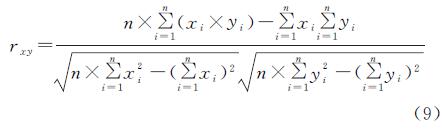1.3.1 NPP的估算
(1)实际NPP的估算。实际NPP(ANPP)用来表示气候变化和人类活动共同影响下的草地的实际NPP,本研究中ANPP由CASA模型模拟得到,该模型主要涉及植物吸收的光合有效辐射(APAR)和光能利用率(ε)两个变量[20]。
NPP(x,t)=APAR(x,t)×ε(x,t)(1)
式中:APAR(x,t)为像元x处t月份吸收的光合有效辐射(MJ/m2); ε(x,t)为像元x处t月份吸收的实际光能利用率(g C/MJ)。
APAR(x,t)=SOL(x,t)×FPAR(x,t)×0.5(2)
式中:SOL(x,t)为像元x处t月份太阳总辐射量(MJ/m2); FPAR(x,t)为植被吸收入射光合有效辐射的比例; 0.5为植被能吸收的有效辐射(0.4~0.7 μm)与太阳总辐射的比值。
ε(x,t)=Tε1(x,t)×Tε2(x,t)×Wε(x,t)×εmax(3)
式中:Tε1(x,t)为低温对光能利用率的影响; Tε2(x,t)为高温对光能利用率的影响; Wε(x,t)为水分对光能利用率的影响; εmax为最大光能利用率(理想状态),本研究中采用的草地的εmax为0.542 g C/MJ。Tε1(x,t),Tε2(x,t)和Wε(x,t)等的具体计算方法可
参考文献[18]。
