3.1 生态系统服务变化状况
为了解普定县退耕还林(草)政策下1990—2017年的4种生态系统服务的变化情况,将1990年、2000年和2010年数据作为生态系统服务的初始状况,2000年、2010年和2017年数据作为生态系统服务的最终状况。获得了1990—2000年、2000—2010年和2010—2017年3个时段的4种生态系统服务的ESCI(表1)。利用ArcGIS 10.2对4种生态系统服务的ESCI进行空间化制图(图2)。
表1 2000-2017年普定县4种生态系统服务的ESCI
土壤保持在3个时段内ESCI的数值及总体分布格局大致相似,3个时段的增益面积、无增益无损失面积、损失面积比例见表2。3个时段无增益无损失面积比例最大,损失面积比例最小。3个时段增益地区主要集中在普定县草地、林地及灌丛覆被处,并与坡度大于25°所在地相吻合,这与该县在坡度大于25°地方实施退耕还林政策有关。既无增益也无损失范围主要集中在普定县较为平坦的中部、南部及西北部的土壤保持量较低的耕地地区。损失地区主要集中在中部、最南部的小部分地区及西南地区,这些地区主要为城市建设用地,且随着西南及南部村落的发展,损失面积逐渐扩大。损失区除集中地外,还呈现分散的形式分布在普定县的各个地区,这些分散地区也主要位于村落及公路建设用地处。1990—2000年时段的中部流域地区出现了较大面积的损失,是由于在1990年此地为耕地和草地,还未建成水库,水库的土壤保持能力小于耕地及草地地区。
图2 研究时段内普定县各生态系统服务ESCI空间分布
产水量在3个时段内ESCI的最小值变化较小,最大值变化较大,表明局部地区的产水量服务变化明显。3个时段增益面积、无增益无损失面积、损失面积比例见表2,增益面积比例在逐渐减小,无增益无损失面积比例除2000—2010年时段外,其余两时段所占面积比例最大。产水量在不同的时段内ESCI的分布格局变化明显。1990—2000年增益地区主要集中在普定县的东北部、中部、西南部及南部小部分地区,这些地区主要为城市建设用地、裸地地区。建设用地产水量大是由于下垫面为硬质地表,下渗几乎为零。裸地产水量大是由于该地基岩裸露,无土壤和植被的覆盖,难以涵养水源。1990—2000年损失地区主要集中在北部大部分地区。其中,中部流域地区出现了较大面积的损失,是由于在1990年还未建成水库,原本的耕地及草地产水量大于水库。2000—2010年全县呈现大面积的损失。因为InVEST模型的产水模块是基于水量平衡原理的,年降水量是极度敏感因子,降雨量的多少对产水量有着很大的影响。2010年平均降雨量少于2000年平均降雨量(减少300 mm左右),因此产水量较少,ESCI出现减损状态。2010—2017年全县由大面积损失转为大面积的无增益无损失状态。因为2017年降雨量相较于2010年相持平,因此无增益无损失面积比例较大。增益地区在东南部也有所增加,这与此地城镇化发展有关。
