资助项目:蒙雨(1998—),女,贵州毕节人,硕士,研究方向为乡村地理与农村发展。E-mail:my18785040702@163.com
第一作者:但文红(1967—),女,贵州贵阳人,教授,主要从事乡村地理与农村发展研究。E-mail:622007761@qq.com
(1.贵州师范大学 地理与环境科学学院, 贵阳 550001; 2.贵州师范大学 贵州省信息与计算科学重点实验室, 贵阳 550001)
(1.School of Geography and Environmental Science, Guizhou Normal University, Guiyang 550001, China; 2.Key Laboratory of Information and Computing Science of Guizhou Province, Guizhou Normal University, Guiyang 550001, China)
evapotranspiration; spatiotemporal characteristics; affecting factors; MODIS; Wujiang Basin
为探讨贵州省乌江流域地表蒸散发(ET)时空特征及其影响因素,运用MOD16A2/ET产品和气象站数据,通过趋势分析与相关分析法,探讨了乌江流域ET时空变化特征及其影响因素。结果 表明:(1)2000—2014年乌江流域年际ET波动较大,年内ET呈周期性单峰变化趋势,ET季节变化表现为夏季(311.31 mm)>春季(245.57 mm)>秋季(138.10 mm)>冬季(132.51 mm);(2)乌江流域ET空间异质性显著,呈西低东高的空间格局,平均ET值为605.43~1 208.26 mm;(3)各气候因子对ET的影响范围由大到小依次为降水量(30.67%)>气温(29.56%)>日照时数(23.84%),三者对ET均以正相关为主。乌江流域ET的时空分布特征虽受气候因子所控制,但各因子对ET的影响程度、范围却存在显著差异。
To explore the spatialtemporal characteristics of surface evapotranspiration(ET)and its affecting factors in Wujiang Basin, Guizhou Province, MOD16A2/ET products and weather station data, trend analysis and correlation analysis were used to explore the spatiotemporal variation characteristics of ET and its affecting factors. The results show that:(1)from 2000 to 2014, the interannual ET in Wujiang Basin fluctuated greatly, and the annual ET showed a cyclical unitary change trend; the seasonal change of ET decreased in the order: summer(311.31 mm)>spring(245.57 mm)>autumn(138.10 mm)>winter(132.51 mm);(2)ET spatial heterogeneity of Wujiang Basin was significant, showing a spatial pattern of low level in the west and high level in the east; the average ET value was between 605.43 mm and 1 208.26 mm;(3)the influence range of each climate factor on ET decreased in order: precipitation(30.67%)>air