(2)潜在NPP的估算。潜在NPP(PNPP)指理想状态下植被的净初级生产力,本研究采用的PNPP由Thornthwaite Memorial估算得到,该模型在Miami模型的基础上提出,并通过Thornthwaite潜在蒸散模型进行了改进[15],其计算公式如下:
PNPP=3000[1-e-0.0009695(v-20)](4)
式中:v为年实际蒸散量(mm)。

式中:r为年总降水量(mm); L为年最大蒸散量(mm); t为年平均气温(℃)。
(3)人为NPP的估算。人为NPP(HNPP)定义为人类活动影响下的植被NPP,该方法假设实际NPP与潜在NPP的差别仅由人类活动引起,HNPP的计算公式如下:
HNPP=PNPP-ANPP(7)
1.3.2 模型验证
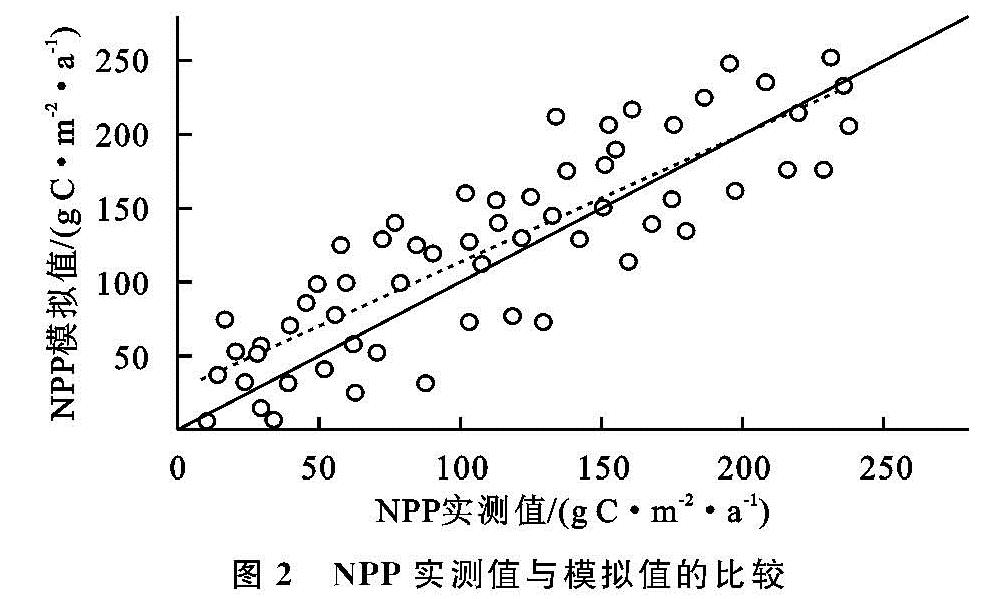
为了验证CASA模型的精度,本课题组于2009年在西北地区进行草地生物量实地调查,共采集60个样点数据。样点的实测数据与同一位置的模拟数据相比较,发现两组数据达到基本吻合(R2=0.74,p<0.01)(图2)。因此,可认为CASA模型适用于西北地区草地植被NPP的估算。
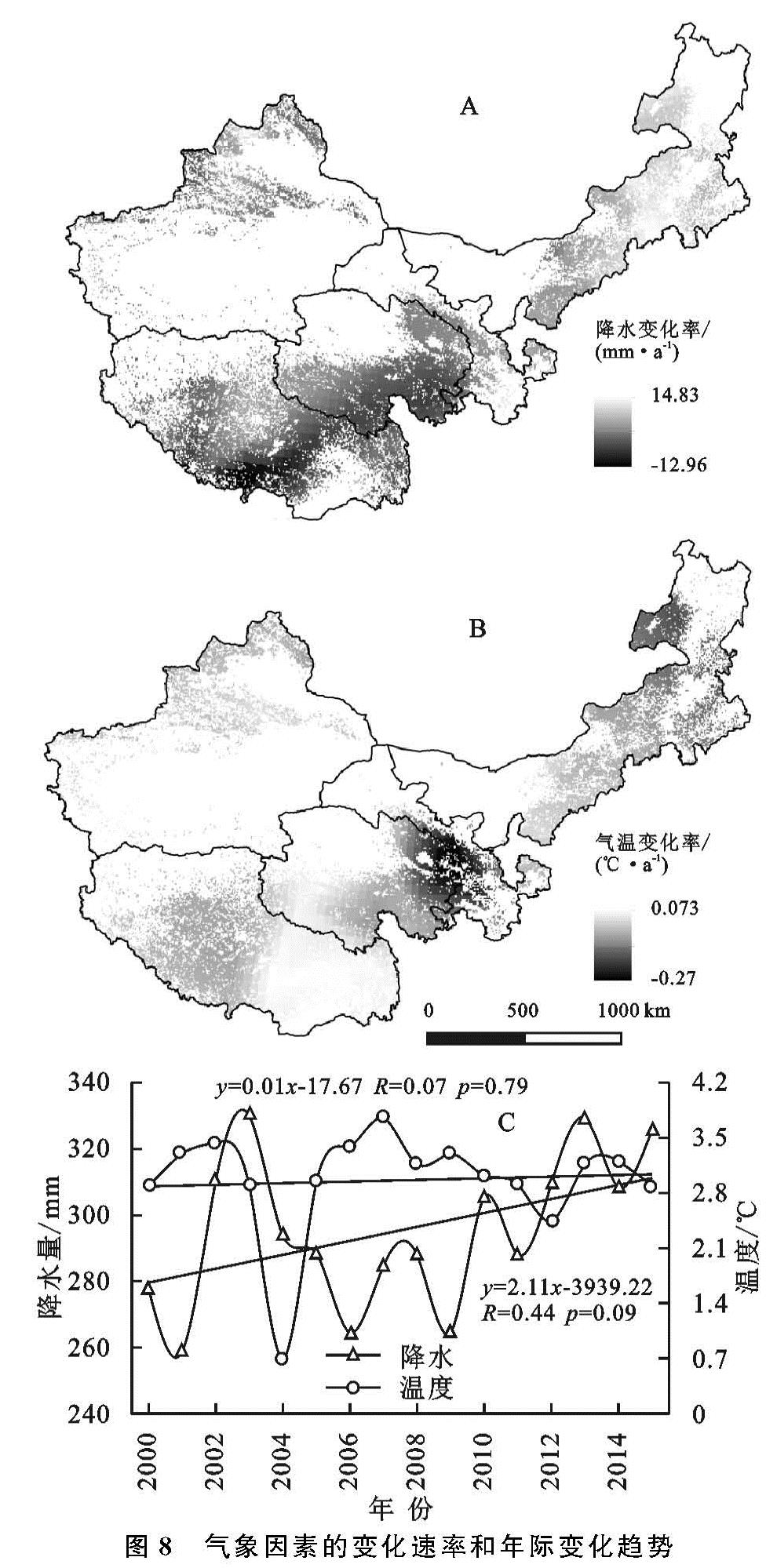
1.3.3 趋势分析
采用一元回归分析方法对草地和气象因素的变化趋势进行研究,其计算公式如下:
slope=(n×∑ni=1(i×vari)-∑ni=1i ∑nn=1vari)/(n×∑ni=1i2-(∑ni=1i)2)(8)
