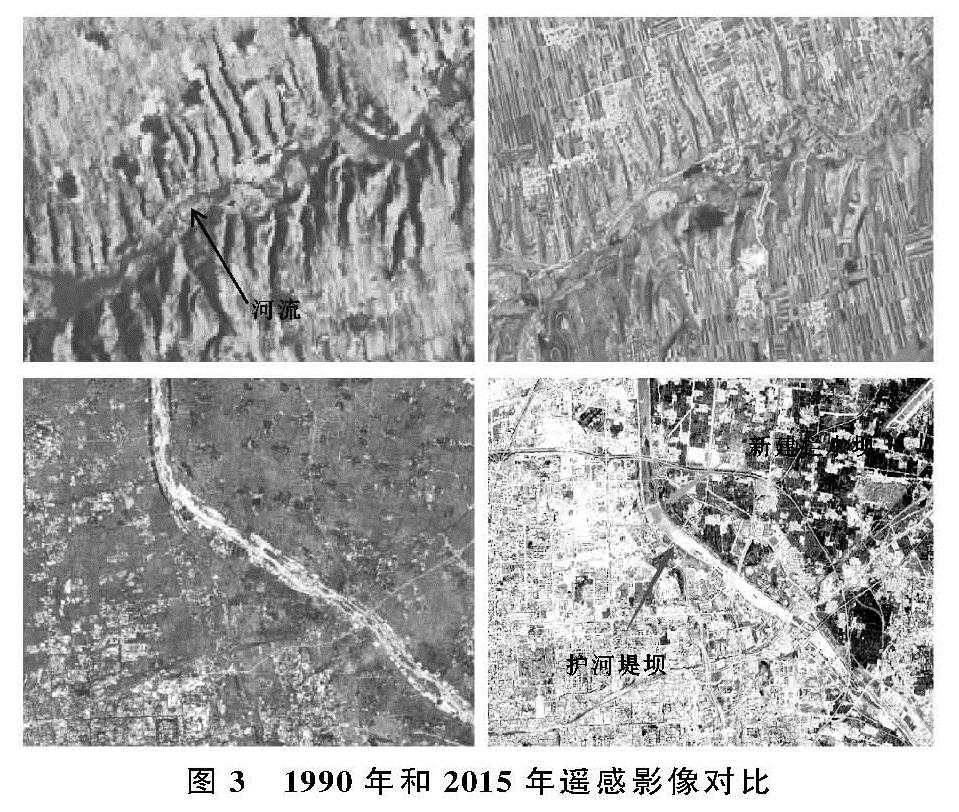
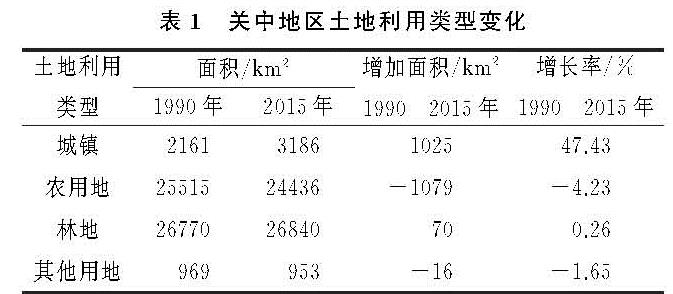
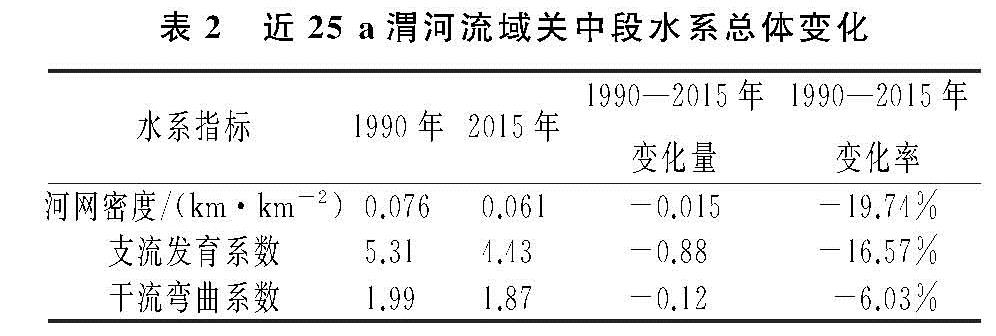
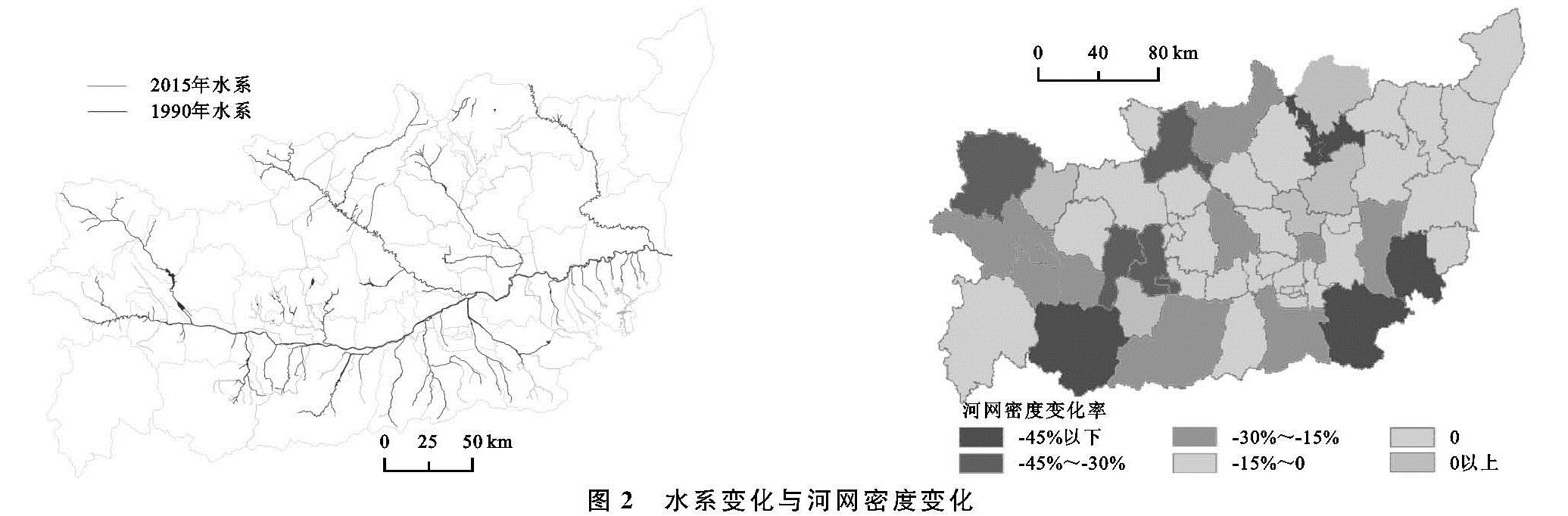
4.1 渭河关中段水系演变特征及其对城镇化的响应
河流的演化一般与河床质地,地形、气候、人类活动有关,但是在短时期内,河流水系的变化的最主要因素还是人类活动[13]。关中地区作为陕西省工、农业中心地区,25 a间经济迅猛发展,随之而来的是大量的农用地和河流被侵占转化为建设用地。通过对水系变化剧烈地区的分析发现,河网水系的萎缩与城市化建设存在着正相关关系,但是具体河流水系特征指标的衰减需要因地而异。关中段渭河水系指标衰减的原因可以分为4类:(1)平原区域水系衰减的主要原因为城镇建设或农田对河道的占用、填埋,导致河流变窄或消失,从而降低河网密度和支流发育系数;(2)关中南部地区属于秦岭北麓,由于地势问题,土地资源利用较为困难,道路、房屋等均沿河谷而建,涉河工程以及河道两侧耕地对河流的占用是导致当地河流消失的主要原因,其中地质灾害也是山区河道发生变化的主要影响因素之一[14],如宝鸡太白县;(3)城镇地区建设用地增长,建筑施工对河道进行占用以及城市人口增长对水资源需求的增加,致使区域内的水资源逐渐减少,河流也随之消失,如铜川市王益、印台区;(4)渭河干流周边地区,为了增加河流的防洪功能以及生态环境功能,沿线地方政府对河道进行裁弯取直修建护河堤坝、湿地公园,进而导致Ⅰ级河流长度以及曲率降低,如西安主城区。
总体来说,从对关中段渭河水系变化的规律研究发现,在城市化速率不同的区域,各项水系指标的衰减程度并不一致,但水系总体呈现萎缩趋势,水系变化表现为河流数量和长度减少、河流形态结构逐渐单一化,这与苏州市、深圳市、上海市等国内城镇化程度较高的平原地区的河网研究结果基本一致[15-17],且Ⅱ级、Ⅲ级河流受城市化进程的影响更大,这与嘉兴市河流水系变化特征相符[9]。