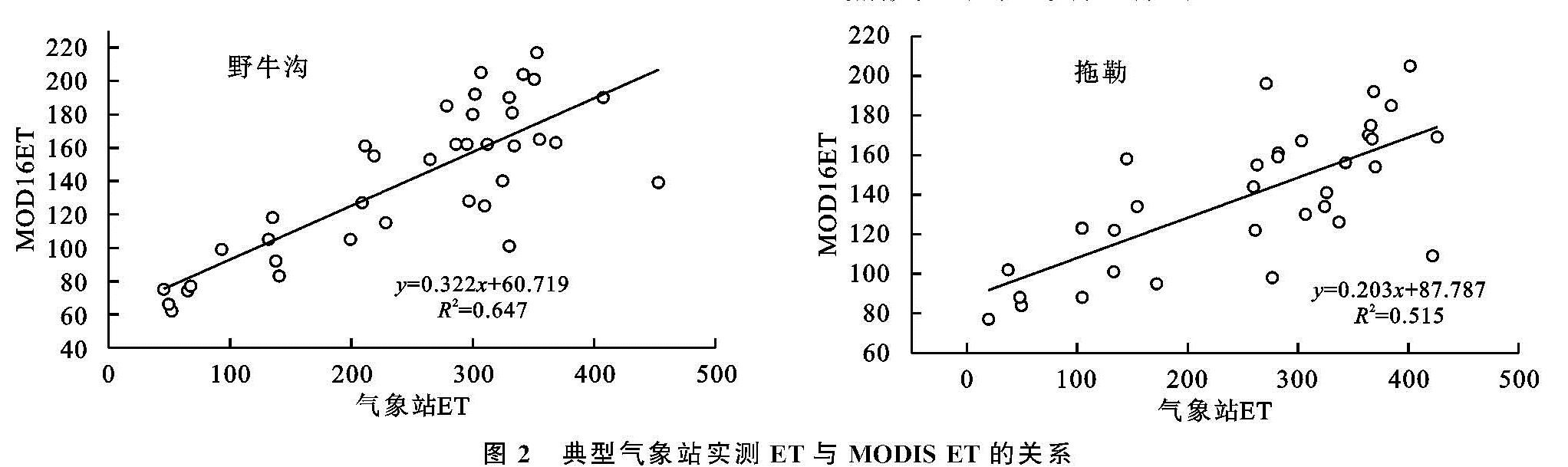
3.1 祁连山ET的时间变化特征
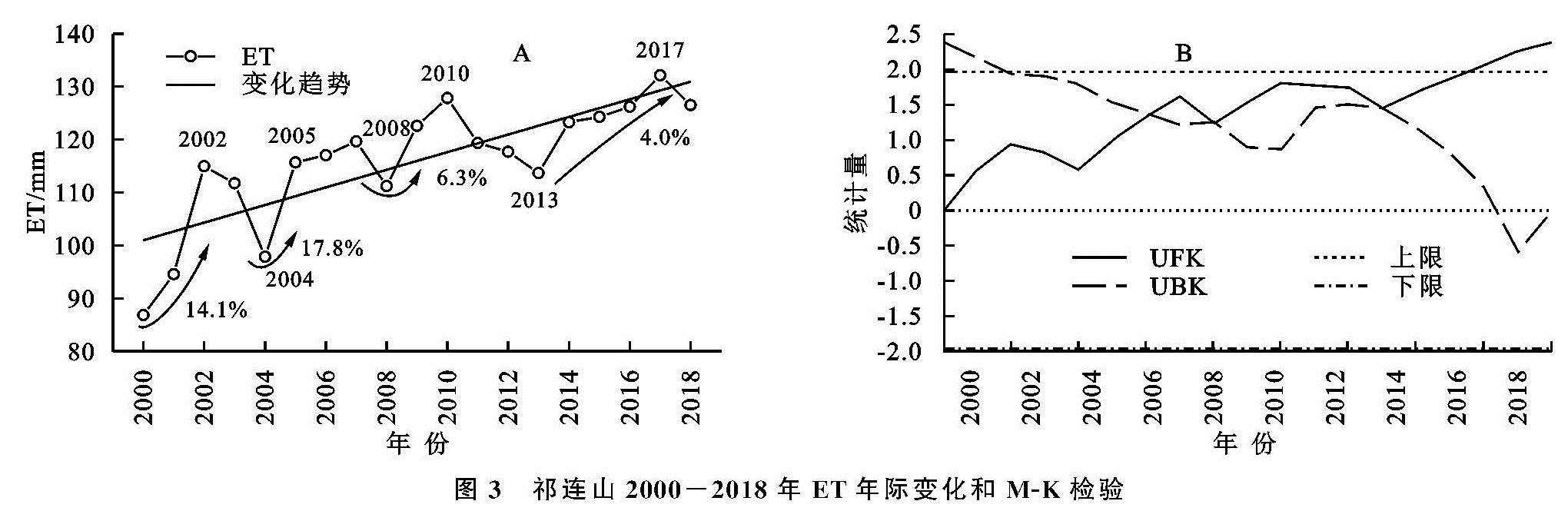
2000—2018年祁连山ET年均值为115.96 mm,最大值和最小值分别出现在2017年(132.15 mm)年和2000年(86.81 mm)。ET的年际变化表明,近19 a祁连山ET以1.66 mm/a的速率微弱增加。经历了2000—2002年、2004—2005年、20008—2010年、2013—2017年4个增长期,增长率分别为14.1 mm/a,17.8 mm/a,6.3 mm/a,4.0 mm/a。而在2003年、2007年、2010—2013年,ET呈显著减小趋势。2000—2008年ET增加速率(3.02 mm/a)远大于2009—2018年(1.14 mm/a),2008年以后,由于暖湿化趋势的减缓,ET增加趋势也有所减缓,这一结论与中国西北地区近年来ET时间序列的研究结果一致[3],黄会平等研究得出西北诸河区PET在1992—2009年有所增加,2009年后又逐渐降低[10]。ET季节性趋势分析发现,祁连山ET在春,夏,秋季呈增加趋势,变化率分别为2.14%,3.74%和0.74%,夏季有显著上升趋势,冬季ET以0.05%的速率缓慢减少(图3A)。
