3.1 生态系统服务价值变化分析
3.1.1 生态系统服务价值时间变化分析
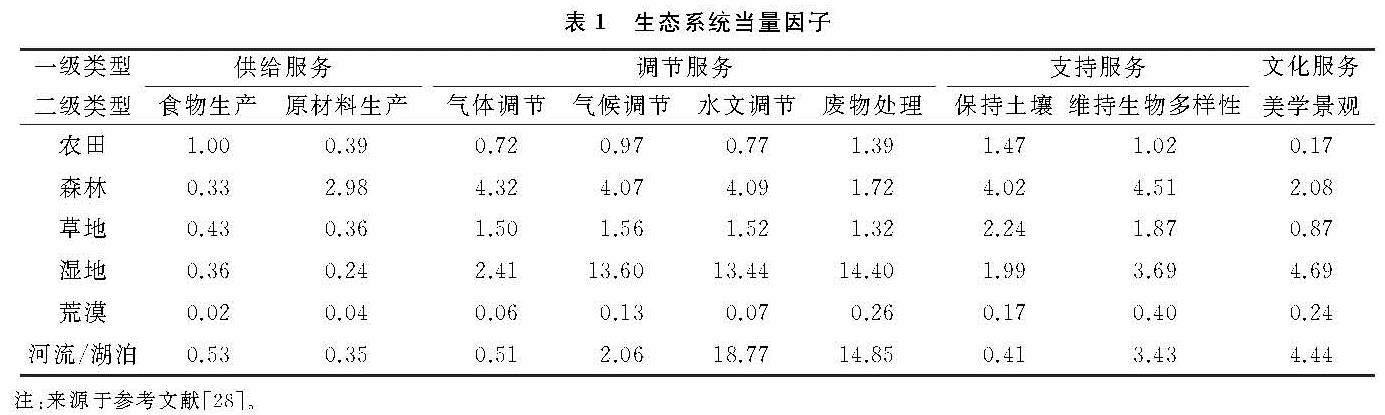
通过公式(4)求得1990—2015年武汉市各生态系统服务功能价值(图1):1990—2015年武汉市生态服务功能价值从99.34亿元减少至82.98亿元,降幅为16.47%,年平均减少率为0.66%。其中降幅最大的时间段为2010—2015年,降幅为6.67%; 降幅最小的时间段为2000—2005年,降幅为1.77%。ESV整体呈线性递减过程,经历了“快速—缓慢—快速”的降低过程。
从各生态系统服务功能来看,水文调节和废物处理构成了武汉市ESV的主体,二者的减少值也最大,但水文调节的降幅仅高于美学景观,降幅为13.71%,其次是废物处理,降幅为15.49%; 食物生产的降幅最高,达26.19%,其次保持土壤,降幅为23.44%; 原材料生产、气体调节和维持生物多样性降幅略高于ESV整体降幅,降幅分别为18.03%,19.26%和17.51%。就各阶段而言,各生态系统服务功能均呈线性递减过程,水文调节、废物处理、保持土壤、维持生物多样性和美学景观在1990—2000年,减少速度逐渐加快; 在2000—2005年,减少速度变缓; 在2005—2015年减少速度又逐渐加快,与ESV整体变化相似; 原材料生产和气体调节在1990—2015年,减少速度不断加快; 气候调节在1990—2005年,减少速度逐渐变缓,在2005—2015年,减少速度迅速加快; 食物生产在1990—1995年,2000—2005年,减少速度较缓慢,在1995—2000年,2005—2015年,减少速度较迅速。
