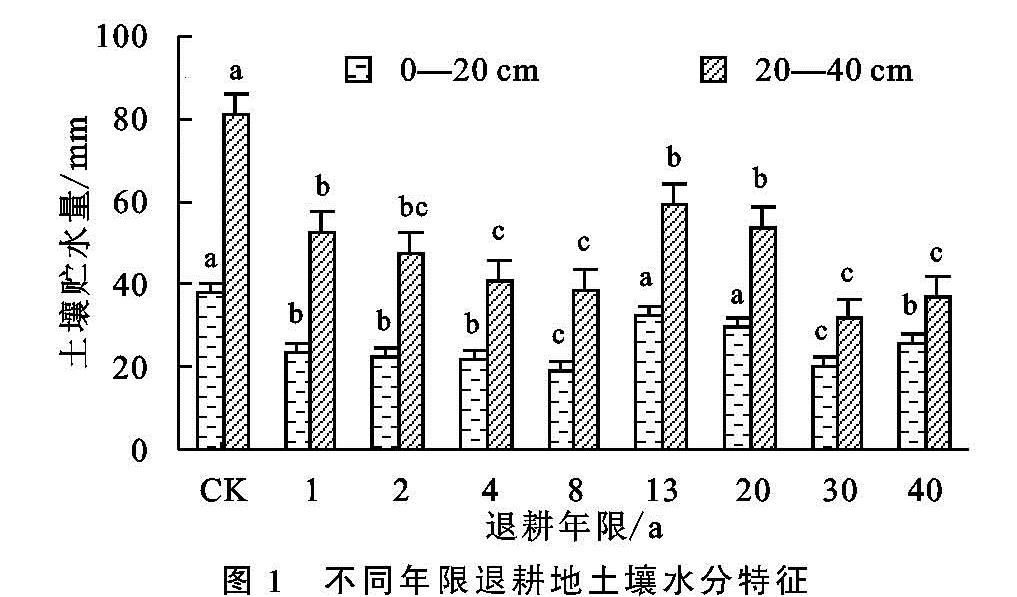
石羊河下游青土湖区,气候干旱,自然条件恶劣,土壤水分是影响植物群落演替与植被恢复的关键因子,因此可以说植被生长与土壤水分之间的关系比其与土壤养分间的关系更为密切[20]。受前期农田耕作活动的影响,CK中0—40 cm土层中土壤贮水量均较大; 退耕1~8 a间,一年生浅根性草本植物对土壤水分的消耗较大,0—20 cm土层贮水量变化较为稳定,但略有随退耕年限增加而减小的趋势,而相比较20—40 cm土层中土壤贮水量减小趋势较为明显,说明农田退耕后,一年生和多年生草本植物逐渐演替为群落内的主要植物种; 退耕13~20 a时,土壤贮水量比退耕1~8 a有一个逐渐增大的过程,主要是由于此阶段植物群落逐渐演替为以黑果枸杞为主的单一群落,降低了对土壤水分的消耗,使其逐渐回升; 而在退耕30~40 a,植物群落发展逐渐稳定,由多年生单一群落逐渐演替为以黑果枸杞和盐爪爪为优势物种的稳定群落,此时土壤水分恢复并逐渐达到稳定状态。
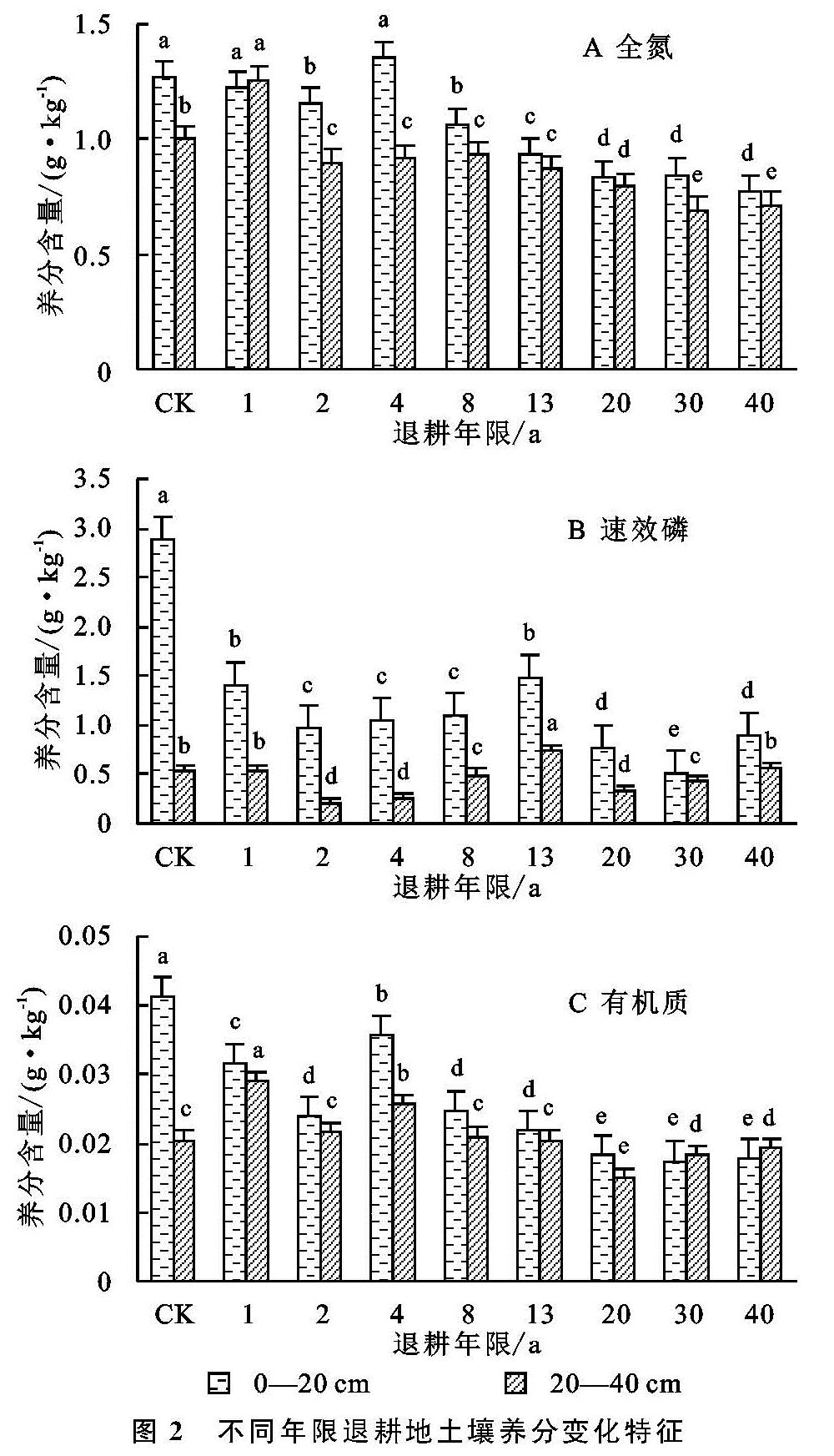
3种土壤养分在土层中的含量总体表现为随退耕时间的延长而呈波动式下降的趋势,其中土壤全氮含量表现出和有机质相同的变化趋势; 前人研究表明,土壤养分中的有机质和氮主要来源于上部植被凋落物的分解及根系分泌物[21],而本文中土壤中全氮含量表现为和有机质相同的变化趋势,也验证了这一结论,说明灌木与草本植被相比,其较深的根系对土壤中N 