2.1 PAM浓度和坡度对堤防坡面产流产沙的影响
2.1.1 PAM浓度和坡度对堤防坡面产流的影响
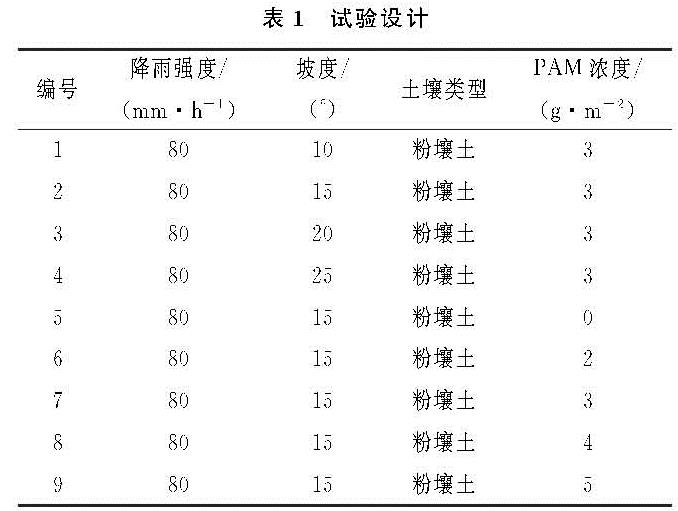
图1A为在雨强和坡度相同时,不同下垫面条件下产流率随降雨历时出现不同程度的波动。如图1B所示,平均产流率以3 g/m2为分界点,大于3 g/m2产流率随浓度增大而减小,浓度小于3 g/m2产流率随浓度增大而增大。3 g/m2平均产流率相比0 g/m2减小了约20%; 不同PAM浓度均表现出土壤入渗增大,平均产流率降低了10.6%~20%,并且平均产流率先减小后增大,即0 g/m2>5 g/m2>4 g/m2>2 g/m2>3 g/m2。分析得出PAM浓度在一定范围内,可以打开土壤下渗通道,提高土壤入渗率,减小径流,超出这个范围时土壤入渗率减小,径流增大。
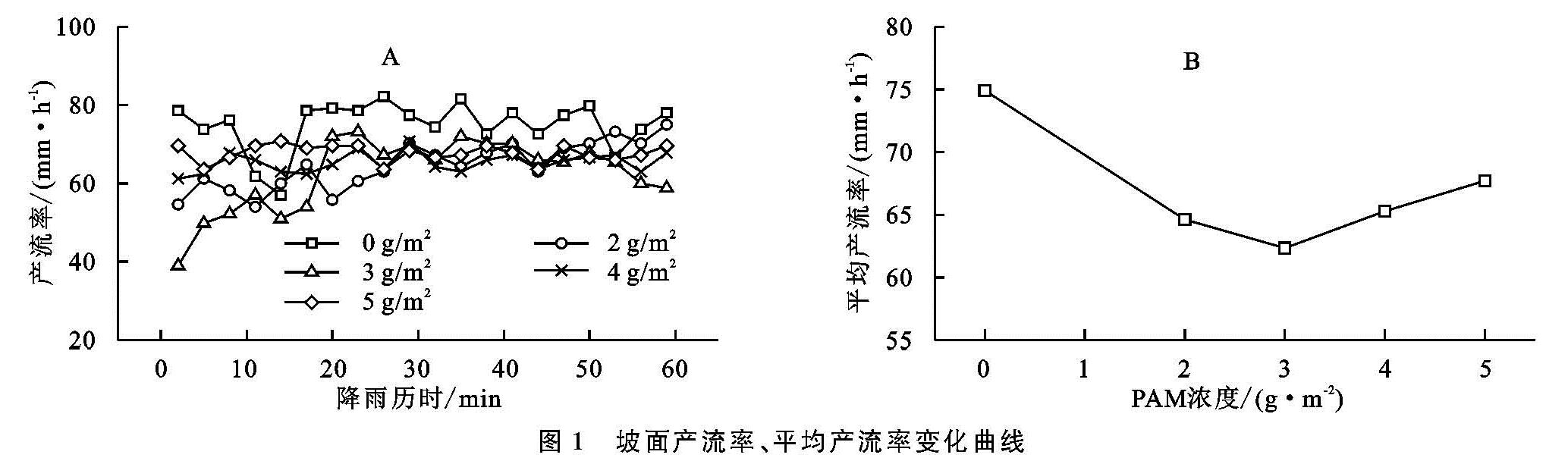
图2显示雨强和下垫面条件相同时,不同坡度每分钟产流率趋势差异较大,随降雨历时先急剧增长,后出现不同幅度的波动,但总体趋势为增大。