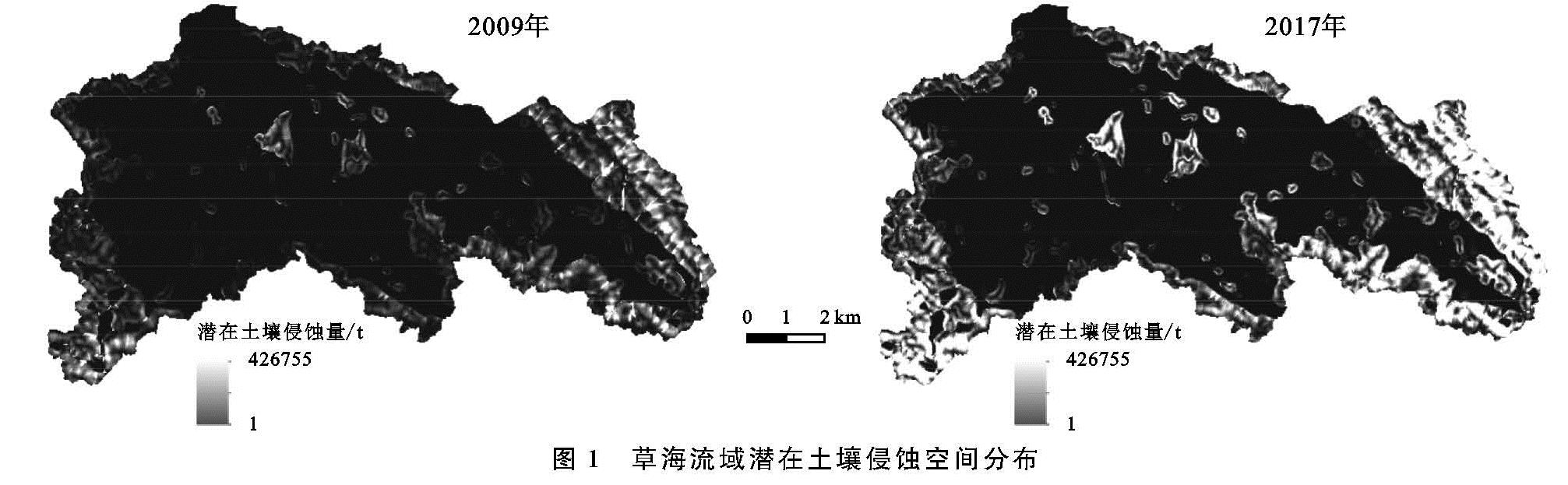
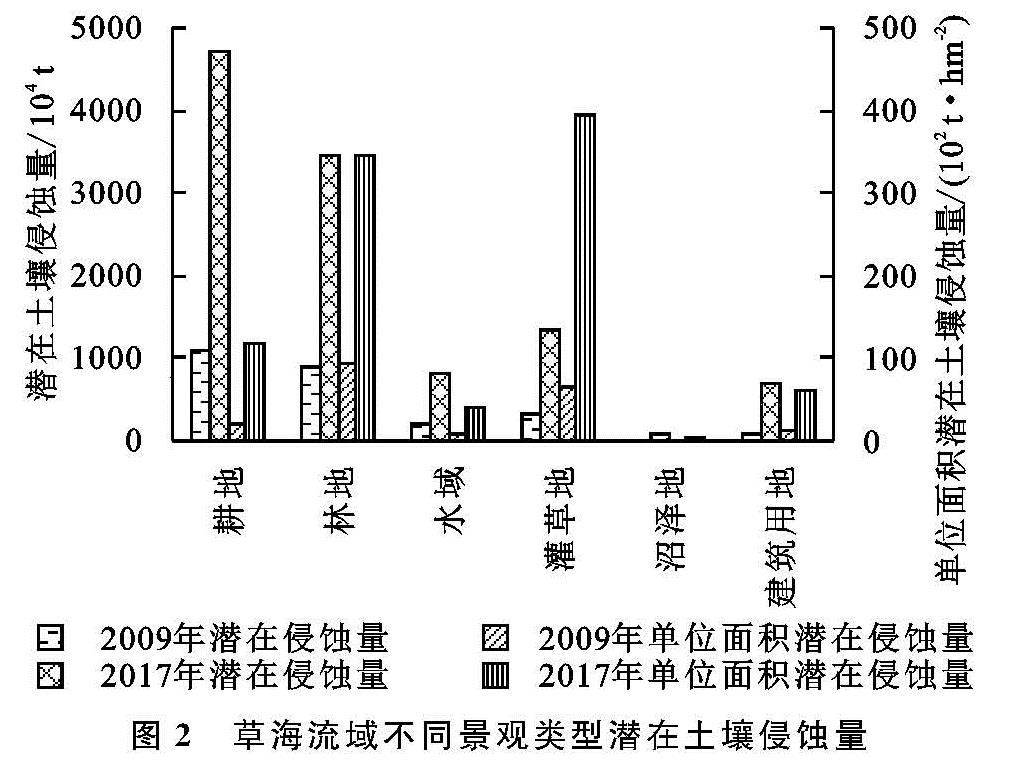
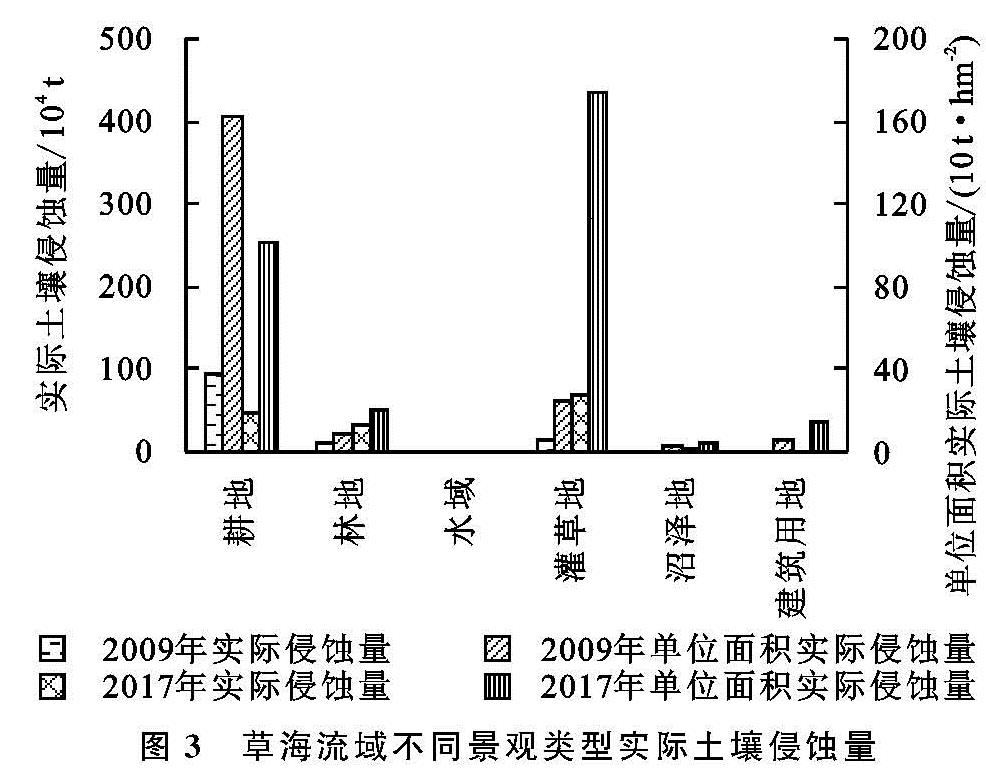
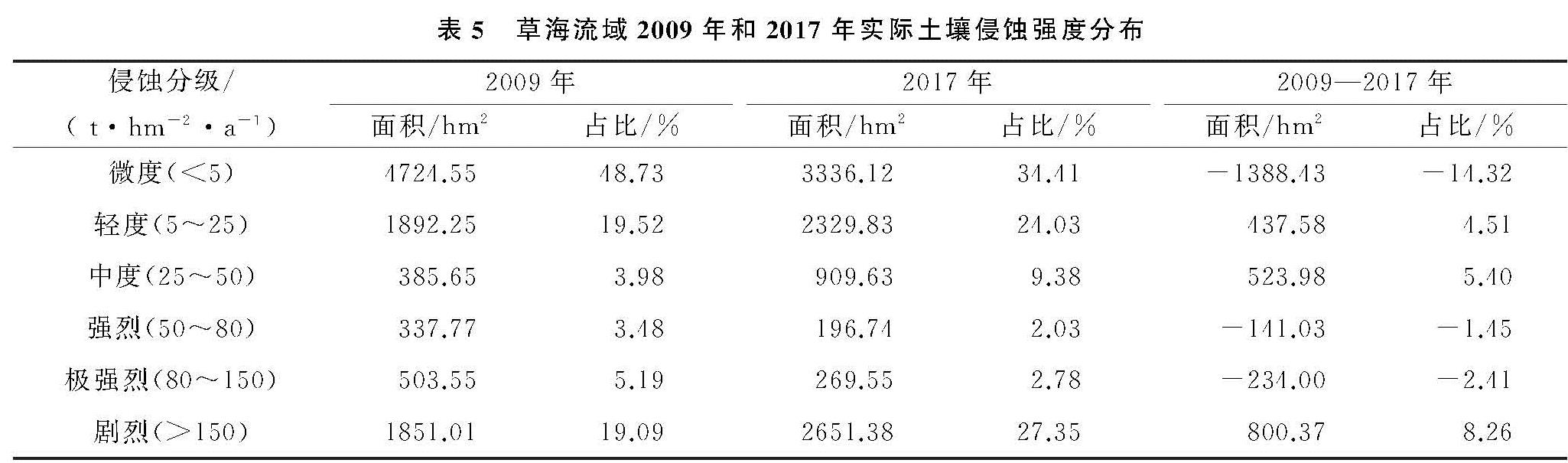
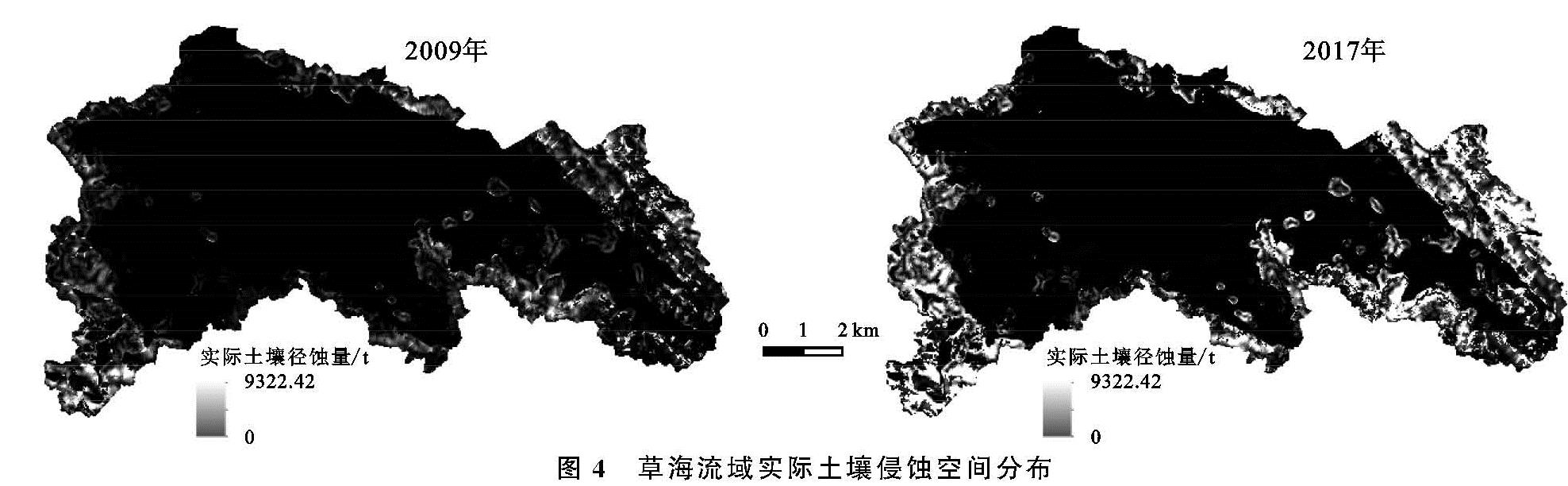
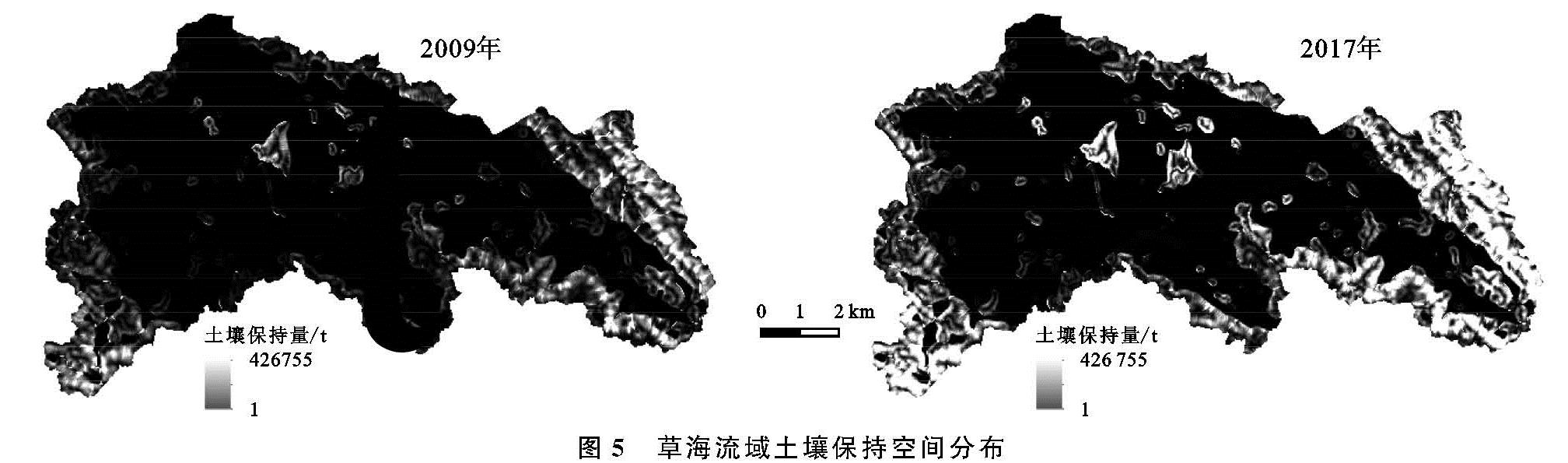
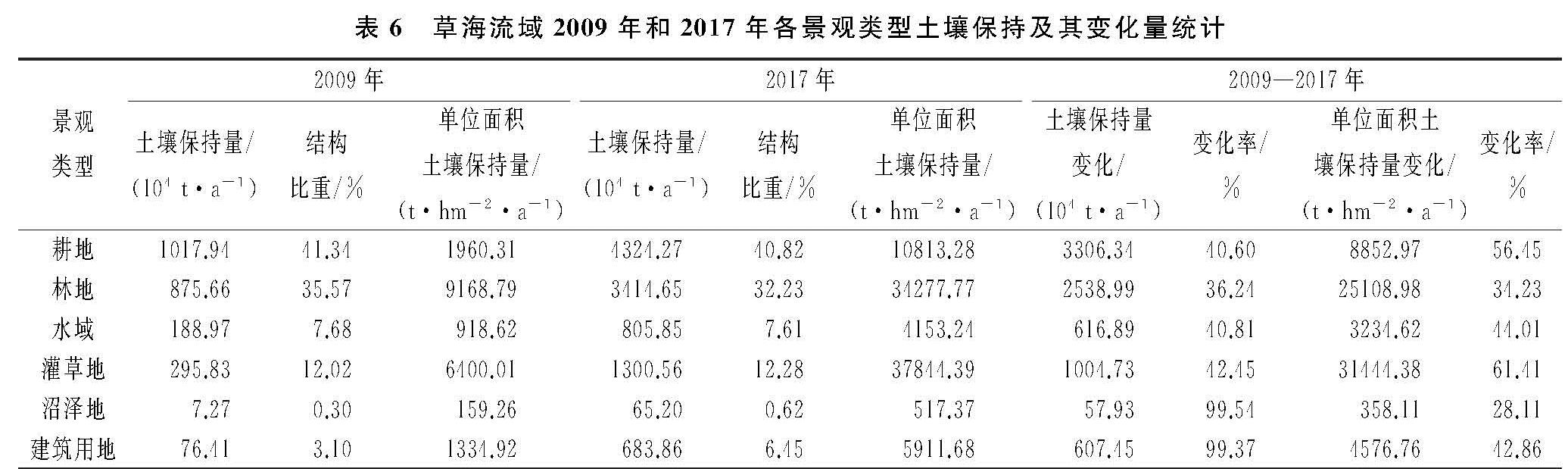
1.1 研究区概况
草海流域(26°47'32″—26°52'52″N,104°10'16″—104°20'40″E)地处贵州省西北威宁县彝族回族苗族自治县县城南侧,是我国特有的黑颈鹤(Grus nigricollis)等珍稀鸟类的栖息地,是一个完整的、典型的喀斯特高原小流域[22]。