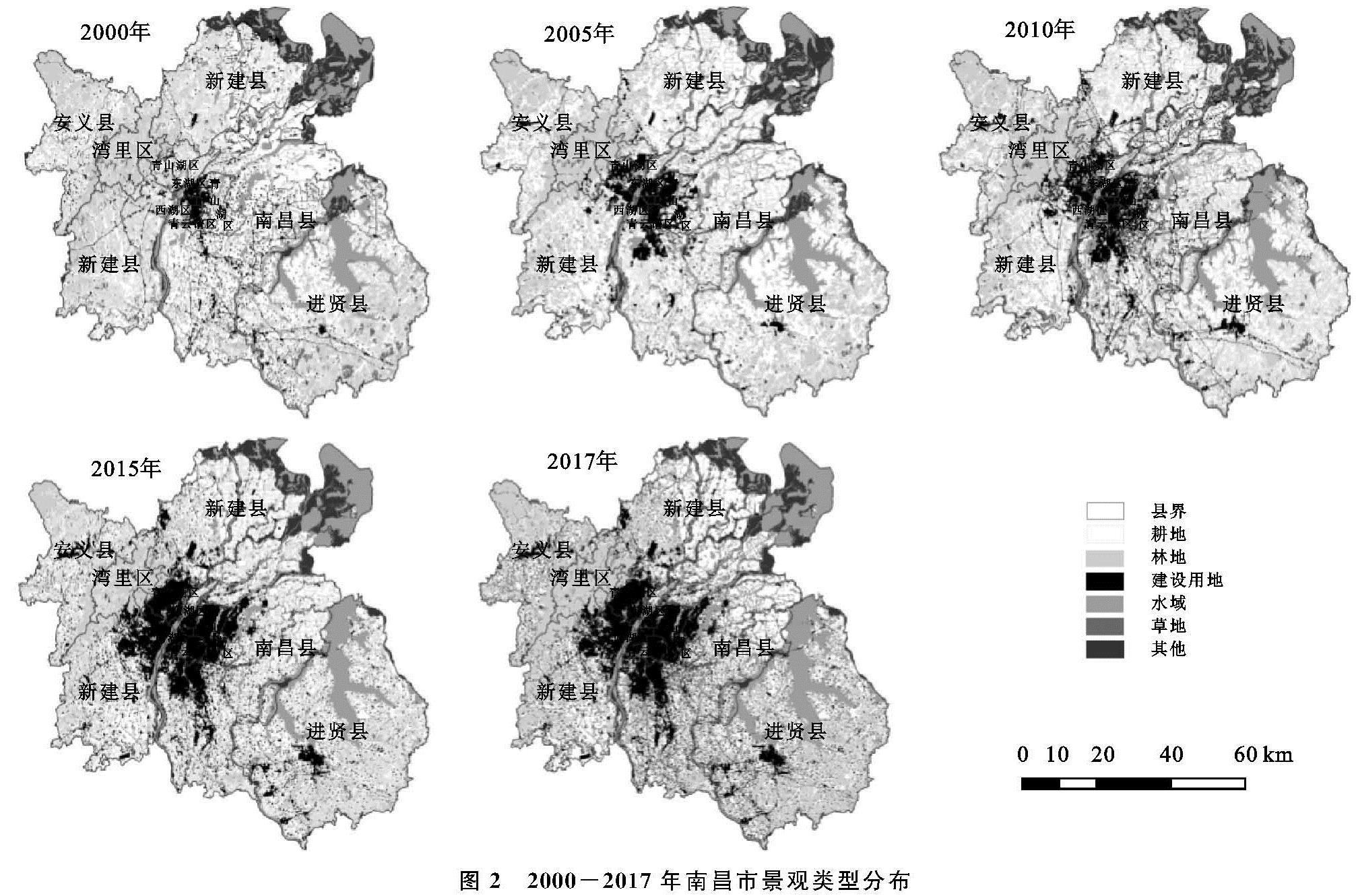
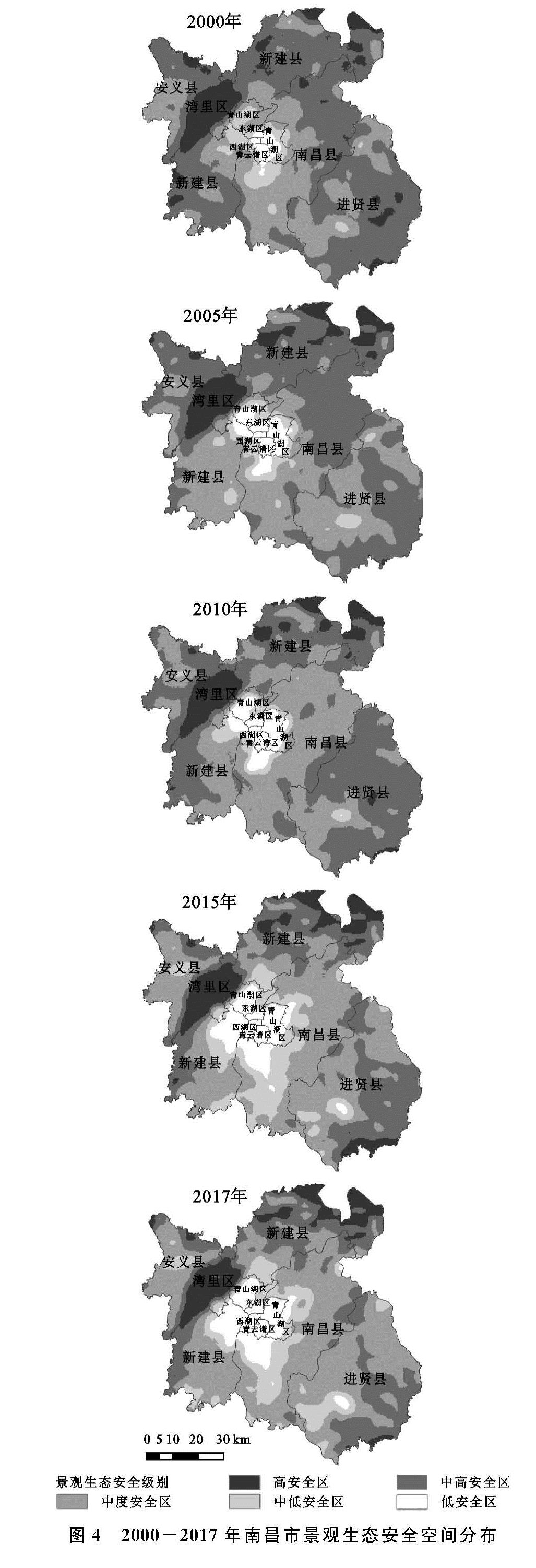
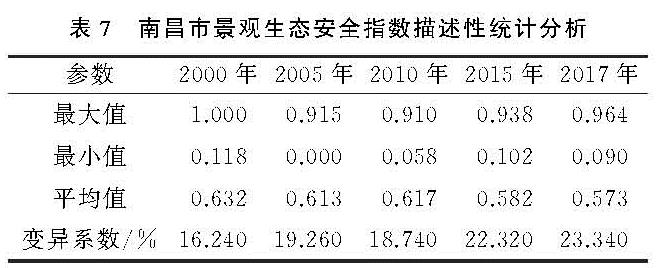
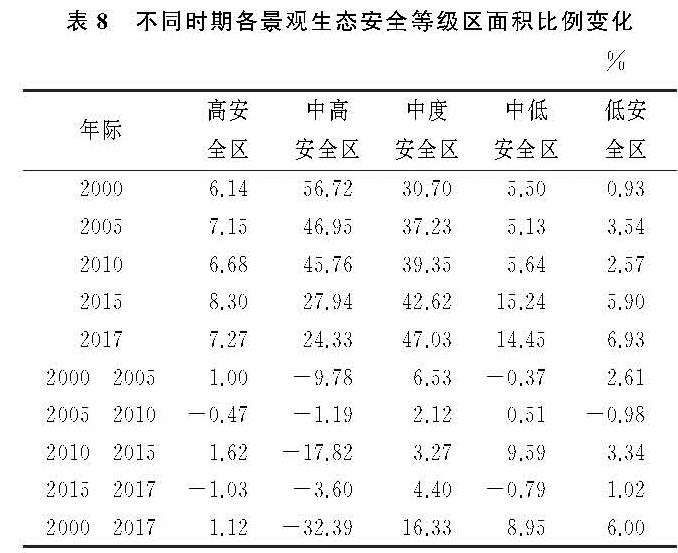
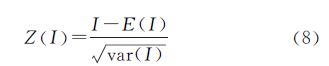2.2 指标体系构建
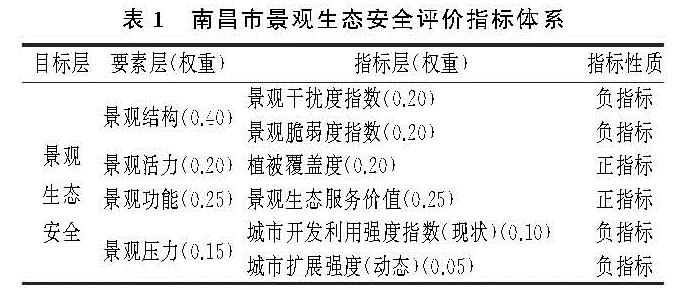
在景观生态安全评价研究中,较多学者采用以干扰度指数和脆弱度指数构建的景观生态安全评价模型[10-11],没有考虑到因景观组分变化而导致的区域生态环境状况变化。因此,本文基于研究区实际情况和相关研究成果[12],构建更为完善的景观生态安全评价指标体系,并采用层次分析法确定指标权重(表1),评价结果可以较真实、全面地反映区域景观生态安全程度。
各评价指标的计算方法及过程如下:
(1)景观干扰度与脆弱度指数反映各景观类型在人类活动或自然胁迫作用下生态环境的变化情况[13-14]。其中,景观干扰度指数(Ii)用于反映不同景观所代表的生态系统受到干扰的程度[15],计算公式见表2。Vi为第i类景观的脆弱度指数,参考相关研究成果[16-17],依据景观指数的重要性及其对景观干扰度的贡献率,将6类景观脆弱程度由高到低进行赋值。其中,建设用地赋值为1,林地为2,草地为3,耕地为4,水域为5,未利用地为6,并进行归一化处理,得到各景观类型脆弱度指数[18-19]。
