资助项目:国家自然科学基金(51878613); 浙江省自然科学基金(LY16E080011); 教育部人文社科规划项目(17YJAZH136)
第一作者:朱晓青(1979—),男,安徽合肥人,教授,硕士生导师,主要从事资源环境科学与生态安全研究。E-mail:Arc_zxq@163.com 通信作者:黄志豪(1995—),男,浙江台州人,硕士研究生,研究方向为资源环境科学与生态安全。E-mail:hzhzujt@163.com
(1.浙江工业大学 城乡发展与人居环境研究中心, 杭州 310014; 2.北九州大学 国际环境工学部, 日本 北九州 808-0135)
(1.Urban-Rural Development and Habitation Environment Research Center, Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou 310014, China; 2.Faculty of International Environmental Engineering, University of Kitakyushu, Kitakyushu 808—0135, Japan)
resource-based city; land development intensity; ecological bearing capacity; coupling coordination; driving factors; Maanshan City
为了厘清资源型城市开发强度与生态承载力的协同发展关系及交互作用机理,选取马鞍山市为典型实证案例,通过构建国土开发强度与生态承载力综合评价指标体系,借助耦合协调度模型、探索性空间数据分析方法和地理加权回归模型,揭示了资源型城市国土开发强度与生态承载力耦合发展的时空特征及其驱动要素。结果 表明:(1)2008—2018年样本区域国土开发强度由0.215 6快速上升至0.538 6,空间异质特征逐步显现,生态承载力由0.420 2平稳上升至0.489 5,空间差异不大且基本保持稳定;(2)国土开发强度与生态承载力耦合协调度保持连续上升的趋势,由中度失调阶段逐步向低度协调阶段转变,整体呈现中部高两侧低的分布格局,且空间集聚态势愈加显著,冷热点区分布较为稳定;(3)国土开发强度与生态承载力耦合协调发展的驱动要素时空差异明显,主次顺序依次为产业转型、经济发展、政府调控、资源集聚。基于上述解读,提出了促进国土开发强度与生态承载力协调发展的对策建议。
In order to clarify the collaborative development relationship and interaction mechanism between resource-based city development intensity and ecological bearing capacity, the spatiotemporal characteristics and driving factors of coupling development intensity and ecological bearing capacity of resource-based cities were revealed by constructing a comprehensive evaluation index system of land development intensity and ecological bearing capacity, and by means of coupling coordination degree model, exploratory spatial data analysis method and geographic weighted regression model. Maanshan City was selected as a typical case study. The results show that:(1)from 2008 to 2018, the intensity of territorial development in the sample area increased rapidly from 0.215 6 to 0.538 6, and the spatial heterogeneity gradually emerged; the ecological bearing capacity increased steadily from 0.420 2 to 0.489 5, with little spatial difference and basic stability;(2)the coupling between territorial development intensity and ecological bearing capacity coordination degree kept a continuous upward trend, and gradually changed from moderate imbalance stage to low coordination stage, showing the overall distribution pattern of high and low sides in the middle; the spatial agglomeration trend was more significant, the distribution of cold and hot spots was more stable;(3)spatial and temporal differences of driving factors for coordinated development of land development intensity and ecological bearing capacity were obvious, the driving role decreased in the order: industrial transformation>economic development>government regulation>resource agglomeration. Based on the above interpretation, some countermeasures and suggestions are put forward to promote the coordinated development of land development intensity and ecological bearing capacity.