temperature(29.56%)>sunshine hours(23.84%), the three pairs of ET were mainly positively correlated. Although the spatiotemporal distribution characteristics of ET in Wujiang Basin were controlled by climate factors, the influence degree and range of each factor on ET were significantly different.
地表蒸散发(Evapotranspiration,ET)是指水分从地表以气态进入大气的过程[1-3],包括地表植被蒸腾、土壤蒸发和水面蒸发[4-5],是水文循环和地表能量平衡的重要环节,影响着地表过程中地、气系统的相互作用[6-8]。准确估算区域地表蒸散发量,探索区域地表蒸散发与气候变化的时空分异规律,对准确掌握生态需水规律、做好生态系统水源涵养与保护以及合理开发利用水资源等具有重要意义。
近年来,遥感数据凭借其快速、动态、覆盖范围广和周期性等优势,成为进行大区域地表蒸散研究的主要手段[9-11]。不少学者利用MODIS产品研究了地表实际蒸散发与潜在蒸散发之间的关系[12-13]或时空分布特征[14-15]或影响因素分析[2,16]。温媛媛等[17]基于MOD16数据研究了2001—2014年山西省实际蒸散发和潜在蒸散发时空变化规律及其影响因素; 杨江州等[18]基于地貌类型分区,分析了贵州省喀斯特山区蒸散发时空演变特征; 范雪梅等[19]基于MOD16产品,结合气象站点实测降水资料,分析了怒江流域中上游蒸散发的时空分布特征及其与降水之间的相关关系; 闫俊杰等[20]探讨了草地退化严重的伊犁河谷蒸散发与气温、降水和NDVI之间的关系; 郭金路等[21]根据辽西地区1965—2015年13个气象站的气象资料,进行了潜在蒸散发敏感性分析及变化成因分析; 王鹏涛等[2]利用MOD16蒸散数据,分析了陕甘宁黄土高原区ET的时空变化特征,并探讨了其影响因素。目前,国内对于蒸散发的影响因素分析主要集中在中国西部、北部、西北部干旱地区,而西南喀斯特山区,虽降水总量丰富,但受其喀斯特二元结构的限制[22],依然存在着严重的工程性缺水现象。因此,研究喀斯特山区蒸散发的时空分布特征及其与气候因子的关系十分重要。
乌江流域位于中国喀斯特地貌类型发育最丰富的西南地区,是典型的喀斯特流域。基于此,本文选取2000—2014年MOD16A2/ET产品,结合流域内及周边11个气象站点的气象数据,分析贵州省乌江流域近15 a的地表蒸散发量时空变化特征,通过趋势分析和相关性分析探讨其影响因素,以期为水资源的合理利用与开发提供科学依据。
乌江为长江上游南岸最大的一条支流,河流、湖泊等分布较多,干流全长1 037 km,流经重庆、贵州等省区。乌江是贵州省第一大河,流经贵州省内42个县(市、区),贵州省境内流域面积为67 500 km2[23]。乌江流域贵州段(25°36'—29°03'N,103°37'—108°15'E)地形起伏度大,海拔为205~2 888 m(图1),地势西高东低,地貌类型包括岩溶峡谷、岩溶高原、岩溶槽谷。乌江流域属亚热带湿润季风气候,年均气温在13~18℃,年均降水量在800~1 600 mm[24],多集中在5—8月。
Monteith[1]基于Penman-Monteith模型计算全球陆地表面蒸散发量而形成的灰度遥感影像数据集统称为MOD16产品数据集,包括MOD16A2,MOD16A3两个子数据集,空间分辨率为1 km,时间分辨率有年、月和8 d共3种尺度。MOD16数据集内有地表实际蒸散发量(ET)、潜在地表蒸散发量(PET)、潜热通量(LE)、潜在热通量(PLE)和质量评估数据(ET_QC)5种数据,涵盖时间段为2000—2014年。
