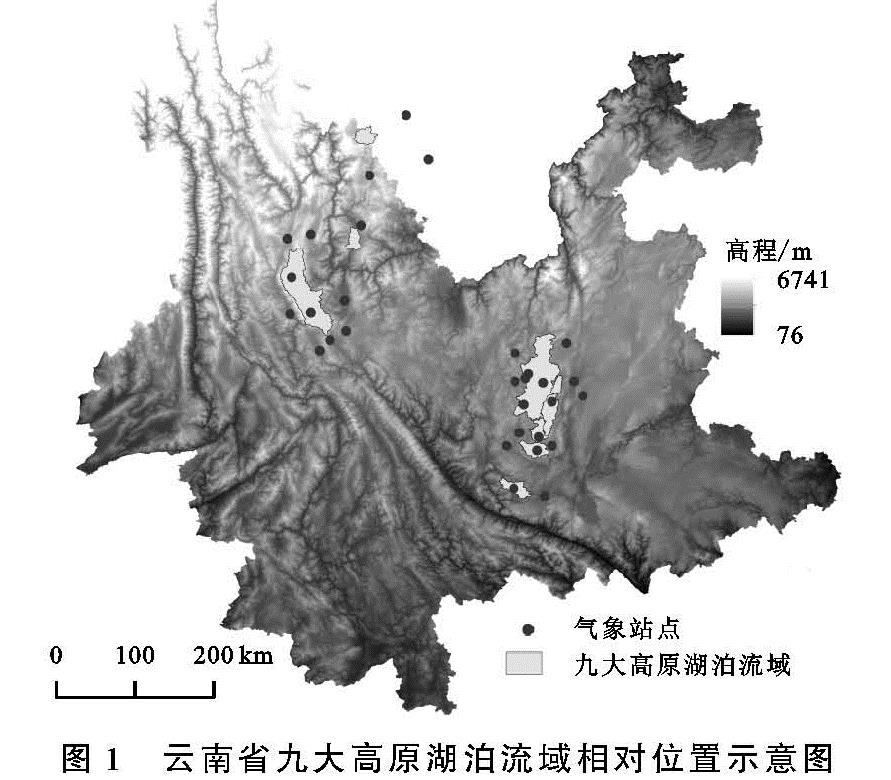
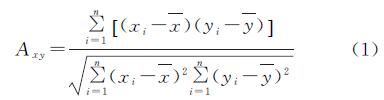2.1 九大高原湖泊流域多年NDVI时间变化特征
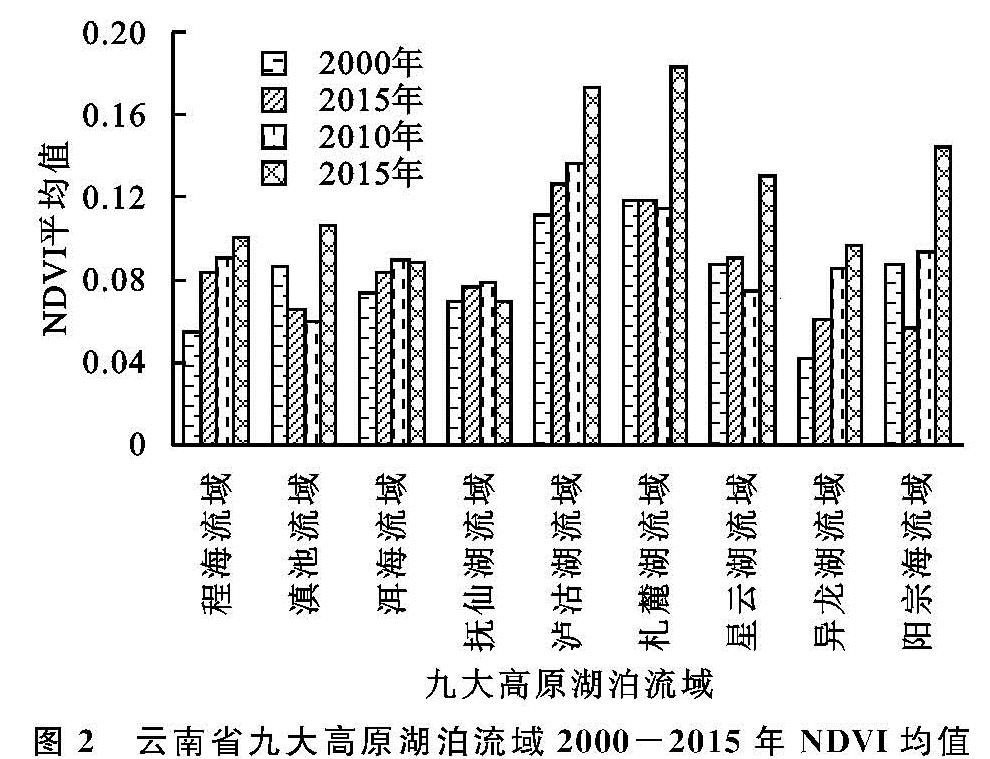
根据九大高原湖泊流域近16 a的平均NDVI值统计结果如图2所示,16 a来九大高原湖泊流域NDVI值总体以2.6%/10 a的速率上升,从年际变化上分析,2000—2015年,九大高原湖泊流域整体NDVI均值表现出上升的趋势,说明九大高原湖泊流域总体植被覆盖度在不断增加。从NDVI变化的总体趋势上来看,九大高原湖泊流域近16 a以来NDVI值变化呈现波动的趋势,在2005—2010年研究时段内,部分流域NDVI值出现了下降的情况[16]。
在研究时间段内,各个湖泊流域的NDVI均值变化情况为:首先,程海流域、异龙湖流域的变化趋于平稳,流域NDVI值缓慢上升; 滇池流域、星云湖流域近年来NDVI值波动相似,总体呈现增加的趋势; 洱海流域近16 a以来,NDVI值变化不显著,说明其在研究时段内植被覆盖保持良好; 抚仙湖流域在九大高原湖泊流域中总体的NDVI值较低,但在近16 a以来,其植被覆盖总体保持良好。其次,泸沽湖流域与杞麓湖流域NDVI值高于其他各流域,表明两个流域植被覆盖比其他地区好。最后,阳宗海流域在2005年以后植被覆盖度增长幅度较大。
图2 云南省九大高原湖泊流域2000-2015年NDVI均值
2.2 九大高原湖泊流域多年NDVI空间变化特征
通过趋势分析法研究2000—2015年云南省九大高原湖泊流域NDVI变化趋势,采用自然间断法进行分级,并统计各变化区间的像元数(图3),结果显示,抚仙湖流域是改善情况较好的流域,说明当地的环境保护措施及其相关的政策具有较大的成效,在当地也设有抚仙湖管理机构,在一定的程度上较好地保护了抚仙湖流域的生态环境。