但在城市化进程较快的地区,如西安市主城核心区,由于人们对水系保护的概念增强,人们自觉保护河流水系,以及当地政府为了减轻城市的防洪排涝压力,缓解干流的防洪压力,部分的二级河道尤其是靠近主干道附近的二级河道会被疏通、扩宽,以保证整个河流的过水能力平衡,在工程建设完成后,其长度和河流曲率均会长期维持在一个稳定的范围内[8],整个区域内的水系指标变化反而会有上升的趋势。
4.2 水系萎缩的不利影响
河流水系涉及城市的给排水、城市气候、城市水环境等诸多方面,是城市不可缺少的水环境因素[4]。河流水系具有很强的调蓄功能,河流的调蓄能力受水系数量和水系结构共同影响,已有的研究表明,在河网中低等级河流越多,其河网的调蓄能力越强[18]。但是在关中地区快速城镇化发展过程中,大量的低等级河流消失,使得水系的自然调蓄功能逐渐降低,渭河中下游年均最高洪峰水位有明显的上升趋势,洪涝灾害的威胁不断增大[19]。另外一方面,由于河流水系结构的变化,阻碍了河流的相互连通,降低了河流的自我净化功能。城镇化使城市不透水面积增加,地表径流携带污染物直接进入河流,致使关中段渭河流域的污染严重。通过对渭河水质的测定,渭河干流水质从咸阳兴平断面至渭南潼关桥断面,共9个断面均属于Ⅴ类水质[20],总体水质较差。同时由于河流的减少,会使区域内地下水补给降低,在遭遇干旱灾害时,会加重干旱的影响。
4.3 河流水系保护建议
关中段渭河水系数量减少主要原因是低等级河流消失,因此在推进城市化过程时,要避免对河流的改造和填埋,尤其注重对低等级河流的保护。合理的控制城市建设用地面积增长,各种土地利用类型均衡发展,增加城市中绿化面积,减少城市中的不透水面积。(1)将河流水系保护纳入到城市管理规划中,健全监管和执法体系,在区域开发规划时,严禁新建工程对河流进行填埋、占用。(2)协调城市发展与河流水系保护,加强河流的治理和恢复,积极开展低等级河流清淤的工程,增强河流的蓄水和防洪能力,在干流修建防洪堤坝时,尽量扩宽治导线,给干流更大的空间,避免河流水系退化和河流骨干化。(3)完善水文化设施,注重临水空间的开发保护,重视河流景观建设,提高居民生活品味,让居民自发性形成保护河流的意识。