本文选用从NTSG(http:∥www.ntsg.rmt.edu/)免费下载且时间分辨率为月的2000—2014年MOD16A2/ET数据,遥感卫星轨道号为h27v06,数据格式为HDF。首先运用专业软件MRT(Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer Reprojection Tools)对下载的原始数据依次进行格式转换、重投影和镶嵌等预处理工作,提取研究所需的ET数据,然后基于IDL语言进行异常值剔除和真实值还原。MODIS产品中的部分异常值区域采用同产品的前一个月或者后一个月的相同位置的值填充,或选择同产品的前一年或后一年的相同时间的相同位置的值做填充处理,或选择其周围相邻3×3位置的像元均值填充。DEM(Digital Elevation Model)数据来源于“地理空间数据云”(http:∥www.gscloud.cn/),空间分辨率为30 m,根据数据说明进行坏值、无值处理和镶嵌、裁剪等预处理工作,最后将其空间分辨率重采样为1 km。
气象资料来源于中国国家气象科学数据共享服务平台(http:∥data.cma.cn/)。选取乌江流域内部及周边共11个地面气象站(图1)2000—2014年气象数据,时间尺度为月,气象因子主要包括平均气温(℃)、日照时数(h)、降水量(mm)、相对湿度(%)和平均2 min风速(m/s)。为了研究地表蒸散发与影响因素的关系,选取气温、日照时数、降水量、相对湿度和风速作为主要气候影响因素,利用Kriging插值法[17]对气象数据进行空间插值处理,并将其空间分辨率重采样为1 km。
本文利用相关系数R、均方根误差RMSE、平均偏差BIAS和平均绝对偏差MAE等[13]指标对MOD16A2/ET数据开展精度评价,计算公式分别为:
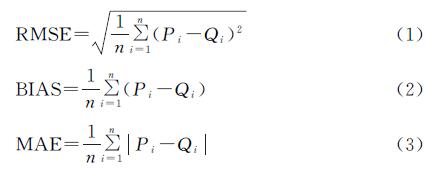
式中:n为气象站蒸发皿蒸散发量观测值个数; Pi为MOD16A2产品模拟蒸散发量; Qi为气象站蒸发皿蒸散发量校正值。
采用基于像元的一元线性回归分析法对乌江流域2000—2014年MOD16A2/ET数据进行趋势分析[25],公式为:
K=(n×∑ni=1(i×ETi)-∑ni=1i∑ni=1ETi)/(n×∑ni=1i2-(∑ni=1i)2)(4)
式中:n为年数; ETi为乌江流域内各像元点在第i年的年ET值; K为2000—2014年乌江流域内各像元点ET年际变化的一元线性回归方程的斜率,即趋势变化率,反映研究时段内ET的总体变化趋势。K>0表明ET总体变化呈增加趋势,反之为减少趋势。
基于像元尺度进行乌江流域地表蒸散发与各气候因子的相关分析研究,简单线性相关系数[16]的计算公式为:
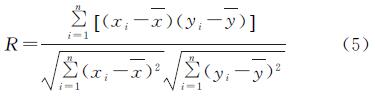
式中:n为年数; R为简单线性相关系数; xi,yi分别为x,y两个因子在第i年的值; x^-,y^-分别为两个因子研究时段内的平均值。
MOD16A2/ET数据的时间尺度是月尺度,因此,将气象站点观测日值数据在剔除异常值后累加到月尺度。由于,各气象站点、同一气象站点不同年份使用的蒸发皿有大、小2种口径,区域范围内长时间序列下,数据口径一致性难以满足。为了保证MOD16A2/ET数据精度评价精度,筛选了乌江流域空间上均匀分布的5个站点,站点在2009—2014年均使用大型蒸发皿。考虑到实际地表环境与蒸发皿环境的不同,参考前人相关研究,将气象站实测蒸散发量乘以折算系数[26-27]得到各站点逐年的月实际蒸散发量。获取5个站点缓冲半径3 km范围内MOD16A2数据的逐年ET月值,计算各个站点蒸散发量观测校正值与MOD16A2/ET数据模拟值的相关系数,在时间尺度和空间上均进行精度评价。数据精度评价结果表明(图2,表1),站点观测校正值与MOD16A2/ET模拟值的相关系数R为0.75~0.80,平均值为0.78; RMSE为0.89~1.60 mm/d,平均值为1.09 mm/d; BIAS为-1.02~-0.22 mm/d,平均值为-0.51 mm/d; RMSE为0.66~1.15 mm/d,平均值为0.79 mm/d。表明MOD16A2/ET模拟值与站点观测校正值在时间和空间分布上保持较高的一致性,MOD16A2/ET数据在乌江流域内的精度满足需要,可用于地表蒸散发时空分布及其与气候因子的关系研究。