研究区地势东部最高,西南部较高,中部为湖区,流域出水口在西北部,平均海拔2 171.7 m,流域面积96 km2左右[22],气候为亚热带季风气候,年均气温10.6℃,年均降雨量约为950.9 mm,降水年均分布不均,主要集中于夏季,干湿季分明,相对湿度79%[23]。流域内的土壤大部分为黄棕壤,呈酸性,具有相对湿度大、淋溶作用强、有机质含量高的特征,常年被湖水淹没的盆地淤泥地带则是泥炭化的沼泽土[24],土地利用类型以耕地、林地、灌草地、建筑用地和水域为主。
1.2 数据来源
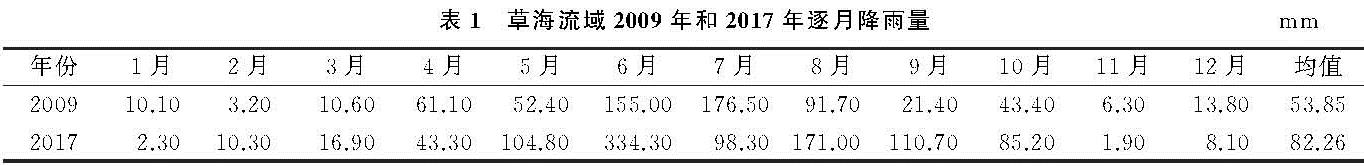
针对InVEST模型土壤保持功能评价的基本框架,结合本研究的主要内容,研究所用数据主要包括草海流域2009年和2017年土地利用景观类型空间数据和逐月降雨量数据、土壤质地和有机质含量数据、DEM数据等。其中,土地利用景观类型数据运用高分辨率遥感图像(空间分辨率为2.5 m×2.5 m),基于ArcGIS 10.5软件平台通过目视解译方法获取; 土壤质地和有机质含量数据由贵州省土壤类型图、中国土壤数据库(http:∥vdb3.soil.csdb.cn)结合相关研究成果获取[25]; 