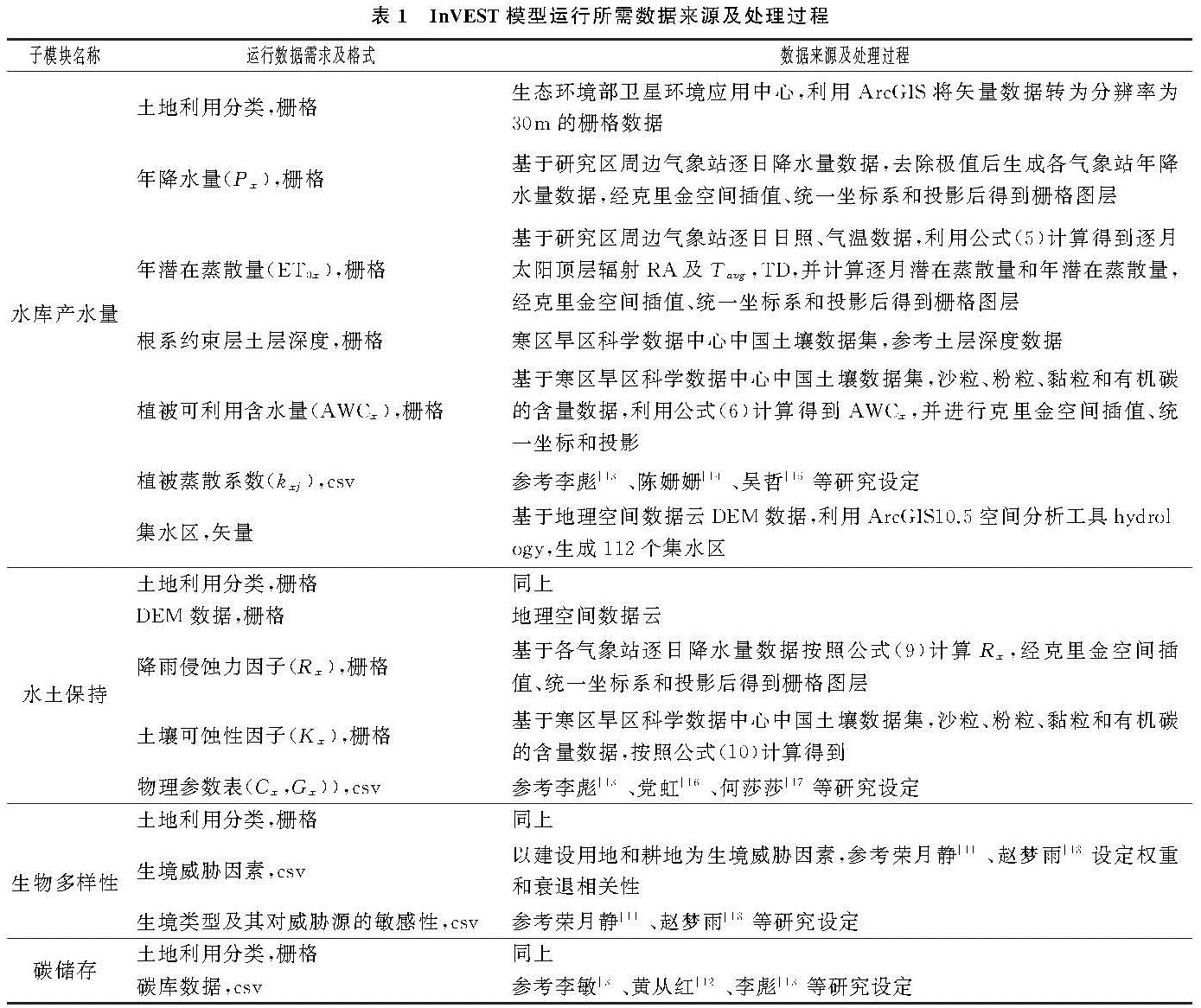
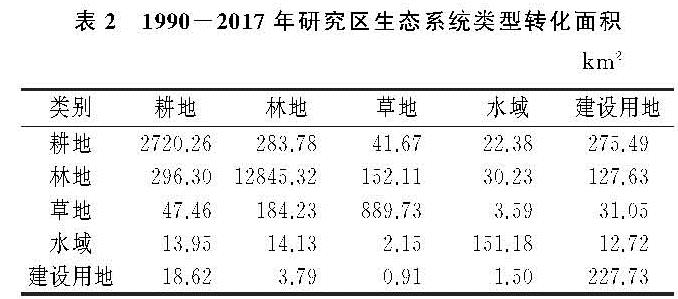
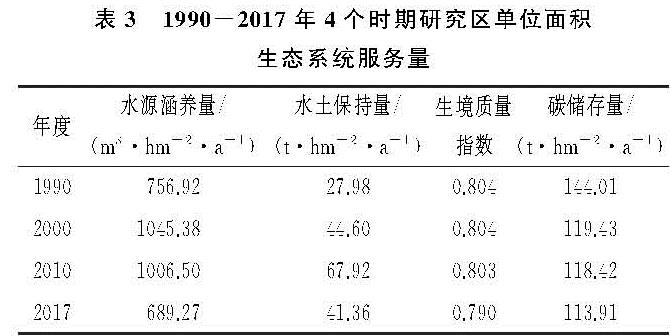
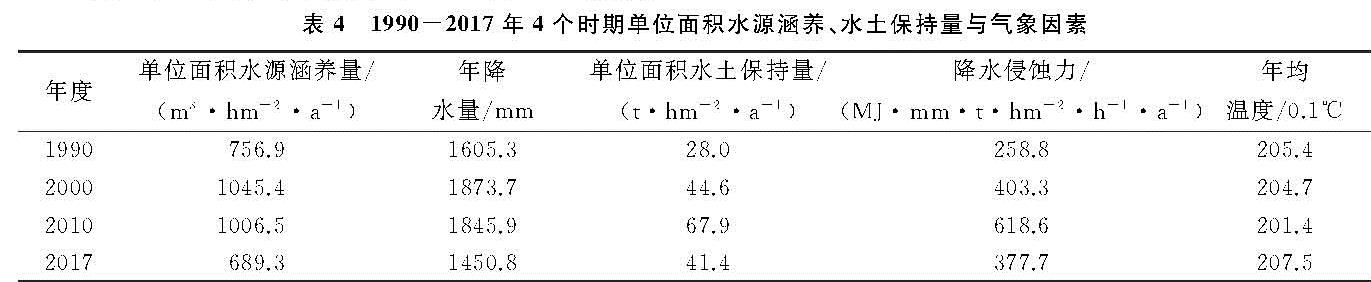
2.1 InVEST模型简介
本文应用的InVEST 3.2.0版本可用于评估两大类生态系统服务功能:一是支持服务,包括生境质量、生境风险评估、海水质量; 二是最终服务,包括碳储存、水源涵养(产水量)、养分持留、土壤保持(泥沙输移)、气候调节、木材生产、作物生产等。另外该模型还可以用于叠加分析(识别重要海洋和海岸带)和海岸脆弱性分析。
2.1.1 水源涵养服务功能
InVEST模型产水量模块(hydropower)基于水量平衡原理计算研究区水源涵养量,由于该模型未考虑地表径流因素,造成林地等生态用地单位面积产水量低于建设用地等不合理结果(区域降水差异不大的情况下,由于林地蒸腾量较高,计算得到产水量较低),因此,在计算结果的基础上,扣除了地表径流产生量。公式如下:
Yxj=Px×(1-(AETxj)/(Px))-Dxj(1)
(AETxj)/(Px)=(1+ωx+Rxj)/(1+ωx+Rxj+1/(Rxj))(2)
ωx=Z×(AWCx/Px)(3)
Rxj=(kxj×ET0x)/Px(4)
ET0x=0.0013×0.408×RA×(Tavg+17.8)×(TD-0.0123Px)0.76(5)
