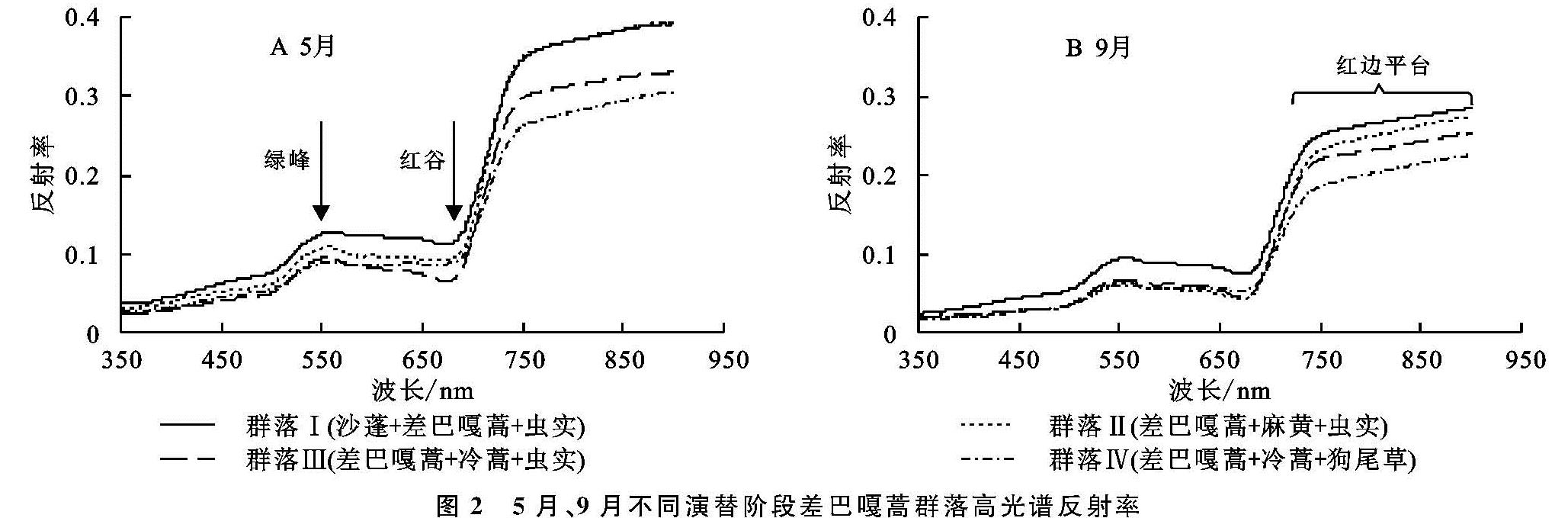
2.1 不同演替阶段差巴嘎蒿群落冠层光谱特征
图2为不同演替阶段差巴嘎蒿群落分别在生长季初期与末期的原始冠层光谱曲线,由图2可知,主要优势种群的冠层光谱反射曲线呈现出同异交错现象,总体表现出绿色健康植被的反射趋势,但局部差异较大。主要表现为,随着植被群落的稳定,植物光合作用能力增强,光谱参数表现出不同的特征:5月份群落Ⅰ与群落Ⅱ的红边基本重合,结合物候期植被调查情况说明,此时植被正处于返青期,群落Ⅱ中以差巴嘎蒿为主,草本植被作为伴生种处于生长初期对整体群落的反射率影响不大。随着演替进行,群落Ⅲ与群落Ⅳ在绿峰处较接近,该波段处主要与叶绿素含量有关,此时群落Ⅲ中的白草与群落Ⅳ中的羊草作为固定群落优势种开始返青,故呈现相似的植被特征。
图2 5月、9月不同演替阶段差巴嘎蒿群落高光谱反射率
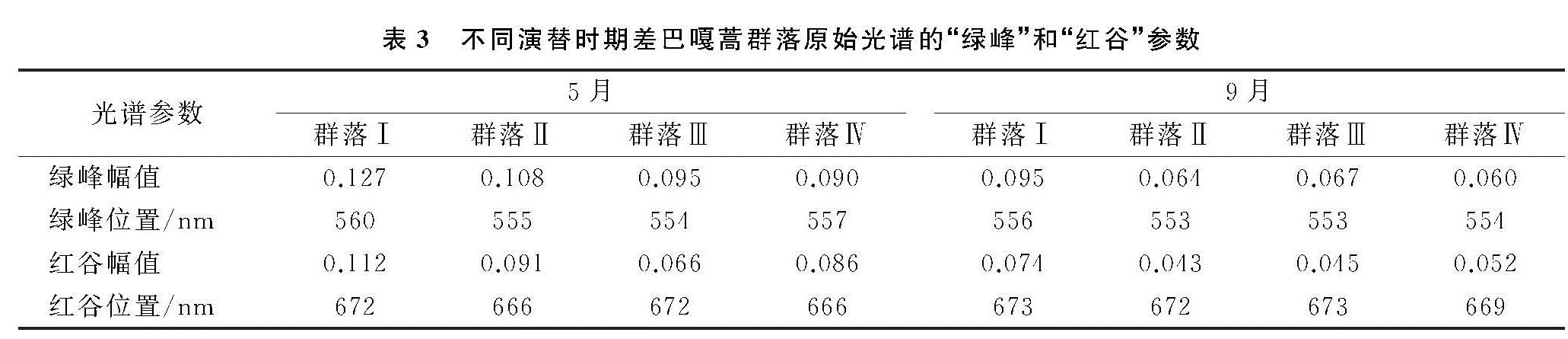