图3 祁连山2000-2018年ET年际变化和M-K检验
为了解近19 a来祁连山ET的突变特征,运用M-K突变检测对研究区年均ET进行突变检验,由UF曲线可知,2000—2018年期间,研究区ET呈不显著增加趋势,2016年以后ET明显增加,达到0.05的显著性水平。UF和UB曲线存在3个交点,为了进一步检验交点是否为突变点,对交点进行滑动t检验,结果未通过显著性检验。故按研究时段特征,将时间序列平均划分为2000—2008年和2009—2018年两个阶段,以分析不同时期祁连山ET的时空变化规律(图3B)。
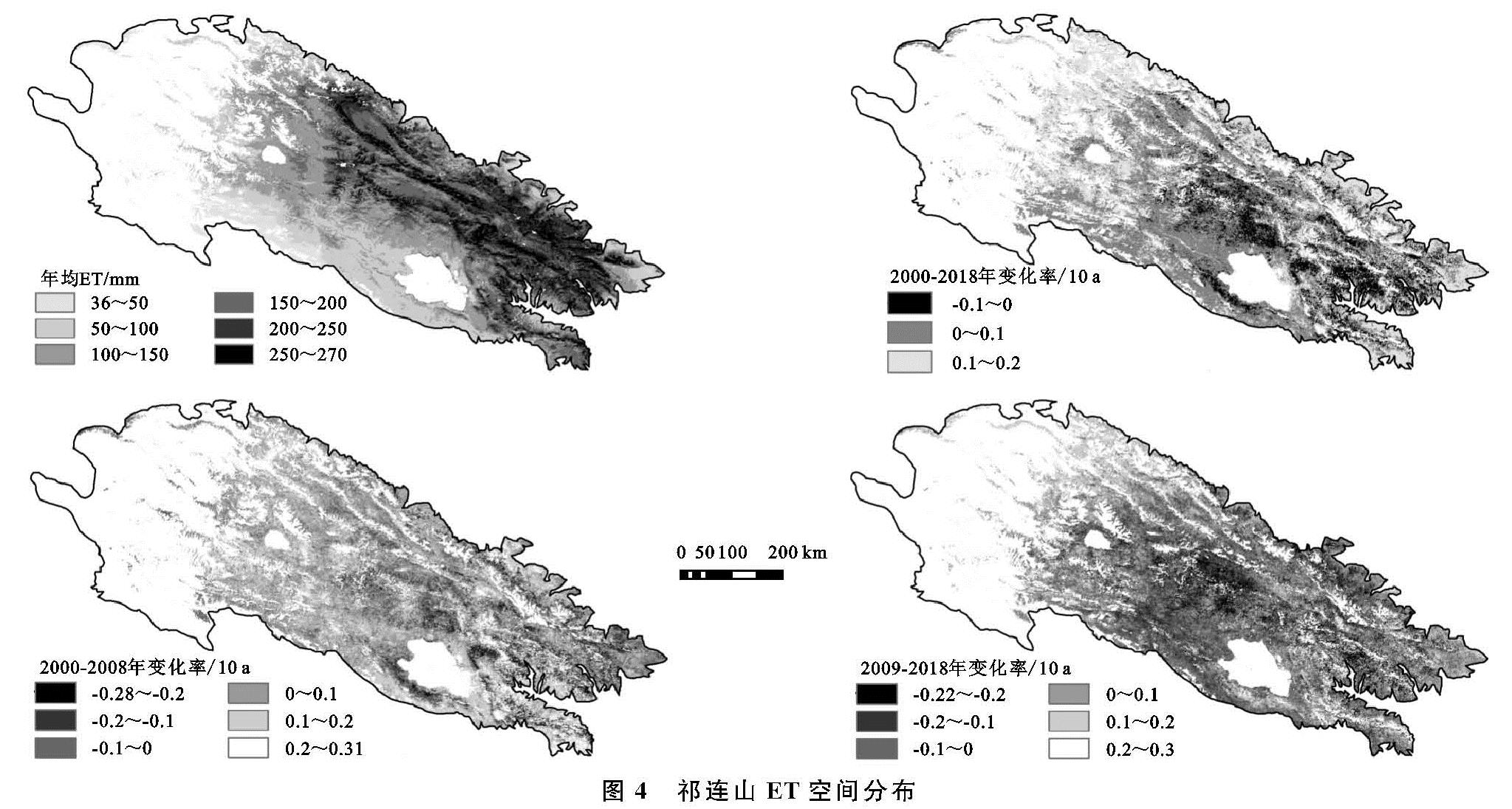
3.2 祁连山ET的空间变化特征
祁连山平均ET在30.66~281.53 mm(图4),受水热条件的影响,空间分布呈东北高西南低的特征。约有2.82%的地区ET值在200 mm以上,ET高值区主要集中在大通河,拉脊山和托来山等东部中高海拔地区; 中西部荒漠与草原交接地带,ET值介于100~200 mm,占总面积的77.93%; 而在西南部的大柴旦,德令哈及中吾农山ET值常年保持在100 mm以下的低值水平。祁连山ET的空间分布特征与植被和降水空间分布近似,刘波等认为在干旱区ET最重要的影响因子是水分[23],降水直接影响土壤含水量大小,进而影响ET的大小,受西南暖湿气流和东南季风扩展方向的影响,祁连山降水呈东高西低的分布形式[3,24]。