在快速工业化和城镇化的背景下,资源型城市国土空间开发与生态环境保护的不协调、不可持续性矛盾日益凸显,长期粗放式的发展模式亟需结构性、根本性的革新[1-2]。
在资源型城市长期演化进程中,由于其主导产业强烈的资源依赖性以及生产过程的特殊性,国土空间开发多呈现“点密、线长、面广”的分散式格局,造成土地资源大面积浪费、生态环境无底线破坏等严峻问题。针对新常态下供给侧结构性改革与全域生态文明建设,探讨并揭示资源型城市国土开发强度与生态承载力的耦合协调关系,寻找切实可行的导控路径是推进资源型城市可持续发展的关键所在。
关于国土开发强度与生态承载力耦合协调发展的相关研究,国外研究侧重于两者相互作用形式及内在联系机制探讨,Beardsley等[3]通过研究认为,城市空间扩展首先对土地、生物资源产生影响,紧凑增长情景下对生态环境负面作用最小; Hasse等[4]认为分散而低效的城市空间开发将会造成基本农田流失、天然湿地丧失以及自然森林环境破坏等现象,且当资源环境受到的胁迫程度达到“质”的突变时,开发建设活动必将受到生态环境的强烈约束。当前,国内主要关注国土空间开发与生态环境保护的耦合响应关系与优化调控策略。刘艳军等[5]通过定量分析近15 a间中国区域开发强度与资源环境水平的耦合协调关系,发现两者耦合协调发展程度不断提高,其中国土开发效率提升是最主要驱动力; 李强等[6]采用差分广义矩估计方法研究城市蔓延影响环境污染的内在机理及其效应,判定我国正处于环境库兹涅茨(EKC)倒“U”形曲线的左侧,经济的快速发展仍将加剧环境污染,制定差异化的区域城镇化和生态文明建设策略是现阶段最主要任务; 赵亚莉等[7]从资源消耗、污染物排放和生态系统价值3方面构建生态环境效应的指标体系,对我国省会城市国土开发强度变化的生态环境效应进行评价,阐释了城市开发强度较低时就需预见生态环境保护的必要性。总体而言,当下相关研究多聚焦于全国[8]、省域[9-10]、城市群[11-14]等大中空间尺度,较少涉及镇域等小尺度格局; 多注重以量化的方式探究两者耦合发展的时空分异特征,忽视了耦合分异格局产生的内在逻辑与机理; 多集中于城际间或区域间两者耦合度的差异性研究,而缺乏对城市内部两者耦合分异机制的剖析与探讨。
本文研究区域为马鞍山市域(东经117°53'—118°52',北纬31°24'—32°02'),位于安徽省东部、苏皖交汇地区,横跨长江,现辖3区3县,国土总面积4 049 km2。1956年,马鞍山于随“马钢”的兴建而设市,经过半个多世纪的蜕变,逐步发展成为以冶炼、电力、化工、建材为主导产业的典型矿产资源型城市。2018年,全市户籍总人口229.11万人,城镇化率49.86%,地区生产总值达到1 918.10亿元,三产比重为4.5:53.6:41.9,其中矿业经济增加值仍占工业增加值的44%,可见第二产业仍为支柱产业,矿业经济的带动力依旧强劲。“十三五”以来,一带一路、长江经济带、皖江城市带承接产业转移示范区等一系列区域战略政策的叠合效用逐渐显现,马鞍山市作为《全国主体功能区规划(2010年)》“两横三纵”城市化战略格局中的重点开发地区以及合肥、南京都市圈的核心层城市,如何协调“开发”与“保护”的关系成为重中之重。因此,本文以马鞍山市各镇域为研究单位(包括建制镇、街道、主城区),以2008—2018年为研究时段,运用耦合协调度模型,结合ESDA和GWR等空间分析方法,揭示其国土开发强度与生态承载力耦合协调发展的总体态势、空间格局及驱动要素,旨在为此类城市开发建设与生态保护战略决策提供意见参考。
