为正相关性特征,但气温偏相关系数均值、与NPP显著性相关面积均大于降水,表明该区NPP更易受到气温影响,气温为主要的气象因子。结合变异系数来看,变异系数相对高的地区,如巴东、怀化等地,植被与气象因子的相关性不高且不显著,说明该地受降水、温度变化的影响不大,人类活动或其他因素可能是主导因子。
地形通过控制水热和土壤条件,影响其他环境变量,进而对区域植被格局产生影响[16]。本文根据文献[15]和研究区实际情况对武陵山区高程和坡度进行分级,统计各分级植被NPP以分析地形的影响(表2)。武陵山区以低山、丘陵为主,高程在200~1 000 m的区域占比约74.31%,其中500~1 000 m的低山所占比例最大,而200 m以下的平原和1 500 m以上的高山分布较少。地理的垂直地带性使得不同海拔等级的植被NPP均值存在显著差异,总体表现为随海拔升高先增后减:200 m以下的平原易受人为干扰,如城镇建设、农业活动,植被生产力较低; 丘陵和低山地带,植被类型以林地为主,生产力较高,并且面积比例大,NPP总量大; 海拔继续升高,在高山地区,环境恶劣、植被稀少导致植被生产力降低,同时面积比例小,NPP总量小。坡度方面,研究区以缓坡和斜坡为主,不同坡度的植被NPP表现出与高程相似的特征,即随着坡度的增大先增后减,但波动程度较高程平缓:微坡植被NPP均值为584.82 g C/(m2·a); 缓坡和斜坡的植被NPP较高,其中缓坡最大,同时两者分布多,NPP总量大; 而当坡度逐渐加大,植被生长受到限制,植被覆盖度降低,NPP下降。
人类活动表现为不同类型的干扰,最显著的是使土地利用方式发生变化,直接或间接地影响植被NPP。土地利用变化对NPP的影响具有两面性:一方面,高生产力用地类型转变为低生产力用地类型造成NPP损失,如林地开垦为耕地; 另一方面,低生产力用地类型向高生产力用地类型转变使得NPP增加,如退耕还林还草。
统计2000—2015年土地利用变化情况,并将土地利用引起的NPP损益(前10)进行可视化(图4)。武陵山区土地利用以林地、耕地和草地为主,在研究期间发生了较大变化,土地利用转移面积为15 318 km2,约占区域总面积的8.94%。耕地面积减少581 km2,主要转向林地(47 748 km2)和草地(1 088 km2),说明整个区域退耕还林还草工作成效显著,另外耕地被建设用地占用322 km2。林地转入转出量均较大,转出中多被开垦为耕地,但总量增加227 km2。草地减少466 km2,大部分转向耕地和林地,而建设用地面积增长近一倍,多为占用耕地和林地,其他用地类型变化较小。总体而言,近16 a武陵山区土地利用变化较为剧烈,主要表现为耕地、草地的减少和建设用地的快速增长,林地面积也有所增加。
地类转换引起NPP损益方面,2015年植被NPP相较于2000年增加,大部分用地类型的转换引起NPP上升。其中,耕地转林地使得NPP变化最大,增加0.375 6 Tg C,林地转耕地(0.155 5 Tg C)、草地转林地(0.103 8 Tg C)及耕地转草地(0.076 2 Tg C)等地类转换也不同程度引起NPP上升,而林地转建设用地(0.012 4 Tg C)和耕地转建设用地(0.003 9 Tg C)导致NPP下降。综合来看,研究区退耕还林还草、封山育林等相关工作的开展使得耕地大量转为林地,由此导致的NPP增加较为明显,是引起NPP变化的主要地类转换。
植被NPP的时空分异是多因子综合作用的结果。本文从自然和人为两方面,选取高程、坡度、降水、气温、土地利用5个因子对武陵山区2000年、2005年、2010年、2015年植被NPP进行因子影响力探测,结果见图5。因子探测的q值最大,表示该因子对NPP的解释力最强,为该年植被NPP空间分异的主导因子。武陵山区植被NPP的4个年份主导因子依次为高程(0.020 9)、气温(0.034 7)、气温(0.018 7)和降水(0.054 2),说明该区NPP没有绝对的主导因子。不同年份不同因子的差异显著,其中降水因子的波动性最大,一定程度上体现了区域降水的时空不均。不同因子4个年份q值均值大小排序为气温(0.023 4)>降水(0.020 8)>高程(0.019 9)>土地利用(0.012 0)>坡度(0.008 2)。就q值均值而言,可以将不同因子划分成主导因子(气温、降水和高程)和重要因子(坡度和土地利用)两种类型。