3.1.2 生态系统服务价值空间变化分析
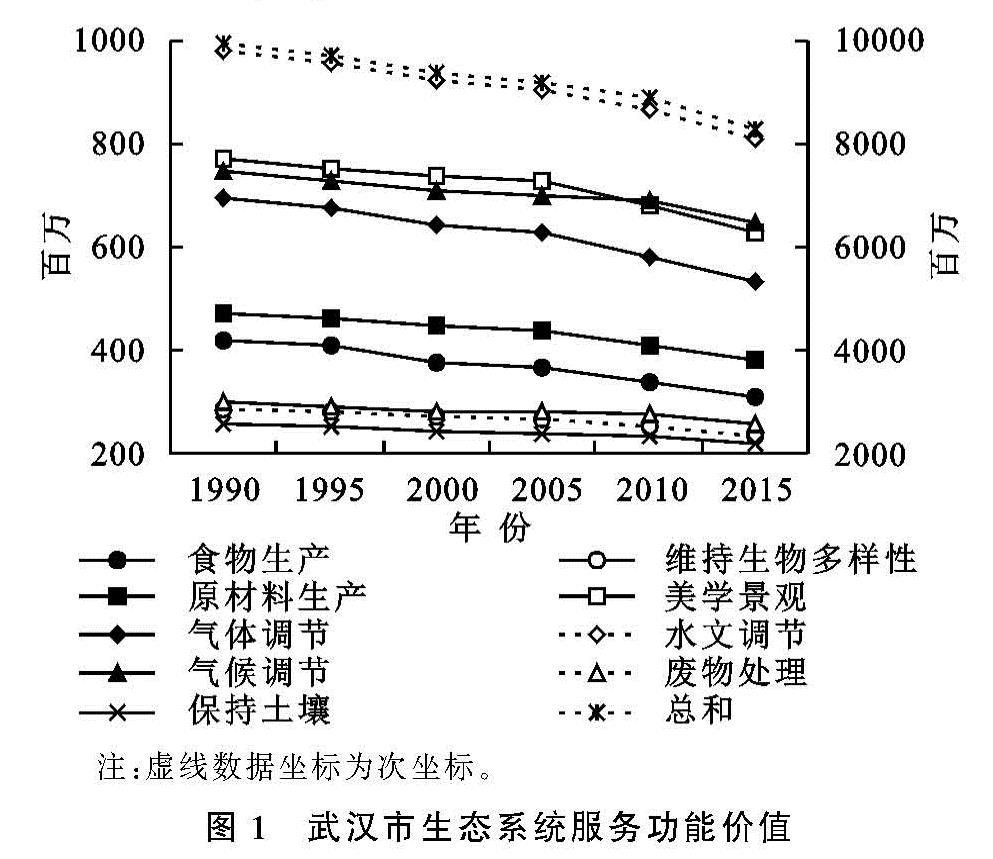
在ArcGIS软件中,将单位ESV分为6类,得到ESV分布图(图2)。由图2可知,武汉市ESV分布较为复杂,中部地区ESV极高和极低地区交错分布; 东北部地区ESV较低; 正北地区除在最北边ESV较高外,其余地区ESV较低; 西部地区ESV极高和较低地区交错分布; 南部地区ESV普遍较高。生态系统价值高值的区域与水域分布较为一致,主要位于中部和南部地区。生态系统价值极低值的区域与建设用地分布较为一致,主要分布在中部地区; ESV较低值区域与农田分布一致,遍布武汉市境内,在中部和南部与水系交错分布,在北部分布较为集中。由于建设用地不断扩张,中部地区的极低值区域不断扩大,在2005—2015年,建设用地扩张进一步加剧,东部地区,北部地区和东北部地区的极低值区域迅速增加,较低值区域不断减少。
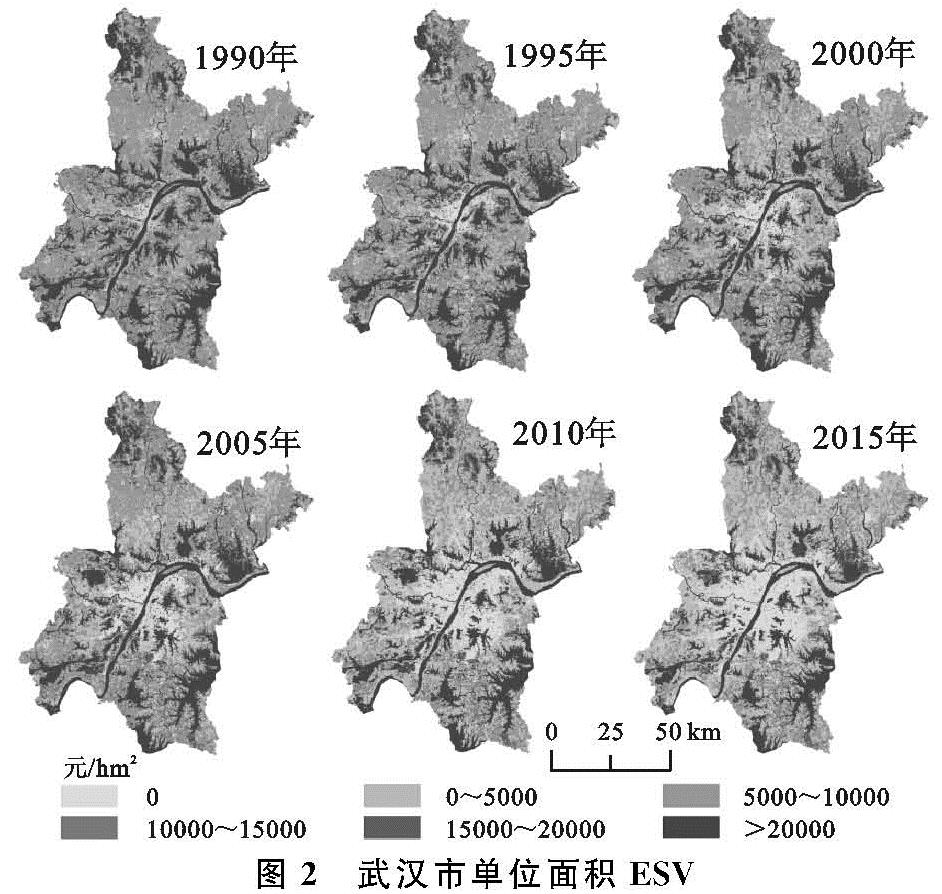
在ArcGIS软件中,根据武汉市高程(图3),通过坡度分析得到武汉市坡度图(图4)。由图3可知,武汉市ESV高值区域分布与水域和林地相同,分布位于武汉市高程极低和极高区域,ESV低值区域和极低值区域均分布于高程较低区域。由图4可知,武汉市坡度较为平坦,除北部和中南部坡度较高之外,其余地区坡度均较低。
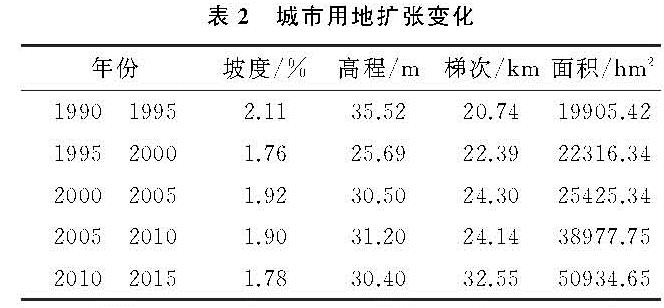
3.2 城市用地扩张变化分析