AWCx=54.509-0.132×SAN-0.003×SAN2-
0.055×SIL-0.006×SIL2-0.738×CLA+0.007×CLA2-2.688×C+0.501×C2(6)
式中:Yxj表示第j种生态系统类型中单元格x上的年水源涵养量; Px表示单元格x上的年降水量; AETxj表示栅格单元x的年实际蒸散量,AETxj/Px是实际蒸散与降水的比值; Dxj表示地表径流量,由x单元格年均降水量与对应生态系统类型的地表径流系数相乘得到; ωx表示植被年需水量与年降水量的比值; Z是降雨深度和降雨时间的分布,其值为常数; Rxj是景观类型j中单元格x上的budyko干燥指数,表示潜在蒸散与降水的比值; AWCx表示植被可利用含水量(mm); kxj是植被蒸散系数,表示不同发育期植被蒸散量ET与潜在蒸散量ET0x的比值; RA是太阳顶层辐射(MJ); Tavg是日最高气温均值和日最低温均值的平均值(℃); TD是日最高气温均值和日最低温均值的差值(℃); SAN,SIL,CLA,C分别是沙粒、粉粒、黏粒和有机碳的含量。
2.1.2 水土保持服务功能
InVEST模型泥沙输移比模块(SDR)首先基于地形和气候条件计算潜在土壤侵蚀量,再基于植被覆盖因子和水土保持措施计算实际侵蚀量,两者的差值即为土壤保持量。
RKLSx=Rx×Kx×LSx(7)
USLEx=Rx×Kx×LSx×Cx×Gx(8)
Rx=∑12i=11.735×10(1.5lg(P2ix)/(Px))-0.8188(9)