本研究从国土开发强度与生态承载力两方面选取指标,依据樊杰著作《资源环境承载能力和国土空间开发适宜性评价方法指南》中的技术规程及林坚[15]、叶菁[16]与金悦[17]等相关研究成果进行初步指标统计与筛选。由于资源型城市的发展过程通常伴随着大规模、高强度的资源开发,其生态系统面临巨大挑战,为准确反映资源型城市国土开发强度与生态承载力协同发展的特有内涵和运行机制,应适当调整国土开发强度核算仅侧重于土地扩张程度,而忽视转型期过程中人口集聚与经济发展水平,并在强调生态系统整体支撑水平与调节能力的同时,更需关注工矿产资源开采、冶炼、利用所带来生态压力的变化。本文结合马鞍山市经济发展阶段、内部资源禀赋以及公共基础设施等实态特征,通过资源型城市的建设规模、承载容量、经济效益等相应指标衡量国土开发强度,并以污染物排放量、人均资源拥有量及除污能力等指标对生态承载力进行测度,进而构建综合评价指标体系(表1)。
本文的基础数据主要包括2008—2018年马鞍山市36个镇域单元的土地利用数据、资源环境现状数据、统计年鉴与历史文献资料。其中,土地利用数据来源于市自然资源局提供的历年土地调查数据; 环境数据(大气环境、水环境等方面的指标数据)来自历年环境状况公报以及市环保局提供的污染物排放数据; 经济社会数据根据近10 a统计年鉴及所辖县(区)的统计资料得出。针对马鞍山市多次行政区划调整问题,本文以2018年最新行政区划结果对原始数据进行归并整合,确保各数据间的准确性与可比性。所用矢量数据来源于地理国情普查平台。部分缺失数据采用相邻年份插值法补齐。
为消除不同指标量纲与量级带来的影响,采用极值法[18]对数据进行标准化处理,使各项指标的标准化值为[0,1],计算公式为:
正向指标:X'i=Xi/Xmax(1)
负向指标:X'i=Xmin/Xi(2)
式中:Xmax为第i项指标的最大值; Xmin为第i项指标的最小值。
评价指标权重采用熵值法[18]计算得出,并运用线性加权法计算样本各区域国土开发强度与生态承载力的综合指数,方法如下:
LD=∑ni=1LD'iωi, ∑ni=1ωi=1(3)
式中:LD为国土开发强度的综合评价指数; LD'i为标准化后的指标值; ωi为熵值法所得权重。
EC=∑ni=1EC'iλi, ∑ni=1λi=1(4)
式中:EC为生态承载力的综合评价指数; EC'i为标准化后的指标值; λi为熵值法所得权重。
“耦合”通常解释为多系统或多要素之间通过交互作用进而彼此影响乃至联合协调的现象[19]。本文引入耦合协调度模型来揭示国土开发强度与生态承载力的耦合协调关系,其优势在于,一方面能够综合测度两系统间相互作用的强弱程度,另一方面能准确反映系统间和谐一致、良性配合的关系,表达式如下:
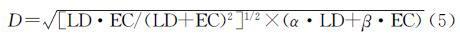
式中:D为国土开发强度与生态承载力的耦合协调度; α,β为待定参数,反映两系统的相对重要程度,鉴于国土空间开发与生态环境保护同等重要,且设定α=β=0.5[20-21]。通常情况下,根据耦合协调度D大小划分为6大类[22-23](表2)。
本文采用探索性空间数据分析(ESDA)[24]中的全局Moran's I指数和局部Getis-Ord G*i指数探测耦合协调度分布的空间关联特征,前者用于检验空间邻接或临近研究单元属性值的相似程度,后者用于分析局部地区高值或低值聚集状态,计算公式分别为:
Moran's I=n∑i∑jWij(xi-x^-)(xj-x^-)/∑i∑jWij(xi-x^-)2(6)
Getis-Ord G*i=∑j(Wij·xj)()∑jxj(7)