2000—2008年,祁连山ET呈显著增加趋势,显著增加面积占21.47%,其中极显著增加为14.21%,主要分布在哈科尔山,青海南山,西宁等南部地区及北部黑河流域。ET显著减少区域仅占2.37%,主要集中在东部的日月山,达坂山和大通山。2009—2018年祁连山ET显著增加和减少面积分别为9.81%和3.56%,具有不显著增加趋势。显著改善区域主要分布于北大河和托来山等西北部地区,而显著退化主要集中在中部的大通山,野牛沟等地。总体而言,近19 a,祁连山ET以增加为主,但不同时期变化率有所不同,空间变化分布也有所差异。2008年以前,研究区东南部ET显著增加,而2008年以后,增加趋势有所减缓,显著增加面积占比从21.47%下降至9.81%,显著增加区域转移至研究区的西北部,中部大通山等区域ET减小趋势明显。
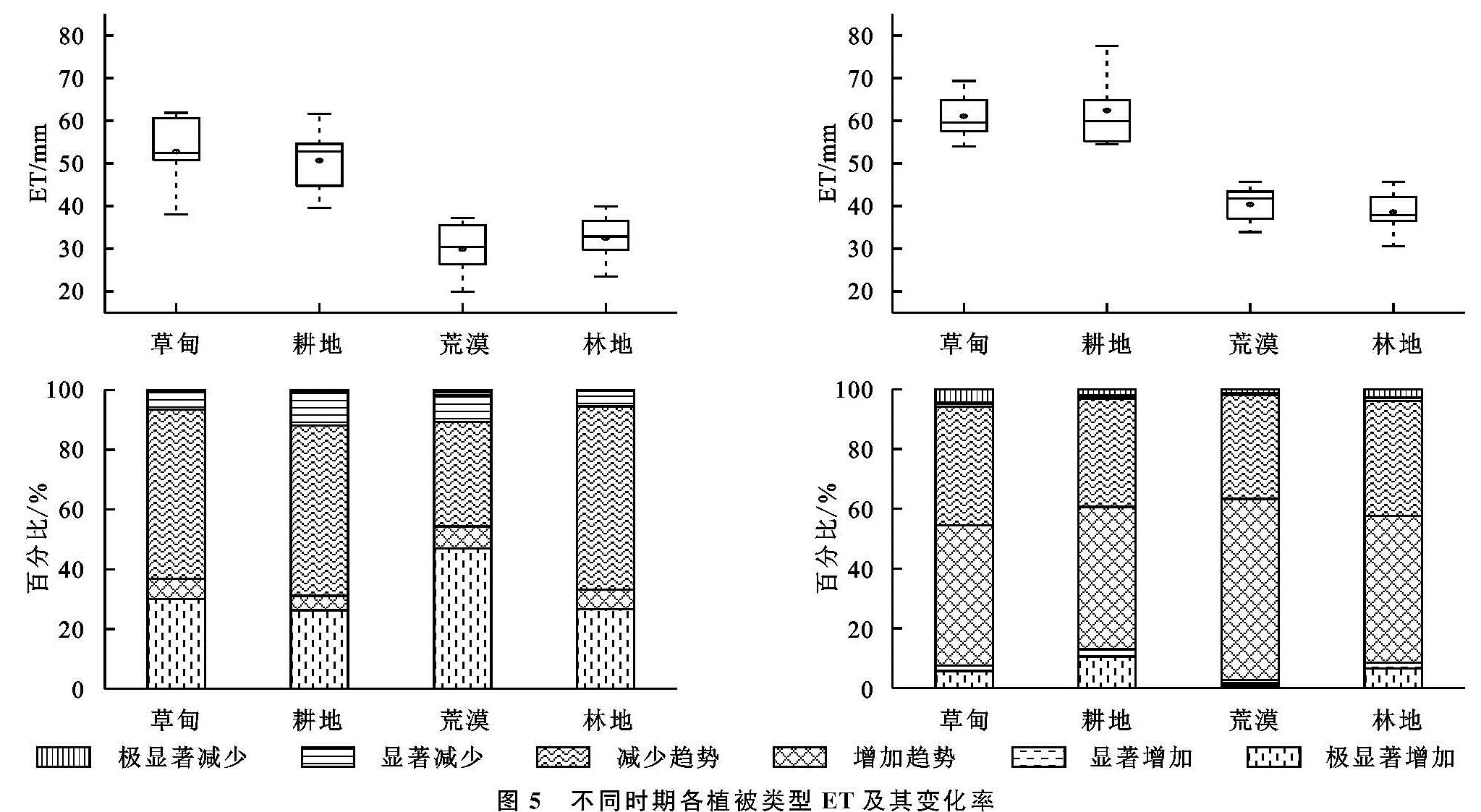
不同植被类型下ET存在明显的差异(图5),祁连山草甸ET(56.35 mm)明显高于其他植被类型,其次为耕地ET(55.01 mm)和林地ET(35.39 mm),荒漠ET(34.10 mm)值最低。2000—2008年期间,草甸,耕地,荒漠和林地4种植被类型ET显著增加面积分别为29.94%,26.25%,46.91%和26.58%,其中荒漠ET增加最为显著,而林地ET减少面积最大(5.46%)。