资助项目:贵州省科技计划项目“贵州省山地特色休闲养生旅游资源开发与服务企业行动计划”(黔科合平台人才[2017]5720)
第一作者:王焕(1993—),女,贵州省毕节人,硕士,主要从事自然资源开发与规划相关研究。E-mail:2325605282@qq.com 通信作者:梅再美(1961—),男(土家族),贵州省贵阳人,教授,主要从事自然资源开发与规划及环境保护与治理相关研究。E-mail:meiminggui@qq.com
(School of Geography and Environmental Science, Guizhou Normal University, Guiyang 550025, China)
evapotranspiration; spatiotemporal characteristics; climatic factors; MOD16; Guizhou Province
探究贵州省地表蒸散发(ET)时空特征及气候变化对其的影响,对理解气候变化和水资源的关系具有重要的意义。基于2000—2014年的MOD16A2/ET产品和气象站数据,综合运用单相关、偏相关和复相关分析法,分析了研究区ET的时空变化特征及其与气候因子的关系。研究表明:(1)蒸发皿观测值折算所得的实测ET与MOD16/A2ET呈强相关(R=0.80),能满足ET相关研究的需要;(2)ET具有明显的空间异质性,由西北向东南,ET逐渐变大,ET与海拔区间呈负相关;(3)研究时段内,ET的年际波动增加速度较缓,ET的年内变化呈单峰型,7月为高峰;(4)ET与同期气温和降水量在整个研究区呈正相关关系,与同期日照时数呈正相关的区域大于呈负相关的区域。降水量是对贵州省ET年内变化影响最大的气候因子,驱动力分析表明贵州省ET的主要驱动类型为降水量强驱动型和降水量驱动型。
To explore the spatiotemporal characteristics of surface evapotranspiration(ET)and the influence of climate change on these characteristics is of great significance to understand the relationship between climate change and water resources. Based on the data of MOD16A2/ET products and meteorological stations from 2000 to 2014, single correlation, partial correlation and complex correlation analysis were comprehensively used to analyze the spatiotemporal variation characteristics of ET in the study area and their relationship with climate factors. The results show that:(1)the measured ET converted from the observed value of evaporating dish is strongly correlated with MOD16/A2ET(R=0.80), which can meet the needs of ET related research;(2)ET has obvious spatial heterogeneity; from northwest to southeast, ET gradually increases, and ET is negatively correlated with elevation interval;(3)during the study period, the fluctuation of inter-annual variation of ET increases slowly, and the ET shows a periodic unimodal trend and peaks in July;(4)there is a positive correlation between ET and the temperature and precipitation in the whole study area, and the area with a positive