如图3所示,2000—2014年乌江流域ET的年际起伏明显,整体呈中间年份(2005—2009年)高而两端年份(2000—2004年和2010—2014年)低的变化特点,距平相对变化率波动较大。研究时段内,多年平均ET值为830.08 mm,距平相对变化率为-4.53%~3.21%,有10个年份的ET高于平均水平,5个年份低于多年平均ET值; 年ET的最大值出现在2005年,为856.71 mm,2014年的851.67 mm次之; 年ET的最小值出现在2001年,为792.50 mm,其次为2010年的800.43 mm; 年ET最高值与最低值之差为64.21 mm。从图3可知,乌江流域年ET的变化规律表现为在2003—2009年波动轻微减少,2001—2003年和2011—2014年ET则明显增加。
2000—2014年乌江流域ET及其影响因素的年内变化特征如图4所示。ET、气温、日照时数、降水量、相对湿度和平均风速的多年月均值分别介于50~115.11 mm,4.42~24.59℃,46.51~163.77 h,21.25~201.53 mm,75.56~81.76 mm,1.44~1.85 m/s。ET、气温、日照时数和降水量均呈周期性单峰变化趋势,低值区均为11月—次年2月且其变化特征不显著; 其中ET和降水量的高峰出现在6月,气温和日照时数的高峰出现在7月。相对湿度和平均风速的年内变化特征相对复杂,6月和10月是相对湿度的两个高峰,并且是平均风速的两个低峰,相对湿度与平均风速的变化规律相反。从年内变化来看,乌江流域气温、日照时数和降水量均与ET的变化规律关系密切,说明ET的年内变化在乌江流域与水热同期。
季节性差异是地表蒸散量年内变化的重要特征,对2000—2014年乌江流域各季节蒸散量进行空间统计(图5),结果表明,春季和夏季的空间分布空间分布表现为东高西低,与多年平均格局(图6)基本一致,而秋季和冬季的空间分布表现为南高北低,与多年平均格局(图6)不同,由于受季节性气温、日照时数、降水量、相对湿度、平均风速等影响因素年内分布不均的影响,乌江流域四季蒸散量空间分布表现出一定差异性。春季(3—5月)ET为168.4~381.1 mm,均值为245.57 mm,占全年29.68%。春季气温逐渐回升,日照时数逐渐变长,此时正值农作物快速生长的季节,需水量逐渐增加,虽然春季的降水量较少,但大量的人工抽水灌溉使土地中水分依旧比较充足,较大的平均风速能为蒸散发提供良好的动力条件,因此蒸散量仍能保持较高水平。夏季(6—8月)ET为202.8~533.3 mm,均值为311.31 mm,占全年37.62%,为一年中蒸散量最高的季节,此外各地蒸散量相差最大,主要是因为夏季较高的气温、较大的降水量以及充足的日照时数都给蒸散发提供了良好的条件。秋季(9—11月)ET为104.3~187.0 mm,均值为138.10 mm,占全年16.69%,受降雨量减少、空气温度下降、日照时数逐渐缩短的影响,蒸散量也逐渐减小。冬季(12月—翌年2月)ET为92.5~181.7 mm,均值为132.51 mm,占全年16.01%,为一年中蒸散量最低的季节。冬季气温、日照时数和降水量均是一年中的最低季节,因此地表蒸散显著低于其他季节。就整体情况而言,乌江流域的季节蒸散量由大到小依次为夏季>春季>秋季>冬季。
2000—2014年乌江流域多年平均ET的空间分布特征如图6所示,具有显著的空间异质性,东部ET明显大于西部,而最大ET位于乌江流域的东南部。从各县(区/市)级行政单元之间来看,麻江县地表蒸散发的程度最强,多年平均ET值高达1 030.70 mm; 黄平、贵定、龙里、施秉、余庆、松桃和石阡7县ET值相对较高,约为912.50 mm; 水城、金沙、纳雍、黔西、大方5县和毕节、仁怀2市以及红花岗、六枝2区地表蒸散发的程度相对较弱,多年平均ET值约为787.41 mm; 而威宁县、赫章县和钟山区县ET值最小,约为736.16 mm/a。乌江流域平均海拔为1 184 m,结合相等间隔分区法,将乌江流域分为1~9个海拔区间(≤700 m,700~900 m,900~1 100 m,1 100~1 300 m,1 300~1 500 m,1 500~1 700 m,1 700~1 900 m,1 900~2 100 m,≥2 100 m),分区统计表明海拔越高的区域多年ET均值越小,即地表蒸散发的强弱程度与高程分布有一定的负相关性。