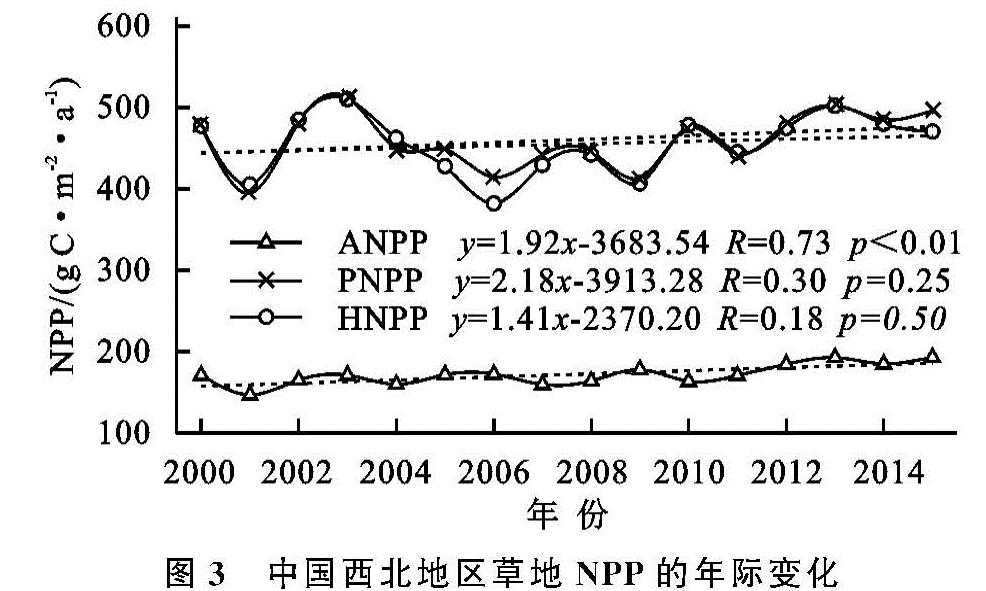
式中:slope为变化斜率; i为第几年; n为研究年限16年; vari为第i年的变化量。若slope>0,表示变量呈现增加趋势,反之则表现出减小趋势。若草地ANPP的slope>0,说明草地出现恢复,若slope<0,则表明草地出现退化。对不同变量的slope进行F检验,具体的计算方法可参照文献[18]。
1.3.5 评估情景的构建
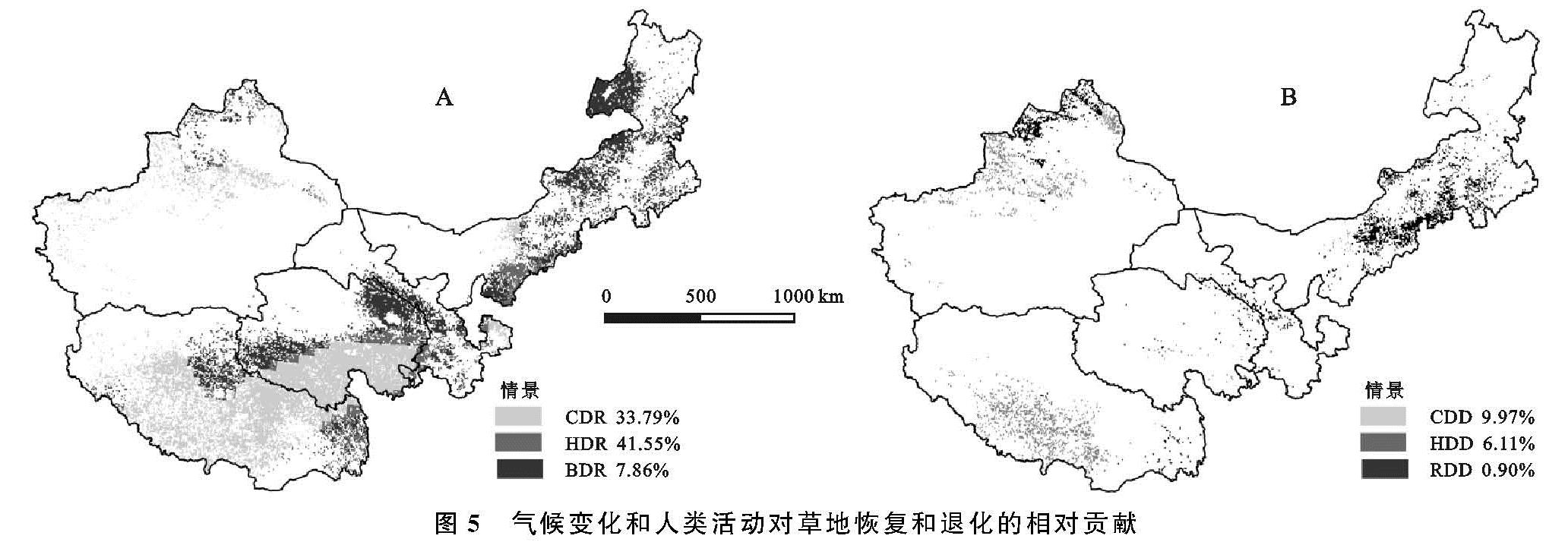
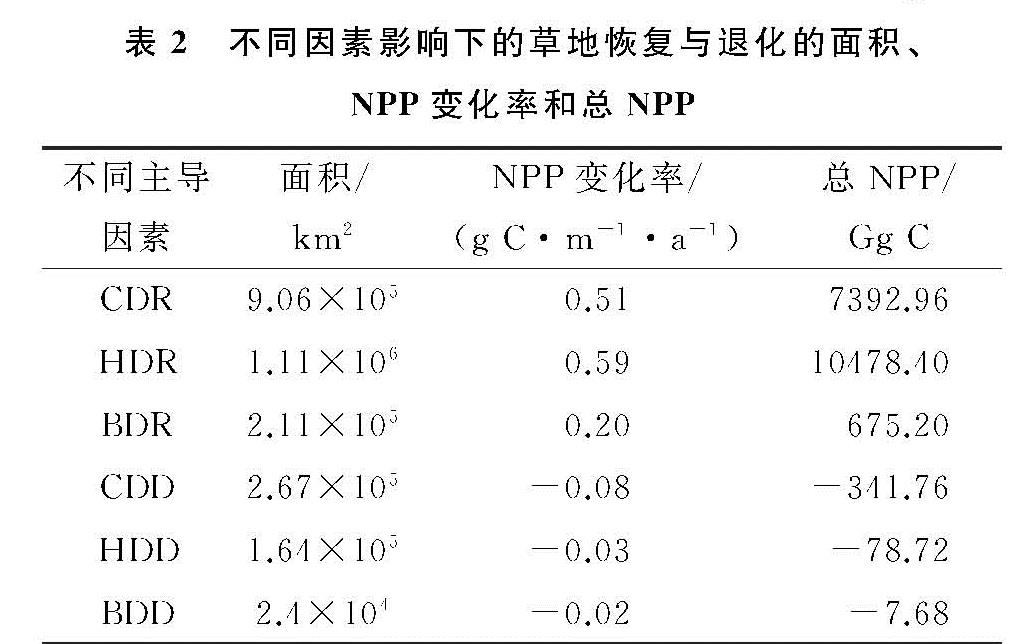