降雨数据来源于威宁县气象局(表1); DEM数据来源于地理空间数据云网站(http:∥www.gscloud.cn)。由于各类数据来源、投影方式和比例尺等不同,在进行相关分析之前对所有数据统一进行几何配准与重采样,将所有数据坐标系统统一为Beijing_1954_3_Degree_GK_CM_105 E投影坐标系统,数据栅格大小统一为30 m×30 m。
表1 草海流域2009年和2017年逐月降雨量mm
1.3 模型因子计算
土壤保持采用InVEST模型中土壤保持模块进行估算[14]。计算公式如下:
SEDRETx=RKLSx-USLEx+SEDRx(1)
RKLSx=Rx×Kx×LSx(2)
USLEx=Rx×Kx×LSx×Cx×Px(3)
SEDRx=SEx∑x-1y=1USLEy∏x-1z=y+1(1-SEx)(4)
式中:SEDRETx为栅格x的土壤保持量; RKLSx为基于地貌和气候条件下栅格x的土壤侵蚀量; USLEx为考虑了管理及工程措施后栅格x的实际侵蚀量; SEDRx为栅格x的泥沙持留量; USLEy为考虑了管理及工程措施后上坡栅格y的实际侵蚀量; SEx为栅格x的泥沙持留量; Rx为降雨侵蚀性因子; Kx为土壤侵蚀因子; LSx为坡度坡长因子; Cx为植被覆盖和作物管理因子; Px为水土保持措施因子。
(1)降雨侵蚀力因子(Rx)反映降雨对土壤剥离、搬运及地表冲刷能力的体现。本研究采用Wischmeier[26]月度计算公式:
Rx=∑12i=1[1.735×10(1.5lg(P2i)/p-0.8188)]×17.02(5)
式中:Rx为降雨侵蚀力[(MJ·mm)/(hm2·h·a)]; Pi为月降雨量(mm); P为年均降雨量(mm),式中Rx单位是(100 ft·t·in)/(ac·h·a),该单位需乘以系数17.02,转换成国际单位[(MJ·mm)/(hm2·h·a)]。
(2)土壤可蚀性因子(Kx)指土壤对侵蚀的敏感性反映,可衡量土壤颗粒被降雨分离和搬运的难易程度。本研究采用EPIC[27]模型中的计算公式计算,公式如下:
Kx={0.2+0.3exp[-0.0256SAN(1-SIL/100)]}
((SIL)/(CLA+SIL))0.3×[1-0.25×(OM)/(OM+exp(3.72-2.95OM))]×
[1-0.7×(SN1)/(SN1+exp(22.95SN1-5.51))](6)
SN1=1-SAN/100(7)
式中:Kx为国际值单位的土壤可蚀性(t·hm2·h)/(hm2·MJ·mm); SAN为沙粒的含量(%),SIL为粉粒的含量(%),CLA为黏粒的含量(%),OM为土壤有机碳的含量(%)。
(3)坡长坡度因子(LSx)是形成具有侵蚀能力径流并导致侵蚀事件发生的主要地形因子,可表示地形地貌特征对土壤侵蚀的影响。本研究根据前人的相关研究结果,坡度与侵蚀的规律大体上呈现钟形的关系,有一临界坡度25°,因此将25°规定为转折坡度,计算公式如下:
LSx=((Fa×Cs)/(22.13))n×[(sin(s×0.01745))/(0.09)]1.4×1.6(8)
n={0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2 s>5%
3.5%<s≤5%
1%<s≤3.5%
s≤1%(9)
式中:Fa为汇水累积阈值; Cs为栅格大小; s为坡度(%); n为与坡度有关的参数。
当坡度大于坡度阈值时,地形因子计算方法[28]如下:
LSx=0.08β0.35s0.6(10)
β={Cs
1.4Cs 流向=1,4,16,64
其他流向(11)
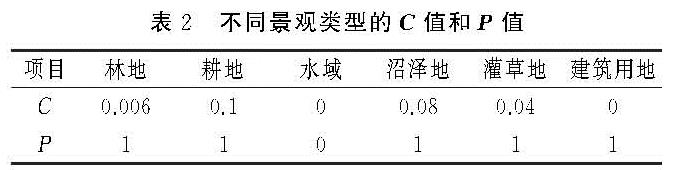
(4)地表覆盖管理因子(Cx)指一定条件下,某类特定作物或植被实施植被管理措施后的土壤流失量与未实施管理措施时的土壤流失量的比值; 土壤保持因子(Px)是在有、无水土保持措施情况下,土壤流失量的比值,值域为0~1,数值大小与水保措施效果呈负相关[14]。参考秦志佳[29]的研究成果,并结合本研究中对草海流域土地利用景观结构特征,将C因子和P因子值赋予相应的景观类型(表2)。
(5)泥沙持留量(SEx)代表了侵蚀产生的泥沙在输移过程中,植被过滤、拦截上游地块泥沙沉积物的能力,其值越大,则持留率越高[14]。