乌江流域年ET在2000—2014年的趋势变化率空间分布见图7,趋势变化率为-20~32 mm/a,平均趋势变化率为0.51 mm/a,整体呈增加趋势。根据ET趋势变化率范围定义为严重减少(K<-10)、轻微减少(-10≤K<-3)、基本不变(-3≤K<-3)、轻微增加(3≤K<10)、明显增加(K≥10)共5个变化区间[8]。基本不变的面积最大,占全流域面积的83.88%; 其次是轻微减少和轻微增加,分别占全流域面积的6.79%,6.51%; 明显增加的面积占全流域总面积的2.74%,而严重减少的面积最小,仅占全流域面积的0.08%。从趋势变化率的空间分布格局来看,严重减少区与多年平均ET的低值区在乌江流域西部有重叠发生,说明多年平均ET值的空间分布与其趋势变化率有一定的对应关系。
气候变化是影响区域水热分布的重要环境因素,气温和日照时数表征热力条件,降水量和相对湿度表征水分条件,平均风速表征动力条件。年内变化特征(图4)表明乌江流域ET的变化与该区域水热变化规律密切相关,气温、日照时数和降水量的变化是影响ET变化的重要气象因子,因此本文选用热力条件(气温、日照时数)和水分条件(降水量)作为影响乌江流域ET的主要气候因子进行相关分析。
整体上,2000—2014年乌江流域ET与气温、日照时数以及降水量均呈正相关关系。ET与气温的相关系数为-0.82~0.85,平均值为0.33; 与日照时数的相关系数为-0.80~0.86,平均值为0.28; 与降水量的相关系数为-0.89~0.89,平均值为0.31。乌江流域ET与气温、日照时数和降水量的显著相关性(p<0.05)在空间分布上具有明显的空间分异特征(图8)。降水量与ET的显著相关范围最广,约占乌江流域总面积的30.67%,其中显著正相关区域占91.25%,主要集中在乌江流域西部海拔相对较高的赫章县、七星关区、纳雍县、大方县、黔西县、修文县以及流域中游少部分区域,而显著负相关区域仅占8.75%。气温与ET的显著相关范围约占乌江流域总面积的29.56%,其中显著正相关区域占76.36%,主要集中在北部的道真县、务川县、沿河县、印江县、思南县和石阡县,而显著负相关区域仅占23.64%,主要集中在纳雍县、大方县和七星关区。日照时数与ET的显著相关范围约占乌江流域总面积的23.84%,其中显著正相关区域占63.26%,主要集中在赫章县、七星关区、纳雍县、大方县、平坝县、清镇市和修文县,而显著负相关区域占36.74%,主要集中在红花岗区、思南县和沿河县。日照时数和降水量与ET的显著相关范围在乌江流域上游重叠区域较大,这些区域海拔较高,喀斯特地貌分布广泛,水土流失严重,石漠化分布较广,土壤含水能力差且植被覆盖度较低,不利于土壤蒸发和植被蒸腾,该区域与乌江流域多年平均ET的低值区(图6)相一致。乌江流域下游降水量较高,较高的气温使蒸散发较强。
(1)2000—2014年乌江流域年际ET起伏较大,整体呈中间年份高而两端年份低的变化特点,其值为792.50~856.71 mm,距平相对变化率波动较大; 年内ET变化规律表现为周期性单峰变化,与该区域气温、日照时数和降水量的变化基本一致; 乌江流域ET具有显著的季节性,四季ET值由大到小依次为:夏季(311.31 mm)>春季(245.57 mm)>秋季(138.10 mm )>冬季(132.51 mm)。
(2)2000—2014年乌江流域多年平均ET具有明显的空间异质性,呈西低东高的空间格局,多年平均ET值为605.43~1 208.26 mm; 春季和夏季空间分布与多年平均格局基本一致,而秋季和冬季的空间分布与多年平均格局略有不同。从变化趋势空间分布来看,以基本不变为主,明显增加区主要分布在乌江流域中、下游。
(3)乌江流域ET与气候因子的相关分析表明,各气候因子与ET的显著相关范围由大到小依次为:降水量(30.67%)>气温(29.56%)>日照时数(23.84%),三者对ET的影响均以正相关为主; 日照时数和降水量与ET的显著相关范围在乌江流域上游有部分重叠区域,而乌江流域下游则仅与气温显著相关影响。