式中:n是研究单元数; xi,xj为研究区域i和j的属性值; X^-是为研究样本属性的平均值; Wij为空间权重矩阵。其中Moran's I指数一般介于[-1,1]; I>0说明耦合协调度在区域内分布存在空间正相关性,表现为高—高集聚或者低—低集聚; I=0意味着空间不相关,表现为随机分布。I<0表明空间负相关性,表现为高—低集聚或者低—高集聚。Getis-Ord G*i指数若为正数,说明该地域属于高值空间集聚(热点区型); 反之则为低值空间集聚(冷点区型)。
为探寻不同影响因子在不同地理位置的空间分异特征及规律,本文引入地理加权回归模型(GWR),该方法是在最小二乘法(OLS)模型基础上改进,将数据的空间属性融入模型计算中,以便更好地刻画局部参数空间位置分布及演化特征,其模型[25]如下:
Yi=α0(Ui,Vi)+∑jαk(Ui,Vi)xik+εi(8)
式中:Yi为观测值;(Ui,Vi)是i点地理坐标; α0(Ui,Vi)为常数项; αk(Ui,Vi)为i点第k个解释变量的回归系数; xik为i点第k个解释变量; εi为残差项。
采用综合评价指数模型,以2008年、2013年、2018年为典型时间节点,结合标准化处理后的数据,绘制样本城市国土开发强度与生态承载力的综合评价指数图(图1)。
国土开发强度呈现快速的上升趋势且空间异质性愈加凸显。从整体演变趋势看,3个年份各镇域国土开强度均值分别为0.215 6,0.431 9,0.538 6,年均增长率达到14.98%,10 a间大规模、高强度的重工业发展带动产业配套设施用地需求不断增加,导致城市人口与产业集聚效应加强、建设用地规模迅速扩张。从区域内部看,3个年份各镇域国土开发强度指数的标准差依次为0.078 4,0.107 4,0.121 4,空间异质特征逐步显现。高值区包括博望、姑孰与太白等“经济重镇”,主要分布于长江(马鞍山段)两岸及中部城镇发展轴,恰与城市“十字廊架”发展结构相契合,该区域依托于得天独厚的区位、政策优势,人口与产业集聚态势持续增强,城镇建成区面积迅速拓展。相较之下,湖阳镇、大陇乡3个年份国土空间开发强度均值仅达到0.229 2,这与其经济基础薄弱、矿产资源不足、地形地貌限制等密切相关。
生态承载力呈现平稳的上升趋势且空间差异不明显。从总体发展特征看,3个年份各镇域生态环境承载指数均值分别为0.420 2,0.460 9,0.489 5,年均增长率仅为1.65%。由此可见,资源型城市生态环境水平的提升更趋于循序渐进的过程,并且治污减霾、生态修复等活动缺乏足够重视,导致生态承载指数增长缓慢,甚至部分镇域存在波动。从空间属性看,3个年份各镇域生态环境承载指数的标准差数值为0.089 4,0.090 4,0.089 7,可见空间差异不大且基本保持稳定,呈现以长江(马鞍山段)为界,西部略高于东部的空间分布特征。究其原因:江东片区作为承接南部产业转移的主战场,忽视资源环境容量问题,缺乏长远科学规划,造成生态压力较大; 江西片区大部分镇域属于省级主体功能区划层面下的限制开发区[26],资源环境支撑力相对较高,但生态系统调节力稍显不足。