在显著性水平为0.05时,使用单因素方差对每分钟产流率进行分析,发现坡度对坡面产流率有显著性影响,平均水平差异较大。图2B显示在下垫面条件相同时,15°和20°坡面平均产流率相近,25°坡面平均产流率急剧减小,但都大于10°坡面平均产流率。即平均产流率15°>20°>25°>10°。在坡度较大时,受雨面积减小,在同一入渗的条件下,坡面径流量理论上应该逐渐递减,但本次试验以15°坡面为分界点,>15°时产流率随坡度增大而减小,<15°时产流率随坡度增大而增大。
2.1.2 PAM浓度和坡度对堤防坡面产沙的影响
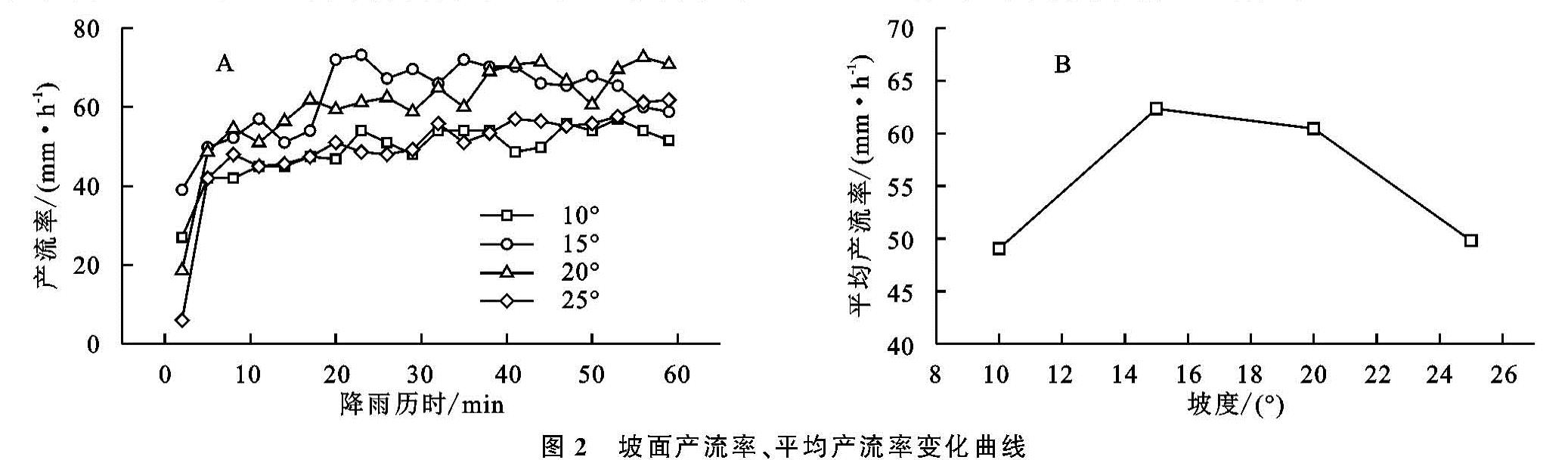
图3A显示在雨强、坡度相同时,不同PAM浓度产沙率趋势变化显著。PAM浓度为0,2,3,5 g/m2坡面每分钟产沙率随降雨历时先增大,后出现不同程度的波动,未趋于稳定。PAM浓度为4 g/m2坡面每分钟产沙率随降雨历时先缓慢增大,后趋于稳定。不同坡面每分钟产沙率随着PAM浓度的增大,产沙率逐渐减小。对不同浓度下每分钟产沙率,在显著性水平为0.05时,使用单因素方差对每分钟产流率进行分析,发现浓度对产沙率影响显著。