correlation with the duration of sunshine in the same period is larger than the area with a negative correlation; precipitation is the climate factor that has the greatest influence on ET variation in Guizhou Province. The driving force analysis shows that the main driving types of ET in Guizhou Province are precipitation-strong-drive and precipitation-drive.
地表蒸散发(Evapotranspiration,ET)是指地表土壤和植被向大气传输的水汽总通量[1-3],包括地表植被蒸腾、土壤蒸发和水面蒸发[4-5],是全球气候变化和水文循环的重要参数[6],影响着地表过程中地、气系统的相互作用[7-9]。ET的影响因素[10-11]主要包括热力因素(气温、太阳辐射、日照时数等)、水分因素(降水量、相对湿度等)和动力因素(风速等)。如何能精准估算ET,分析其时空分布特征及气候因子对ET的影响,对促进区域水资源的科学分配、提高水资源的开发利用效率等具有重要意义。
蒸发皿、径流计、蒸渗仪、涡度相关、波文比、通量塔、大孔径闪烁仪等仪器虽然能够获取相对准确的均匀下垫面的ET,但大多局限于站点或田间尺度,难以反映ET的空间异质性[12]。遥感数据以其快速、覆盖范围广、周期性等优势,使长时间序列、大区域尺度的蒸散发研究成为可能,已成为目前大区域地表蒸散研究的主要手段[13-16]。估算ET的遥感数据主要包括具有高空间分辨率的Landsat和ASTER数据,具有高时间分辨率的MODIS和NOAA AVHRR数据,以及能够穿云透雨、不受天气限制的微波遥感数据[12]。全球陆地蒸散发产品MODIS MOD16/ET通过了全球通量塔站台的检验,在全球得到了广泛应用[17-21]。国内外对于ET的研究主要集中在模型估算[22-24]、精度验证[25-26]、时空特征[27-29]及影响因素分析[10,30]等方面。刘健等[10]采用统计学方法分析了鄱阳湖流域站点尺度上实际蒸发量的时间变化特征,结合变化趋势探究了实际蒸发量的影响因素; 王鹏涛等[31]采用基于像元的单相关分析法探讨了黄土高原区蒸散发的时空变化特征及其影响因素; 叶红等[32]以MODIS ET产品为数据源分析了黄河源区地表蒸散发的时空变化特征,并引入单相关、偏相关和复相关分析,重点探讨了ET与气候因子的关系; 黄葵等[6]基于MOD16/ET定量分析了海河流域ET的时空变化特征,综合运用单相关、偏相关和复相关分析,定量探索了ET与气候因子的驱动力关系。引入可有效排除其他因子干扰的偏相关分析和综合考虑多个因子共同作用的复相关分析,已经成为探究气候因子对蒸散发影响的有效方法。杨江州等[33]基于MOD16分析了贵州省不同地貌类型区蒸散发的时空变化特征。蒋翼等[34]分析了2000—2014年贵州省实际蒸散发和潜在蒸散发的时空变化特征及不同土地覆被类型下的实际蒸散发特征。目前,学者对贵州省蒸散发的研究多集中于时空分布特征,而关于气候因子对蒸散发的影响方面的研究尚不多见。
贵州省位于中国西南喀斯特地区,虽然水资源总量丰富,但基岩裸露率高且水土流失严重[35],故生态环境脆弱、水资源开发利用难度大,结构性缺水问题日益突出。基于此,本文选取2000—2014年贵州省MOD16A2/ET产品、省内及周边34个气象站点的气象数据,分析贵州省ET的时空变化特征,结合单相关、偏相关和复相关分析探究各气候因子对ET的影响,对理解贵州省水资源和气候变化的关系具有重要的意义。
贵州省地处中国西南地区24°37'—29°13'N,103°36'—109°35'E,总面积约176 200 km2,包括贵阳、遵义、铜仁、毕节、六盘水和安顺6个地级市以及黔东南、黔南和黔西南3个少数民族自治州。地貌以岩溶高原、岩溶槽谷、岩溶峡谷、断陷盆地、峰丛洼地和非喀斯特地貌为主[33],海拔127~2 890 m,平均海拔为1 100 m左右,地势西高东低。研究区内河流、湖泊发育,主要有八大水系,分属珠江和长江两大流域。贵州省90%以上的区域为林地、耕地和草地,气候类型属于亚热带湿润季风气候。2000—2014年贵州省17个气象站点数据统计表明,月均气温5.27~24.50℃,月均日照时数52.64~160.34 h,月均降水量21.11~221.74 mm,5—8月降水量比较集中,占全年降水量的60%以上。