2008年以后,各植被类型ET值均有不同幅度的上升,荒漠年均ET值从30.38 mm上升到41.81 mm,上升幅度最大。但是ET增加面积明显小于前9 a,显著增加面积占比为耕地(12.99%)>林地(8.47%)>草甸(7.54%)>荒漠(2.69%),显著减少面积草甸(5.83%)>林地(3.85%)>耕地(3.09%)>荒漠(1.84%)。其中,耕地ET增加最为显著,而草甸ET减少最为明显,荒漠ET变化率最小,最为稳定。植被对土地水源涵养具有重要意义,人工种植和灌溉,使得耕地ET具有明显的变异性,故而变化率最大,已有的研究显示过去50 a中国西北地区耕地ET的增加与耕地面积的扩大密切相关[25]。此外西北部稀疏植被区植被覆盖的改善对提高当地土壤水分,调节气候具有现实意义[4]。
3.3 ET与气候因子的关系
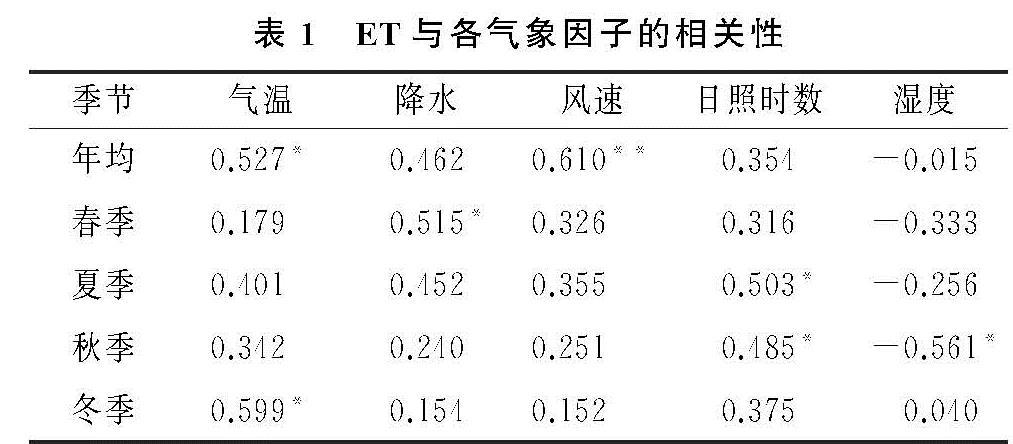
本研究选取了气温,降水,风速,日照时数和相对湿度5个因子探讨气候对ET的影响(表1),结果表明除湿度外,其余4个气象因子与ET均以正相关为主,其中风速与ET呈极显著正相关,气温与ET为显著正相关。各季节ET变化的主控气候因子不同,降水是春季ET增加的主要驱动力。夏季气温和日照时数均达到年内最高值,成为ET增加的主要控制因子。同时风速对ET正向作用也为全年最大。秋季ET与日照时数呈显著正相关,此外湿度对秋季ET变化也具有显著负向影响。