且平均产沙率0 g/m2[0.077 76 kg/(m2·min)]>2 g/m2[0.061 88 kg/(m2·min)]>3 g/m2[0.056 81 kg/(m2·min)]>4 g/m2[0.049 27 kg/(m2·min)]>5 g/m2[0.036 94 kg/(m2·min)]。
图3B显示在80 mm/h降雨强度下,不同坡度产沙率趋势变化较大。坡度为10°,15°,20°坡面产沙率呈现先急剧增大后缓慢减小的趋势; 25°坡面产沙率呈现先急剧增大,后出现较大的波动。随着坡度的增大,坡面产沙率为增大趋势。在显著性水平为0.05时,使用单因素方差对每分钟产流率进行分析,发现坡度对产沙率影响显著。且平均产沙率25°[0.083 93 kg/(m2·min)]>20°[0.065 10 kg/(m2·min)]>15°[0.056 81 kg/(m2·min)]>10°[0.051 28 kg/(m2·min)]。
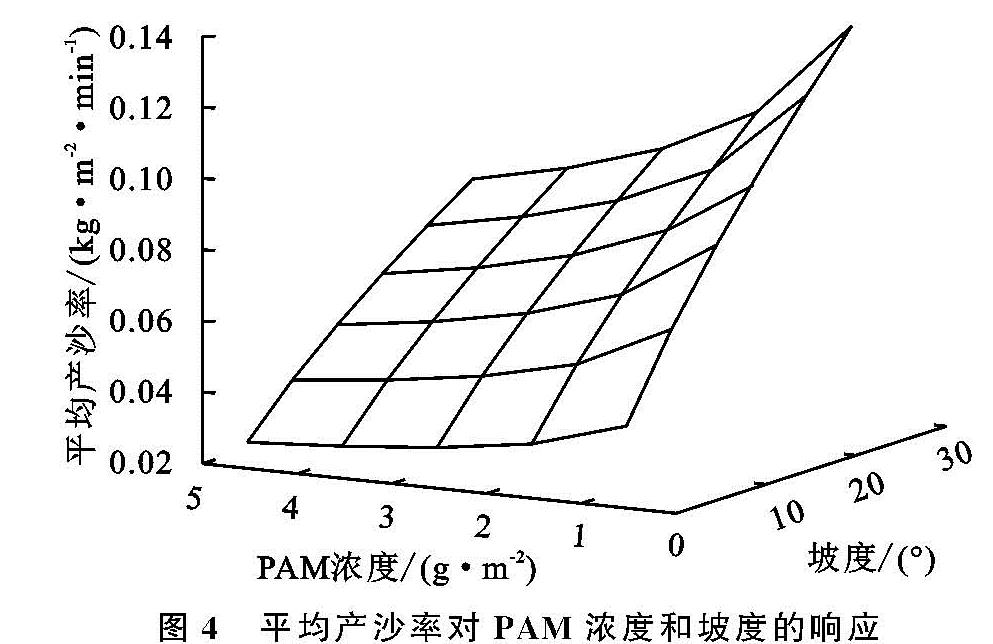