武陵山区地形复杂、多云,导致NPP反演结果中、高等级多年平均可信度相对其他地区较小,但精度能够满足研究要求。本文利用MOD17A3数据得到2000—2015年武陵山区植被NPP多年均值是593.52 g C/(m2·a),与孙庆龄等[15]所得该区2000—2010年多年均值590 g C/(m2·a)接近、空间格局一致,高于同期全国均值273.5 g C/(m2·a)[14]。Nemani[23]认为全球变暖导致北半球温带植被NPP增加、热带和亚热带下降。而武陵山区北部为暖温带、南部为亚热带,过去16 a植被NPP北增南减的变化趋势与Nemani结论一致。
气候变化是陆地植被活动年际变化的主要影响因素[24]。气温、降水的增加对植被生长有一定的促进作用,但过高(多)或过低(少)会抑制植被NPP的积累,如气温过高会增强植被的呼吸作用,植物气孔关闭进而影响植被的光合作用。近16 a,武陵山区86.22%的区域气温呈上升趋势,69.86%的区域降水呈下降趋势,说明该区气候整体趋向干燥,植被生长受到一定威胁,导致研究期间植被NPP总体呈微弱的减小趋势。植被NPP与气温、降水的正相关面积均大于负相关且偏相关系数均值大于0,表明武陵山区植被NPP与气温、降水两个气象因子主要表现为正相关性特征,与仲晓春等[25]研究结果相吻合。2002年、2013年研究区植被生产力较高,其中2002年最大,前一年份年均气温低于多年平均、降水量为多年最大,降水充沛能够弥补温度过低的不足,促进植被NPP的积累,而后一年份与此相反,年均气温为多年最高、降水小于多年平均,温度弥补了降水不足。在植被生产力最低的2011年,年均气温、降水量均低于多年平均,水热不足导致生产力较低。此外,植被NPP与气温偏相关系数均值、显著性相关面积均大于降水,所以气温为影响武陵山区植被生长的主要气象因子。
因子影响力分析中,气温q值均值大于降水,表明气温对武陵山区植被NPP的空间分异解释力更强,与相关分析结论一致,但两者均为主导因子。地形因子的高程解释力强于坡度,主要是高程直接影响植被类型分布和气温状况,而坡度通过坡面侵蚀强度起着间接作用的结果[12]。虽然过去16年武陵山区土地利用变化变化较为剧烈,但土地利用结构并未发生较大变化,仍以林地、耕地和草地为主,相对于气象因子,对植被NPP影响不大。
(1)武陵山区植被生产力水平总体较高,NPP总趋势为不显著下降,年际波动性明显。NPP总量介于87.06~116.90 Tg C,多年均值是101.89 Tg C; 年均NPP为507.12~680.96 g C/(m2·a),多年均值是593.52 g C/(m2·a)。区域NPP主要集中在400~700 g C/(m2·a),所占比例在53.61%~90.24%变化。不同植被类型生产力存在差异,常绿针叶林和常绿阔叶林是该区固碳、生产能力最强的植被。
(2)武陵山区各地NPP均值变化范围为78.13~1 209.71 g C/(m2·a),空间差异显著,整体呈现中部高、四周低的空间格局,没有明显集中的高值区。NPP空间波动性小、总体趋于稳定,变化趋势为微弱的减少和北增南减,增长、减少趋势的区域分别占比44.13%,55.87%。未来趋势以反持续为主,表明区域未来NPP可能呈增加趋势。
(3)武陵山区NPP与降水、气温均为正相关,受到气温的影响更大,气温为主要气象因子。植被NPP随着高程、坡度的增加均表现为先增后减的趋势。土地利用变化对NPP的影响具有两面性,耕地转林地是土地利用变化引起NPP变化的主要地类转换。
(4)因子影响力上,武陵山区植被NPP没有绝对的主导因子,4个时期因子影响力均值大小为气温>降水>高程>土地利用>坡度,气温、降水和高程是NPP时空分异的主导因子,坡度和土地利用是重要因子。总体而言,自然因素主导着武陵山区植被NPP的时空格局,人为因素影响较弱。