的消耗量较大,并且随着群落演替的进行,产生大量的枯枝落叶,使归还土壤的有机质不断增加,而土壤中的N元素可以通过有机质来供给,从而出现了上述现象[22]; 土壤磷素是土壤中的矿质营养元素,在无外源施肥条件下,土壤磷含量主要来源于土壤母质及大气沉降,本研究0—20 cm土层速效磷含量受退耕年限影响较大且变化较为剧烈,其含量显著大于20—40 cm,而20—40 cm土层中速效磷含量受退耕年限的影响较小,变化较为平缓,这种现象和杨万勤等[23]研究的关于地表植物对土壤磷素的生物表聚作用有关,而在较深土层中,只有当地上植物非常丰富时,这种现象才比较明显,但在干旱荒漠地区的退耕地上,这种结果很难实现,这可能也是不同年限退耕地中,0—20 cm土层速效磷含量显著大于20—40 cm土层的主要原因。
土壤水分和养分是土壤环境的一部分,对植被恢复具有极其重要的作用,影响着植被恢复的程度和速度,并能协调植物生长的环境条件、营养物质。从青土湖区不同年限退耕地土壤水分和养分的变化分析,两者的变化趋势基本一致,即均表现为随退耕年限的增加而呈波动式降低。这一结论与黄土高原[24]或高寒草地[25]的试验结果随着耕地撂荒年限的增加,土壤养分增加的趋势相反,显示了该地区的特殊性,出现这一现象的主要原因是由于该地区干旱少雨、土壤非常瘠薄,退耕初期,由于之前农业生产中施入的水、肥尚有残余,因此次生草地呈正向发展,但随着退耕年限的延长,残存水、肥逐渐耗减,土壤微生物数量多样性发生了改变,植物残体分解缓慢,土壤质量下降。因此,该区农耕地在退耕4~5 a后,如果不采取任何的农业管理措施,随着退耕年限的延长土壤中养分含量呈现出下降趋势,土壤盐渍化与沙漠化程度会越来越严重[26]。