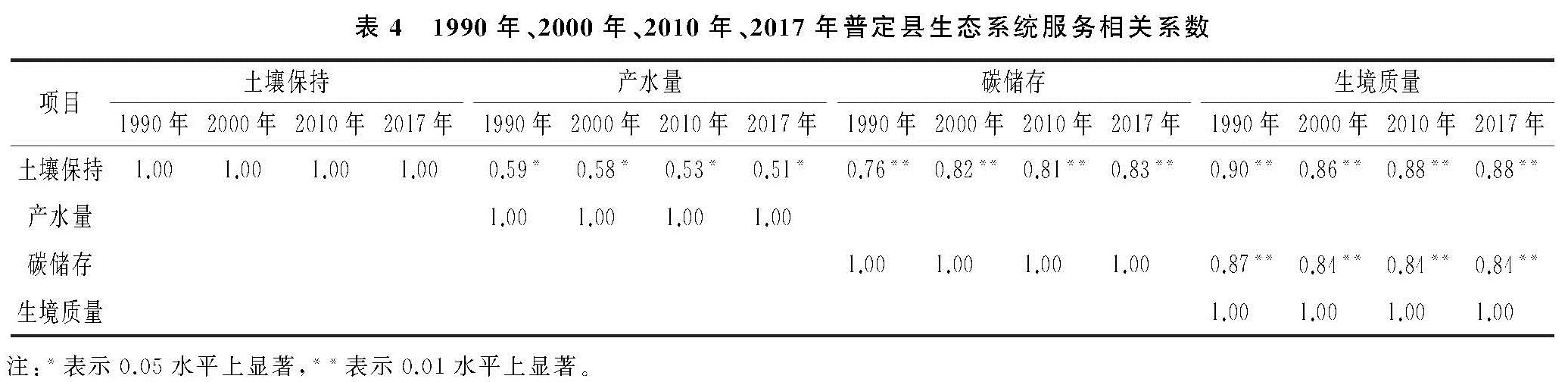
碳储存在3个时段内ESCI的最小值无变化,最大值变化较大,相差1倍多,表明局部地区的碳储存服务变化大。3个时段增益面积、无增益无损失面积、损失面积比例见表2,3个时段无增益无损失面积比例最大。碳储存在3个时段的空间分布上表现出南北相反的分布格局:1990—2000年增益地区分布在南部及西南部地区的耕地地区,随着南部及西南部城镇化的发展,碳储存服务降低,在2000—2010年及2010—2017年时段转为损失地区。无增益无损失范围主要集中在耕地及草地地区。1990—2000年损失地区分布在中部流域地段及东北部地区,流域地段是由于1990年水库未修建,水体的碳储量低于原本耕地的碳储量,以及普定县政府实施的流域附近退耕种草政策有关,而草地的碳储量低于农田的碳储量[25-26]。东北部地区由于持续的毁林开荒,农田碳储量低于林地的碳储量,因而呈现减损状态。2000—2010年及2010—2017年东北及西北部地区碳储量呈现增益状态,是由于退耕还林政策的实施,土地利用类型由耕地、裸地转为了林地。
生境质量在3个时段内ESCI的数值变化不明显,增益面积、无增益无损失面积、损失面积比例见表2,除2000—2010年时段损失面积比例最大外,其余两时段无增益无损失面积比例最大。3个时段ESCI时空分布的增益范围都主要分布在水体、林地、草地所在地。无增益无损失主要集中在耕地所在地。损失地区主要分布在南部、西南部、东部的建设用地和西部及东部的裸地处。1990—2000年损失所占面积较小,到2000—2010年时,损失范围明显增大,面积增加,这个时段为该地迅速发展时期,并从发展中心向南部及西南部拓展,生境质量呈现连片式恶化,但在2010—2017年的发展时段里,可以看出这种连片式的恶化得以缓解和隔断,根据土地利用转移结果,这与此地植树种草有着很大的关系。
表2 2000-2017年普定县4种生态系统服务所占面积比例%
3.2 主导生态系统服务
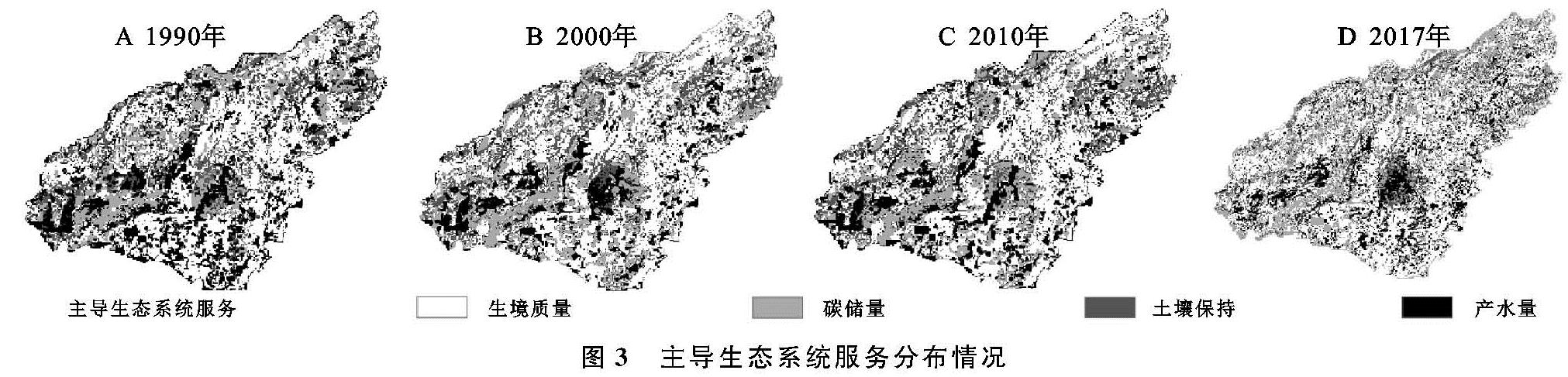