杞麓湖与星云湖流域植被覆盖状况总体比其他几个流域好,但研究发现近年来NDVI值出现了较高程度的退化,这两个流域是云南省重要的蔬菜、花卉、烤烟基地,经济发展程度较高,人类活动方式多样而且较为频繁,工业与城镇集中,人地矛盾突出。需要说明的是异龙湖与杞麓湖流域湖泊西侧出现了一片具有明显改善趋势的区域,这是由于2000—2015年期间,两个流域湖泊大面积萎缩,西侧区域有水体转化为了耕地等土地利用类型,所以该区域的NDVI表现出改善的趋势。程海流域,阳宗海流域,洱海流域NDVI变化趋势相似,出现严重退化的区域多为湖泊南岸的平坦地域,明显改善的地区分布于流域的山麓地带,基本不变的区域面积占比较大。3个流域的发展模式也存在相似的地方,旅游业发展在区域的GDP中占有一定的比重,旅游开发规模大,是云南省乃至全国著名的旅游地。其中,洱海流域与程海流域当地民族独特的环保观念也对区域的植被覆盖产生了积极的影响。滇池流域是云南省经济发展程度最高,人类活动影响程度最深的区域,在研究时段内,流域内的城市开发强度较大,在其滇池的周围区域出现了大面积的退化,明显改善的区域很小,表明在经济高速发展及人类较强的活动下,对流域内的植被覆盖产生了极大的影响。
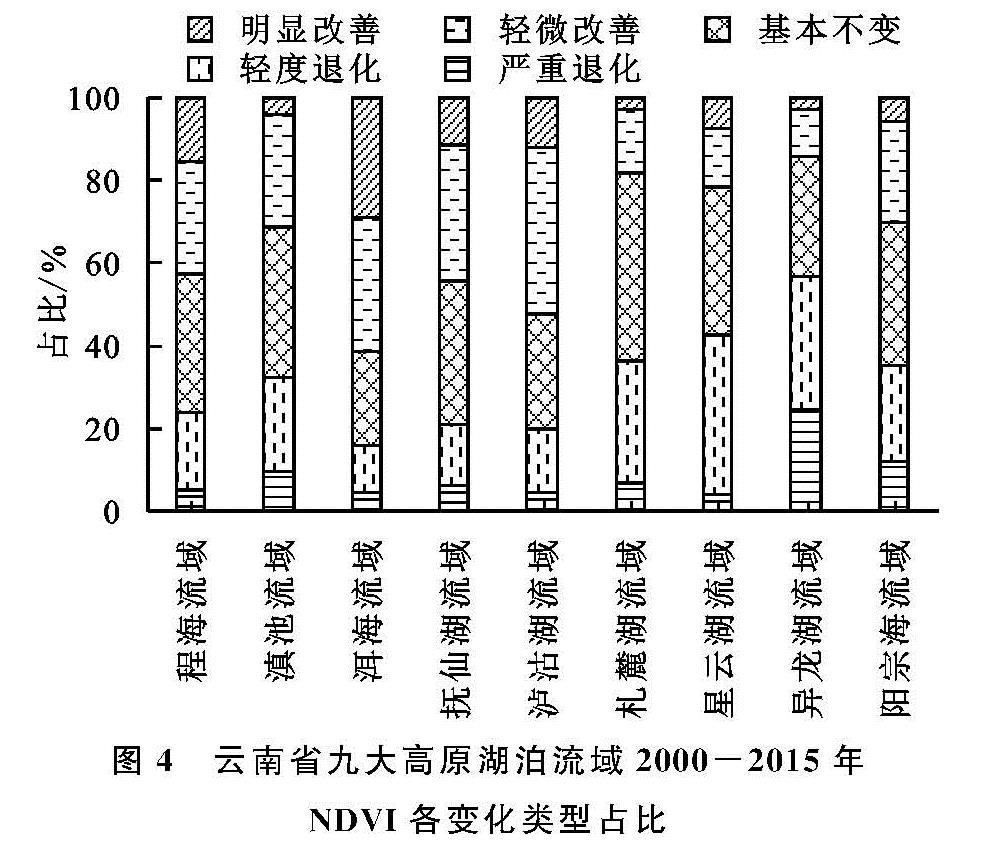
将各个流域不同变化区域面积占比进行统计(图4),可以看出,杞麓湖流域严重退化面积占流域面积比重最大,抚仙湖流域明显改善的面积占比较大,植被覆盖保持良好的为滇池流域,各个流域均出现了一定程度的退化。泸沽湖流域是NDVI严重退化程度较小的流域,人类活动受到海拔及山地地形的影响,尽管当地旅游业蓬勃发展,但人类活动对其影响较小。然而处于湖泊周围的地区,人类对其影响较为显著。在研究时段内,九大高原湖泊流域NDVI退化的区域主要分布于湖岸、工农业城镇集中连片地区,此区域内人类干预性强,经济开发强度大,对NDVI变化产生了较大的影响。而在人类干预较少的山麓地带,NDVI得到了明显的改善,间接说明九大高原湖泊流域在实施了退耕还林还草等措施之后取得了明显的成效。
