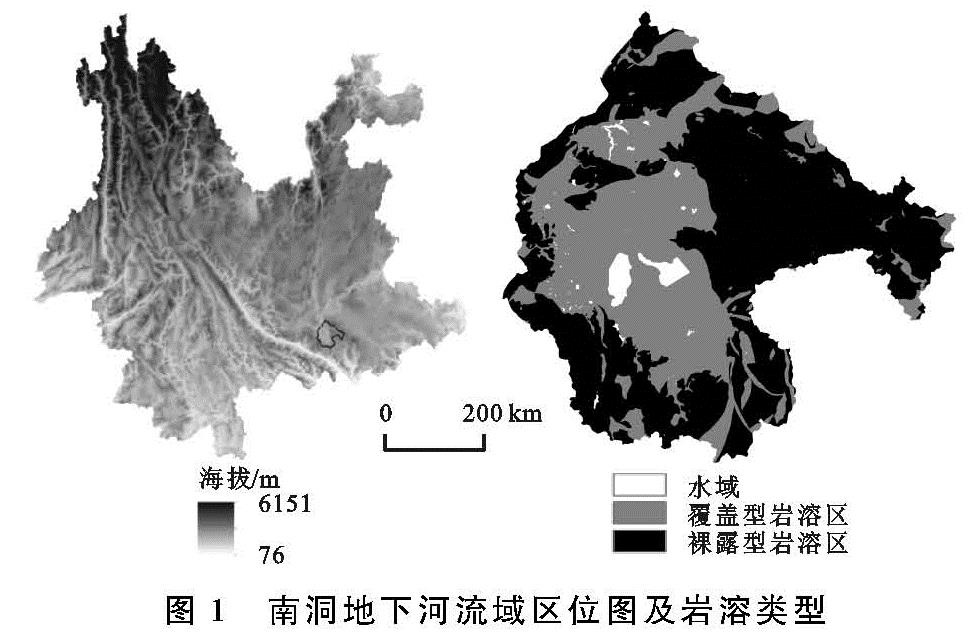
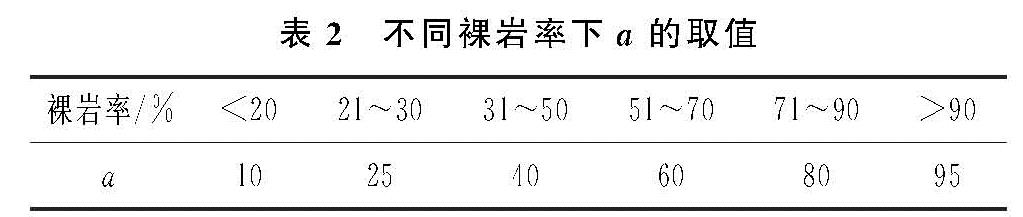
2.2 RUSLE模型
本文采用广泛应用的RUSLE模型计算土壤侵蚀模数及土壤侵蚀量,其表达式如下:
A=R×K×L×S×C×P(1)
式中:A为土壤侵蚀模数; R为降雨侵蚀力因子; K为土壤可蚀性因子; L为坡长因子; S为坡度因子; C为植被覆盖与管理因子; P为水土保持措施因子。
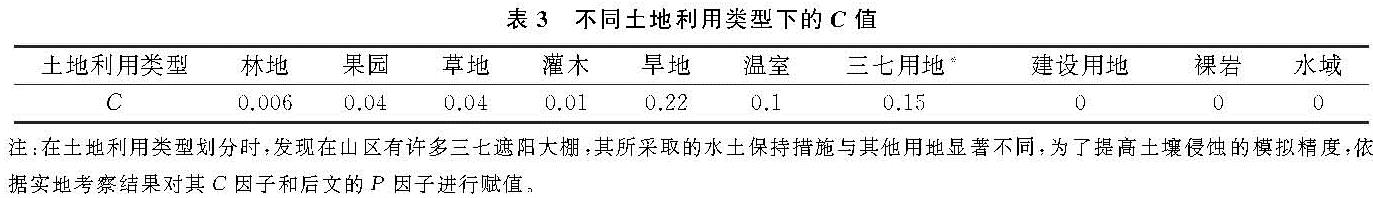
因岩溶区域特殊的地质构造以及石漠化现象的存在,RUSLE模型的传统算法在一定程度上会高估土壤侵蚀量。因此Gao等[21]基于Dai等[12]提出的地表沉积物与裸岩率的关系对RUSLE模型进行了修正,使其适宜于岩溶区土壤侵蚀评价,其修正方法如下:
A=(1-0.0762×a)×R×K×L×S×C×P(2)
式中:a的取值方法见表2。
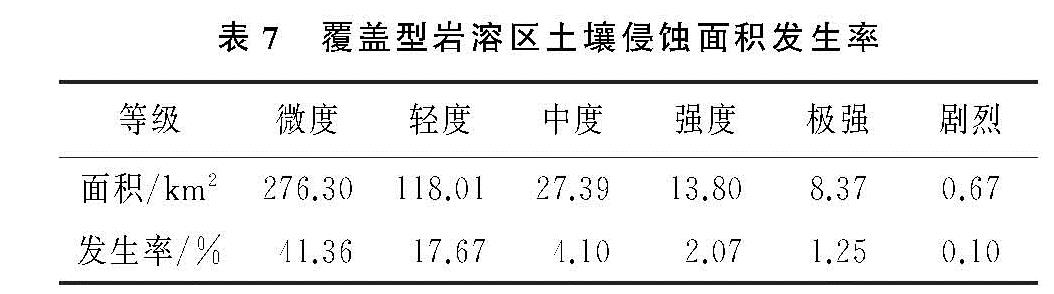
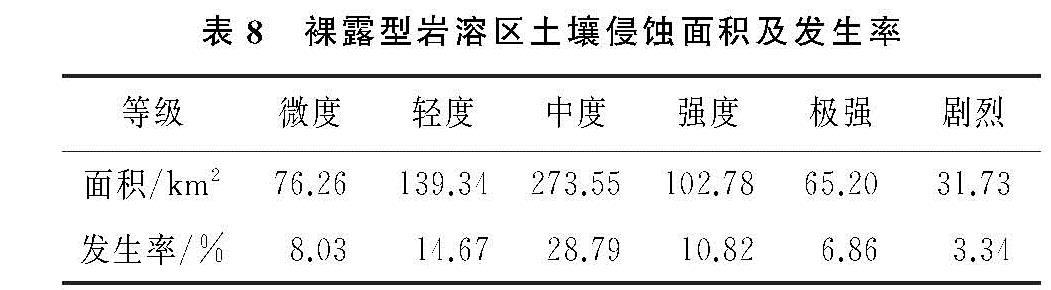
根据研究区实际情况,本研究中覆盖型岩溶区土壤侵蚀模数的计算采用公式(1),裸露型岩溶区土壤侵蚀模数的计算采用公式(2)。
(1)降雨侵蚀力因子。降雨侵蚀力是指降雨引起土壤侵蚀的潜在能力[22]。降雨侵蚀力的计算一般采用经典算法EI30,但是该算法需要大量的自记降雨资料,一般难以获取。因此许多学者提出了降雨侵蚀力的简易算法。胡续礼等[23]的研究表明CREAMS模型计算降雨侵蚀力具有较高的精度。
R=1.03×Pi1.51(Pi>P0)(3)
式中:Pi为日降水量; P0为侵蚀性降水量阈值。根据杨子生在滇东北的研究,区域内侵蚀性降雨的基本雨量标准为9.2 mm[21]。