4种主导生态系统服务的分布格局也展现出显著的空间差异(图3),但在4个年份中各主导生态系统分布格局大致相同。以土壤保持服务为主导的地区呈东北—西南走向贯穿普定县中部及最北部。这些地区为普定县坡度大于25°的山地林地地区。以产水量服务为主导的地区主要分布在城镇、村落和裸地地区,2000年后在西部及东北部的地区,以产水量服务为主导的地区逐步被碳储量服务和生境质量服务替代。根据土地利用转移矩阵结果,西部的小部分栅格处土地利用方式由裸地转化为了林地,东北部由裸地转化为了草地。以碳储量服务为主导的地区从2010—2017年分布范围逐渐扩大,主要呈条带状分布在林地,且随着退耕还林面积的增加,碳储量分布也在不断扩大。以生境质量服务为主导的地区无论在1990年还是2017年都占据着较大的面积,在全县的各个方位都有分布。水域、林地、草地、农田都有以生境质量为主导的服务。4种主导生态系统服务的面积比例见表3。4个年份中以生境质量为主导的服务所占面积比例最大。以产水量为主导的服务所占面积比例最小。在2000年实施退耕还林(草)工程后,产水量主导的生态系统服务面积比例在逐年降低,以碳储量主导的生态系统服务比例在逐年增加。土壤保持主导的服务和生境质量主导的服务所占比例面积未发生较明显的变化。
3.4 热点区识别
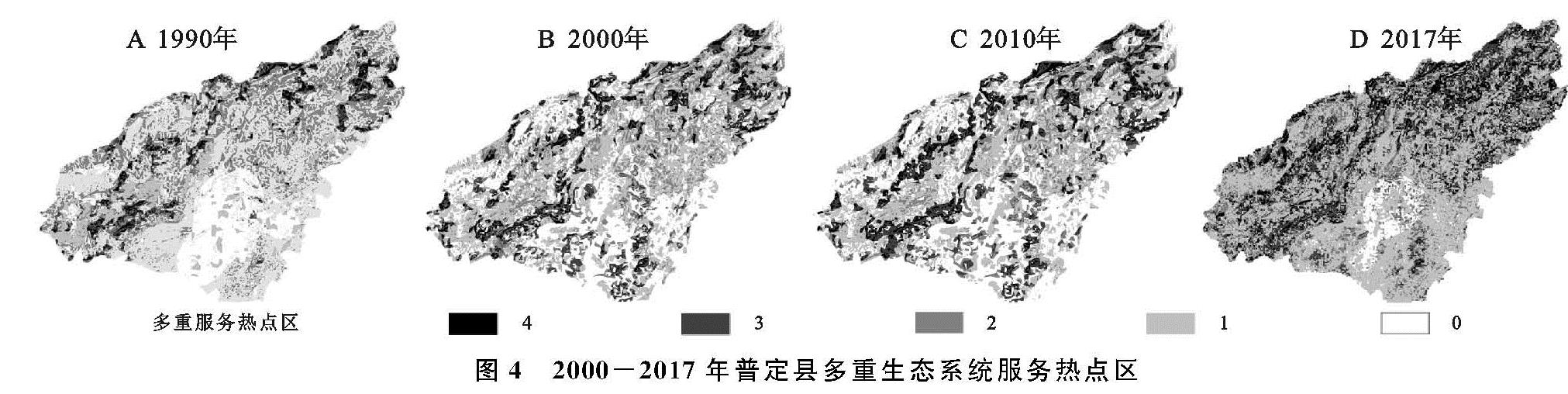
为进一步分析4种生态系统服务在空间上供给能力的差异,对多重服务热点区进行了统计(表5)及空间化制图(图4),1990年、2000年、2010年、2017年4类服务热点区中0类和1类服务热点区所占比重最大。这与当地是石漠化较为严重的生态环境相符合。1990—2017年,4类、3类服务热点区的面积都有所增加,其中2010年4类和3类服务热点区的面积是1990年的两倍,2017年4类和3类服务热点区的面积是2010年的两倍,反映出在县区实行退耕还林(草)后生态环境在不断改善。从空间分异来看,研究区的南部(马官镇、城关镇、化处镇)由于城镇的分布及大面积耕地的存在,提供的生态系统服务能力比其他地区弱; 2010—2017年南部及东部地区1类服务热点区面积在扩展,主要是产水服务功能的上升,也表现出城镇化的加快,但在2017年时,城镇周围出现了2类和3类服务热点区,从土地利用转移中可知,林地和草地面积在建成区的周围增加,表明普定县的退耕还林(草)政策的全面开展及人们对城镇健康发展意识的提高。研究区4类和3类服务热点区主要集中在山地林地地区和草地地区,且呈现逐年增加的趋势。在2017年这一空间变化表现更为明显,这和该县在2000年后实施退耕还林有着密切的关系。
图4 2000-2017年普定县多重生态系统服务热点区