3.1 植被对土壤水分特征的影响
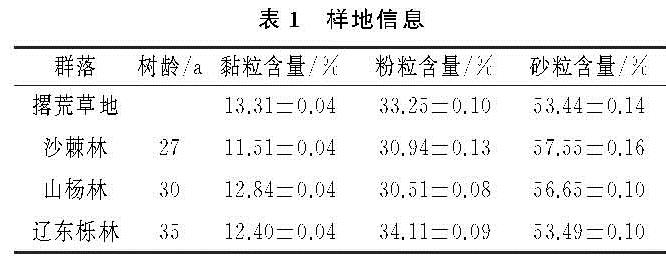
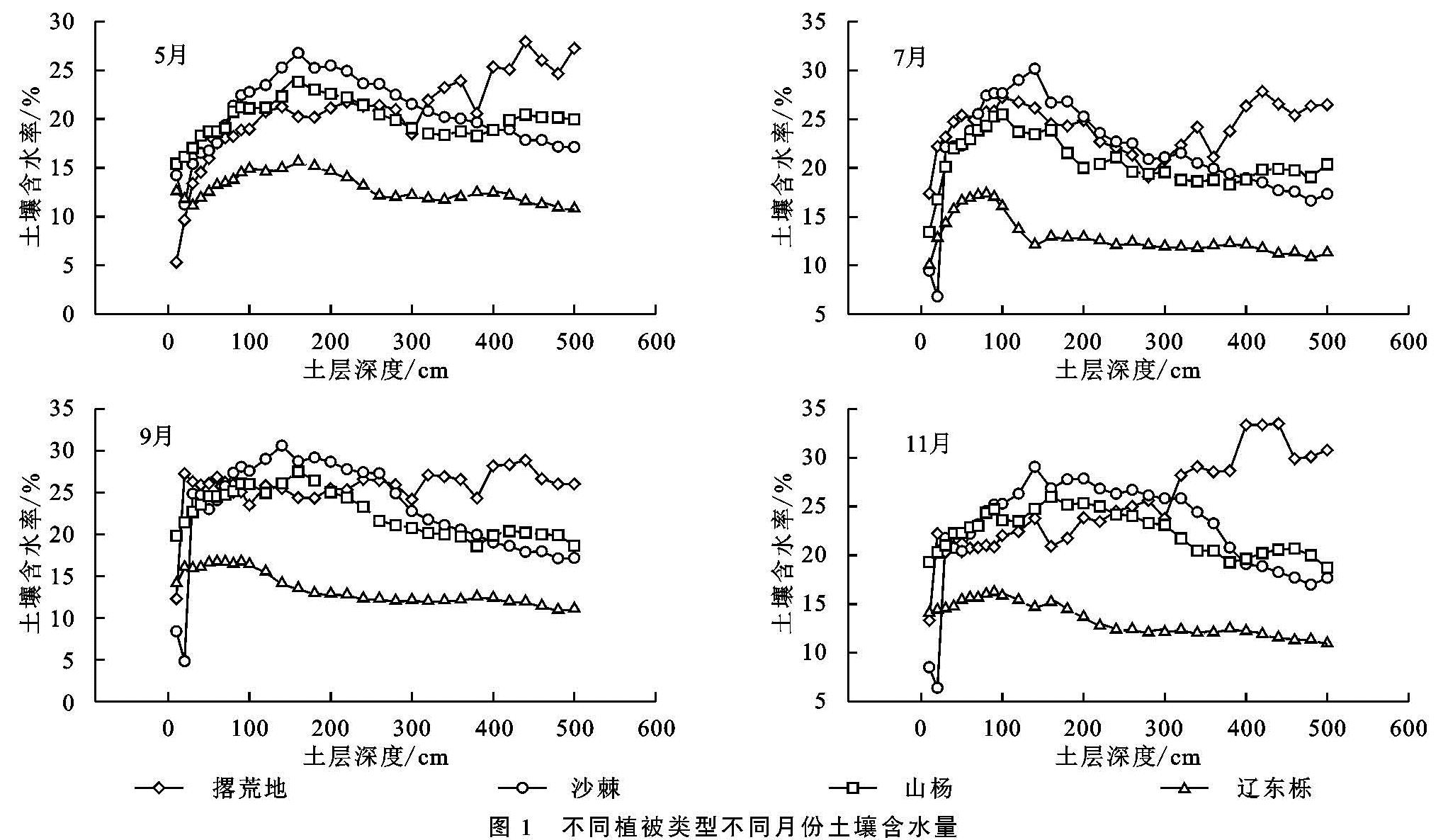
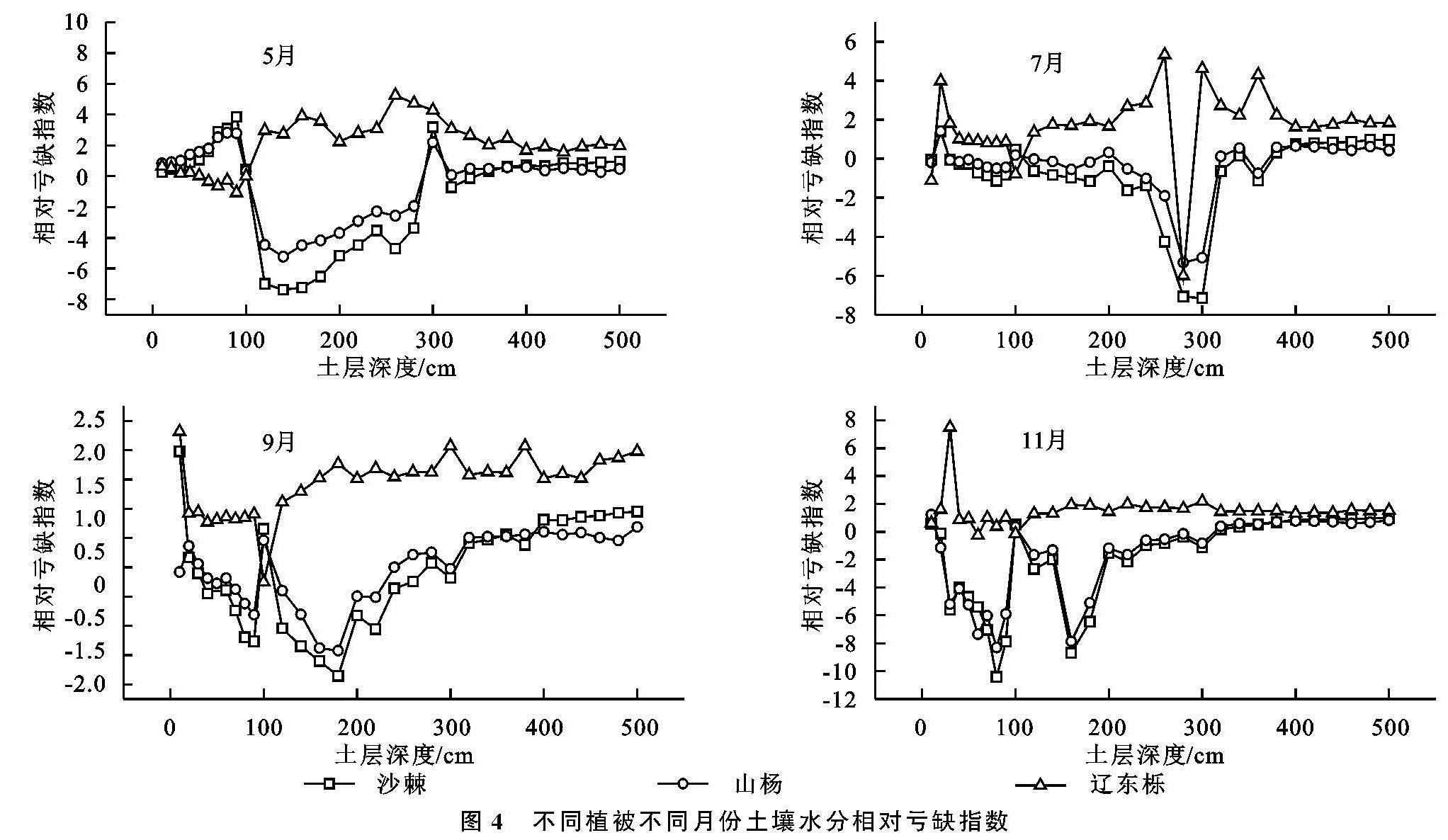
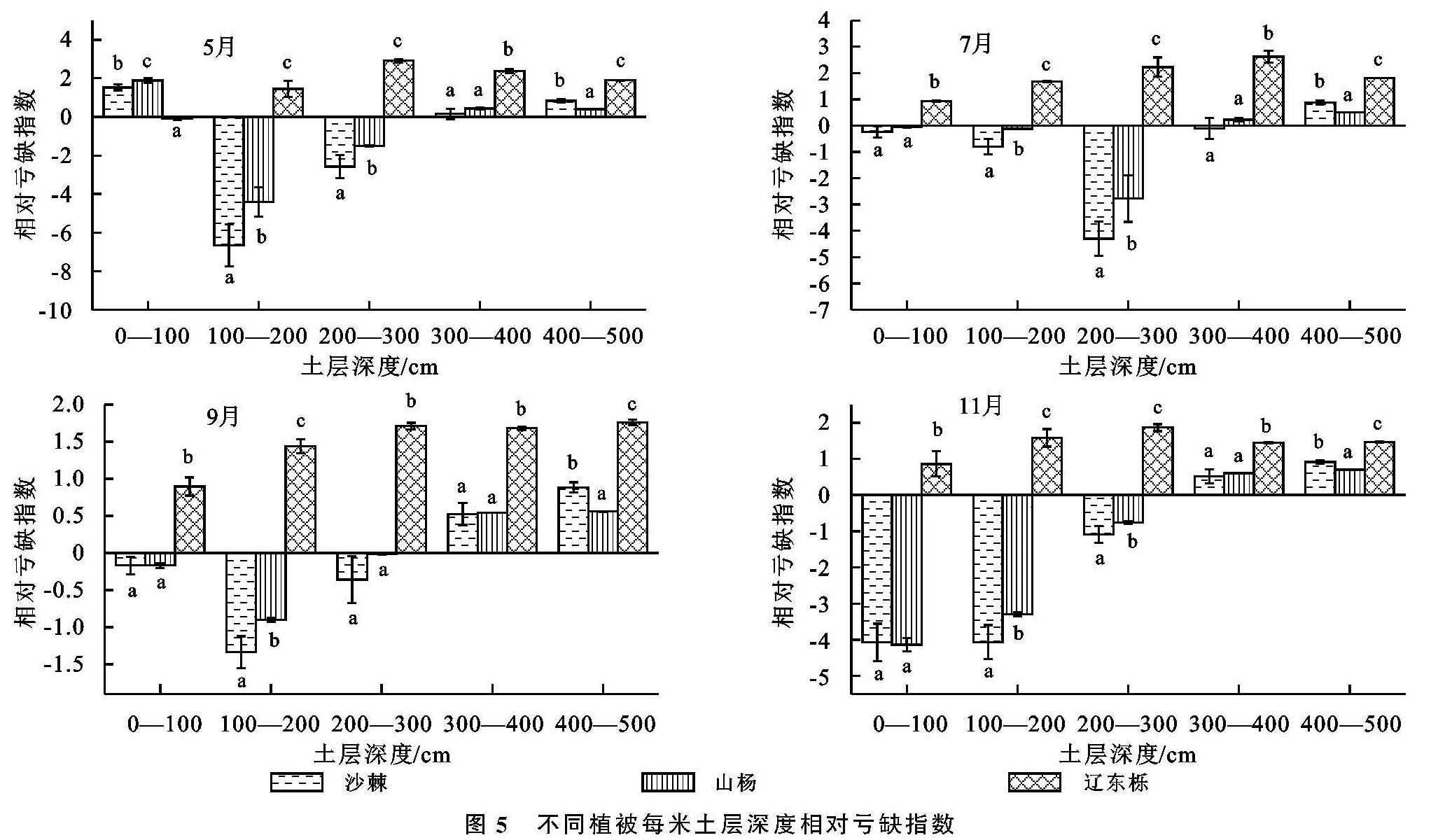
不同植被由于其根系密度和深度的差异导致其消耗土壤水分的深度和强度不同,从而形成了不同植被林下土壤水分的差异[18]。研究中,土壤含水量和土壤储水量随着自然植被恢复从撂荒草地到灌木林地再到乔木林地呈现逐渐下降的趋势,其原因可能是由于随着植被恢复地上部生物量逐渐增大,枝叶更加繁茂,树体的蒸腾能力逐步增强,降水截留增多,树干径流增加,另外,地下部根系逐渐增多,分布增广,对土壤水分的吸收和消耗随之增多,从而引起土壤含水量和储水量的整体下降[19-20]。