国土开发强度与生态承载力耦合协调水平是资源型城市转型的重要标志,根据耦合协调度模型,计算得到2008—2018年马鞍山市各镇域国土开发强度与生态承载力耦合协调度均值及其协调发展类型(表3)。10 a间耦合协调度均值由0.383 2增至0.502 4,保持连续上升的趋势,由2008年的中度失调阶段逐步过渡至2018年的低度协调阶段。随着资源型城市更新迭代的步伐加快,国土开发强度与生态承载力呈现愈加紧密的协调发展态势。依据耦合协调度所处水平可将其大致分为3个阶段:(1)2008—2009年处于(0.3,0.4]的中度失调阶段,国土开发与生态环境接近无序发展,且二者自身综合发展水平较低,导致耦合协调性差。(2)2010—2015年,二者耦合协调度有所提高,上升至(0.4,0.5]的轻度失调阶段,该阶段马鞍山市注重整体产业经济的快速发展,国土开发强度持续上升,以主体功能区控制、新型城镇引入与经济社会品质要求等新时代理念引领高质量国土空间开发的趋势愈加显著,两系统的互动结构也不断趋于合理,二者耦合协调性取得明显成效。(3)2016—2018年逐渐步入(0.5,0.6]的低度协调阶段,随着矿产资源产业转型步伐加快,生态绩效考核落到实处,在长江经济带建设机遇下,“因钢立市”到“以港兴城”的战略转移以及长江(马鞍山段)“1515”基准线的划定,使得国土开发规模扩张减缓,集约利用程度增加,国土开发与环境保护的协同之势增强。
通过对两者耦合协调类型发展态势的基本研判,为更好地解析耦合协调度的动态演化进程及内在联系,结合表3数据,进行可视化处理。根据图2曲线可知,耦合协调度呈现迅猛增长阶段Ⅰ(2008—2014年)与稳步增长阶段Ⅱ(2015—2018年)“两段式”演化路径。第Ⅰ阶段,耦合协调度快速增长,年均增长率达到4.89%。马鞍山市依托自身资源禀赋以政策优势,着重发展以资源能源为核心的城市产经体系,借助土地扩张、人口集聚与产业带动,实现国土开发强度的快速提升,然而资源配置效率低下、生态环境持续恶化等隐患随之而来。第Ⅱ阶段耦合协调度稳步增长,保持良好的上升态势,年均增长率为0.34%。该趋势显现出样本城市由传统高能耗、高污染的工矿资源型城市逐步向绿色生态、智慧共享的可再生型城市转变,国土空间更加注重系统化、精细化开发,环保治污力度空前,两者自身综合水平也在日益提升,协同效应愈趋良好。这与“十三五”以来,“五大发展理念”提出、国家供给侧结构性改革与生态文明体系推行等新时代可持续发展观密切相关。
为进一步细化国土开发强度与生态承载力的空间耦合特征,采用3个时间节点各镇域的耦合协调度数据,绘制耦合协调类型的空间梯度演化图(图3)。整体上看,马鞍山市国土开发强度与生态承载力的耦合协调水平呈现出中部高两侧低的空间分布梯度,具体类型分为:(1)中度协调型。全市仅有主城区达到中度协调状态,凭借区位、政策的相对优势,更易吸纳社会投资,扩大城市土地规模,提高经济、社会发展效益,且作为全市产业转型升级的龙头地区,环境保护工作已进入实质性实施阶段。(2)低度协调型。由长江(马鞍山段)沿岸向中部重点城镇发展轴上延展,3个年份镇域数量占比分别为2.78%,19.44%,47.22%,且大多由轻度失调类型演化而来,预示着整体朝着良性方向发展。(3)轻度失调型。2008年、2013年、2018年分别有11个、26个、18个镇域,主要分布于含山县、和县以及当涂县南部镇域,该地区未来主导战略的精准定位是资源型城市破解当前困境的关键所在。(4)中度失调型。2008年镇域数量较多,主要以鸡笼山保护区及石臼湖湿地为核心向周边扩散,至2013年,仅有石杨镇、年陡镇与善厚镇,地域生态敏感性较强、城镇空间难扩张等是限制两者协同发展的重要原因。
为揭示样本区域国土开发强度与生态承载力耦合协调水平的空间集聚特征,通过测算全局Moran's I指数,衡量两者耦合协调水平的空间自相关程度(表4)。结果显示,3个年份的Moran's I值均为正值,且均通过显著性检验,表明马鞍山市国土开发强度与生态承载力的耦合协调水平具有显著的空间正相关性。2008—2013年,Moran's I指数基本保持稳定; 2013—2018年,Moran's I指数轻微上浮,耦合协调水平的空间自相关性不断增强,数值较高地区与较低地区的空间集聚态势愈加显著。