2.3 九大高原湖泊流域多年NDVI与气候因子的相关性分析
九大高原湖泊流域不同区域的植被长势会受到气象因子的影响与控制,气候通过气温的变化及其降水的改变来影响植被的长势与分布。在研究植被动态与气候变化关系时,应考虑不同的土地利用与植被类型,因为植物的光合作用和呼吸作用都受到不同的植被类型温度与降水的季节变化控制[17]。结合所获取的气象数据,运用偏相关分析方法,统计各个流域的偏相关值见表2,研究发现:九大高原湖泊流域中,除程海流域外,其他各个流域的NDVI值与气象因子均存在一定的相关性,但相关性不明显,相关性程度差异较大,这与刘群等[5]学者的研究有一定的相似。
图3 云南省九大高原湖泊流域2000-2015年NDVI变化趋势
表2 云南省九大高原湖泊流域气候因子与NDVI的平均偏相关系数
从表2可以看出:(1)在滇西、滇西北地区的流域(洱海流域、泸沽湖流域)气温与NDVI值的相关性大于降水与NDVI值的相关性,气温对植被生长的影响超过了降水,表明在这些区域气温在一定的程度上是制约植被生长的重要因素,结合云南省的综合自然区划,该流域处于大理、丽江盆地高山区,现有的森林主要为针叶林,海拔3 000 m以下的主要为云南松林和华山松林。3 000 m以上的以云杉冷杉林为主,该区域的植被及其作物受气温的影响极大,旱地和水浇地较多,随着海拔的增加结合气温的降低,复种指数也明显下降。
图4 云南省九大高原湖泊流域2000-2015年NDVI各变化类型占比
(2)滇中地区的流域(滇池流域、抚仙湖流域、星云湖流域、杞麓湖流域、阳宗海流域)则是降水与NDVI值的相关性大于气温与NDVI值的相关性,该地区植被类型多为半湿润常绿阔叶林红壤地带,林地多为云南松林与华山松林,多数林地为混交林。坝子地势平坦,耕地集中,灌溉和生活用水量很大[18]。星云湖流域、杞麓湖流域,降水较为丰富,地形平坦的山麓及其湖泊两侧,相关性却比较低,水资源供需矛盾比较突出,降水满足不了工农业发展时,植被与降水的影响关系被打破,造成了流域内湖泊两岸及平坦地区的NDVI与降水的相关性比较低的情况。