研究中,不同植被的土壤水分亏缺现象,与撂荒草地相比,处于自然植被恢复顶级群落的辽东栎林的土壤水分相对亏缺显著高于植被恢复中期阶段的沙棘林和山杨林,且各植被的土壤在雨季和非雨季都呈现出深层的亏缺程度较浅层严重,这是由于植被生长与土壤水分是相互作用的,辽东栎林较沙棘和山杨林消耗更多的水分,且降水由于其较强的树冠截留和降水的补给量较少,降水资源对土壤亏缺的缓解能力大大下降,更加不能对深层次的土壤补充水分,从而导致了深层次土壤的亏缺现象的加重,这与郭忠升和程积民等的研究结果[21-22]一致,高宇等认为在黄土高原不同区域,由于植物耗水量高于降水量导致植物消耗大量土壤储水而可能出现土壤水分负平衡现象[18],这也是产生土壤水分亏缺现象的一个重要原因。陈洪松等的研究结果也表明土壤储水量出现负补偿的深度会达到300 cm左右[23],王力等的研究结果表明黄土高原的耗水量大于补充量所造成的亏缺现象是普遍存在的,其土壤特性和气象因子是造成亏缺的决定因素,并不是由生物利用导致的[24]。
3.2 土壤特性对土壤水分特征的影响
土壤水分除了受植被类型的影响外,还受土层深度、颗粒组成、入渗和季节等的影响。Yang等的研究表明,随着植被恢复,土壤含水量显著降低,不同植被下土壤水分在表层差异不显著,在深层却显著不同,且在土壤深层的土壤水分表现一定的时间稳定性[25],这与本研究的结果一致,本研究中,撂荒草地的土壤含水量与储水量呈逐渐上升的趋势,这可能由于随着土层的加深,草地的根系越来越少,对水分的消耗就相应地减少了,而沙棘、山杨和辽东栎林的土壤含水量和储水量呈先升高后下降的趋势,而拐点在150 cm左右的土层深度,这可能是由于在150 cm左右深度的土层中,根系逐步变得密集,并且其入渗深度有限,不能及时地补充到下层土壤中,从而使下层的土壤含水量不断下降,甚至出现干层。另外,本研究中的非雨季的土壤储水量显著低于雨季的土壤储水量,但与撂荒草地相比,灌木林地和乔木林地在雨季的土壤水分亏缺现象比非雨季的明显,表明雨季的降水资源较非雨季增多,较多的降水在一定程度上增加了土壤表层的储水量,缓解了表层的亏缺状况,但是其入渗深度不够,加之雨季虽降水较多,其正值旺盛生长期,耗水量较非雨季要多,所以其深层次的亏缺状况并没有明显改善,在雨季深层次的土壤储水量要低于非雨季。另外,相同土层撂荒草地的土壤含水量要高于灌木林地和乔木林地,这与Yang等的研究结果[26]一致,这可能是由于土壤黏粒含量在撂荒草地中较高,而砂粒在灌木林地和乔木林地中较高,黏粒较砂粒能吸收更多的水分[27],这也是导致灌木林地和乔木林地的土壤水分亏缺高于撂荒草地的另一个原因。因此,植被类型、土壤质地和土层深度是影响植被演替过程中土壤水分亏缺状况的关键因子。