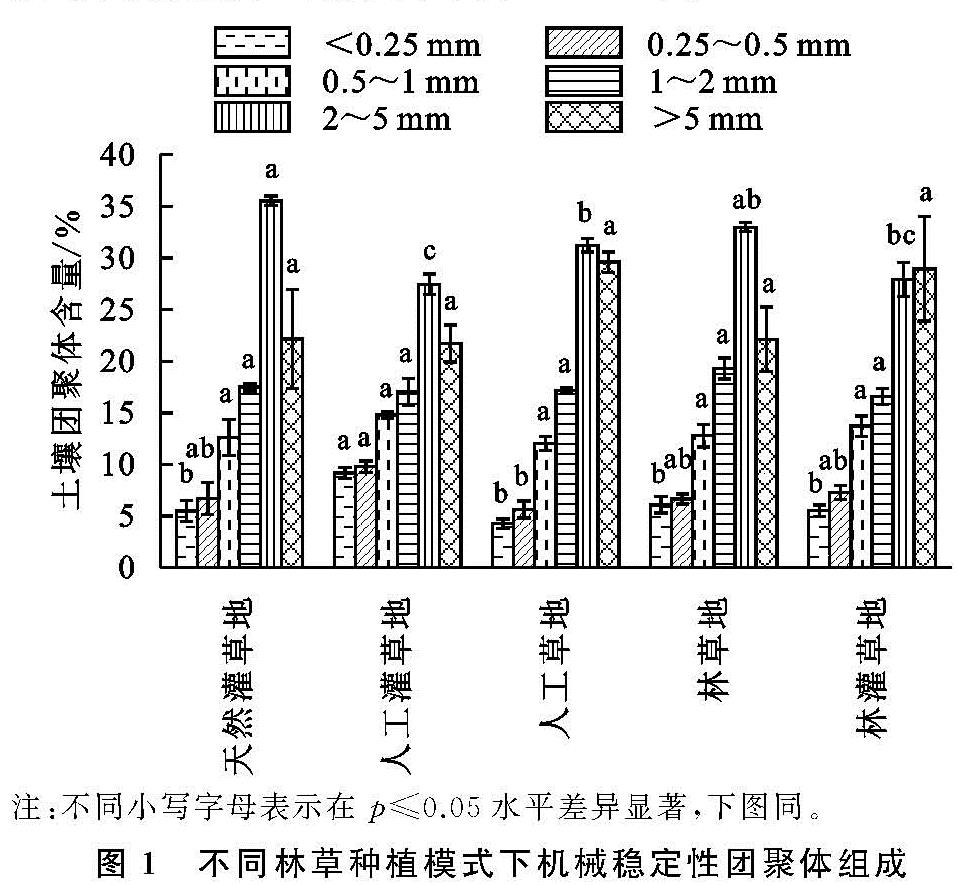
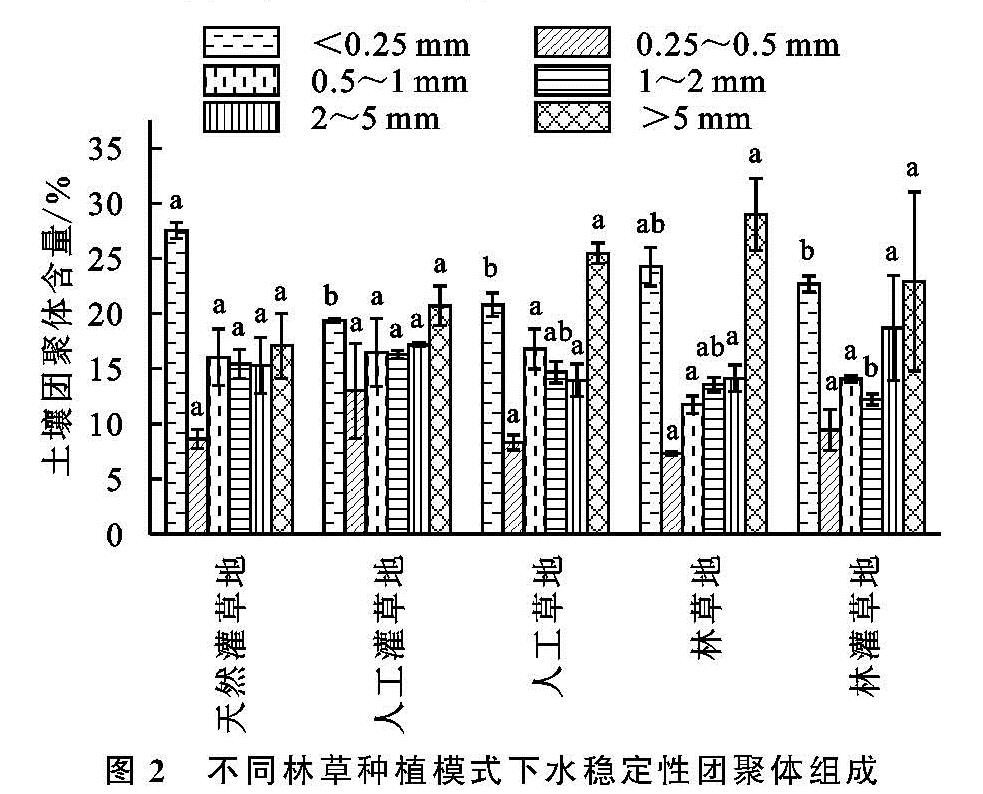
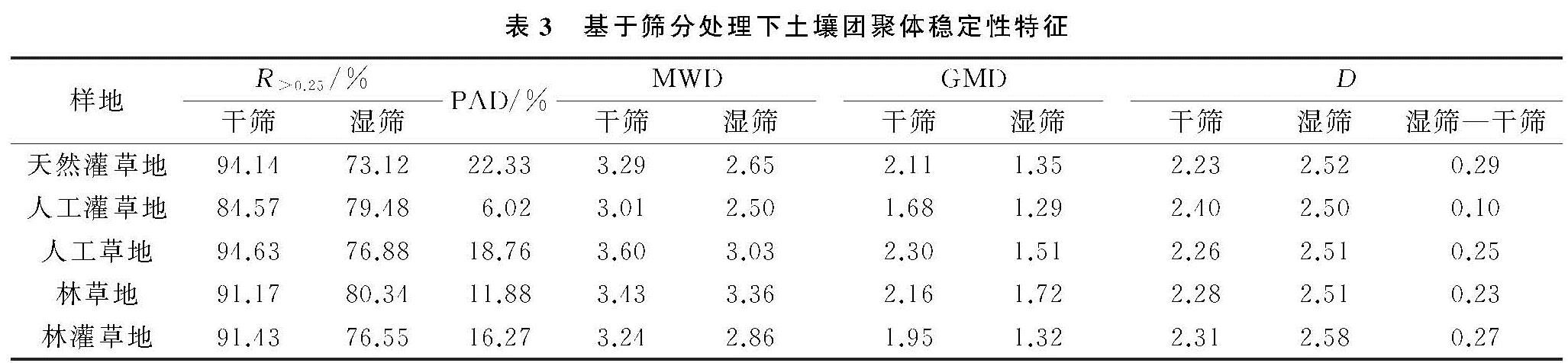
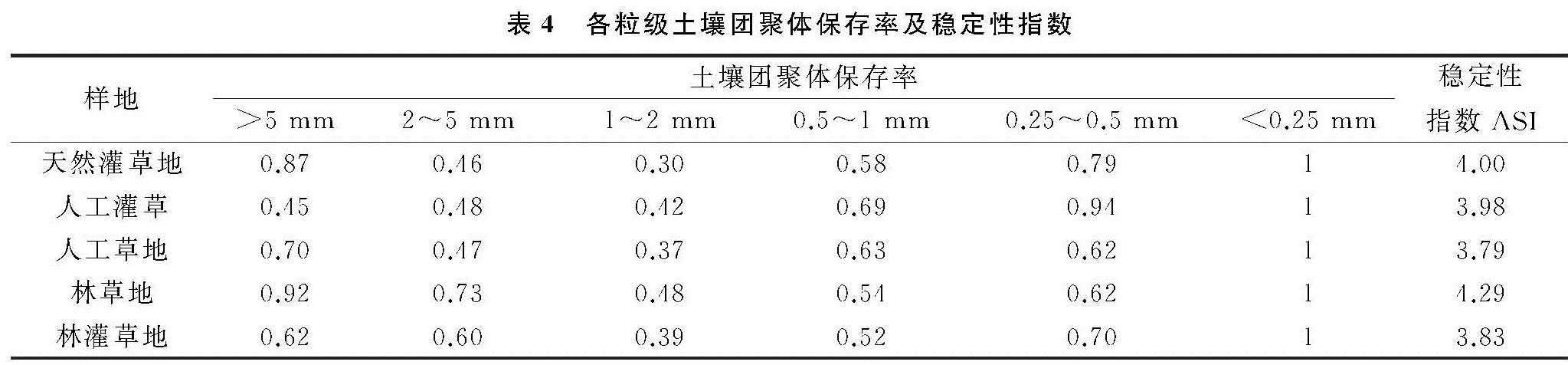
喀斯特石漠化地区由于独特的二元地貌结构,地表、地下水土流失严重[20-21],林草复合模式有利于石漠化地区退化生境的恢复[13]。已有研究证实土壤团聚体稳定性受植被覆盖、结构体特征、种植年限、植物根系等方面的影响[22-25],林草复合模式能有效地增加地表植被覆盖率,促进根系正常生长,改善土壤基本性质,提高土壤抗蚀性[13,26-27]。本研究中干筛条件下,以>0.25 mm的机械稳定性大团聚体为主,这与汪三树等[9]的研究结果一致。