为了更好地分析平均产沙率与坡度和PAM浓度的关系,将三者进行拟合,结果表明:平均产沙率与坡度和PAM浓度的关系可以用幂函数Se=a·Sb·Cd表示。式中:Se为平均产沙率[kg/(m2·min)]; S为坡度(°); C为PAM浓度(g/m2); a,b,d均为拟合参数。
表2为不同坡度和PAM浓度与产沙率的经验方程。产沙率随降雨历时的变化规律可以用幂函数进行描述,产沙率(Se)与坡度(S)是正相关,坡度越大,产沙率越大; 与浓度(C)为负相关,浓度越大产沙率越小,决定系数为0.86,显著性水平为0.05。图4为平均产沙率与PAM浓度和坡度拟合图形。
2.2 PAM浓度和坡度对地方坡面流速的影响
坡面径流是水力侵蚀发生、发展的主要动力,流速是坡面径流最重要的水力学要素[14-16]。在试验中通过染色法测定流速v,同时根据监测到的水温,获得雷诺系数,从而获得修正系数α。已有研究表明,在PAM单独使用情况下,由于其水溶液黏性较强,会影响土壤水分的运动[17]。PAM的用量越大,这种黏滞作用也越大[18],从而引起水分入渗阻力的增大,土壤饱和导水率降低也越多[19]。
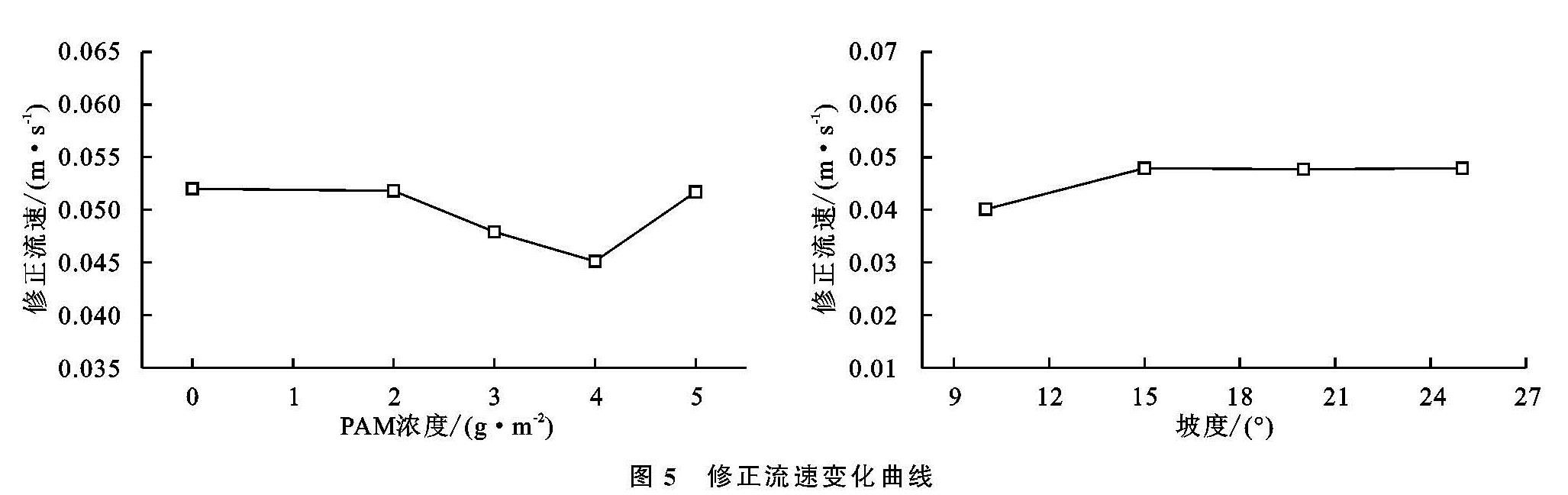