由表3可以看出,随着演替的推移,9月时680 nm处的红谷由低到高依次为群落Ⅱ<群落Ⅲ<群落Ⅳ<群落Ⅰ,说明作为能够诊断植被健康程度的敏感性特征,随着植被种类增多,稳定性增加,叶绿素浓度增加,群落中开始呈现叶片较多的状态。群落Ⅰ在可见光波段的绿峰和红谷位置与其他群落差异最大,这是由于其盖度较低,植被种类单一,受土壤影响大,对光的强反射和强吸收信息被大大减弱,虽然在绿峰强反射波段内反射率仍最高,却相对弱化了与其他可见光波段反射率的差异性,显示演替初期群落生长环境对植被的影响较严重,且相比较5月份群落反射率值,除了群落1总体反射率值变化不大,总体反射率值比5月份呈下降趋势,这是由于群落1生长环境恶劣,群落组成变化不大。
表3 不同演替时期差巴嘎蒿群落原始光谱的“绿峰”和“红谷”参数
2.2 不同演替阶段差巴嘎蒿群落红边分析
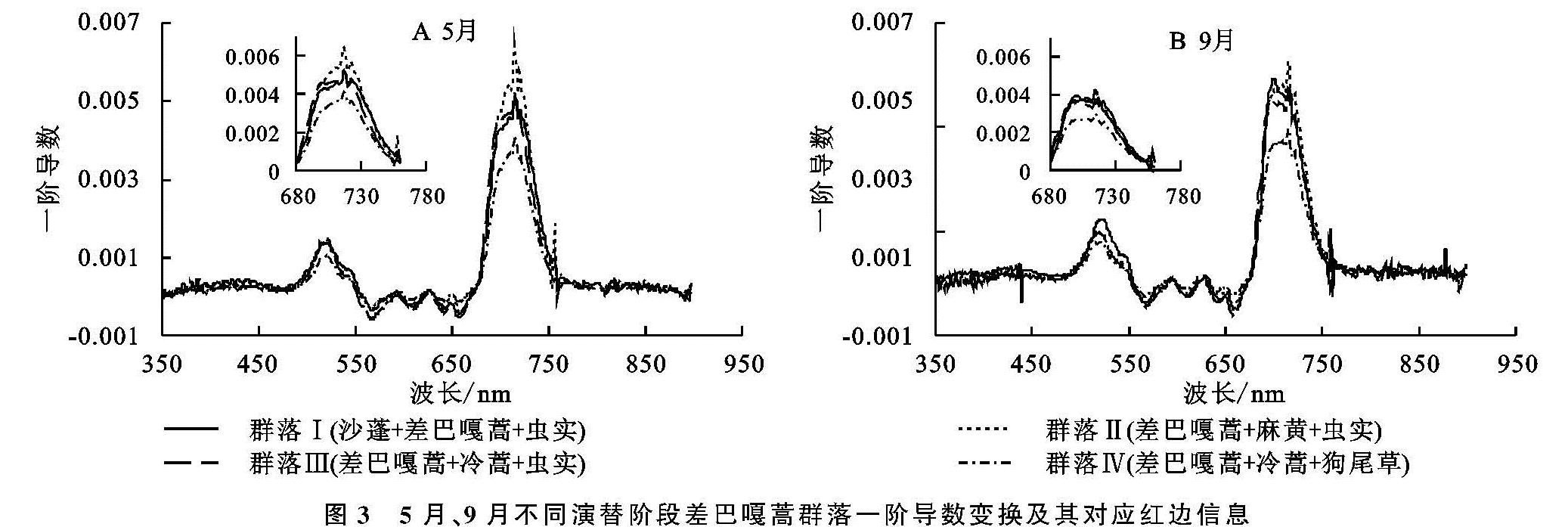
原始光谱的导数变换能够反映出反射率增减幅度。图3为350~900 nm范围内原始光谱的一阶导数曲线及其红边图。可见光波段是以植物叶片的吸收为主,反射率值相对较低,一阶导数值在350~550 nm范围内虽然也有波动,但均为正值,呈不断增加趋势; 550~670 nm波段范围内为负值,说明这一阶段光以吸收为主,反射率逐渐减小。