(3)位于滇南的蒙自、元江高原盆地峡谷地区的异龙湖流域,NDVI值与气温和降水相关性差异不大,季风常绿阔叶林是该区域的主要植被类型,红河谷地海拔低下,相对高差达1 500~2 000 m,是云南省内最为干热的河谷,除局部的河谷外区域内山地海拔多处于2 000 m以下,热量充足,雨量适中,种植制度多样,春旱较严重,森林多以云南松为主。
(4)位于金沙江河谷地区的程海流域,NDVI值与气温和降水呈负相关,干热河谷的特殊气候是由谷地气流的局部环流和焚风效应相结合而形成的,在这种特殊条件下所发育的植被也与云南省总的气候殊异[19]。该区域处于少雨的范围,一年之中旱季较为漫长,区域内径流资源较少,气温颇高,人类活动对其干预强度较大,加之河谷地区焚风效应的影响,造成了气温对植被的负相关影响。程海是区域内最大的湖泊,但其湖面蒸发较大,降水量较少,湖泊补给少,湖面萎缩,年降水量较小,而蒸发量较大,导致水量的交换处于停滞状态下,对区域局部小气候影响较小。水位逐年下降,湖水的矿化度持续上升,湖泊周围农田需水量巨大,所以降水对程海流域植被NDVI的生长影响较小,这一研究结论与张亮等[20]的一致,金沙江流域植被覆盖度与降水和气温的偏相关系数都呈负相关。
(5)流域内湖泊东侧地区NDVI值与降水因素的相关性比西侧地区好,NDVI值与降水因素相关性较好的区域主要分布于迎风坡的山麓地区这一特点在滇池流域表现较为明显。九大高原湖泊流域NDVI值与气温的相关关系分析,九大高原湖泊流域NDVI值与气温存在一定的的相关性,但地区间差异大,处于滇西地区的流域,气温对植被的生长影响更为明显。
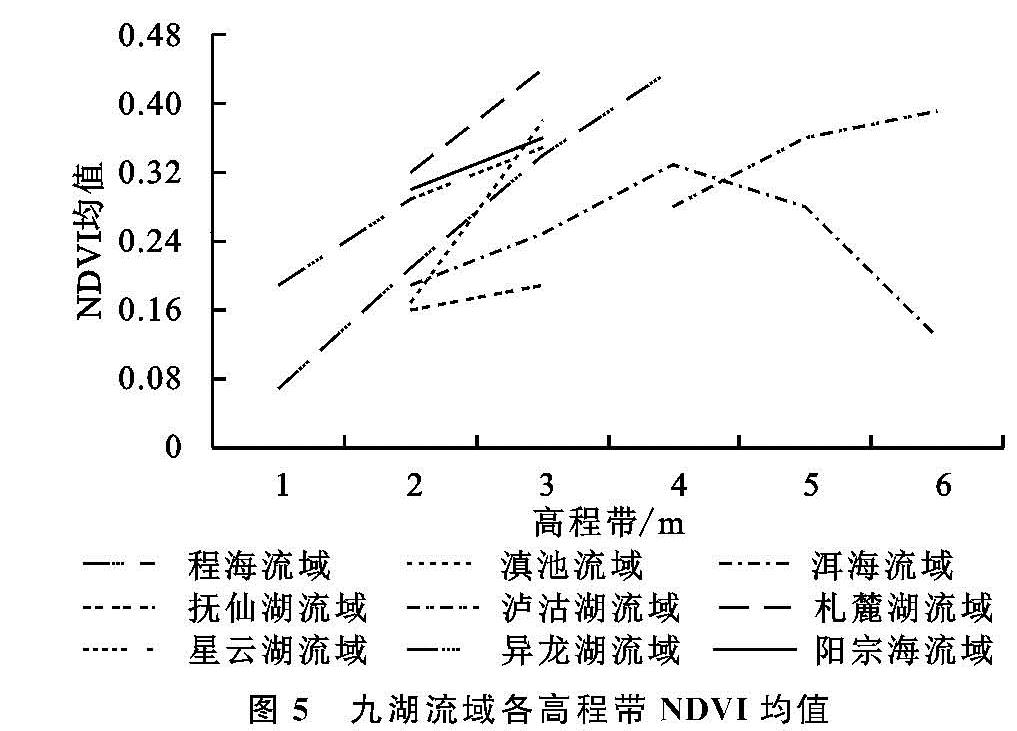
2.4 九大高原湖泊流域多年NDVI与高程的相关性分析