(2)土壤可蚀性因子。土壤可蚀性因子是指土壤抵抗流水冲刷和侵蚀的能力。对于K值的计算比较成熟的有Wischmeier提出的田间实测法和诺谟图法以及EPIC模型,但是由于田间实测法要耗费大量的人力,财力,许多学者通过研究证明了诺谟图法不适合中国土壤可蚀性因子的计算[24]。因此本研究K值的计算选择Williams提出的EPIC模型[25],其计算公式如下:
K=0.1317{0.2+0.3exp[-0.0256SAN(1-(SIL)/(100))]}×
((SIL)/(CLA+SLA))0.3×[1-(0.25C)/(C+exp(3.72-2.95C))]×
[1-(0.7SN)/(SN+exp(22.9SN-5.51))](4)
式中:SAN为砂粒含量百分比; SIL为粉砂含量百分比; CLA为黏粒含量百分比; C为有机质含量百分比,SN=1-SAN/100。
(3)坡度坡长因子。地形对于土壤侵蚀具有较大的影响,地形平坦能够降低重力势能,进而减小土壤侵蚀发生的可能性,相反地形高差大则会增加重力势能,在一定程度上就会增加土壤侵蚀风险。利用研究区30 m分辨率的DEM数据采用刘斌涛[26]提出的西南土石山区坡度因子的修正算法以及张宏鸣研发的LS-TOOL进行坡度S和坡长L因子的计算,其计算方法如下
LS=L×S(5)
L=(λ/22.13)α(6)
α=β/(β+1)(7)
β=sinθ/[3sinθ0.8+0.56](8)
S={10.8sinθ+0.03
16.8sinθ-0.50
20.204sinθ-1.2404
29.582sinθ-5.607(θ≤5°)
(5°<θ≤10°)
(10°<θ≤25°)
(θ>25°)
(9)
式中:θ为坡度; λ为坡长,α为坡长因子指数。
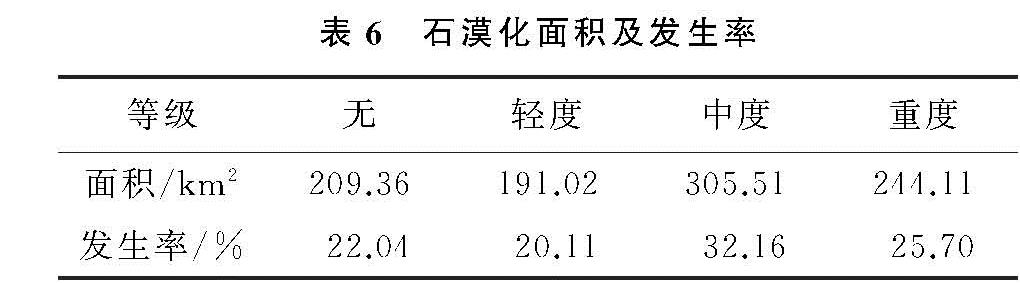