图3 5月、9月不同演替阶段差巴嘎蒿群落一阶导数变换及其对应红边信息
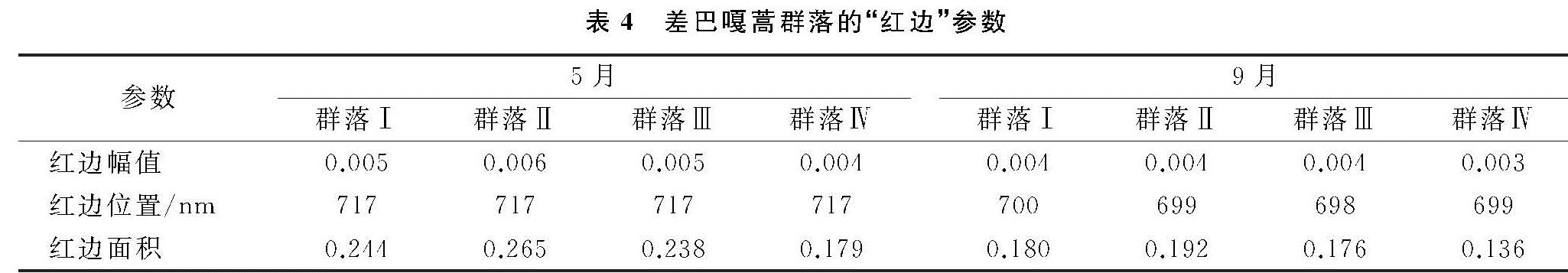
进一步分析差巴嘎蒿群落在不同季相不同演替阶段的“红边”特征,对5月群落冠层光谱680~760 nm波段范围内的一阶导数进行分析。结果显示4个群落在不同时期均具有明显的“双峰”现象,且5月与9月最大峰值分别出现在717,699 nm处(表4),红边向短波方向移动,是由于成熟期叶片叶绿素含量增多,旱情得到缓解。其中,9月的群落Ⅰ与群落Ⅲ在695 nm处有个不明显的峰值,呈现“三峰”特征,峰值的“红移”显示随着生长期推移,生物量增加、植被盖度增加,土壤背景对光的反射影响变小,峰值整体降低。
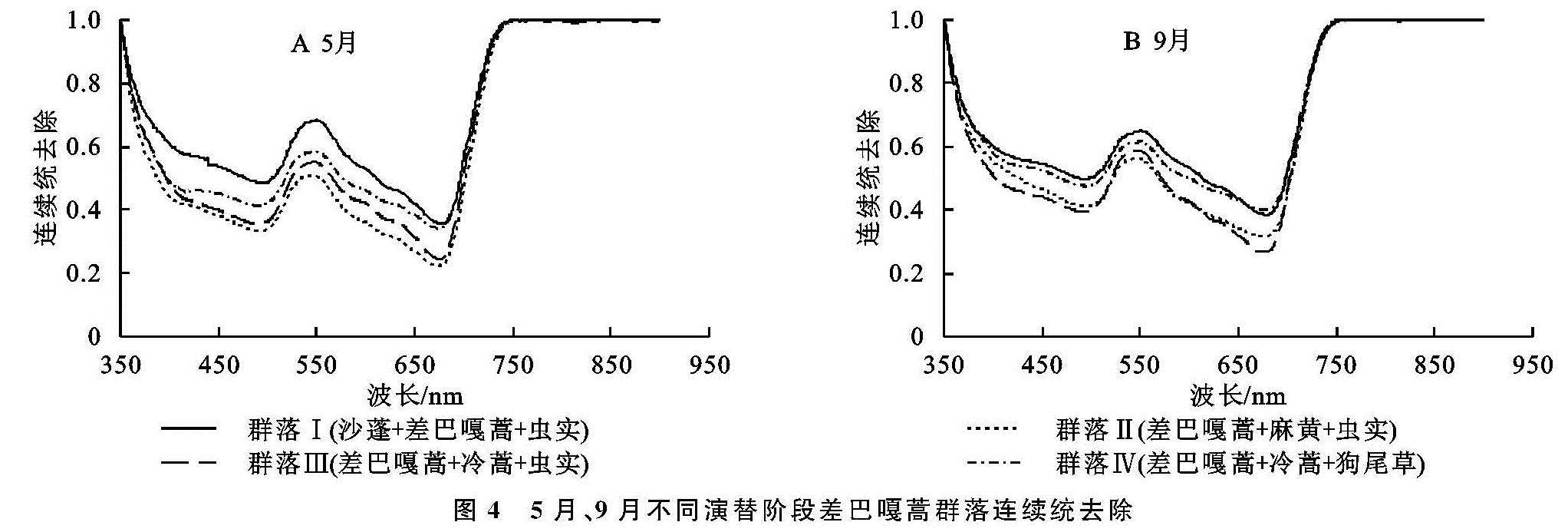
2.3 不同演替阶段差巴嘎蒿群落连续统去除分析
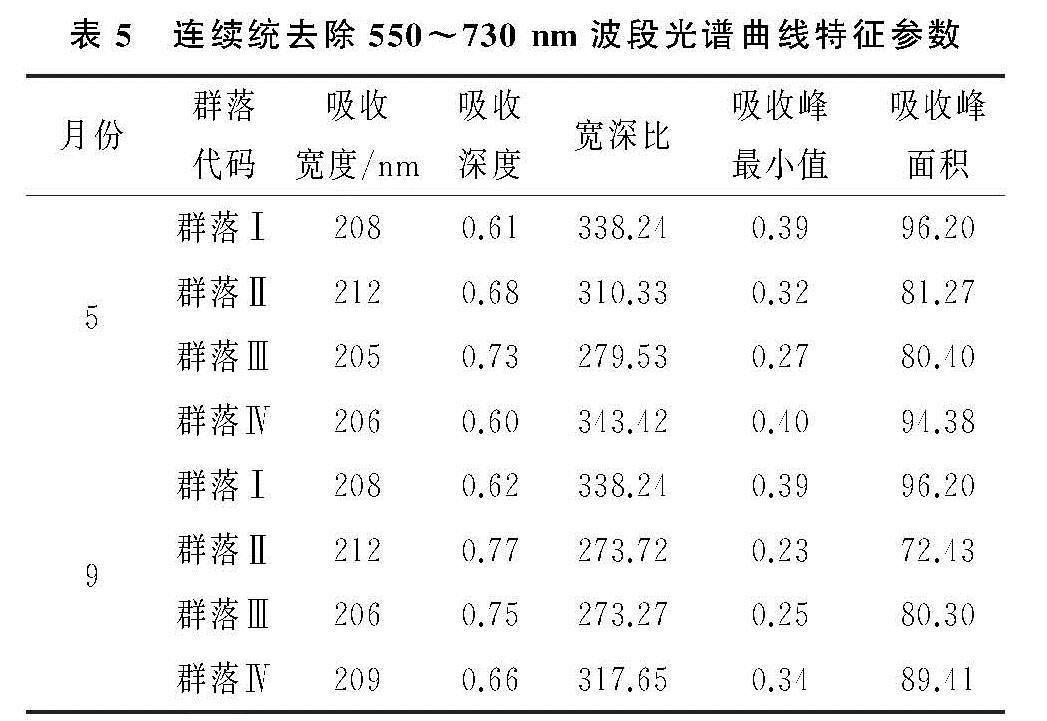