云南省地势西北高东南低,自北向南呈阶梯状下降。相关研究表明,高程因子在一定程度上影响植被覆盖度的空间分布[21]。基于此,将九大高原湖泊流域的高程带进行依据相关标准和结合九大高原湖泊流域高程的实际情况进行重分类,九大高原湖泊流域的高程处于1 213~3 910 m之间,并分为1 213~1 660 m,1 660~2 110 m,2 110~2 560 m,2 560~3 010 m,3 010~3 460 m,3 460~3 910 m共6个高程带,并且统计九大高原湖泊流域各高程带NDVI均值与九大高原湖泊流域各流域在各个高程带内的NDVI均值结果见图5。研究表明,总体上具备自然地带的基本特征,在1 000~3 000 m的区域,NDVI值随着高程的增加而增加; 在2 500~3 000 m的高程带内,NDVI值同样随高程的增加而增加,但增加率比1 000~3 000 m高程带的低; 在3 000~4 000 m高程带内,NDVI值随高程的增加而急剧降低。由此可知,3 000 m是NDVI值减少的一个节点,结合云南省的地形,高程大于3 000 m的流域主要分布于滇西或滇西北地区,该区域地势险峻,气温低,降水少,气候因子成为了植被生长的限制性因子。
同时,九大高原湖泊流域的各个流域因所处的高程不同,也存在着一定的空间异质性,针对泸沽湖流域而言,2 560~3 010 m,3 010~3 460 m,3 460~3 910 m高程带内,NDVI值随高程的增加而增加,这与九大高原湖泊流域整体NDVI和高程的分布有所差异; 程海流域NDVI随高程的增加变化明显,而滇中地区的几个流域因为其经济发展程度较高,人类活动干预强度较大,NDVI随高程的增加变化不显著,滇西地区的洱海流域NDVI值随高程的增加而出现了较大的波动。
2.5 九大高原湖泊流域多年NDVI变化轨迹分析
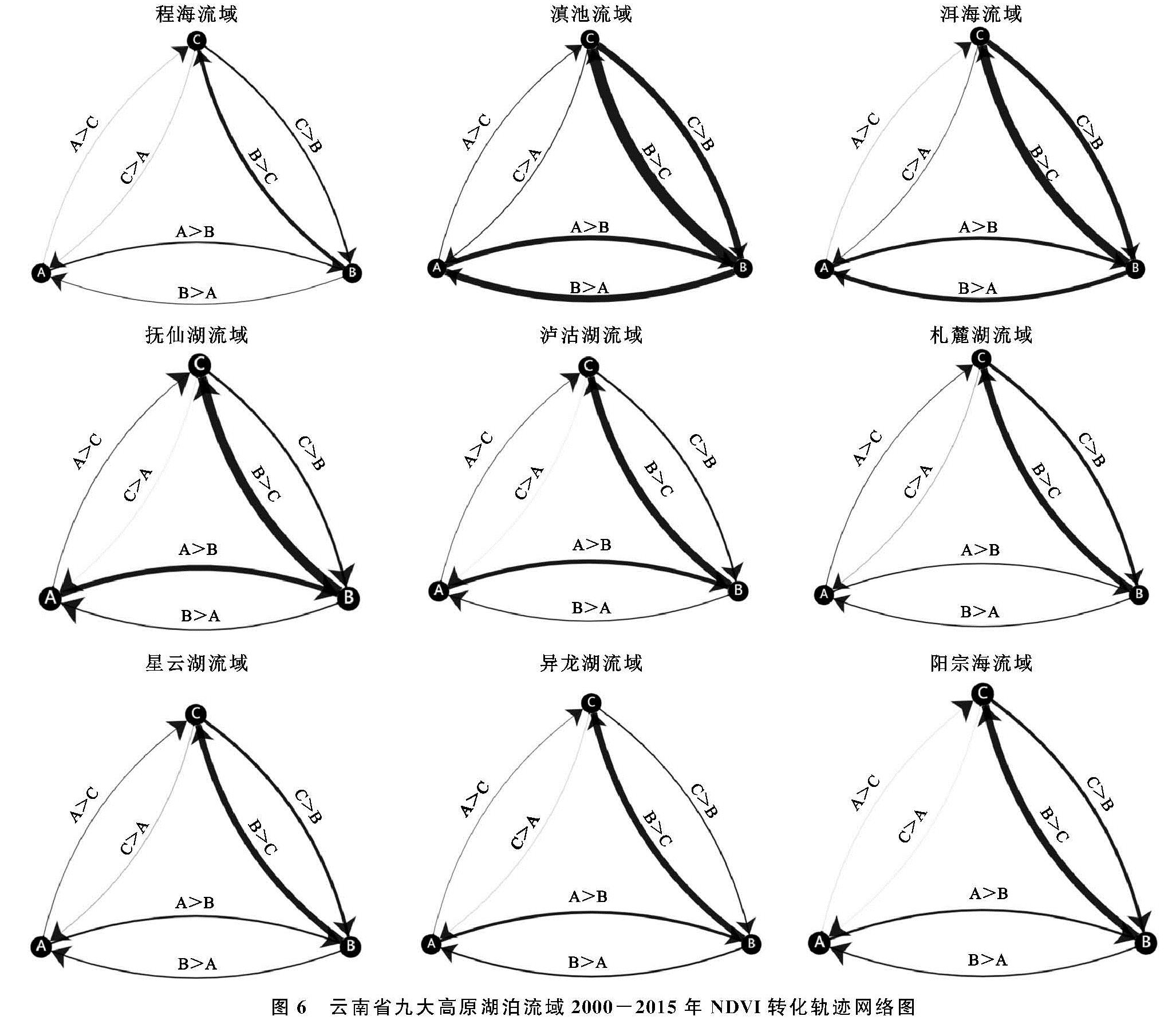