武汉市城市用地扩张变化如表2所示:过去25 a武汉市建设用地扩张量显著,增加了4倍。就发展阶段而言,1990—2005年武汉城市扩张面积缓慢增长,在2005—2015年迅速增长; 但就增加速率而言,在1990—1995年,增长速率最大,为50.92%,2000—2005年最小,为31.27%。在空间形态上,在1990—2010年,武汉市扩张距离稳定在20~25 km内,而在2010—2015年,迅速扩散至30 km以上; 在坡度上则变化不大,城市用地扩张的地形较为平坦; 在高程上,1990—1995年,扩张高程最高,平均达35 m以上,在1995—2000年,扩张高程最低,平均为25 m,在2000—2015年,扩张高程较为稳定,平均为30 m; 扩张破坏权重呈“W”波动变化,在1990—1995年,2010—2015年最大,1995—2000,2005—2010年最小,证明武汉城市用地扩张侵占的地类在1990—1995年,2010—2015年,高生态价值地类(水域、林地)的比例较大,对生态的破坏性相对较高。
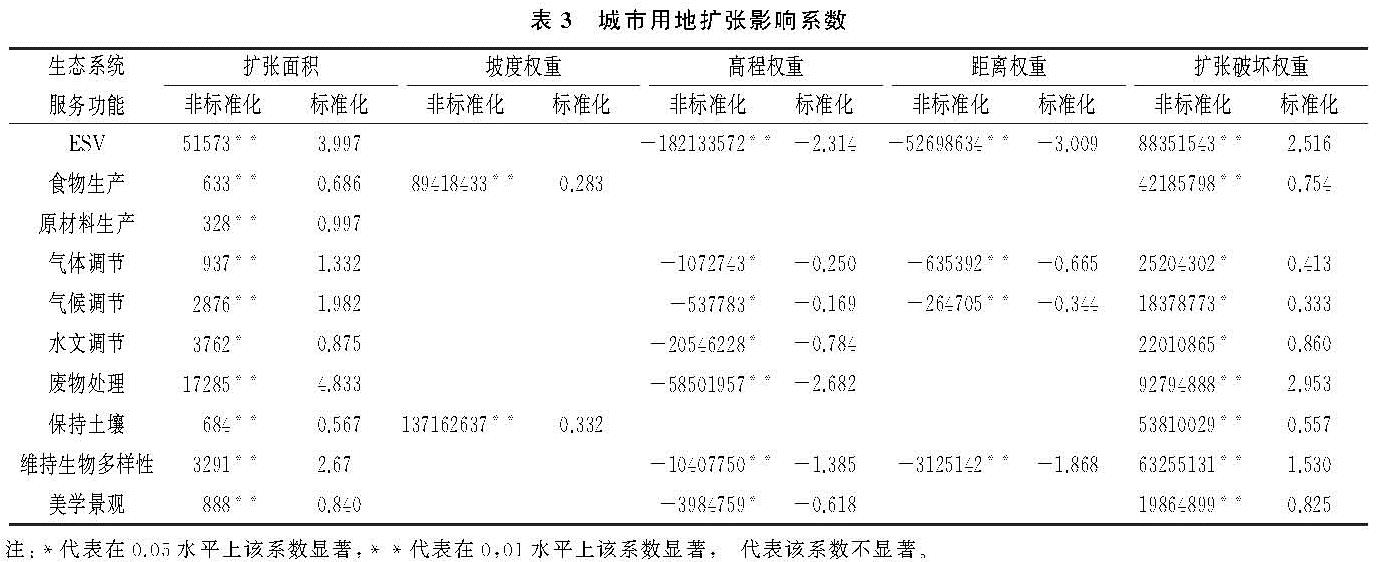
3.3 城市用地扩张影响分析
由SPSS 22.0逐步回归分析可得城市用地扩张对生态系统服务功能的影响系数如表3所示:ESV整体受城市扩张面积、扩张高程、扩张距离和扩张破坏权重影响,其中ESV受扩张面积和扩张破坏权重负面影响,即扩张面积和扩张破坏权重分别每增加1 hm2,1单位,ESV减少值分别增加51 573,88 351 543元; ESV受高程权重和距离权重正面影响,这是由于武汉市高ESV区域主要分布于低高程地区和武汉市中南部,而武汉市城市扩张主要集中在中部和中北部区域,因此ESV减少值会随着城市扩张高程和距离的增多而减少; 而坡度高值区域和低值区域均主要为高ESV区域,坡度中值区域则为低ESV区域,因此,城市用地扩张的坡度变化对ESV整体影响较低。