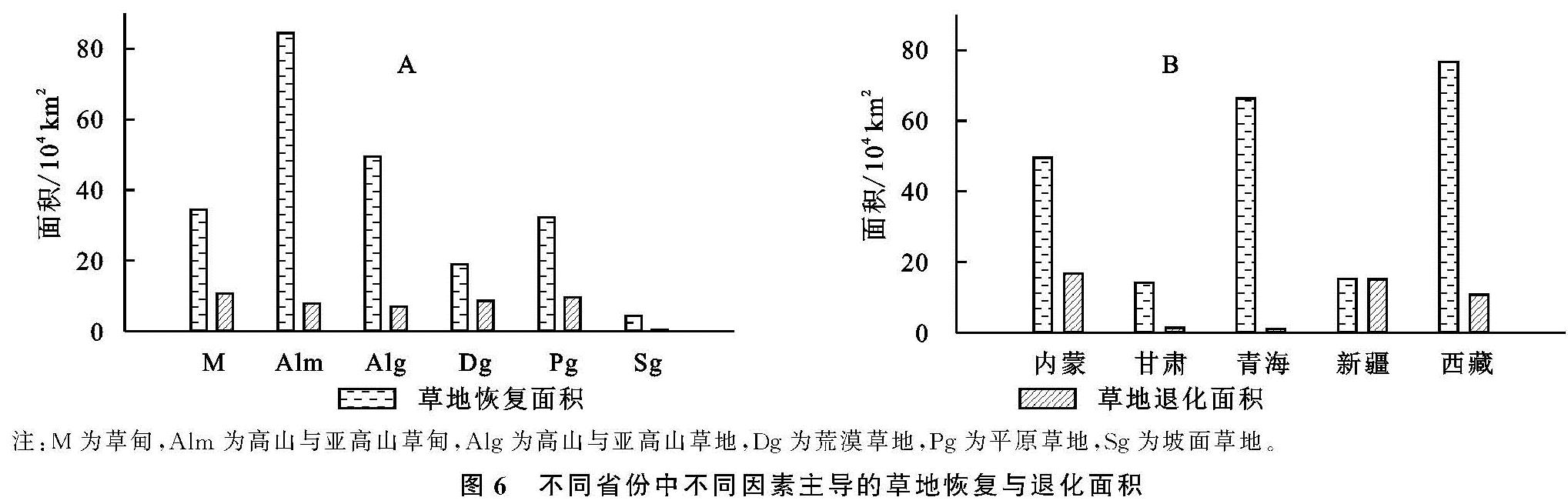
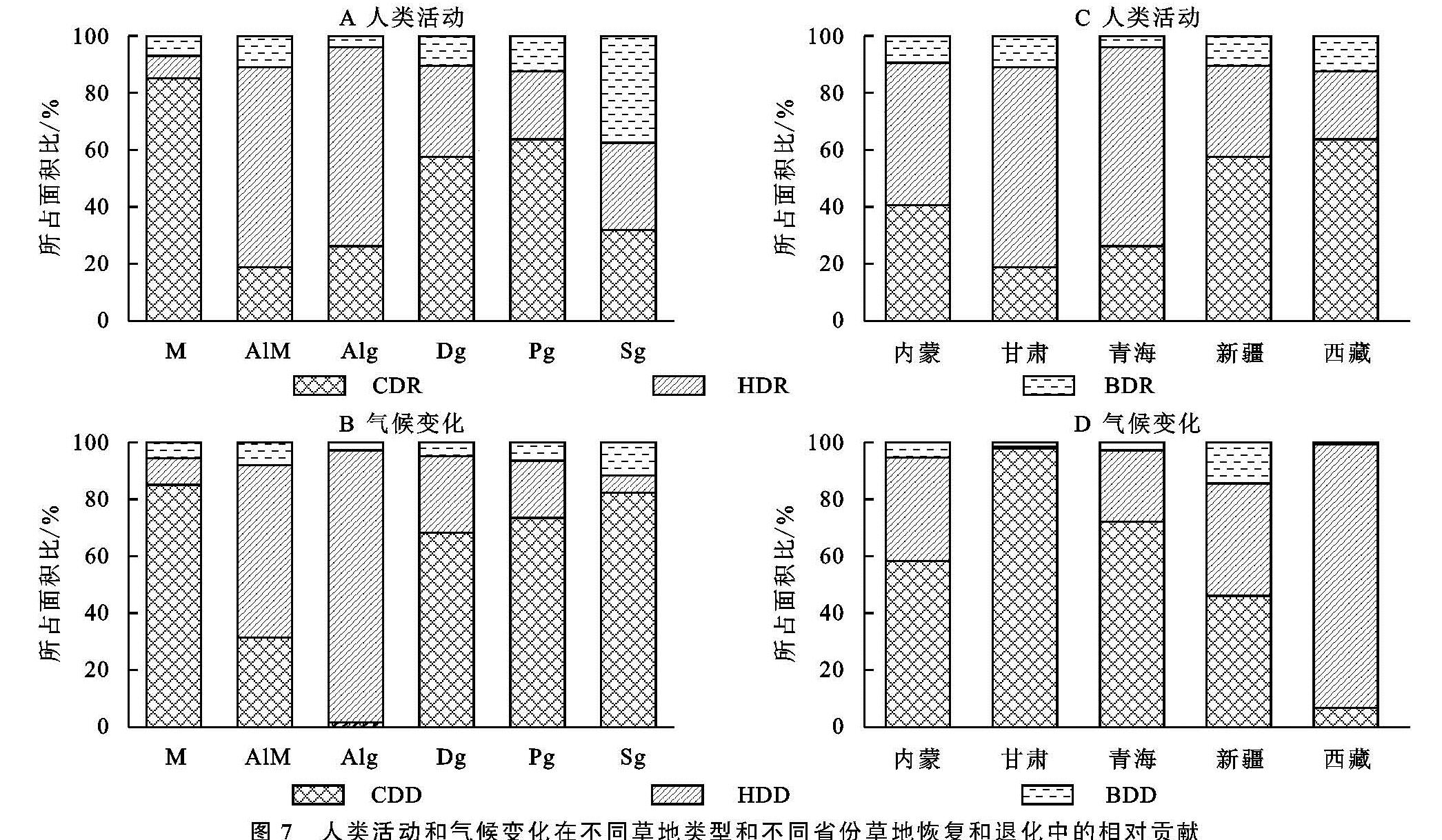
本研究将上述3种NPP(ANPP,PNPP,HNPP)的slope进行比较,对人类活动和气候变化在草地退化和恢复的相对贡献进行区分,定义草地变化的6种情景(表1)。表中,SA为正值说明草地出现恢复,而SA为负值说明草地呈现退化。SP大于0说明气候变化有助于植物的生长,而SP小于0表示气候变化抑制植物的生长。SH大于0代表人类活动引起草地退化,SH小于0表示人类活动引发草地恢复[3]。
表1 气候变化和人类活动影响草地恢复与退化的6种情景