冬季降水和风速对ET的影响逐渐减弱,气温成为ET变化的主要影响因子,气温与ET间呈显著正相关关系。ET变化趋势是不同气象因子综合作用的结果,但总体而言,气温和风速是祁连山ET年际变化的主要影响因子,这与段春锋等对西北地区ET的研究及曹广超等对祁连山ET特征的讨论结果一致[6,26]。但研究区气温和风速与ET的相互关系仍需进一步讨论。
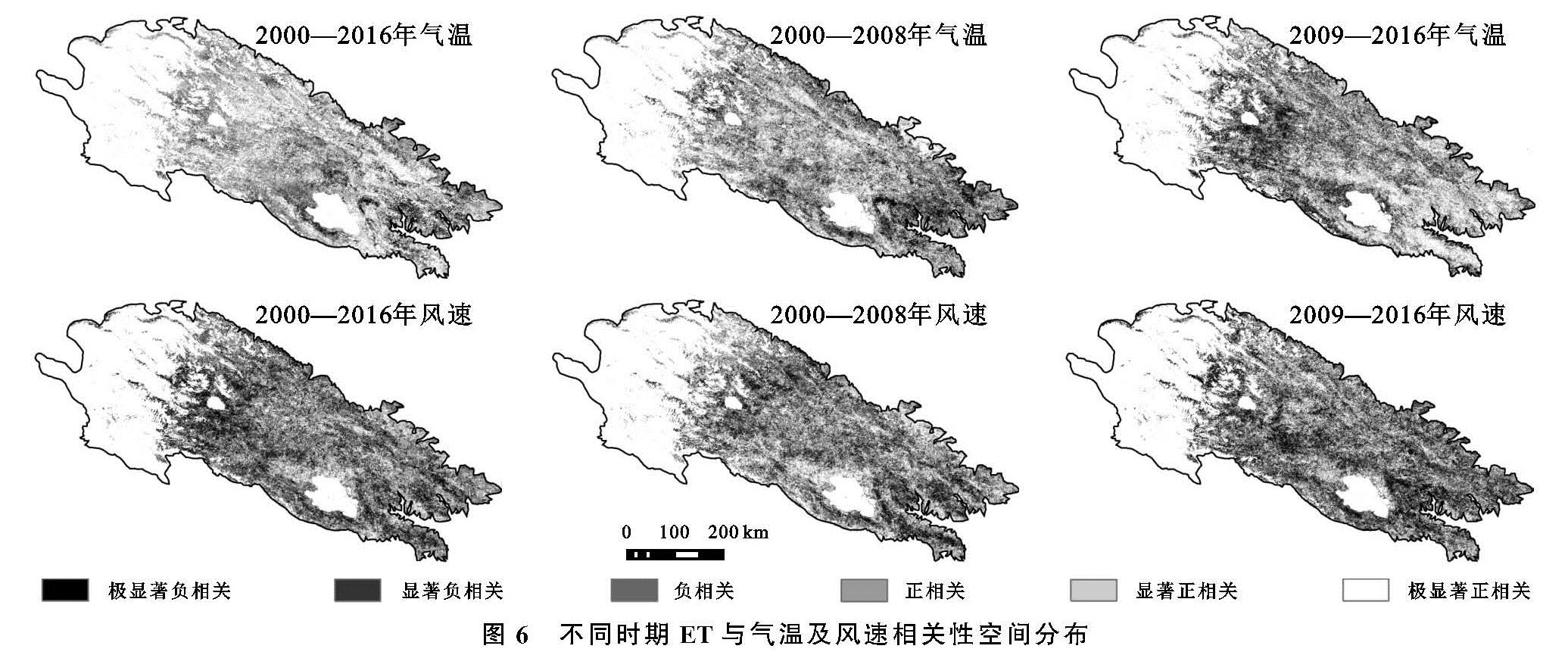
气温作为祁连山ET重要的气候影响因子,对ET的年际变化影响以正相关为主。显著正相关面积占6.71%,其中极显著正相关(3.29%)主要分布在托来南山,疏勒南山,哈科尔山和青海南山。2000—2008年,气温与ET以显著正相关(15.86%)为主,正相关区域空间分布与17 a整体分布相似,但在西宁,乌鞘岭等东部地区气温的负向作用较为明显,显著负相关区域占1.32%。2009—2016年,气温对ET的影响进一步扩大,显著正相关面积上升至19.29%,显著负相关面积也从1.32%上升至5.17%。但值得注意的是,东部青海南山,日月山,达坂山等负相关为主区域在2008年以后气温对ET的影响转变为正相关为主,而西部疏勒南山,哈科尔山等正相关地区则变为负相关,这可能与2008年以后祁连山气温的空间变化趋势有关(图6)。