湿筛处理后,风干土结构体被破坏导致大团聚体含量降低,微团聚体含量增加,这是因为在湿润条件下,部分团聚体容易发生断裂破碎[7]。相较于天然灌草地,4种林草配置模式下土壤机械稳定性、水稳定性大团聚体含量较高,结构破坏率较低,这是因为林草复合系统能有效提高土粒团聚程度[28],再加上部分天然灌草地表土流失,岩石裸露面积较大所致。这也表明林草复合模式有利于减少团聚体结构破坏率,提高土壤结构稳定性。
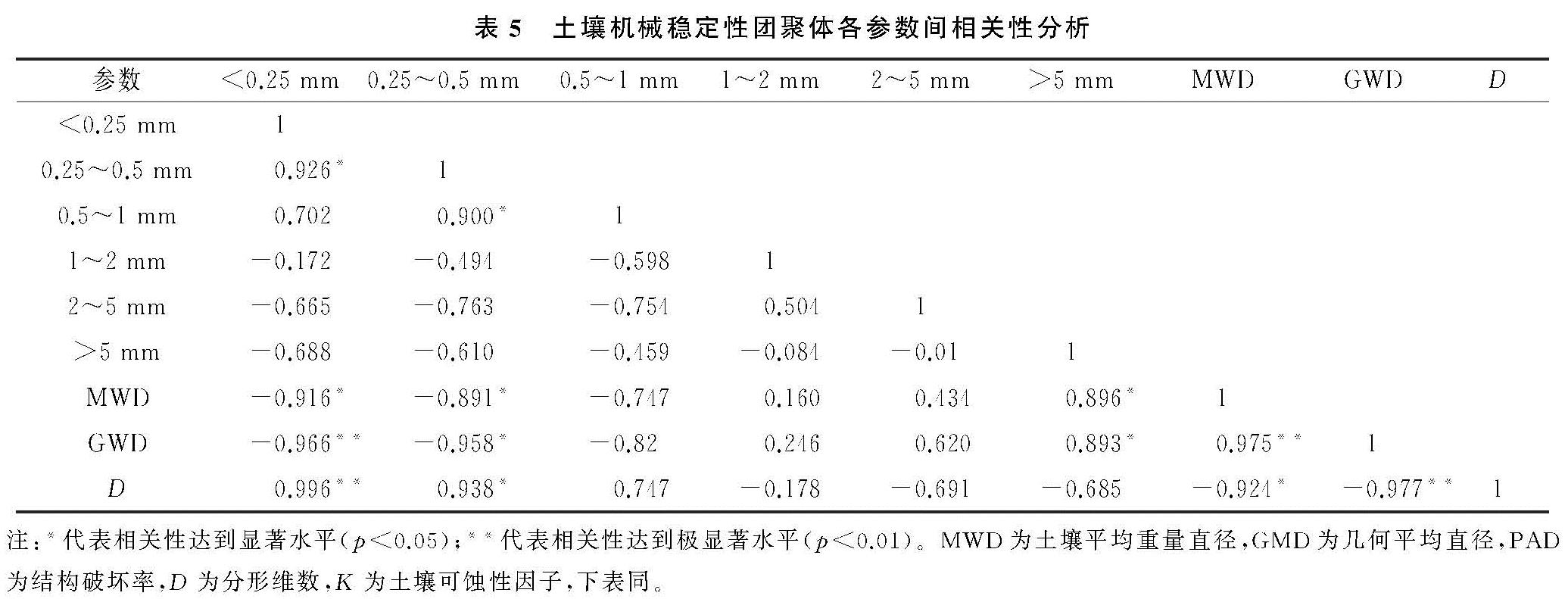
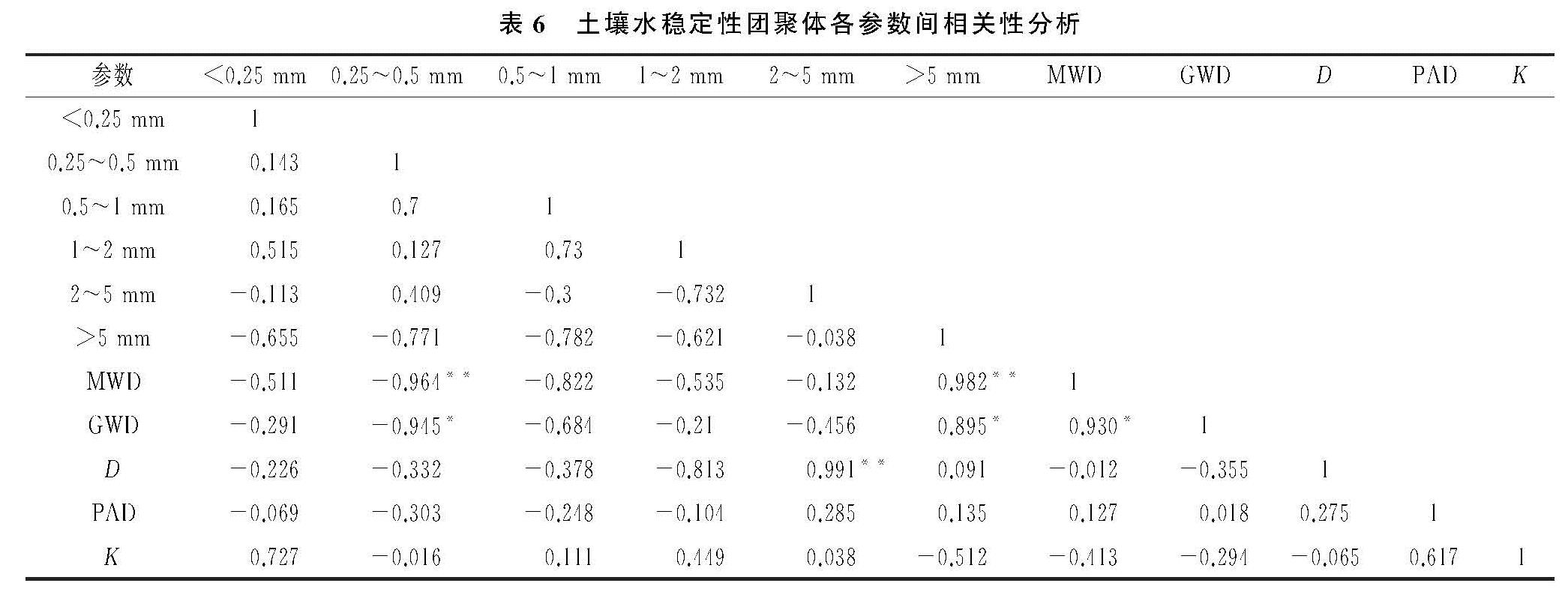
林草复合模式作为一种新型的土地利用方式[29],直接改变地表植被类型,有效提高植被覆盖水平,会引起团聚体稳定性变化。