K=(0.2+0.3e(-0.0256SAN(1-SIL)))×
((SIL)/(CLA)+SIL)0.3×((1-0.25C)/(C+e3.72-2.95C))×
((1-0.7SN1)/(SN1+e-5.51+22.9SN1))(10)
式中:RKLSx为栅格x的土壤潜在侵蚀量,是仅考虑地貌与气候条件下的计算结果; USLEx是栅格x的实际土壤侵蚀量,主要考虑了植被覆盖、拦截作用及实施了水土保持措施后的计算结果; Rx为降雨侵蚀力; Kx为土壤可蚀性; LSx为坡度坡长因子; Cx为植被覆盖因子; Gx为水土保持措施因子。Px表示降水量; SAN,SIL,CLA,C分别是沙粒、粉粒、黏粒和有机碳的含量; SN1=1-SAN。
2.1.3 生物多样性维持功能
InVEST模型利用生境质量表征生物多样性维持功能(表1)。生境质量模块结合土地覆被和生物多样性威胁因素生成生境质量地图,计算公式为:
Qx,j=Hj×(1-(Dx,j)/(Dx,j+k))
式中:Qx,j是土地利用与土地覆盖j中栅格x的生境质量; Dx,j是生境类型j栅格x的生境胁迫水平。
2.1.4 碳储存功能
碳储存模块通过输入各年度土地利用数据及对应碳密度数据评估区域生态系统碳储量。本文考虑四大碳库(表1),即地上生物碳、地下生物碳、土壤碳和死亡有机碳,计算公式如下:
Ctot=Cabove+Cbelow+Csoil+Cdead
式中:Ctot为碳存储量(t/hm2·a); Cabove,Cbelow,Csoil,Cdead分别是地上生物碳、地下生物碳、土壤碳、死亡有机碳。