图5为坡面施加PAM后流速随着其浓度和坡度变化的情况。在PAM浓度一定时,流速随坡度增大,先增大后趋于稳定,这表明施加PAM后坡面流速随坡度增大是在一定范围内的。在坡度不变时,流速在PAM浓度为0~2 g/m2内趋于稳定,在2~5 g/m2内先减小后增大,总体趋势为减小。
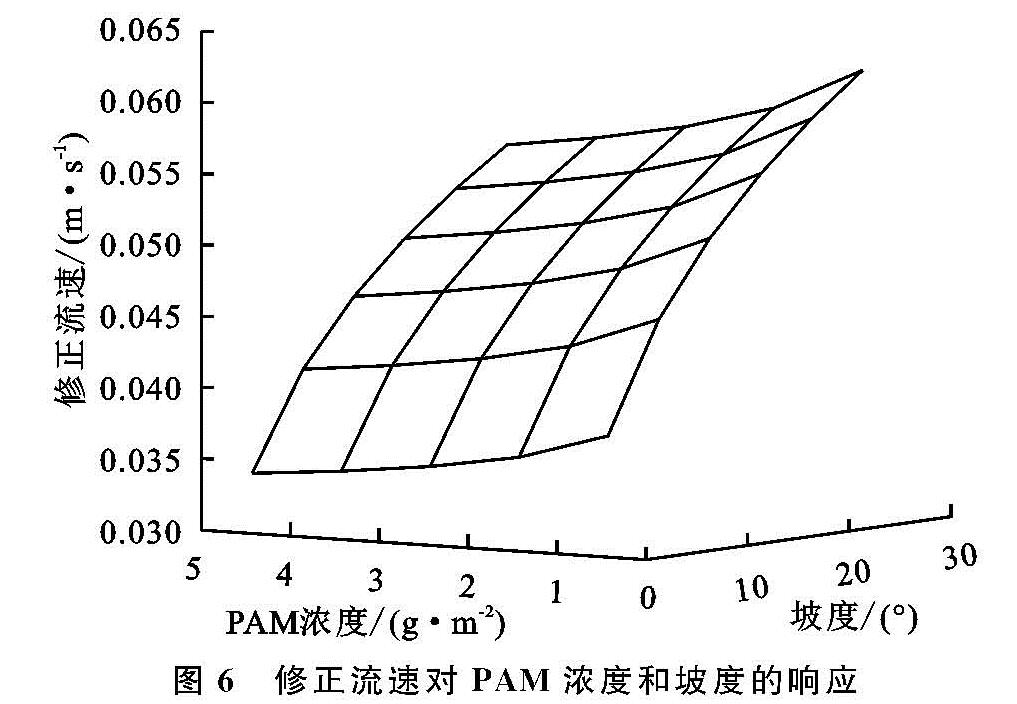
对修正流速与坡度和PAM浓度进行拟合,结果表明:修正流速与坡度和PAM浓度的关系可以用幂函数V=e·Sf·Ch·表示。式中:V为修正流速(m/s); S为坡度(°); C为PAM浓度(g/m2); e,f,h均为拟合参数。
表3为PAM浓度和坡度与修正流速的经验方程。流速随降雨历时的变化规律可以用幂函数进行描述,流速与坡度是正相关,坡度越大,流速越大; 与浓度为负相关,浓度越大流速越小,决定系数为0.68,显著性水平为0.05。图6为修正流速与坡度和PAM浓度拟合图形。
2.3 坡面侵蚀的形态特征
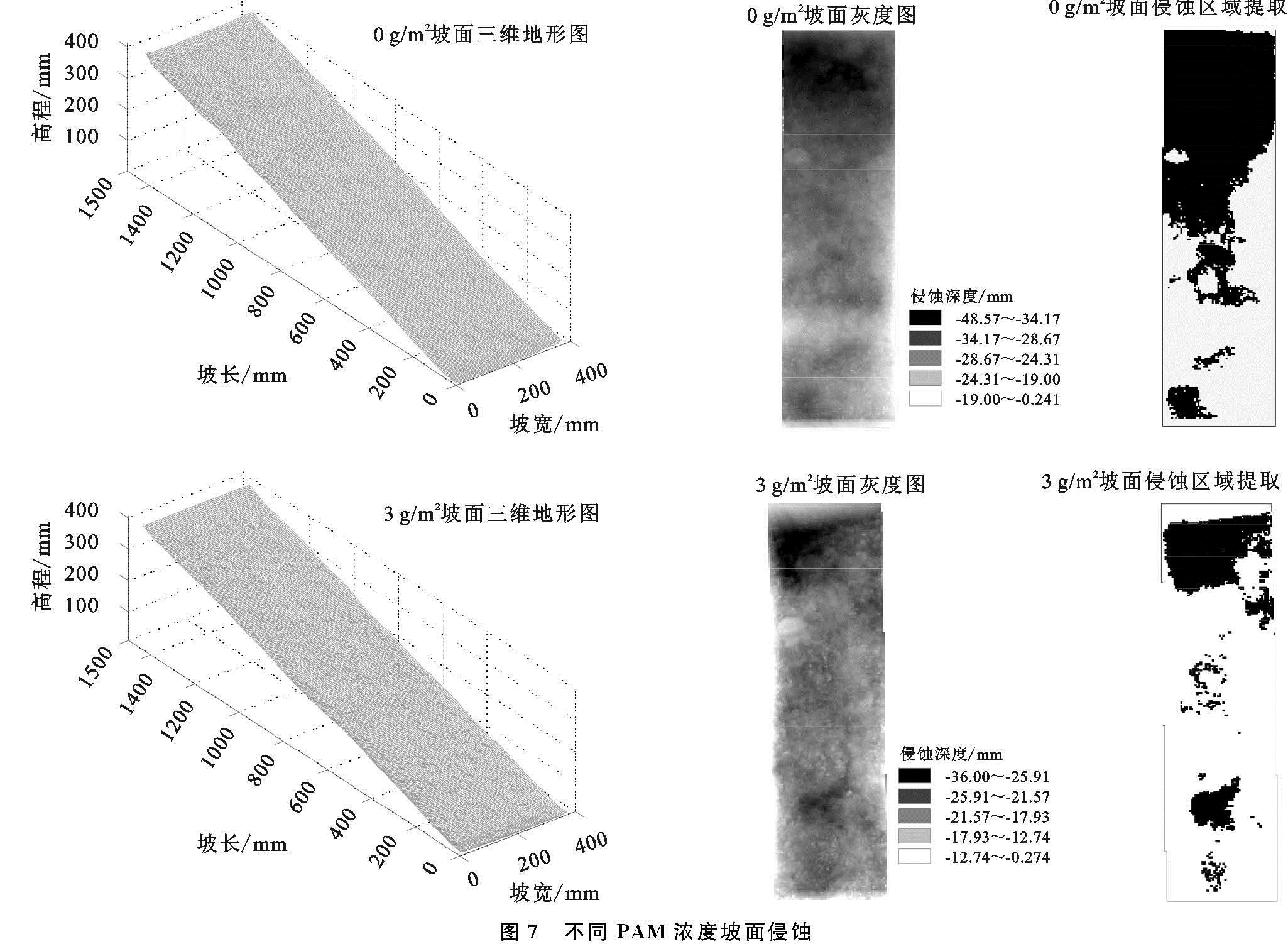