多数研究表明[8,15,30],团聚体MWD,GMD指数越大,表明土粒集聚程度越高,结构稳定性能越好。本研究综合考虑筛分结果发现,林草复合系统中林草混种模式下MWD和GMD最高,灌草套种模式下MWD和GMD最低,核桃是一种典型的落叶乔木,林下凋落物丰富,凋落物中所含腐殖质是影响团聚体形成的重要胶结物质[31],同时其有利于增加林下土壤动物的数量和提高土壤微生物活性,从而提高土壤团聚体稳定性[32]。本试验结果显示,干湿筛处理所得到的结果差异明显,机械稳定性团聚体D值依次排列为人工灌草地>林灌草地>林草地>人工草地>天然灌草,而水稳性团聚体D值为天然灌草地>林灌草地>林草地=人工草地>人工灌草,这主要是因为水稳性团聚体D值仅反映部分团聚体的影响[33]。
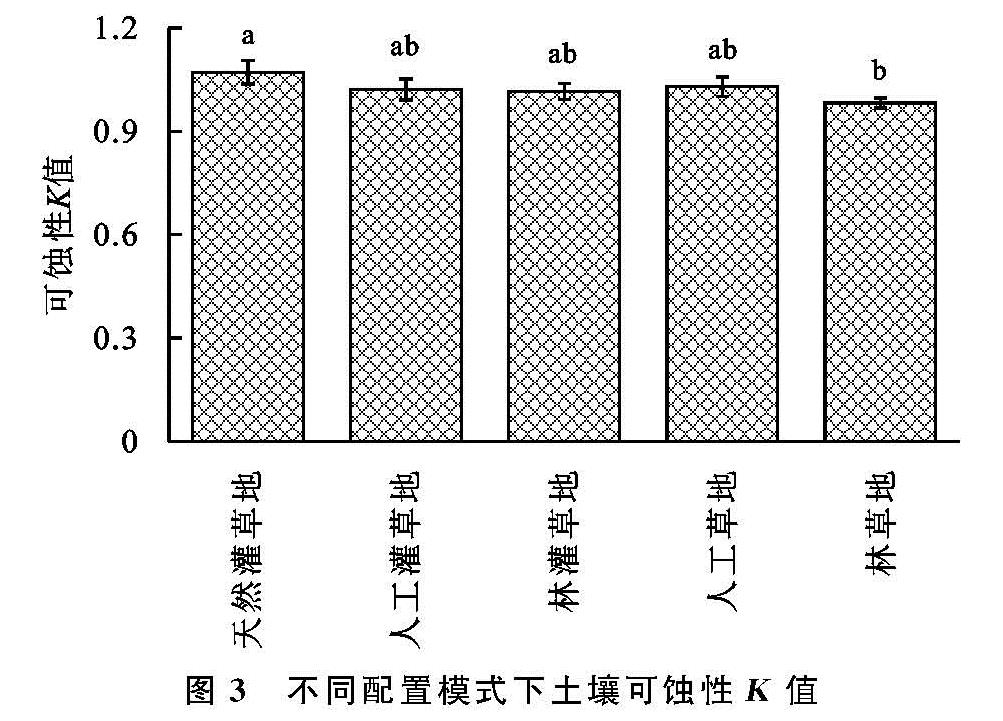