基于全局空间自相关分析结果,为更有效地揭示局部冷热点区域空间的演化情况,计算2008年、2013年、2018年耦合协调水平的局部Getis-Ord Gi*指数,并通过Jenks自然断裂点法将G*iz-score指数划分为4种类型,分别为冷点区、次冷点区、次热点区和热点区(图4)。从整体上观察,2008—2013年冷热点空间布局变化显著,以次冷点区向次热点区跃迁为主要演变方式,2013—2018年则保持相对稳定。具体来看,冷点区空间分布相对集中,主要位于马鞍山市东南部,数量上经历了先减后增的变化趋势; 次冷点区范围逐步缩小,主要分布集中于含山县下辖乡镇; 次热点区数量持续增大,2013年基本形成以主城区为中心辐射姑孰镇、历阳镇等次热点区的空间圈层分布格局; 热点区始终保持稳定,主要以市辖区范围为界(博望镇除外),空间集聚态势显著。
国土开发强度与生态承载力耦合协调发展受到资源环境、社会经济及宏观政策等多重因素综合影响[10],尤其是资源型城市的工业经济发展水平、转型结构及其演化周期对土地综合开发利用与生态环境保护的影响更为深入,进而选取人均GDP、城乡居民可支配收入、人口密度、常住人口城镇化率、第三产业增加值占GDP比重、地均规模以上工业总产值、地均固定资产投入、地均财政支出8项指标作为解释变量。同时为避免各指标间的多重共线性对拟合结果产生影响,运用SPSS的描述性统计功能将预选指标进行标准差标准化处理,并利用回归分析方法对标准化后的指标变量进行共线性检验,剔除方差膨胀因子大于10的指标选项,保留人均GDP、人口密度、第三产业增加值占GDP比重及地均财政支出4项指标分别表征经济发展阶段EDS、资源集聚程度DRA、产业结构水平ISL、政府调控能力GRA。
基于ArcGIS 10.2地理加权回归模块中“Adaptive”核函数类型及AICc带宽方法,构建马鞍山市国土开发强度与生态承载力耦合发展驱动要素GWR模型,模型结构为:
Yi=α0(Ui,Vi)+α1(Ui,Vi)EDSi+α2(Ui,Vi)DRAi+α3(Ui,Vi)ISLi+α4(Ui,Vi)GRAi+εi(9)
式中:Yi为第i个地域空间的国土开发强度与生态承载力耦合协调度;(Ui,Vi)是第i个地域空间单元的地理坐标; α1(Ui,Vi)为经济发展阶段回归系数; α2(Ui,Vi)为资源集聚程度回归系数; α3(Ui,Vi)为产业结构水平回归系数; α4(Ui,Vi)为政府调控能力回归系数。
通过计算得出GWR模型检验结果(表5),3个年份的拟合系数R2分别为0.779 6,0.680 4,0.719 8,调整后的拟合系数R2分别为0.696 9,0.579 7,0.625 0,说明GWR模型能够较好地拟合各要素对两者协调发展的驱动程度。
通过计算整合样本区域2008年、2013年、2018年各驱动要素的平均回归系数(表6),可知各要素对国土开发强度与生态承载力耦合协调发展的驱动程度存在一定差异。全域驱动作用由大到小依次为:产业转型>经济发展>政府调控>资源集聚,平均值分别为0.742 4,0.601 2,0.567 7,0.532 2。从时序演变上看,产业转型因子3个年份均是驱动两者协调发展的首要因素,2008年资源集聚与政府调控发挥了重要作用; 而2013年与2018年主要受产业结构及经济水平等要素影响。由此可见,马鞍山市长期倚靠的不可持续、不可复制的资源开发模式难以为继,新型工业化、城镇化内涵下的结构调整、产业转型势在必行。在大力追求经济效益的同时,更注重生态、环境效应,尤其是提高生态经济比例。而具体到各基层实操层面,缺乏精细化、具体化的指标导控机制,上级行政命令难以得到有效贯彻等问题逐步显现。