风速对ET的影响整体以正相关为主(图6),但相关性不显著。极显著正相关仅占总面积的5.32%,主要集中在西部的冷龙岭,托来山和中部的布哈河流域。显著负相关主要分布在疏勒南山,哈科尔山和中吾农山。2000—2008年,风速对ET的正向作用较为显著,极显著正相关占8.39%,尤其是在张掖等黑河中下游地区及布哈河流域。作为西北气流和冷空气的通道,河西地区较大的风速有利于水汽传播散失,进而使ET增加[27]。2009—2016年,风速对ET的负向影响增强,显著负相关面积由4.14%增加至15.21%,尤其是在西宁盆地和哈科尔山,风速对ET的负向作用尤为显著。这些地区人类活动对气候变化的影响较为强烈,一方面城市化规模的不断扩大使风流动阻力增大,进而影响风速。另一方面,地区LST明显上升也是风速减小的主要原因[28]。
3.4 植被对ET变化的影响
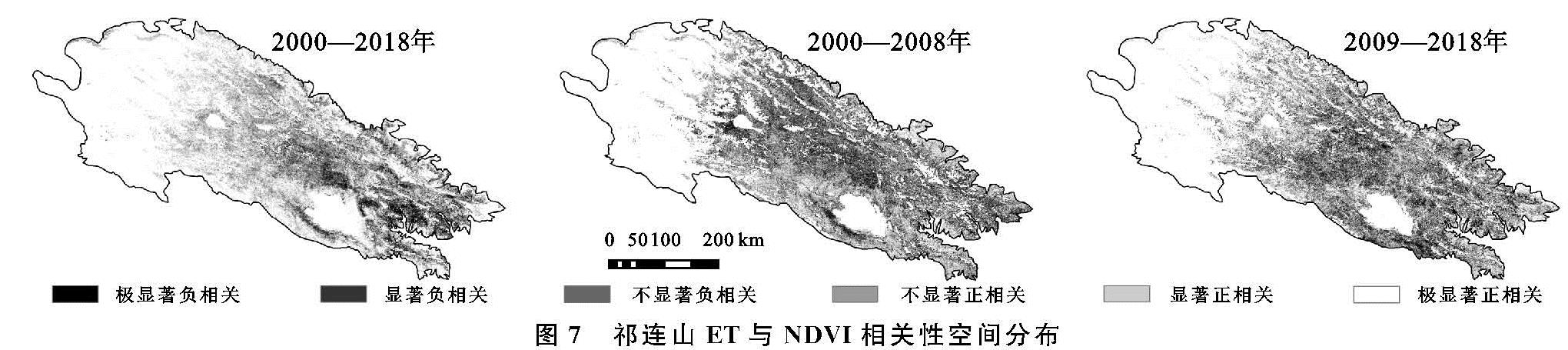
植被覆盖亦影响ET的空间变化见图7。2000—2018年,NDVI与ET以正相关为主,约有86.70%的区域NDVI与ET呈正相关,其中极显著正相关占21.27%,主要分布在研究区北部和南部的冷龙岭,走廊南山,青海南山,日月山等地区。仅有少部分地区NDVI与ET呈负相关,显著负相关仅占2.49%,主要集中在大通山,达坂山和湟水等中部和东部低海拔地区,植被类型主要以耕地和草甸草原为主。