根据NDVI指示意义及相关学者的研究,李亚飞等研究迪庆地区景观类型时采用0.3作为植被与非植被的阈值[22],甘淑等对澜沧江流域山区土地覆盖遥感监测分类时则选用了0.15作为植被与非植被的阈值[23]; 同时结合研究区实际及野外实测数据,对植被与非植被的像元进行抽样比较,在充分考虑研究的植被季像与地方种植制度等因素之后最终确定研究区分类的阈值。将研究区NDVI值分为3类,分别为水体与建筑(A)和裸地与其他(B)、植被(C),植被与非植被的NDVI采用0.25作为分类的阈值,水体和建筑NDVI值则采用≤0作为分类的阈值。将NDVI值根据上述标准进行重分类,通过将各年度的NDVI栅格数据进行叠加分析,最终得到各流域近16 a新的NDVI栅格数据属性值,同时形成一个新的变化图谱(图6)。本文使用python作为开发语言在echarts的环境下,实现NDVI变化轨迹网络动态可视化。其中A,B,C分别代表不同的NDVI类型,箭头方向表示转化的方向,线条的粗细表示转换次数的多少。
图6 云南省九大高原湖泊流域2000-2015年NDVI转化轨迹网络图
从图6可以看出,在研究时段内,总体上各个流域均有一定数量植被类型的转入,除泸沽湖、阳宗海之外,其他流域由裸地转为植被的数量较多,抚仙湖流域、滇池流域、洱海流域在研究时间段内其他类型的NDVI转化为植被的数量较多。抚仙湖流域植被类型转为其他类型的次数较少,间接说明抚仙湖流域植被恢复及退耕还林(草)及流域保护工作取得显著成效[24]。滇池流域由裸土类型转为水体或建筑类型的数量在九大高原湖泊流域中是最多的,表明滇池流域在近16 a以来,城市扩张面积比其他流域大。
同时,异龙湖流域也出现了一定数量的非植被类型转换为植被类型的情况,这主要是因为异龙湖流域西侧的湖泊面积缩小[25],原来的湖泊演变为耕地等土地利用类型,所以增加了非植被类型转换为植被类型的数量。各个流域中,植被与水体或建筑之间的转化次数都比较少。综上,九大高原湖泊流域在研究时段内转换次数最多的是由非植被类型转化为植被类型的转移方式。