结合回归系数的可视化结果(图5),分析各要素驱动作用空间分异性的演化趋势:
(1)经济发展阶段(图5A—C)。2008年、2013年经济发展的回归系数高值区集中分布于马鞍山市辖区,具有显著的空间集聚特征,低值主要分布于含山县南部; 2018年经济发展的回归系数呈现西低东高的分布格局,高值区为博望区及当涂东南部镇域。由此可见,马鞍山市域内经济发达地区更加注重国土空间有序开发及生态环境综合治理,经济水平的提升对两者耦合发展具有较强驱动力,而欠发达地区由于自身经济基础薄弱,对生态资源保护的关注度较低,经济带动两者耦合发展的驱动作用不明显。
(2)资源集聚程度(图5D—F)。2008年资源集聚的回归系数呈现中部高而东西两侧低的“凸”字型格局,和县北部地区(石杨、善厚、香泉3镇)尤为突出; 2013年和2018年资源集聚的驱动作用较强的镇域主要集中于鸡笼—褒禅山生态功能区。根据上述观察,全市生态保护重点区域国土开发强度与生态承载力耦合协调度整体较低,人力、基础设施等资源分布相对欠缺,对资源集聚要素敏感性强,当地政府应结合当地实际,因地制宜得颁布相应的人口、产业政策。
(3)产业结构水平(图5G—I)。3个年份产业结构回归系数的空间分布变动较大,2008年系数较大区域为姥桥、白桥及含山县中部镇域(包括环峰、清溪两镇),而花山、雨山、博望3区系数均较小; 2013年高值区域则在市域东南部的黄池镇及周围地区; 2018年呈现出以主城区为高值核心,向东西两侧逐步降低的分布格局。“十二五”期间,花山、雨山区等部分地区通过产业能级提升,引领绿色革命,摒弃过去高能耗、高排放的粗放型产业经济发展路径,走新型低能耗、低排放的节约型城市发展模式,进而提高国土空间开发效率,降低资源环境约束强度,实现国土开发与生态环境可持续协同发展。
(4)政府调控能力(图5J—L)。2008年高值主要分布于长江(马鞍山段)以南及含山北部地区,低值区则位于和县各镇域,呈现中部低而东西两侧高的“凹”字形分布格局; 2013年回归系数呈现由北到南逐渐递减的分布格局,尤其是毗邻南京市的镇域回归系数较高; 2018年系数较大的区域主要位于城市中部发展轴上,最大值落在历阳镇,最小值落在石杨镇。整体上看,政府为缓和人地压力,积极发挥政策的调控力,干预国土空间开发及资源环境保护,对两者耦合协调发展起重要作用。从历年高值区分布格局及回归系数演变上看,充分响应了马鞍山市2011年行政区划调整后一江两岸协同发展战略。
综上,资源型城市国土开发强度与生态承载力耦合协调发展的驱动要素具有显著的时空异质性,各地域宜结合自身发展轨迹,提出应变性、多样性的国土开发路径及生态资源管控模式。
如图6所示,两者的耦合协调发展是基于各驱动要素间的交互耦合进程,形成资金流、信息流、技术流等要素流引导下的驱动路径,进而促进国土开发强度降速提质与生态承载力降压提效,并达到对驱动要素的优化反馈与适应调整的目的。从具体实操系统上看,国土开发层面主要利用区域资源优化配置、传统产业转型更新、优势产业链条延伸等“存量发展”策略,生态承载层面通过循环利用技术提升、生态环境修复与生态文明制度约束等“绿色发展”路径,降低国土空间开发对生态环境的胁迫程度,减弱资源环境对开发建设的约束效应,从而促进资源型城市国土空间开发与生态环境保护的耦合演化关系不断改善,以至于两者达到协同共生状态,最终实现地域的可持续性发展。