2.2 地理探测器简介
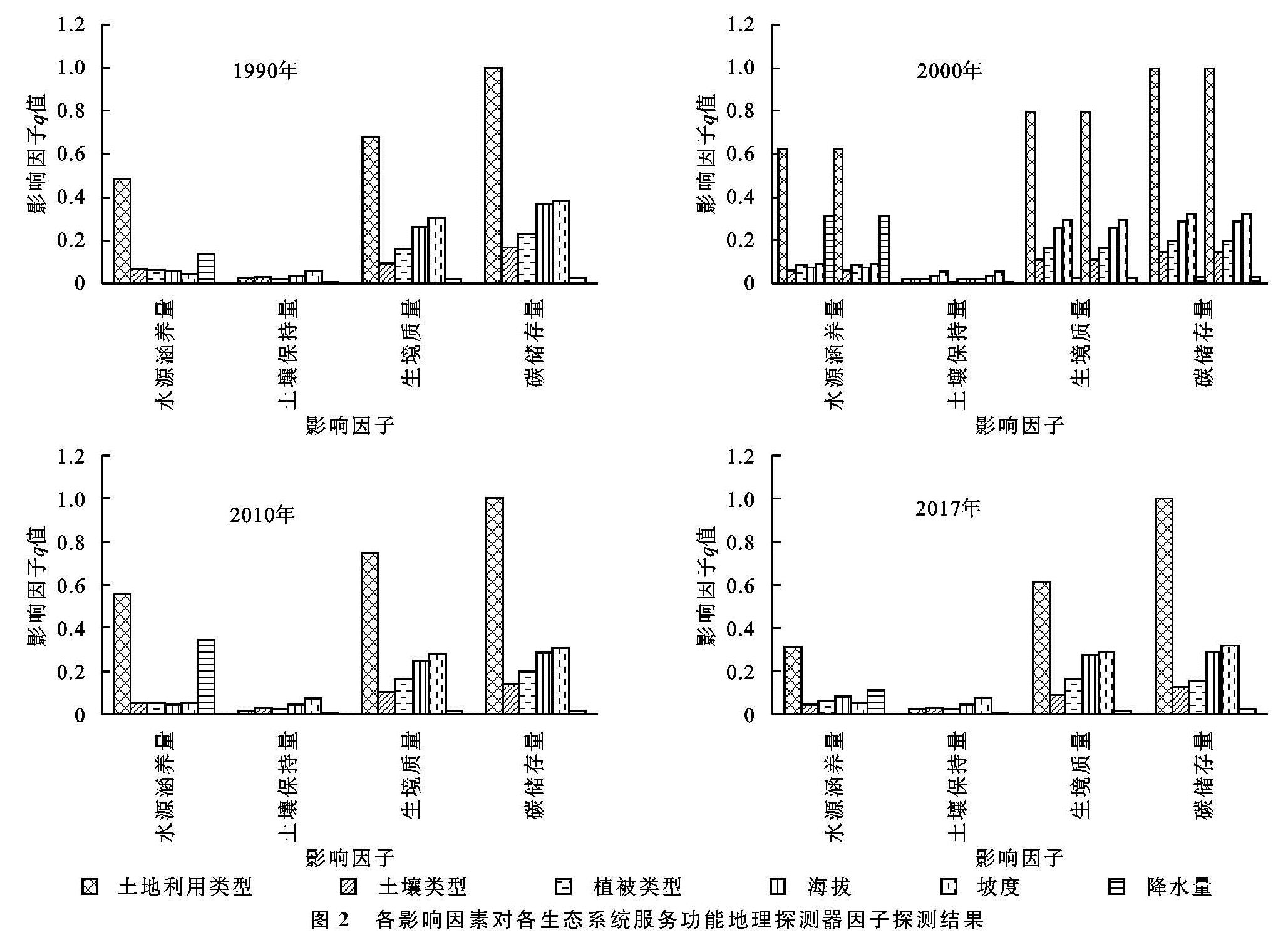
地理探测器是度量、挖掘和利用空间异质性的新工具,其理论核心是通过空间异质性来探测因变量与自变量之间空间分布格局的一致性,据此度量自变量对因变量的解释度,即q值。统计结果q值越大表示自变量对因变量的解释力越强,反之则越弱。地理探测器比一般统计量有更强的势(Power),因为两个变量在二维空间分布一致比两个变量的一维曲线的一致要难得多[19]。利用地理探测器分析时,自变量为类型量(数值型变量可离散化为类型量),解决了本文拟分析的土地利用类型、土壤类型为非数值量而无法进行相关分析的问题。
2.3 数据来源
本文涉及数据包括:(1)土地利用分类数据:1990年、2000年、2010年、2017年土地利用数据来源于生态环境部卫星环境应用中心,将研究区划分为耕地、林地、草地、水域、建设用地5个一级类,及旱地、水田、有林地、灌木林、湖泊、城镇用地等20个二级类;(2)气象数据:来自国家气象信息中心,包括4个年度广东省及周边84个气象站降水、温度、日照逐日数据;(3)土壤质地数据:来源于寒区旱区科学数据中心(http:∥westdc.westgis.ac.cn/)中国土壤数据集;(4)高程数据:来自地理空间数据云(http:∥www.gscloud.cn/)。(5)植被类型数据:中科院资源环境科学数据中心(http:∥www.resdc.cn/data),用于研究生态系统服务功能影响因素。