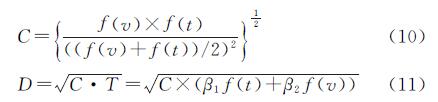2.2.2 指标权重的确定
采用熵权赋值法和AHP模型计算指标权重。熵权赋值法具有一定的客观性,同时AHP法专家打分具有较强的主观性[30],采用熵技术支持下的AHP法可以有效中和二者的优缺点。熵技术对AHP法确定的权系数进行修正步骤为[31]。
(1)根据层次分析法的一般步骤:建立层次结构模型,构造判断矩阵,层次单排序以及一致性检验,最后得到各指标的权重值WHi。
(2)采用极差标准化方式对本文选取的五大生计资本的各项指标进行标准化处理。
在有m个评价指标,n个评价对象的评估问题中,第i个指标的熵定义为:
Hi=-k∑nj=1fijlnfij (i=1,2,3,…,m)(1)
式中:fij=rij/∑nj=1rij; k=1/lnn,当fij=0时,令fijlnfij=0。
最后,定义熵权。定义了第i个指标的熵之后,第i个指标的熵权定义为:
WEi=(1-Hi)/(m-∑mi=1Hi)(2)
(3)熵技术支持下的AHP模型计算评价指标的权系数修正公式为:
Wi=WEiWHi/(∑ni=1WEiWHi)(3)
式中:Wi为采用熵技术支持下的AHP法求出的指标权重; WHi为采用AHP法求出的指标权重; WEi为采用熵值赋权求出的指标权重。
2.2.3 生计稳定性的测算
本文通过采用极差标准化方式对数据进行标准化处理后,采用熵权赋值法和AHP模型计算指标权重,获得农户各项资产产值Cj,计算公式为:
Cj=∑mi=1XijWj(4)
式中:m表示为所有农户家庭个数,本文中m为125; i为第i户农户家庭; j为第j项生计指标; Xij为经过极差标准化处理后,农户每一项指标的生计资本值; Wj为第j项生计资本指标的权重。
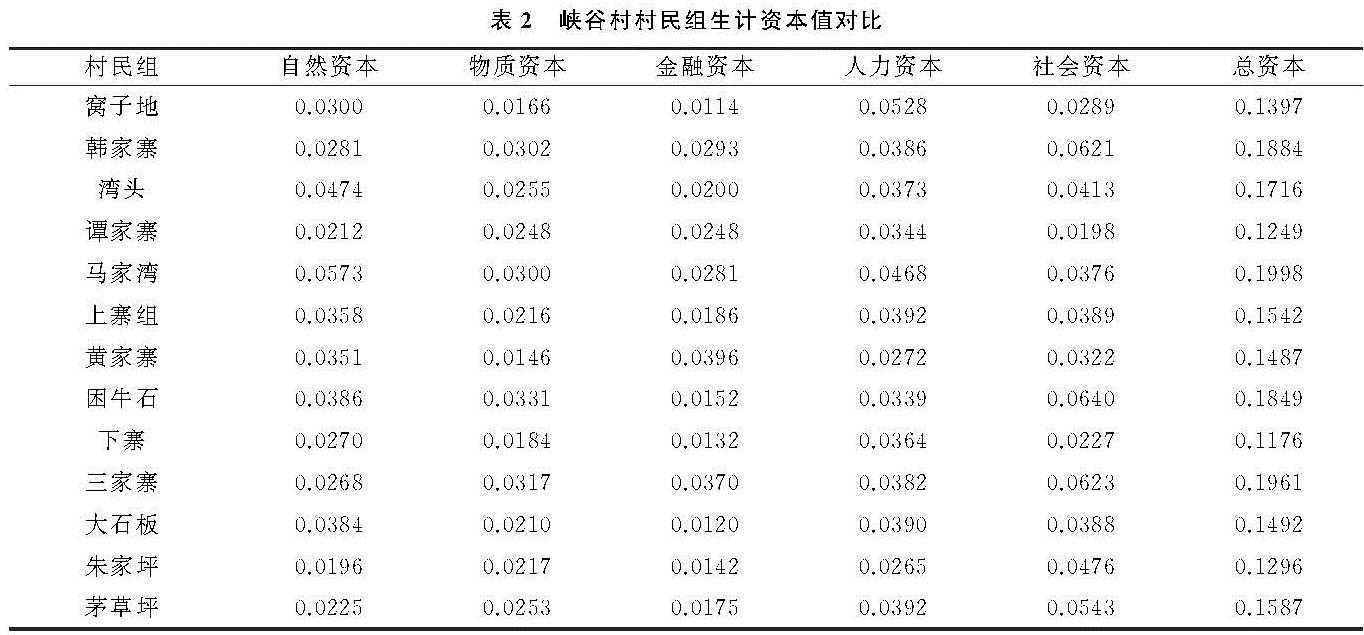
使用公式(4)计算后,将数据整合汇总得到自然资本V1,物质资本V2,金融资本V3,人力资本V4和社会资本V5每一分项的资产值,得到峡谷村农户生计资本综合值f(t):