进一步通过标准化系数分析各因素对生态系统服务功能的影响程度,扩张面积的影响程度最大,其次是距离权重,高程权重的影响程度相对最低,但除坡度外,影响程度相差不大。
就各生态系统服务功能而言,气体调节、气候调节、维持生物多样性受城市用地扩张的影响与ESV整体较为相同,但由于各地类的气体调节能力和气候调节差值不大,导致气体调节和气候调节主要受扩张面积影响; 而各地类的维持生物多样性能力构成与ESV整体构成相似,所以各因素对维持生物多样性影响程度与ESV整体相似。食物生产和保持土壤受城市用地扩张影响相同,均受扩张面积、坡度权重、扩张破坏权重负面影响,且扩张面积和扩张破坏权重的影响程度均较高,坡度权重的影响程度稍弱。这是由于食物生产主要由农田提供,保持土壤主要由农田和森林提供,但由于武汉市森林面积较少且变化不大,所以食物生产和保持土壤主要受农田变化影响,扩张破坏权重影响程度较高; 食物生产和保持土壤高值区域主要分布于中低坡度地区,低值区域则分布于低坡度地区,所以食物生产和保持土壤减少值随城市用地扩张的坡度增加而增加。除森林外,各地类的单位面积原材料生产价值变化不大,而森林面积较少且变化不大,导致原材料生产受城市用地扩张的影响与其余生态系统服务功能均不相同,其仅受扩张面积影响。水文调节、废物处理和美学景观构成较为单一,主要由水域和湿地构成,且两者的单位面积水文调节和美学景观价值远大于其余地类,也主要分布于低高程区域,导致扩张破坏权重的影响程度与扩张面积相同,高程的影响程度略低于扩张面积。