MOD16产品是指Monteith等[36]基于Penman-Monteith模型计算全球陆地表面蒸散发量而形成的数据集,包括MOD16A2和MOD16A3两个子数据集,空间分辨率为1 km,时间分辨率有8 d、月和年3种尺度,涵盖时间段为2000—2014年。本文选用在NTSG(http:∥www.ntsg.rmt.edu/)下载的2000—2014年MOD16A2/ET数据,时间分辨率为月,遥感卫星轨道号为h27v06,数据格式为HDF。数据格式转换、重投影和影像镶嵌等预处理工作在专业软件MRT中进行,异常值剔除和数据分析利用IDL语言进行。
数字高程模型(Digital Elevation Model,DEM)数据在“地理空间数据云”(http:∥www.gscloud.cn/)下载,空间分辨率为30 m。首先在ENVI5.3软件中,根据数据说明对原始影像进行预处理,主要包括坏值和无值处理、镶嵌、裁剪等; 然后利用ArcGIS 10.2将其空间分辨率重采样为1 km。
本研究使用的气象数据为2000—2014年贵州省内部及周边34个地面气象站的气温(℃)、日照时数(h)、降水量(mm)、相对湿度(%)、风速(m/s),时间分辨率为月,下载地址为中国国家气象科学数据共享服务平台(http:∥data.cma.cn/)。参考叶红等[32]的相关研究,采用Kriging插值法对气温、降水量和日照时数进行空间插值处理,并重采样其空间分辨率为1 km。位于贵州省西部的威宁和位于贵州东部的铜仁2个站点作为插值验证点,另外的32个站点数据用于空间插值。气温、降水量和日照时数3个气象因子采用Kriging插值法在研究区的精度验证如图1所示,R2为0.77~0.99,均值为0.95,说明在研究区采用Kriging插值法对气温、降水量和日照时数进行空间插值的结果较为理想,能满足后续研究的需要。
采用简单线性相关系数分别对贵州省ET与各气候因子(气温、日照时数、降水量、相对湿度和风速)的相关性进行研究,计算公式[32]如下:
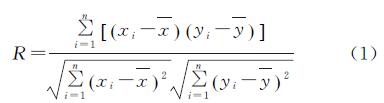
式中:n为样本个数; R为简单线性相关系数; xi与yi分别是x,y两个因子的第i个样本值; x^-与y^-分别为两个因子所有样本的平均值。
探究气温或降水量对ET的影响,通过分析ET与气温、ET与降水量之间的偏相关程度,可以排除降水量或气温的干扰[37],偏相关系数的计算公式如下:
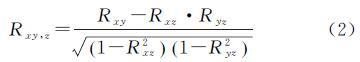
式中:x,y,z分别为ET、降水量和气温; Rxy,z为在气温不变的情况下; ET与降水量的偏相关系数; Rxy,Rxz,Ryz分别表示ET与降水量、ET与气温、气温与降水量的简单线性相关系数。参考王永财等[38]的研究,偏相关分析的显著性检验选用经典的t检验法。
引入复相关系数[39]可以综合考虑气温和降水量等多因子对ET的共同影响,计算公式如下:
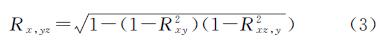
式中:Rx,yz为ET与降水量和气温的复相关系数; Rxy为ET与降水量的简单线性相关系数; Rxz,y为在降水量不变的情况下; ET与气温的偏相关系数。参考王永财等[38]的研究,复相关分析的显著性检验选用F检验法。
基于像元尺度进行ET与气候因子的单相关、偏相关和复相关分析,探讨了ET与气候因子的空间相关性。
为了说明MOD16/A2ET在贵州省地表ET时空反演的适用性,通过实测年均ET与MOD16/A2产品反演的年均ET的简单线性相关系数进行精度验证。张鑫等[40]的相关研究表明,中国西南地区实测ET值月值是小型蒸发皿测得的ET值的0.65~0.85倍,平均为0.75倍。因此,本文将所能获取的研究区内空间上均匀分布的8个站点内小型蒸发皿测的月ET值乘以0.75所得的数据计为实测月ET,然后将实测月ET合成实测年ET; 其中毕节、贵阳和遵义3个站点的小型蒸发皿观测时间段为2002—2014年,安顺、都匀、凯里、思南和兴仁5个站点的小型蒸发皿观测时间段为2009—2014年。MOD16/A2ET为以站点为中心3 km为半径的圆形缓冲区内的年ET均值。结果表明(表1):实测值与反演值的相关系数R为0.77~0.83,平均值为0.80,表明MOD16/A2产品反演的ET值与站点实测蒸散发量在时空分布上保持较高的一致性,研究区内MOD16/A2ET数据精度满足要求,可用于地表蒸散发的相关研究。