f(t)=∑ZP=1VP/Z(5)
式中:VP为第P项生计资本的分项值; Z为分项生计资本的个数,在本文中Z为5。
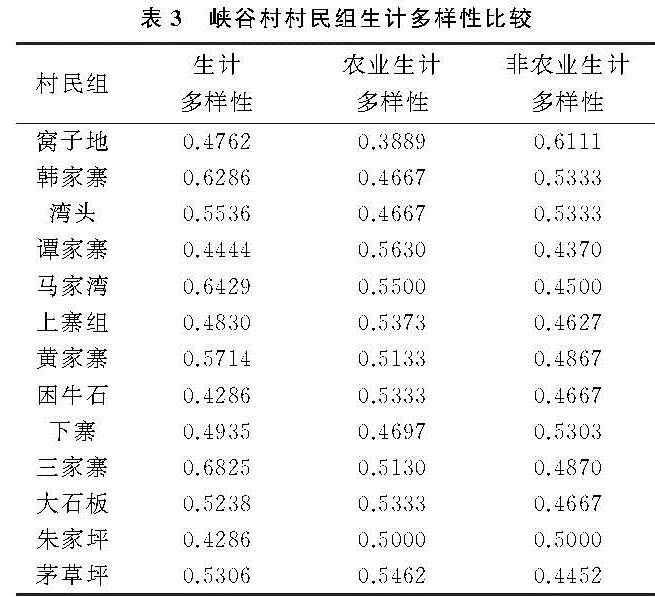
(1)多样性指数计算。在生态环境脆弱的情况下,农户可采取土地扩张化及生态移民等策略以规避恶劣的自然环境所有可能带来的风险。农户生计多样性指数采用农户家庭从事的生计活动的种类来计算[32]。农户农业生计活动和农户非农业生计活动构成农户生计多样性。在农户生计策略中,生计多样性的丰富可以有效增加农户收入,提高农户生活质量[33],提高农户抵御风险的能力。计算公式为:
Kact=Yi/Y(6)
式中:Kact为农户生计多样性; Yi为第i户农户拥有的生计活动种类的个数; Y为农户全部的生计活动种类的个数。其中农业生计活动包括耕地农作物种植、林地农作物种植以及牲畜养殖; 非农业生计活动包括工资性收入、转移性收入(家庭非常住人口带回或寄回、政府惠农补贴)、财产性收入(房屋租金、土地征用补偿金、土地流转金)和家庭借贷款。
收入多样性指数主要用于表示农户收入来源多样性的高低以及各种收入的均衡程度。本文选取香农·威纳(Shannon-wiener)的多样性测算方法,用以计算农户收入多样性指数[34]。当收入多样性指数为0时,表明农户只有一种收入来源; 当收入多样性指数数值增大,表明农户的收入来源多样化并且各种收入来源的收入在家庭总收入中的占比较为均衡,农户的生计稳定性提高,计算公式为:
Kinc=∑Sn=1PnlnPn(7)
式中:Kinc为农户收入多样性指数; Pn为第n种收入来源下的农户家庭收入与农户家庭总收入的比值; S为收入来源的种类。
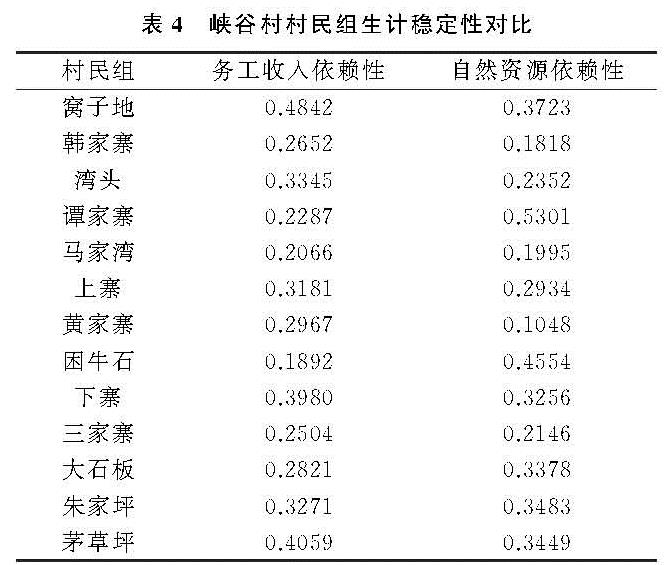