水力侵蚀在不同阶段表现出不同的形式,同时会影响产流产沙,因而分析其形态对研究坡面产流产沙规律有重要的意义。相同坡度下,未施加PAM和PAM浓度3 g/m2为例进行分析。从图7中可以发现,0 g/m2坡面侵蚀主要发生在坡面中上部,施加PAM坡面侵蚀区域呈现较均匀分布,两个坡面都是以面蚀为主,伴有溅蚀。0 g/m2侵蚀严重区域主要表现为片状,侵蚀区域集中,面积较大,部分呈现出跌坎特征,侵蚀深度为24~48 mm; PAM坡面侵蚀严重区域主要表现为鳞片状,侵蚀严重区域为较集中,面积较大,部分出现层状特征,侵蚀深度为21~36 mm。通过提取坡面侵蚀区域,发现0 g/m2侵蚀严重区域面积为0.293 2 m2,占坡面面积的48.86%; PAM坡面侵蚀严重区域面积为0.133 2 m2,占坡面面积的22.2%,施加PAM后使得坡面侵蚀严重区域相比于0 g/m2减小了约54.57%。施加PAM后坡面侵蚀程度减缓,说明施加PAM起到了防止侵蚀的效果。0 g/m2受到薄层水流冲刷明显,侵蚀特征主要为片蚀,侵蚀区域为片状。PAM坡面受到雨滴溅蚀的影响,坑洼感较强,侵蚀区域连续,加上薄层水流冲刷,局部出现高地,这可能是因为PAM与土壤拌和不均匀导致的。