2000—2014年贵州省ET多年ET均值的空间分布见图2。由图2A可知,多年ET均值为531.3~1 299.6 mm,平均值为855.90 mm; 多年ET均值地域分异明显,由西北向东南逐渐变小,最强ET位于贵州省南部。研究区内各市(州)单元之间ET差异显著,从小到大依次为:六盘水市(753.29 mm)<毕节市(759.85 mm)<遵义市(821.56 mm)<安顺市(847.53 mm)<贵阳市(849.10 mm)<黔西南州(860.18 mm)<铜仁市(874.32 mm)<黔东南州(928.08 mm)<黔南州(939.67 mm)。贵州省平均海拔为1 108 m,通过手动分类法,将贵州省分为1~10个海拔区间(≤550 m,550~700 m,700~850 m,850~1 000 m,1 000~1 150 m,1 150~1 300 m,1 300~1 500 m,1 500~1 700 m,1 700~2 000 m,≥2 000 m),分区统计表明海拔越高的区域多年ET均值越小,即地表蒸散发的强弱程度与高程分布有一定的负相关性。
(1)年际变化特征。图3A为2000—2014年贵州省ET及气候因子的年际变化。2000—2014年贵州省年际ET值为822.28~879.19 mm,多年平均ET值为855.90 mm; 贵州省在2003—2010年ET表现为波动减少,2001—2003年和2010—2014年间ET表现为波动增加,研究时段内贵州省ET总体上呈缓慢增加趋势; 贵州省ET年最大值出现在2003年、2014年次之,而ET年最小值出现在2010年。单相关分析(表2)表明,研究时段内,贵州省ET与降水量、相对湿度、气温、日照时数、风速的相关系数分别为0.18,-0.01,0.10,-0.15,0.22,说明在年际变化上ET与各气候因子的相关性均不显著。
(2)年内变化特征。图3B为2000—2014年贵州省ET及气候因子的年内变化。贵州省多年月平均ET值为33.11~126.41 mm,其变化规律呈单峰型,高峰出现在7月。ET月均值的低值区出现在11月—次年1月,且波动变化不明显; 2—7月为ET的上升区,7—11月为ET的下降区。单相关分析(表2)表明,研究时段内ET与降水量、相对湿度、气温、日照时数、风速的相关系数分别为0.92,-0.18,0.81,0.71,0.17,说明在年内变化上ET与降水量、气温和日照时数均呈极显著正相关(p<0.01),与相对湿度和风速的相关性均不显著。这表明贵州省ET的年内变化与该区域水热变化同期,降水量、气温和日照时数是引起ET变化的重要气候因子。
气候变化是影响区域水热分布的重要环境因素,气温和日照时数表征热力条件,降水量和相对湿度表征水分条件,平均风速表征动力条件。年内变化特征(图3B)表明贵州省ET的年内变化与该区域水热变化规律密切相关,降水量、气温和日照时数的变化是影响ET变化的重要气象因子,因此本文选用水分条件(降水量)和热力条件(气温、日照时数)作为影响贵州省ET的主要气候因子进行相关分析,以便讨论贵州省ET的驱动类型。
贵州省ET与降水量、气温和日照时数的空间简单线性相关系数分布见图4。由图4可知,ET与降水量的相关系数为0.72~0.98,空间平均相关系数为0.89; 与气温的相关系数为0.63~0.95,空间平均相关系数为0.79; 与日照时数的相关系数为-0.33~0.86,空间平均相关系数为0.61。研究区ET与降水量和气温均呈正相关关系,ET与日照时数相关关系以正相关为主,小部分区域为负相关。空间分异性分析表明,ET与降水量的相关系数在空间上差异最小,ET与日照时数的相关系数在空间上差异最大。ET与降水量在整个研究区均呈显著正相关(p<0.01); ET与气温呈显著正相关(p<0.01)的区域占研究区总面积的95.53%,另外的4.47%呈正相关,零散分布于贵阳市、遵义市、铜仁市、黔东南州和黔南州; ET与日照时数呈显著正相关(p<0.01)的区域占研究区总面积的18.28%,在毕节市、安顺市和黔西南州分布比较集中,而遵义市分布则比较零散; 呈正相关的区域占79.21%,另外的2.58%呈弱负相关,集中分布在毕节市西部。
简单相关性分析表明,贵州省降水量和气温对ET的影响远大于日照时数对ET的影响,故本文选择降水量和气温进行与ET的偏相关分析和复相关分析。贵州省ET与降水量、气温的空间偏相关系数分布见图5。
由图5A可知,ET与降水量的偏相关系数为0.10~0.92,平均值为0.69,均呈正相关关系。显著性水平(α=0.05)的双侧t检验表明,ET与降水量的偏向关系数通过显著性检验的区域(t≥t0.01)在铜仁市、黔东南州、黔南州、黔西南州和六盘水其均有集中连片分布,总面积95 910 km2,占降水量偏向关系数呈正相关区域的54.47%; 通过显著性检验的区域(t≥t0.05)在遵义市分布最集中,总面积68 173 km2,占降水量偏向关系数呈正相关区域的31.72%。