(2)植被覆盖度采用基于NDVI的像元二分模型进行估算[20-22],主要包括归一化植被指数(NDVI)计算和利用NDVI反演植被覆盖度。
归一化植被指数又称标准化植被指数,具有消除地形以及大气条件有关辐照度的变化等优点[23-24],计算公式为:
NDVI=(NIR-R)/(NIR+R)(1)
式中:NDVI为归一化植被指数; NIR为近红外波段的反射率; R为可见光红光波段的反射率。NDVI数值越大代表植被的覆盖状况越好,植被的生物量越多[25]。
在NDVI的基础上进一步计算研究区的植被覆盖度FVC,公式如下:
FVC=(DNVI-NDVIsoil)/(NDVIveg-NDVIsoil)(2)
式中:NDVIsoil为裸土覆盖像元的NDVI值; NDVIveg为纯植被覆盖像元的NDVI值。
(3)本文在借鉴相关学者[26]的基础上结合南昌市实际情况,使用当量因子法来确定南昌市不同景观类型生态服务价值。基于实际情况的考虑,将不同景观类型生态服务价值当量因子代替相对应的生态服务价值系数,计算公式如下:
ESV=∑ni=1∑mj=1Ai×VCij(3)
UESV=ESV/A(4)
式中:ESV为生态系统服务价值; i为景观类型; j为生态系统服务功能的类型; Ai为第i种景观类型的面积; VCij为第i种景观类型第j种生态服务价值的系数; UESV为单位面积生态系统服务价值; A为所有景观类型总面积。
城市建设用地扩张是快速城市化过程中的城市面临的首要景观生态压力,也是引起区域生态系统退化的主要因素[27-29],因此,景观压力指数由城市开发利用强度及城市扩展强度共同确定。其中,城市开发利用强度以建设用地面积/土地总面积表征; 城市扩展强度指数用于衡量城市扩展的速度,计算公式为:
Ulli,t~t+n=[(ULAi,t+n-ULAi,t)/n]×100/TLAi(5)
式中:Ulli,t~t+n分别为空间单元i在t~t+n时段内的城市扩展强度指数以及t+n及t年时的城市土地利用面积; TLAi空间单元i的面积。
2.3 空间统计学方法
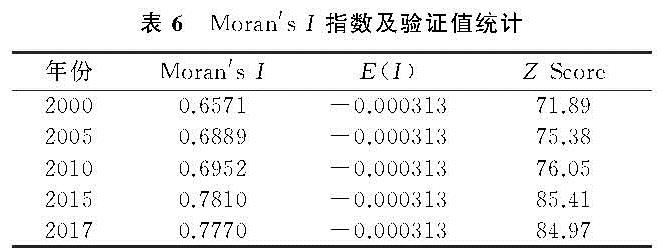
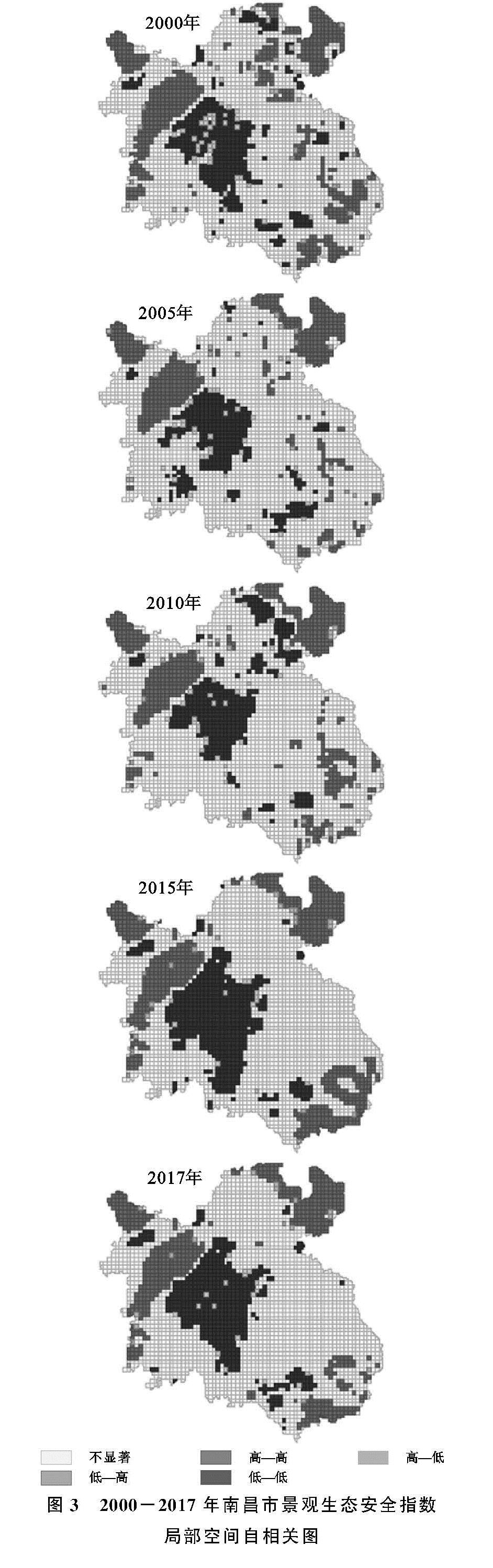
(1)空间自相关。空间自相关分析是通过计算空间自相关系数来分析某一变量是否在空间上相关及其相关程度,以发现研究对象间的空间相互作用现象[28-29]。本研究使用全局空间自相关(Moran's I)以及局部空间自相关(LISA)分析景观生态安全指数的空间模式。
(1)全局空间自相关(Moran's I)。Moran's I系数反映空间邻近区域单元属性值的相关程度,计算公式如下:
I=(n∑ni=1∑mj=1Wij(xi-x^-)(xj-x^-))/(∑ni=1(xi-x^-)2(∑ni=1∑mj=1Wij))(6)
式中:n为栅格数; xi,xj是变量x在相邻配对空间单元(或栅格细胞)的取值(或属性); x是研究对象x的均值; Wij是空间权重矩阵。
(2)局部空间自相关(LISA)。LISA反映的是局部小区域单元上的属性值与相邻局部小区域单元上同属性值的相关程度[30],计算公式为:
Ii=((xi-x^-)∑nj=1Wij(xj-x^-))/(1/n∑ni=1(xi-x^-)2)(7)
Moran's I值一般在[-1,1]区间内,小于0为负相关,大于0为正相关,等于0则表示不相关。通常采用Z检验法对Moran's I值进行统计检验,其公式为:
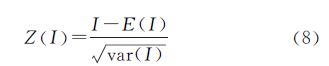
式中:Z(I)、E(I)分别为Moran's I的Z法检验值和数学期望。
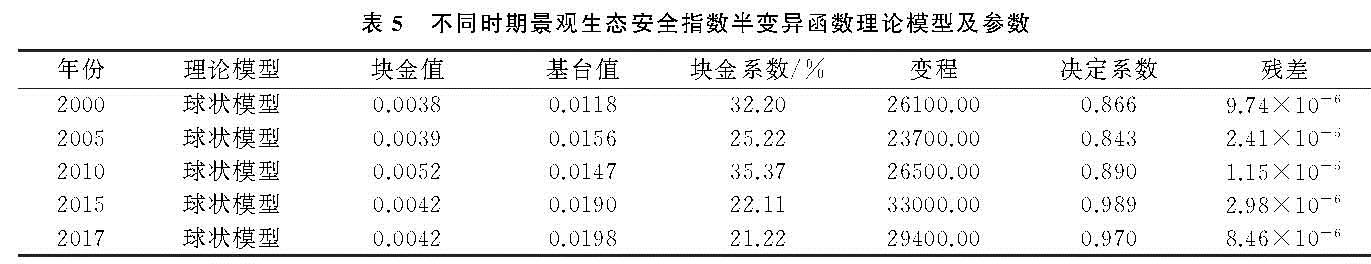
(2)地统计学分析方法。地统计学分析的半变异函数法不仅能解释属性或现象的空间相关,而且可以模拟和估计空间上的未知变量[31-33],计算公式为:
r(h)=1/(2N(h))∑N(h)i=1[Z(xi)-Z(xi+h)]2(9)
式中:h为样本间隔距离; N(h)为相隔距离为h时的样点对数,Z(xi); Z(xi+h)分别为变量在位置xi,xi+h处的值。