为了弱化土壤背景对植被光谱特征的影响,强化波段350~900 nm区域内反射率的特征信息,采用连续统去除提取光谱特征。如图4所示,不同演替阶段的差巴嘎蒿群落连续统去除位于510 nm与680 nm附近具有两个明显的吸收谷,而红波段处的吸收效应大于蓝波段的吸收效应。经过计算得到红光波段(550~730 nm)处的吸收信息,见表5。
生长季初期,在550~730 nm范围内,红波段处的吸收深度由大到小依次为群落Ⅲ>群落Ⅱ>群落Ⅰ>群落Ⅳ,群落Ⅲ在650 nm附近的吸收深度最大,说明在这个时期群落Ⅲ中的植被种类增多,生物量较大,对光的吸收强度也较大,虽然群落Ⅳ为差巴嘎蒿群落相对较稳定的演替后期,但是群落中的草本植被萌芽期较晚,所以吸收深度最小,即可以根据吸收深度来区分群落Ⅲ和群落Ⅳ。
生长季末期,在550~730 nm范围内,红波段处的吸收深度由大到小依次为群落Ⅱ>群落Ⅲ>群落Ⅳ>群落Ⅰ,群落Ⅱ在650 nm附近的吸收深度最大,说明在这个时期群落Ⅱ中的植被种类增多,群落间生长状态不一致,与付元元等[25]的研究结果规律一致,群落Ⅱ植被组成接近群落Ⅲ,最佳识别群落Ⅱ与群落Ⅲ的参数确定为吸收宽度。