2000—2008年和2009—2018年两个时期NDVI与ET的相关性空间分布大致相同,与19 a整体分布有所差异。显著正相关区域主要集中在研究区北部和南部边缘地带的冷龙岭和青海南山南部,分别占24.21%和15.13%。负相关关系在研究区中部和东部广泛分布,尤其是在大通山,日月山,青海南山,哈科尔山,布哈河等地区,NDVI与ET负相关最为显著,2000—2008年和2009—2018年NDVI与ET显著负相关占比分别为7.25%和10.97%,略高于19 a整体值。植被对于区域水源涵养具有重要意义,近年来祁连山中部高山植被区随着气温的升高而呈现退化趋势,而人工绿洲的开发和耕地面积的增加也对当地水量分配和气候环境具有深远的影响[29]。此外,退耕还林和畜牧区的整治工作,促使研究区东北部植被和气候条件有所改善,从而使ET增加。表明人类活动在不同地区对于ET同时存在促进和抑制影响。
时间序列上,2000—2018年,祁连山ET与NDVI的相关系数为0.677,呈极显著相关。并且NDVI与ET年际变化具有良好的一致性,除2006年,2012年,2015—2016年外,其余年份NDVI均随ET的变化而变化。此外,武正丽等研究发现祁连山NDVI在2008年具有极小值[18],徐浩杰等,蒋友严同样得出祁连山高山草原,高寒草甸,高山森林NDVI在2008年出现最小值[17,30],植被的变异性可能是2008年祁连山ET发生突变现象的主要原因。