(4)植被覆盖与管理因子。植被覆盖与管理因子是土壤侵蚀的抑制性因子,充足的植被覆盖与良好的管理措施有助于减缓土壤侵蚀速率,减少土壤侵蚀量。目前对于C值的计算还未有统一方法,参照蔡崇法[27]、许月卿[28]等人的研究结合研究区的实际情况进行C因子赋值,赋值方法见表3。
(5)水土保持措施因子。水土保持措施因子是指采取专门措施后的土壤流失量与顺坡种植时的土壤流失量的比值,其值在0~1之间,0表明不发生水土流失,1表示未采取任何水土保持措施[29]。P因子一般是根据土地利用类型进行赋值,根据许月卿[28]、杨子生[30]等的研究以及野外观测P值赋值方法见表4。
2.3 石漠化遥感解译
从地理空间数据云获取Landsat 8数据,在ENVI 5.3中经过辐射定标、大气校正等处理后,计算南洞地下河流域归一化植被指数(NDVI),计算方法如下:
NDVI=(NIR-R)/(NIR+R)(10)
式中:NIR为近红外波段; R为红波波段。
在地质图的辅助下,对南洞地下河流域岩溶区NDVI图层进行裁剪以计算裸岩率。采用像元二分法模型,在置信度为5%,95%区间内,计算植被覆盖度(FVC),公式如下:
FVC=(NDVI-NDVImin)/(NDVImax-NDVImin)(11)
式中:NDVImin为NDVI最小值; NDVImax为NDVI最大值。
根据裸岩率与植被覆盖度的关系计算得到南洞地下河流域岩溶区裸岩率。
裸岩率=1-FVC(12)
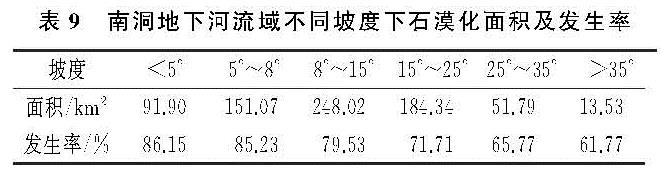
参照《DD2004—02区域环境地质调查总则》,以及有关石漠化遥感解译分级标准(表5)[31-32],根据裸岩率进行石漠化等级划分。
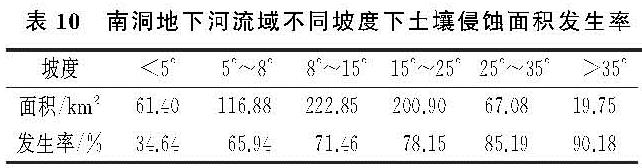
将以上有关土壤侵蚀的6个因子图层及裸岩率分布图统一至30 m分辨率进行土壤侵蚀和石漠化强度分析。