而群落Ⅰ和群落Ⅲ的宽深比差异最大为64.97,区分效果最好。生长季末期的宽深比和吸收峰面积相对差异较大,所以9月整体识别效果优于5月。综合结果看连续统去除变换后,4种群落的吸收宽度在这两个吸收波段差异不大,不能更好地区分,而区分不同演替阶段差巴嘎蒿群落最有效的特征参数是吸收深度和宽深比。
图4 5月、9月不同演替阶段差巴嘎蒿群落连续统去除
表5 连续统去除550~730 nm波段光谱曲线特征参数
2.4 马氏距离法对不同光谱变换形式波段选择结果及精度识别
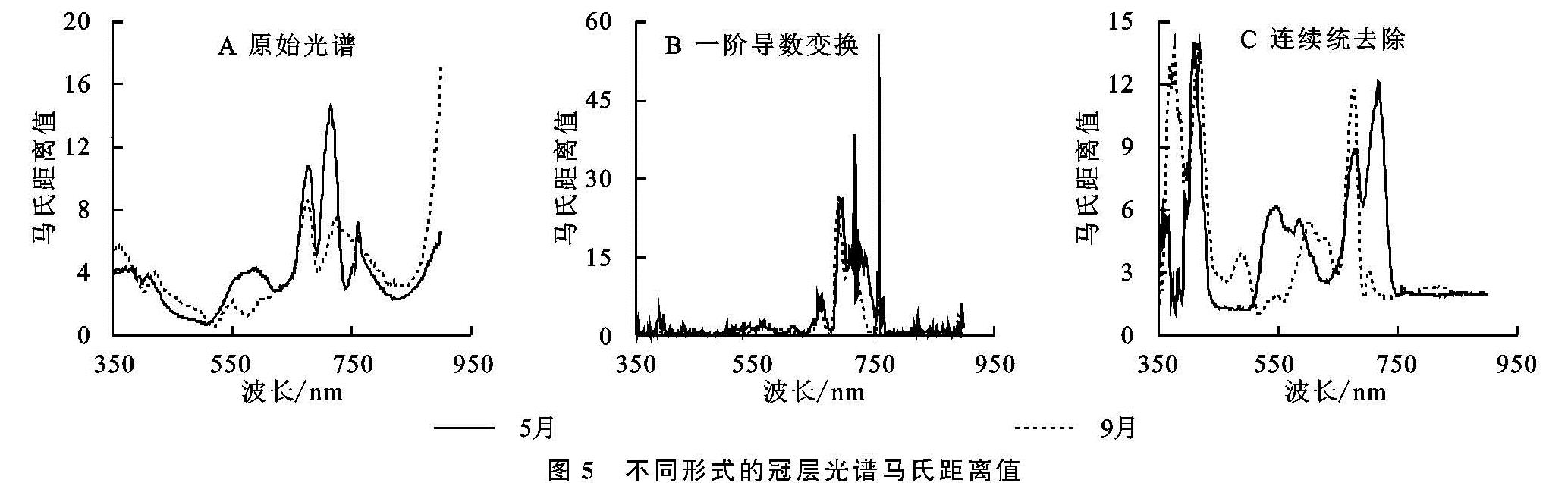
通过获取差异较大波段可实现不同演替阶段物种分离,可见光波段中,绿峰总体向短波方向移动,红谷及红边位置向长波方向移动,这是由叶绿素含量决定的。植被的红边平台特征由叶片细胞结构决定,是绿色健康植被的光谱共性,其差异性也受这些因素的影响。马氏距离能够消除变量间的相关性干扰且不受量纲的影响,利用马氏距离进行特征波段的选择可快速有效地提取该波长内的显著差异波段。选取的差异显著波段的马氏距离值要高于各波段的平均值,同时,为便于实测光谱数据与高光谱遥感数据相结合,规定马氏距离值高的波段必须连续出现10 nm以上。图5为不同演替时期差巴嘎蒿群落冠层原始光谱差异波段选择结果,马氏距离值越大的波段表明不同群落在此波段内差异越显著,容易识别。
通过对原始光谱曲线、一阶导数以及连续统变换进行马氏距离的计算得到差异较大的特征波段(表6),特征波段数量的减少说明导数变换以及连续统去除有效降低了特征波段维数。马氏距离均值由高到低依次为一阶导数(9.44)>连续统去除(7.32)>原始光谱(6.00),且光谱变换前后差异显著波段均处于红波段处,说明红波段处包含的信息最多,侧面表明了基于马氏距离的波段选择结果有效且准确,同刘波[10]的研究结论相似。3种光谱曲线得到的差异显著波段有所不同但均存在共同点,原始光谱所提取的差异波段集中于可见光以及近红外波段,一阶导数变换后差异表现在红波段以及绿波段处。两个季相的群落演替均遵循此规律,说明作为干旱半干旱地区差巴嘎蒿群落作为主要指示种生长较稳定。