本研究表明4种林草配置模式下的K值明显小于天然灌草地,且林草地和天然灌草地的差异性达到显著性水平,不同林草模式间K值差异较小。说明天然灌草地土壤的抗侵蚀能力弱,不同的林草复合模式有利于提高土壤抵抗侵蚀的能力,这是由于不同林草复合模式下基岩裸露面积较小,在降雨时地表植被能有效减缓对土壤的破坏作用[34]。相关性分析表明,团聚体含量和机械稳定性团聚体MWD,GMD以及D值均以1 mm为正负相关性分界线; 水稳性团聚体MWD,GMD以及D值与少部分级别团聚体呈显著性相关,其中团聚体含量与MWD,GMD正负相关性的分界线为5 mm,与其D值分界线为2 mm。这说明在土壤团聚化过程中,1,2,5 mm是重要的临界点。姜敏等[4]研究也认为在1 mm和5 mm粒径的分界在微团聚体(<0.25 mm)—大团聚体(>5 mm)转化过程中具有重要作用,能有效影响土壤团聚体结构特征。
喀斯特石漠化是我国生态环境治理的重要部分,目前林草植被恢复模式是多数学者进行石漠化治理研究的重点关注内容。石漠化问题较为突出的西南八省实施的林草植被恢复措施主要包括封山育林、人工造林、人工种草修复、生态林治理以及林草复合治理等[13]。董莹珠[35]研究发现,云南省鹤庆县实行封山育林与人工造林相结合的治理模式后,地表植被覆盖率在3年增加了2%,土壤肥力得到提高; 四川省盐源县较为典型的治理措施为经果林治理模式,主要树种是青花椒、苹果、核桃等,有效地减少了水土流失[36]; 张靖宙等[37]通过模型研究得到不同石漠化治理模式对土壤碳储功能的提升有重要的影响。本文从团聚体稳定性和土壤可蚀性的角度评价目前实行的林草配置模式优劣性。研究发现,对比天然灌草地,其余人工林、灌、草种植模式下团聚体稳定性更优,并且林草(核桃+黑麦草)混种模式的效果最好。