(2)依赖性指数计算。收入依赖性指数是农户收入对某一收入来源的依赖性的体现,若农户收入种的某一项收入在总收入中占比较大,我们就认为该农户对这一来源收入具有依赖性,占比越大,收入依赖性越高。收入依赖性高表明农户生计稳定性有待提高,需要拓宽收入来源或缩小各收入来源的收入差距[35],计算公式为:
Dinc=∑sn=1(Xn(Xn-1))/(X(X-1))(8)
式中:Dinc为收入依赖性指数; Xn为农户在第n种收入来源下的收入; X表示农户家庭的总收入。
农户对自然资源的依赖程度即自然资源依赖指数。在本文中用家庭经营收入表示农户对自然资源的依赖程度,家庭经营收入包括耕地种植作物收入、林地种植作物收入、牲畜养殖收入。农户的收入依赖性、生计风险与农户自然资源依赖指数呈正相关,生计稳定性与自然资源依赖指数呈负相关[36],计算公式为:
Dsou=N/T(9)
式中:Dsou为自然资源依赖指数; N为农户自然资源收入,即家庭经营收入; T为农户家庭总收入。
2.2.4 生计资本与生计稳定性的耦合协调度模型
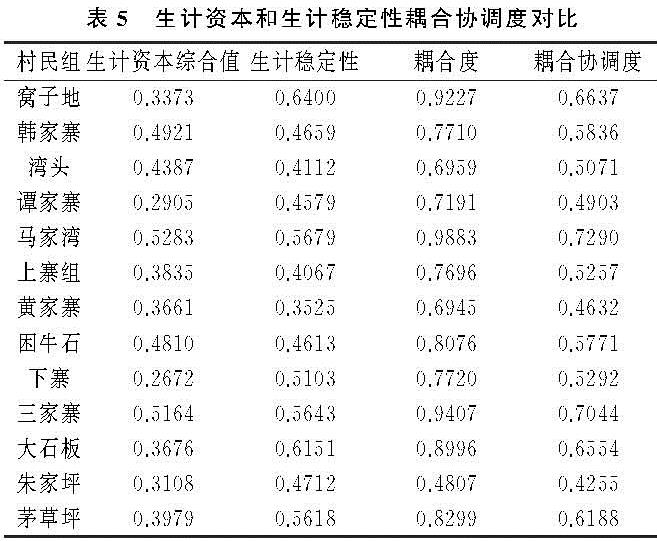
耦合是通过对系统关系的研究,揭示系统间或要素间相互作用的现象,是系统内要素之间相互影响[37],相互作用的关系。耦合协调度是衡量系统内耦合情况及协调发展状况的依据,耦合协调模型表示系统之间的相互作用强弱和相互影响程度[38]。在本文中,农户的生计可持续状况可以通过农户生计资本综合值和生计稳定性之间的相互影响、相互作用和协同发展的程度即生计资本与生计稳定性耦合协调度来计算。计算公式为:
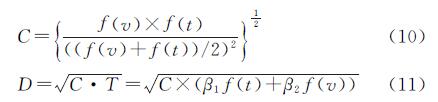
式中:C为耦合度; f(t)为生计资本综合值; f(v)为生计稳定性综合值; D为耦合协调度; T为生计资本综合值和生计稳定性综合值两系统的综合评价得分。在本文中认为,生计资本与生计稳定性在模型中同等重要,因此赋值β1=β2=0.5。
结合相关研究[39],将耦合协调度(取值在0~1)分为3个等级,从低到高分别为低级耦合(0~0.35)、中级耦合(0.35~0.7)和高级耦合(0.7~1)。