由图5B可知,ET与气温的偏相关系数为-0.57~0.87,平均值为0.13,整体呈正相关关系的区域大于呈负相关关系的区域,偏相关性呈正相关的区域主要分布在贵州省西、西南和东南部,总面积为109 650 km2,占流域总面积的62.27%,中部和北部主要呈负相关关系,总面积为66 423 km2,占流域总面积的37.73%。贵州省ET与气温的偏向关系数通过显著性检验的区域(t≥t0.01)主要分布在黔西南州的南部边缘地区,总面积为1 822 km2,仅占气温偏相关系数呈正相关区域的1.66%; 通过显著性检验的区域(t≥t0.05)主要在六盘水市南部和黔西南州集中分布,总面积11 169 km2,占降水量偏相关系数呈正相关区域的10.19%。
在空间差异性上,ET与气温的偏相关系数大于ET与降水量的偏相关系数。显著性检验表明,贵州省ET与降水量的偏相关显著性要明显强于气温,表明降水量对贵州省ET的影响比气温大。
贵州省ET与降水量和气温的空间复相关系数分布见图6,复相关系数为0.76~0.99,空间均值为0.90,高值区主要分布在贵州省西部的六盘水市和黔西南州,低值区主要分布在贵州省北部的遵义市。F检验结果表明,通过显著性检验的区域(F>F0.05)总面积为80 km2,仅占研究区总面积0.05%; 研究区其余的99.95%区域均通过显著性检验(F>F0.01)。
大量相关研究[6,10,32]表明,区域水热的时空分布与各气候因子紧密相关,为深入理解降水量和气温对贵州省ET的影响,基于偏相关和复相关分析,参考叶红等[32]的研究拟定的贵州省ET的驱动规则见表3。
图6B为2000—2014年贵州省ET的驱动分区图,贵州省ET受气候因子驱动的地区主要表现为降水量强驱动,面积为89 849 km2,占研究区总面积的51.03%,主要分布在贵州省东部的黔东南州和东北方向的铜仁市,另外的7个市(州)则分布相对零散; 其次为降水量驱动型,面积为64 570 km2,占研究区总面积的36.67%,主要分布在贵州省北部的遵义市以及毕节市、安顺市、黔南州一带; 降水量气温共同驱动型的面积为9 121 km2,占研究区总面积的5.18%,集中分布在黔西南州的南部边缘; 其他因子驱动型的面积为8 663 km2,占研究区总面积的4.92%; 气温驱动型、气温强驱动型和降水量气温共同强驱动型的面积分别为2 644 km2,684 km2,542 km2,分别占研究区总面积的1.50%,0.39%和0.31%。贵州省87.70%的区域属降水量强驱动型或降水量驱动型,表明研究时段内降水量是贵州省ET年内变化的主要驱动因子,即降水量的增加是ET增强的主要原因。
降水量是对ET影响最大的气候因子,且与ET以正相关为主,这与前人研究一致[6,31-32]。气温和日照时数对ET影响较大,也以正相关为主,与部分研究一致[10,32],而王鹏涛[31]等在陕甘宁黄土高原区的研究则认为气温和日照时数对ET的影响以负相关为主,黄葵等[6]在海河流域的研究也表明气温与ET呈负相关。这可能是因为贵州省属亚热带湿润季风气候,是湿润地区,阔叶林分布广泛,属于能量控制型蒸散发,黄土高原区和海河流域均属于温带气候类型,降水量较少,气温和日照时数较大的情况下不利于阔叶林的生长,地表覆被类型多为草地和针叶林。许多研究表明风速与ET有显著正相关关系[10,31,41],而本文中风速与ET虽呈正相关关系(表2),但相关性极小,说明风速对ET的影响基本可以忽略,这与前人研究[10,31,41]明显不同。贵州省位于云贵高原,海拔127~2 890 m,地表起伏较大,山地和丘陵广泛分布,平均风速仅为1.60 m/s(图3A),故与充足的水分和热力条件相比,微弱的动力条件对ET的影响并不显著。
本文基于MOD16/A2ET产品,在精度验证的基础上,结合气象数据,分析了2000—2014年贵州省ET的时空变化特征,通过单相关、偏相关和复相关分析探究了气候因子对ET的影响,并对ET的年内变化进行了驱动类型分析。主要结论如下:(1)空间上,ET呈由西北向东南增加的变化特征,随着海拔的增加ET逐渐减小;(2)时间上,从2000—2014年贵州省ET整体上表现为波动缓慢增加,年内ET呈单峰变化,高峰出现在7月,与该区域气温、降水量和日照时数呈强正相关关系;(3)贵州省87.70%的区域属降水量强驱动型或降水量驱动型,表明研究时段内降水量是贵州省ET年内变化的主要驱动因子。