(1)通过综合评价指数模型计量,反映出2008—2018年马鞍山市国土开发强度快速上升,空间异质性愈加凸显,高值聚于长江(马鞍山段)两岸及中部城镇发展轴,低值以点状形式分布于生态敏感区内; 生态承载力平稳上升,空间差异不大且基本保持稳定,呈现以长江(马鞍山段)为界,西部略高于东部的空间分布特征。长期以来,资源型城市以牺牲自然环境为代价,大力推动工业化、城镇化进程,导致开发强度快速上升,而生态承载力整体缓慢提升。
(2)基于耦合协调度模型测算,10 a间,样本区域国土开发强度与生态承载力耦合协调度保持连续上升的趋势,由中度失调阶段逐步过渡到低度协调阶段。随着资源型城市更新迭代的步伐加快,国土开发强度与生态承载力呈现愈加紧密的协调发展态势。空间上,耦合协调度呈现中部高两侧低的分布格局,且空间集聚态势愈加显著,冷点区主要位于马鞍山市东南部,次冷点集中于含山县下辖乡镇; 次热点区分布于主城区外围圈层; 热点区始终以市辖区范围为界(博望镇除外)。由此可见,资源型城市耦合协调发展度的区域空间分异特征明显,且“高值”与“低值”的空间分布较稳定。
(3)利用地理加权回归模型分析,显示出样本城市国土开发强度与生态承载力耦合协调发展的驱动要素具有显著的时空异质性。关键要素驱动作用由大到小依次为:产业转型>经济发展>政府调控>资源集聚,3个年份产业结构转型均是最主要的驱动要素。经济发展驱动系数的高值区由市辖区范围向博望区及当涂东南部镇域转移; 资源集聚的回归系数由中部高而东西两侧低的“凸”字型格局演变为北高南低的阶梯状分布格局; 产业转型系数的高值镇域呈现由市域西南部、东南部逐渐向主城区周边集聚的趋势; 政府调控的驱动作用由中部低东西两侧高的“凹”字形格局向北高南低的阶梯状格局演化,且城市中部发展轴上驱动系数较大。着眼于资源型城市的演化历程,国土开发与生态保护的协调发展是基于多种驱动要素交互耦合作用的结果。
对于资源城市多年计划经济体制影响下的“顽疾”应对,既不能单停留于“静态化”的数理模型解析,也必须避免“普遍化”的转型更新模式套用,其关键更重于多维度辨析各载体实态特征,并进行“具体而微”的实施操作:(1)探寻“腾笼换鸟”的经济转型升级路径。通过淘汰整治、搬迁集聚、改造提升、兼并重组等方式,加快落后产能的腾退和淘汰步伐,加大新兴产业培育力度,有利于从根本上解决资源型城市经济领域中长期累积的结构性、素质性矛盾与问题。(2)优化“增存挂钩”的建设指标分配体系。针对资源型城市土地粗放利用、生态环境功能衰退、土地复垦难度大等突出矛盾,采取建设用地增量供应指标与存量土地利用状况相挂钩的奖惩机制,制定以批而未供与闲置存量用地为“靶向”的新增建设用地计划,有利于消除国土低效利用现象,激发存量空间再利用潜能,实现经济增长与新增建设用地指标逐渐“脱钩”的“减量化”发展。(3)建立“横纵并施”的生态保护补偿机制。生态补偿是矿产资源区生态化转型的关键举措,涵盖补偿定价、补偿实施和监督保障三方面,具体落实时,应强化识别各资源城市发展阶段特质,增强“横向转移支付”与“纵向转移支付”的协同效应,从而体现出区域间经济与生态的分工关系以及生态服务价值的市场交换能力,最终为资源型城市地域更新、生态修复提供持续动力。(4)重塑“全域统筹”的多元要素互联格局。基于地域主体功能定位与发展战略导向特征,打破固有空间区划下“各自为营”的竞争模式,统筹谋划人口分布、产业布局、生态建设和政策措施,完善“目标性、实效性”的多元要素互联协调机制,推动全域“综合化、精细化”的资源管控模式营建。